economic activity + energy
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Primary sector definition
industry involving extraction of raw materials e.g. farmer
secondary sector definition
industry where you are turning the resources into a product e.g. car factory
tertiary sector definition
service sector, the industry where people are selling the products
quaternary sector
industry involving research, selling their knowledge/expertise to people e.g scientist wha
what is critical renewable
resource can be renewed/keep growing but has to be given time to regrow/reestablish
what is a resource endowment
the raw materials that are provided in an area
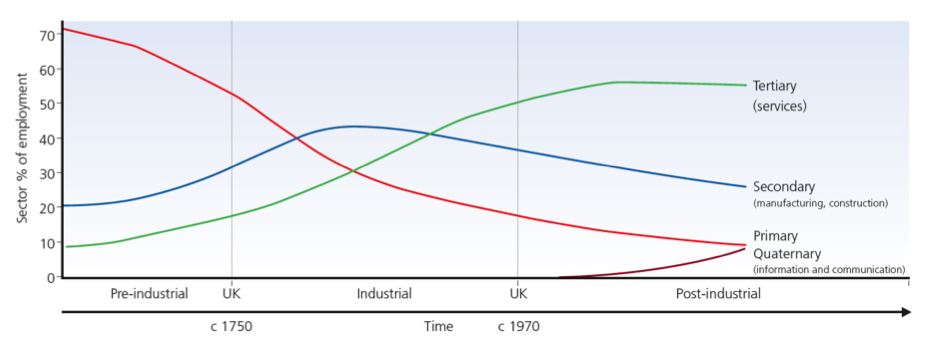
what is this graph? what are some key trends seen? why?
CLARK - FISCHER
primary sector decreases as country develops (can afford to import, education improves)
secondary decreases after industrial (manufacturing happens overseas = cheaper)
tertiary increases (education improves, people can do more skilled jobs)
quaternary is recent emerged - innovation, science, tech (can be done remotely)
Sectoral shifts are part of the developmental process
5 reasons for shift in countries economic sector
Globalisation
easier to import/export, primary decreases in HICs
Raw materials
countries with raw materials = primary, finite resources may run out
Mechanisation/new tech
industrialisation in LICs - more primary/secondary
deindustrialisation in HICs - more tertiary/ quaternary
Government policies
tariffs - high tariffs = decrease trade, increase primary/secondary
trading block/ deals may change sectors
Demographic
older populations - less labour intensive industry
UK gov. policies causing change in economy
1945-1979
state industries
sold off for more competitive business environ.
old industrial areas became financial centres - offices/retail outlets
2010 onwards
rebuilding manufacturing sector, not as reliant on finance
crossrail/HS2
encouraging investment in manufacturing industry
global firms locating in the UK
3 causes of deindustrialisation in UK
Competition - other countries (china, indonesia, malaysia) can manufacture more cheaply - low labour costs
Less investment, expensive labour and old machinery make uk products too expensive
mechanisation
5 human factors affecting location of economic activity
Money - need to attract investment
Labour - need labour pool nearby
transport - for quick despatch + receiving components
Markets - bulky goods need to be produced near market to cut transport costs, fragile goods = near market, services = at market
Government - may provide incentives in some areas
4 physical factors affecting location of economic activity
site - availability/cost - large factories need flat, well drained, solid land
raw materials - locate near to save transport costs
Natural routeways/harbours - little investment needed to establish transport links, opportunities to transport goods in large quantities
climate - farming needs temperate climate for crops to grow
how has location of stores/retail parks changed? why?
then = CBD
now = rural/urban fringe
WHY - land in cbd = more expensive, large stores need more land, better access
how has location of industrial estates changed? why?
