Sleep
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Describe the physiological mechanism of sleep + waking + consider the role of circadian rhythms and biological clock
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
Why do we sleep?
Restoration (immune, wound healing)
Hormone production (GH, prolactin/cortisol, TSH)
Waste clearance (e.g. beta-amyloid)
Memory
Mental health and behaviour
Hormone production (GH, prolactin/cortisol, TSH)
Waste clearance (e.g. beta-amyloid)
Memory
Mental health and behaviour
2
New cards
What nucleus is the caradian pacemaker?
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
3
New cards
What are the important hormones of sleep?
Orexin- epilepsy
Melatonin- sleep
GABA- sedation
Adenosine
Melatonin- sleep
GABA- sedation
Adenosine
4
New cards
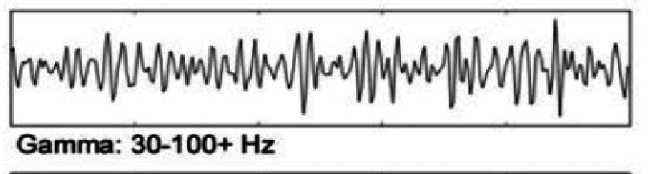
What does this EEG show?
Highly aroused, stimulated
5
New cards

What does this EEG show?
Alert, attentive
6
New cards
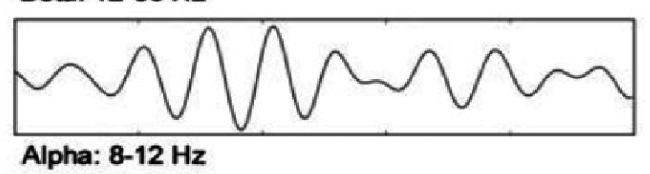
What does this EEG show?
Relaxed, eyes closed
7
New cards
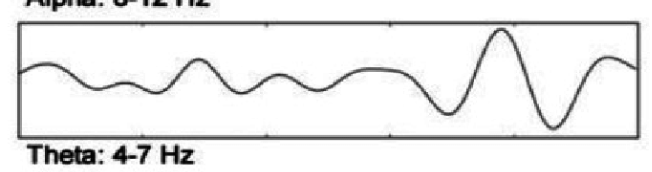
What does this EEG show?
Light sleep/very drowsy (and in kids?)
8
New cards

