posterior ceramic crown preparation
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
i sit more common to do monolithic or laminated crown
monolithic
flexural strength of lithium disilicate
500 MPa
flexural strength of zirconia
550-1200 MPa
which uses only bonding cement
lithium disilicate
zirconia
lithium disilicate
white uses luting/bonding cement
lithium disilicate
zirconia
zirconia
what is luting cematation
little to no chemical adhesion between the tooth and the restoration
replies on the mechanical retention and resistance form

what is bonding cementation
chemical adhesion between the tooth the restoration
improve retention of the restoration

what determines whether you want to use a luting vs bonding cementation
type and quality of tooth structure
anticipated location of the finish lines
size of pre-existing restorations
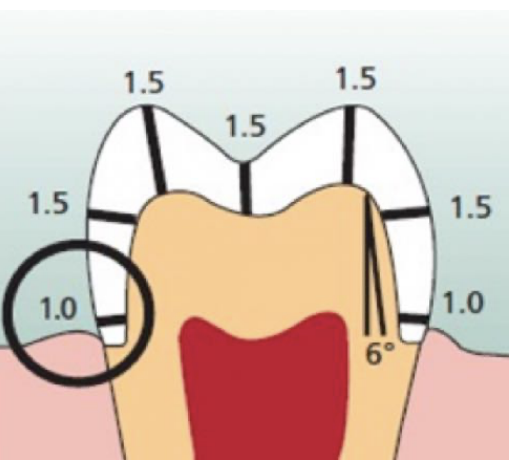