then = inner city
now = rural/urban fringe
WHY - transport improved, labour can access industrial estate. cheaper land = expansion
Positives/negatives of shift in UK - decline and mechanisation of primary sector
Positive
farming has become more streamlined + profitable
Negative
high unemployment in areas of decline e.g. south wales + coal
Positives/negatives of shift in UK - Decline of heavy manufacturing + secondary sector
positive
less air pollution
negative
increased dependence on other countries, lots of abandoned factories in inner city BUT = gentrification
Positives/negatives of shift in UK - rise of high tech manufacture
positive
quicker, more efficient manufacture = lower cost, higher profit
Negative
less labour needed. decrease in low skill jobs = unemployment
Positives/negatives of shift in UK- rise in tertiary employment
positive
range of skill levels required, options for all ages + education level
Negative
people unwilling to return to primary + secondary sector- working conditions
Positives/negatives of shift in UK - emergence of quaternary sector
positive
research leads to development of technologies which benefit everyone
negative
only employs people with very high skill levels
What happened in redcar ? - consequences
massive steel factory, majority of town employed there
shut down
x lost incomes, careers
x business fail on high street
x 2000 unemployed
x not many tourists
x people don’t have disposable income for other businesses
why as the primary industry changed in nigeria?
less employment in agriculture due to mechanisation, better working conditions in other sectors
Oil + gas reserves, primary sector always needs labour
why has secondary industry changed in nigeria?
mechanisation lead to increase of jobs in secondary sector
fastest growing sector due to cheap + plentiful labour, e,mployed by TNCs
why has tertiary sector changed in NIgeria?
poverty/poor education previously limited tertiary employment, as this improves, more people get these jobs
globalisation = improved movement of goods, which are sold in tertiary sector
positive and negative of economic shifts in nigeria - social
Positive
literacy rate improving - 62%in 2015 from 55% in 1991
life expectancy increasing 1980 = 45, 2024 = 56
negative
gov corruption means resources aren’t distributed, despite more money
conflict between ethnic/religious groups worsened by TNCs
positive and negative of economic shifts in nigeria - economic
Positive
10 years expected schooling, up from 6.7 = more earning (teachers and those getting educated)
economic growth as gov. invests money into infrastructure
negative
less employment in primary sector means fewer low skilled jobs
country less self sufficient - imported EU fuel even though they had their own
positive and negative of economic shifts in nigeria - Environmental
Positive
UN investigation highlighted issues shell caused with oil spills = stop future ones
negative
burning gases releases greenhouse gases, causing respiratory issues
80% of nigeria’s forests have been destroyed = worsening air quality and soil erosion
what is a carrying capacity?
the amount a country can handle before the land starts to be diminished/run out of resources
population pressure occurs when
There is not enough resources in an area to provide for/cope with the increasing size of the population in a short amount of time
Malthus
Pessimistic
18th century
only bad can come from population growth - population grows faster than food
influenced by religion - moral duty for low population
unaware of technological innovation, lived before industrial revolution
what is a malthusian crisis/explosion
massive event that would decrease the population to put us back in balance with food
Boserup
Optimistic
‘necessity is the mother of inventions’
food supply would increase to accommodate population growth
better tech, seeds, farming methods
agricultural intensification
she was an economist
primary energy
energy found in nature that has not been subjected to any human engineered conversion process
secondary energy
energy obtained from transforming primary energy
energy gap
difference between the amount of energy countries consume and produce
energy surplus
energy supply exceeds demand
energy deficit
demand exceeds supplu
energy security
having enough energy/access to energy for the needs of an area (reliable, uninterrupted at affordable price)
3 things changing energy demand
population growth
economic development (more infrastructure, desire for resources increases)
technological innovations
non-renewable energy
finite sources of energy, often damaging to environment
renewable energy
infinite sources of energy, sustainable
energy conservation
using less energy by adjusting your behaviours and habits
energy efficiency
involves using technology that requires less energy to perform the same function
2 examples of energy conservation
using public bus to commute to work
buy from local businesses
2 examples of energy efficiency
using long life lithium batteries
buying appliances with A++ energy efficiency ratings
5 ways to make homes more energy efficient
have energy efficient light bulbs - put on timer
solar panels
double glaze windows
shut doors/windows when heating on
insulate house well to reduce heat loss
UK energy strategy
Renewable energy strategy
fossil fuels increase to 2000s, then decline
nuclear increases until 1998, then decline
renewable increases steadily
2019 - 15 operational nuclear power plants, UK had first week without coal