What does this EEG show?
Deep sleep (stage 3)
9
New cards
What are the stages of sleep?
Wakefulness
N1, N2, N3 ( Non-REM stage)
REM
N1, N2, N3 ( Non-REM stage)
REM
10
New cards
What type of rhythm is found in wakefulness?
Alpha rhythm
11
New cards
What type of rhythm is found in N1?
Theta, slow eye movements
12
New cards
What type of rhythm is found in N2?
K complexes and sleep spindles
13
New cards
What type of rhythm is found in N3?
Delta
14
New cards
What type of rhythm is found in REM?
Wakelike EEG, EMG: low chin tone (paralysis), rapid eye movements
15
New cards
What % of sleep is N1?
5-10%
16
New cards
What % of sleep is N2?
45-50% (longest)
17
New cards
What % of sleep is N3?
15-25%
18
New cards
What % of sleep is REM?
20-25%
19
New cards
What hormones causes the pressure to sleep?
Adenosine
20
New cards
What hormones increases the most during sleep?
Melatonin. It sustains sleep
21
New cards
When does melatonin peak during sleep?
After 4 am of sleep
22
New cards
Why does caffeine reduce your ability to sleep?
Is a competitive inhibitor of adenosine. Eventually, the receptors will get saturated and reach a point when increase caffeine will do nothing. Does not affect melatonin.
23
New cards
What is chronotype?
Morning or night person
24
New cards
What is chronotype determined by?
genetics
25
New cards
Can chronotype change?
Yes, changes by age
26
New cards
What decides our circadian rhythm?
Clock genes
27
New cards
What are zeitgebers?
An environmental agent or event.
A cue in the regulation of the body’s circadian rhythm.
A cue in the regulation of the body’s circadian rhythm.
28
New cards
Give an example of zeitgebers.
Natural day light. During winter less light therefore feel sleepier during the day.
29
New cards
What are non-photic zeitgebers?
non-environmental factors that effect sleep.
30
New cards
What are examples of non-photic zeitgebers?
Jet lack – change of down zones suddenly
Temperature- too clod, hot
Exercise at night stops sleeping. During day it can help with sleeping during the day
Stress
Eating- hungry (can’t sleep) + same if too full
Temperature- too clod, hot
Exercise at night stops sleeping. During day it can help with sleeping during the day
Stress
Eating- hungry (can’t sleep) + same if too full
31
New cards
What are good sleep hygiene practices?
Go to bed and get up around the same time each day.
Relaxing routine.- tech giving wake sense
No big meals before bed.
Exercise.
Bed is for sleeping only.
Relaxing routine.- tech giving wake sense
No big meals before bed.
Exercise.
Bed is for sleeping only.
32
New cards
What are the 2 types of insomnia?
Primary and secondary
33
New cards
What is primary insomnia?
Having insomnia alone (isolates). It is not a symptoms of other illnesses
34
New cards
What is secondary insomnia?
Due to co-morbid psychiatric or medical disorder or medication.
35
New cards
Does the treatment of the primary illness always resolve secondary insomnia?
No
36
New cards
What % of insomnia cases are primary?
25
37
New cards
How is insomnia diagnosed?
Decrease in sleep quantity/quality, 3 times a week for more than 3 months.
38
New cards
What is the prevalence of insomnia?
10-15% of population
39
New cards
What is the first line of treatment for insomnia?
Sleep hygiene strategies- not watching tv in bed, clearing mind
40
New cards
What is short-term treatment for insomnia?
Medication (less than a week)
41
New cards
Why is medication a short-term treatment for insomnia?
Tolerance, very addictive
42
New cards
When is medication given for insomnia?
Good for a person who can't go to sleep at all, gives them the pattern to go to sleep. Can break the cycle.
Someone with severe relapse (psychotic) for a mental disorder/ manic episode which can be revered by sleep is given medications short term to help.
Someone with severe relapse (psychotic) for a mental disorder/ manic episode which can be revered by sleep is given medications short term to help.
43
New cards
What medication is given long term to treat insomnia?
Melatonin- long term not over the counter (in America it is OTC)
44
New cards
What type of insomnia does CBT treat?
Primary
45
New cards
What is obstructive sleep apnea?
Firstly snoring, briefly stop breathing then wake up quickly. N3 to N1 quickly. Very tired during the day.

46
New cards
What is the treatment of OSA?
CPAP
Reduces risk of stroke and MIs
Reduces fatigue
Reduces risk of stroke and MIs
Reduces fatigue
47
New cards
What is restless leg syndrome?
Constant urge to move legs at rest, temporarily relieved with activity. Tingling in the legs.
48
New cards
What is Periodic Limb Movements of Sleep?
Repetitive involuntary movements of limbs (usually legs) during sleep.
49
New cards
Are “Hypnic jerks” pathological?
normal phenomenon.
50
New cards
What are the 2 categories of parasomnias?
REM
NREM
NREM
51
New cards
Example of REM parasomnias.
REM sleep behaviour disorder (Movement, such as kicking, punching, arm flailing or jumping from bed, in response to action-filled or violent dreams, such as being chased or defending yourself from an attack). People acting out their dreams.
Nightmares.
Nightmares.
52
New cards
Examples of NREM parasomnias.
- Sleep walking
- Sleep eating/drinking
- Night terrors
- Sleep eating/drinking
- Night terrors
53
New cards
What are night terrors?
Usually in young. Do not remember them at all but will wake up screaming. Not disturbing for the person.
54
New cards
What abnormality is found in REM parasomnias?
In normal REM you should be paralysed (but eyes) but in these disorders they are not so they start walking etc.
55
New cards
What are the 2 types of hypersomnia?
narcolepsy + Kleine-Levin
56
New cards
What is narcolepsy?
Excessive daytime sleepiness, involuntary sleep, cataplexy. Low orexin. (like going in and out of rem sleep)
57
New cards
What is Kleine-Levin?
hypersomnia (sleep too much), hyperphagia (too much eating), hypersexuality episodes. Frontal lobe issue.