tooth preparation dimensions of a monolithic lithium disilicate restoration
funx cusp: 1.5 mm
non-funx cusp: 1.5 mm
funx cusp bevel: 1.5 mm
central groove: 1.5 mm
axial wall: 1-1.5 mm
cervical finish line: 1 mm
axial wall heigh of anterior teeth and premolars for luting cement
> 3 mm
axial wall height of posterior teeth for luting cement
> 4 mm
full coverage posterior crown prep using adhesive cemen vs prep using conventional cement
“new” adhesive cementation preparation can have slightly more conservative reduction but still mosth require the same axial height
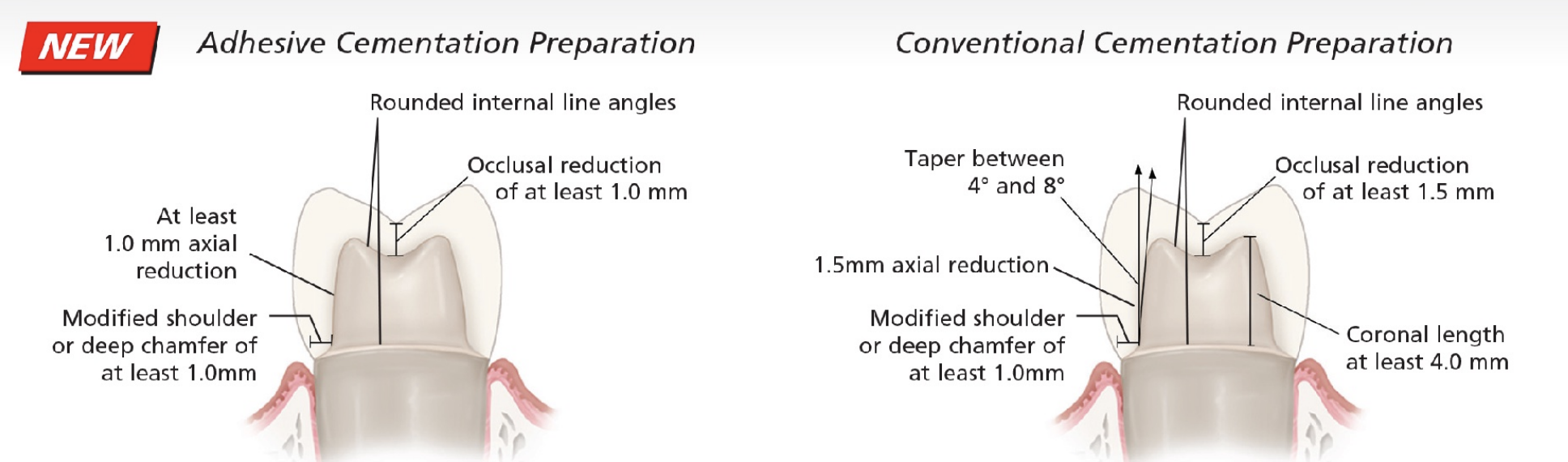
axial wall height required for bonding cement
minimum is 2 mm but the taller the better (>2 mm); can only do IF YOUR TECHNIQUE/TAPER AND PRESERVE AS MUCH ENAMEL AS POSSIBLE
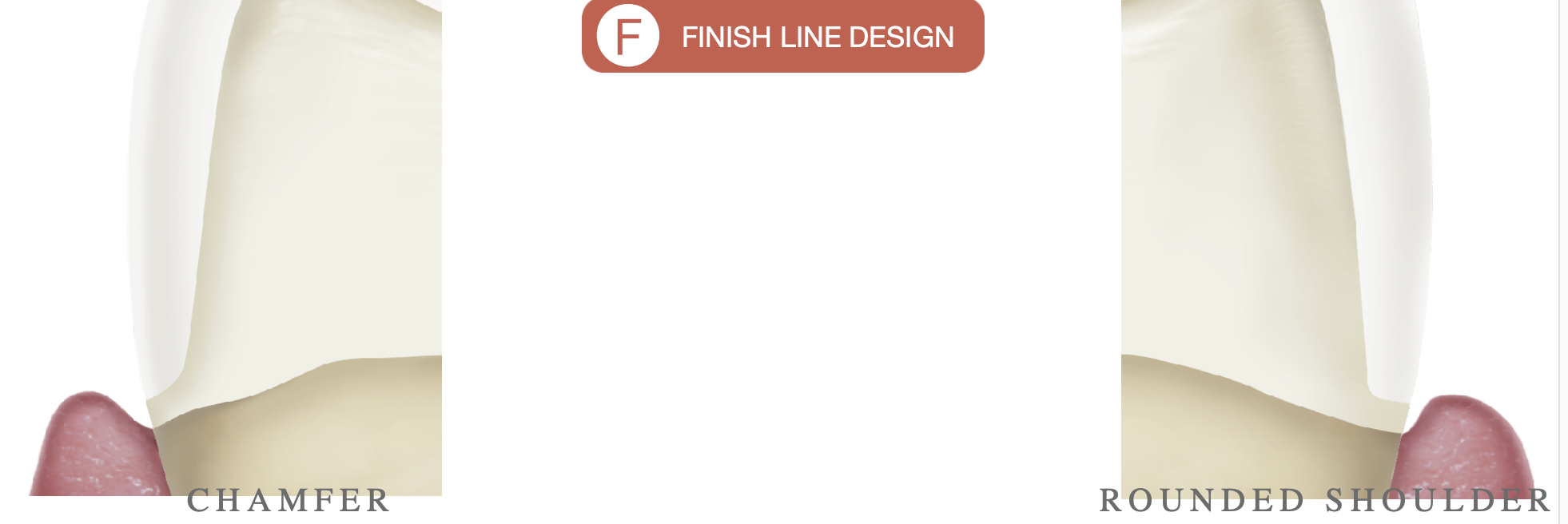
2 types of finish line design
chamfer
rounded shoulder
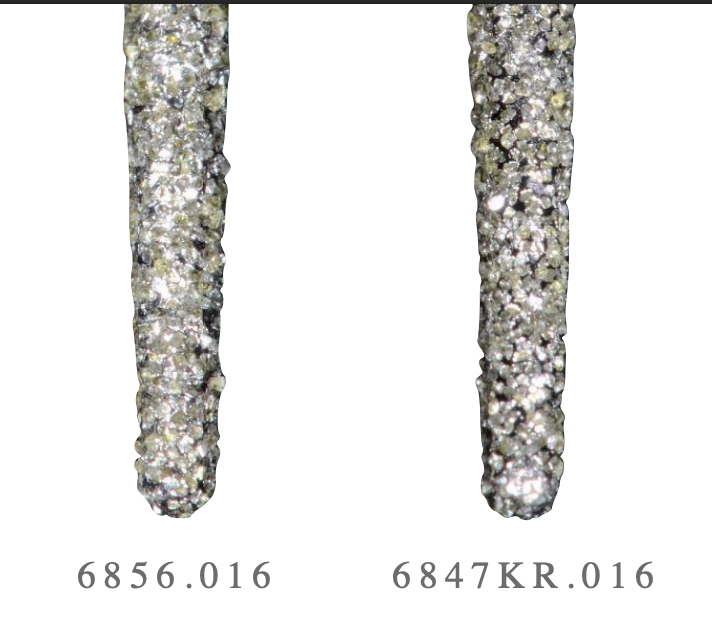

which bur would you use for which finish line desig
KR is more flat; cavosurface angle is 90 → rounded shoulder
6856: cavosurface angle is ~110mdegrees → chamfer

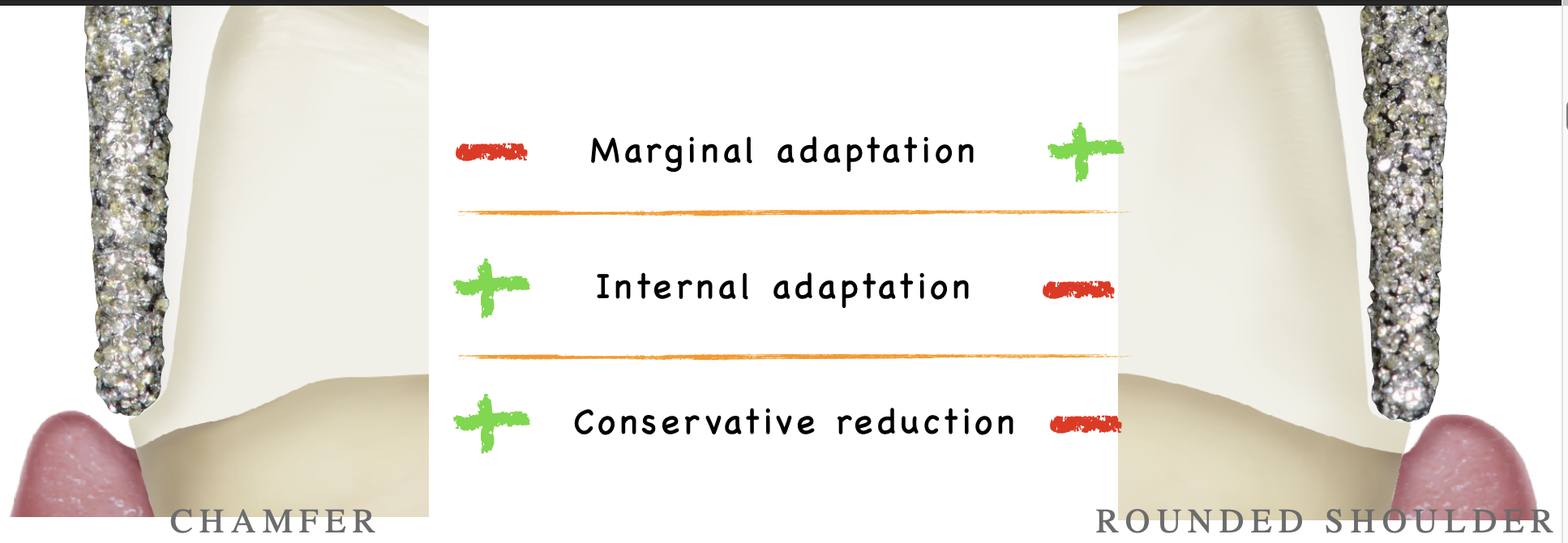
which finish line design requires less reduction given the same thickness of margin
chamfer

which finish line has a better internal adaptation
chamfer (but no affect on clinical success rate); p= 0.02
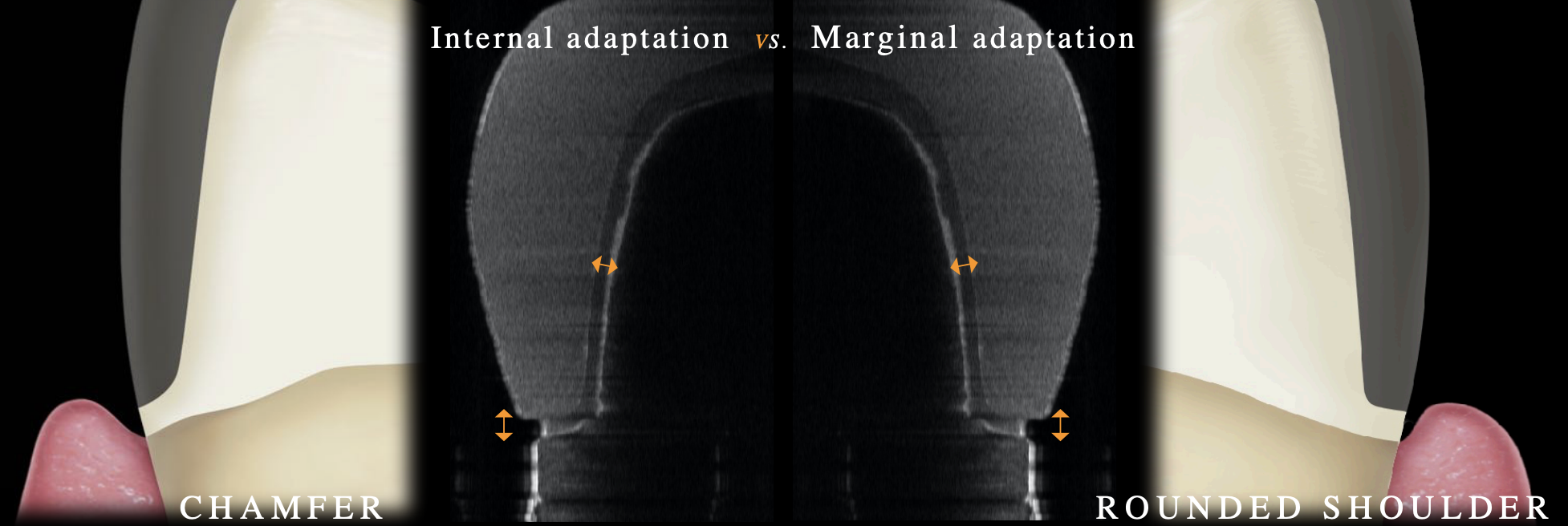

which finish line has better marginal adaptation
rounded shoulder (but no affect on clinical success rate); p< 0.01
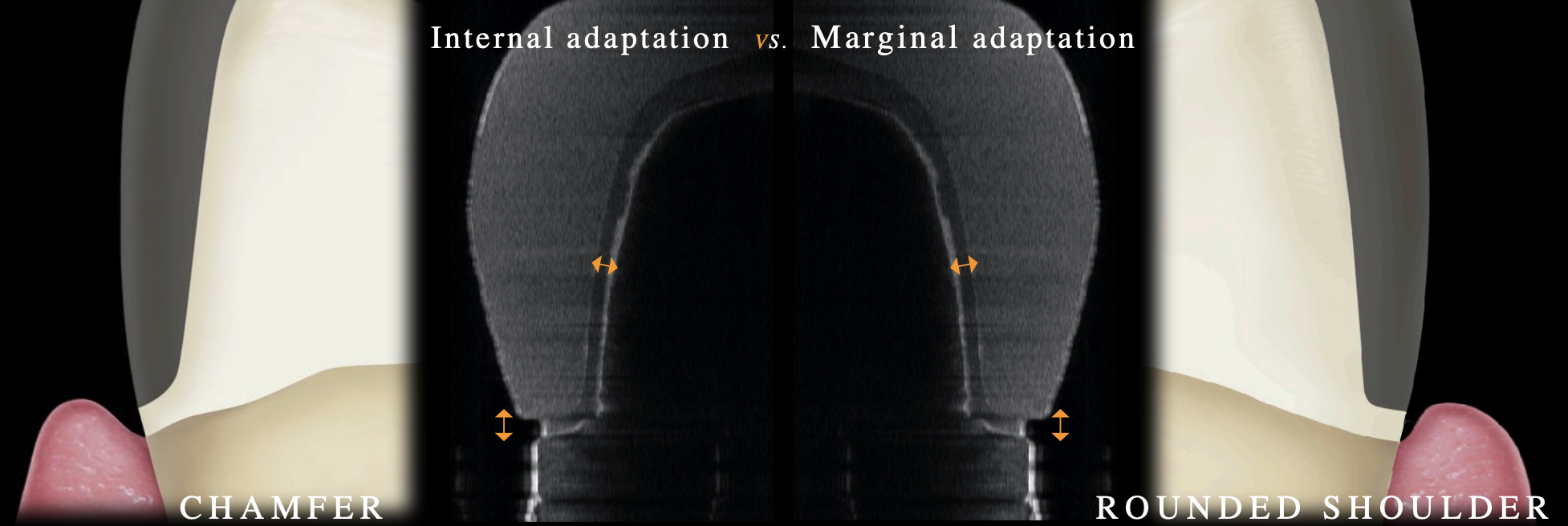

which finish line do you have more conservative reductioin
chamfer
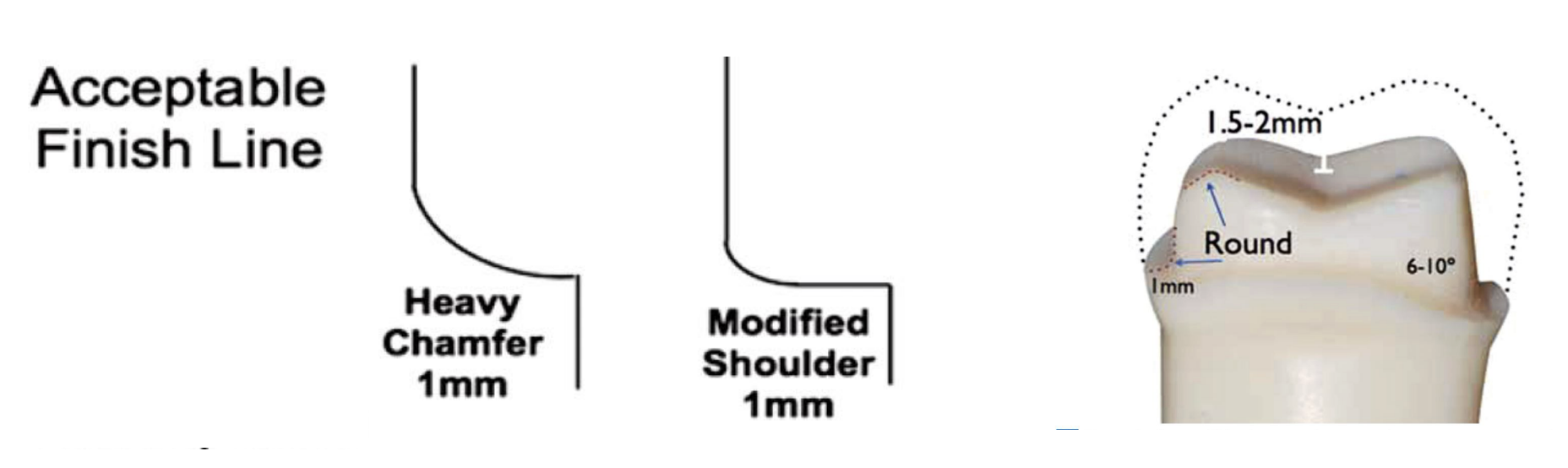
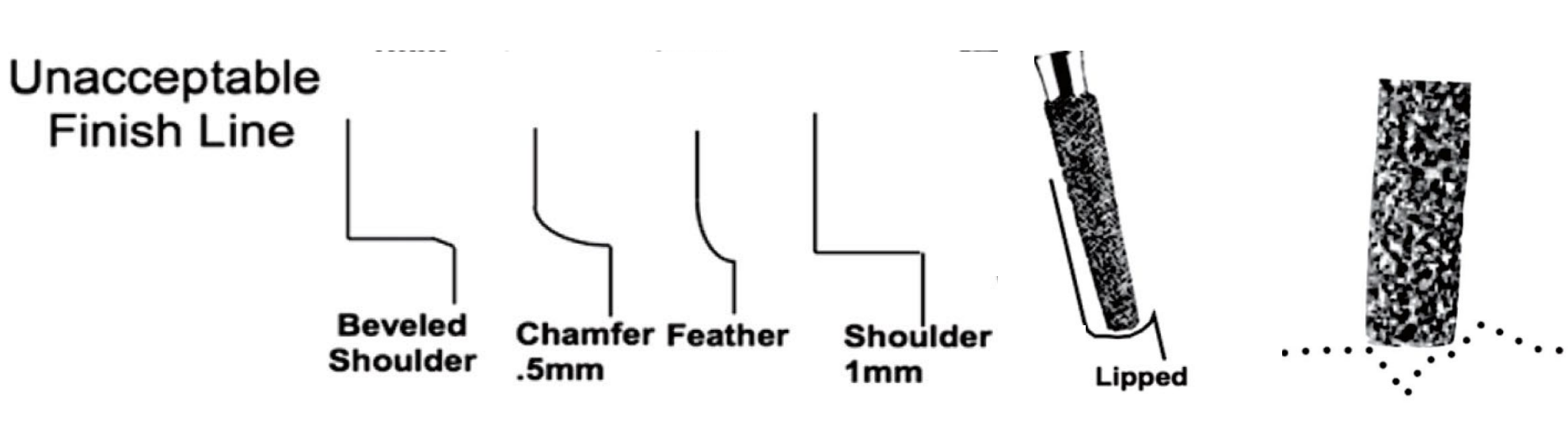
acceptabel finish lines
heavy chamfer 1 mm
modified shoulder 1 mm
unacceptable finish lines
beveled shoulder
chamfer .5
feather
shoulder 1 mm
lipped
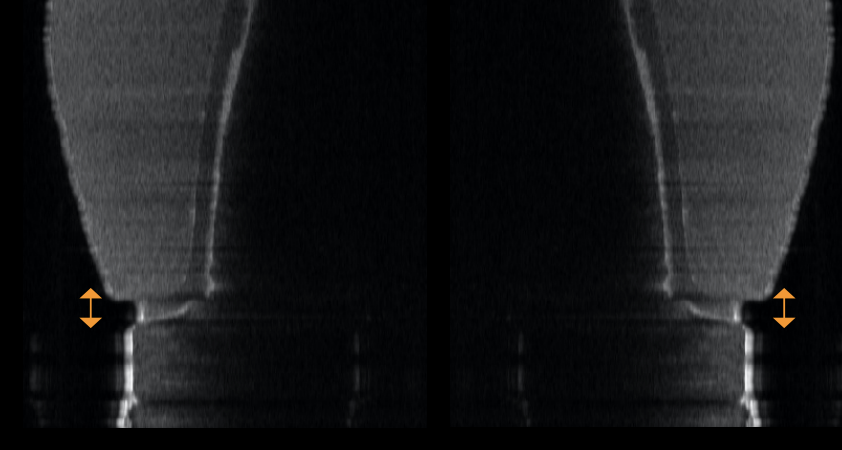
mean marginal gaps; excellent prep _________ fair prep __________ poor prep __________
excellent prep: 38.5 microns
fair prep: 58.3 microns
poor prep: 90.1 microns

the preparation quality has a significant impact on __________ on CAD/CAM crowns
marginal gap
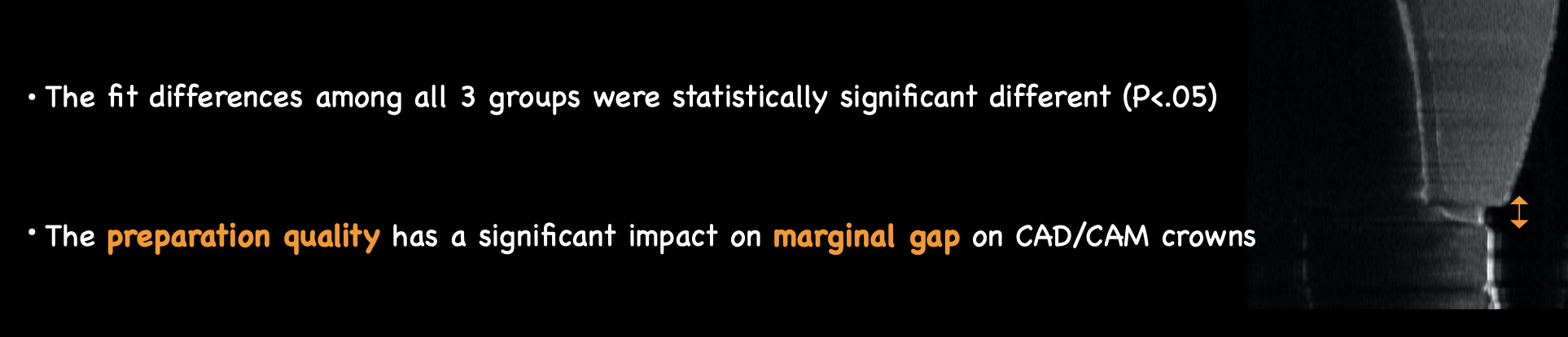
finish line requirements
even finish line width
distinct, smooth and continue
>0.6 mm clearance w adjacents
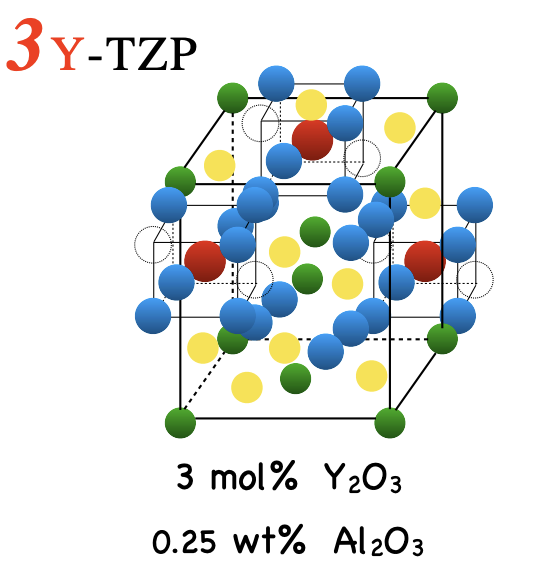
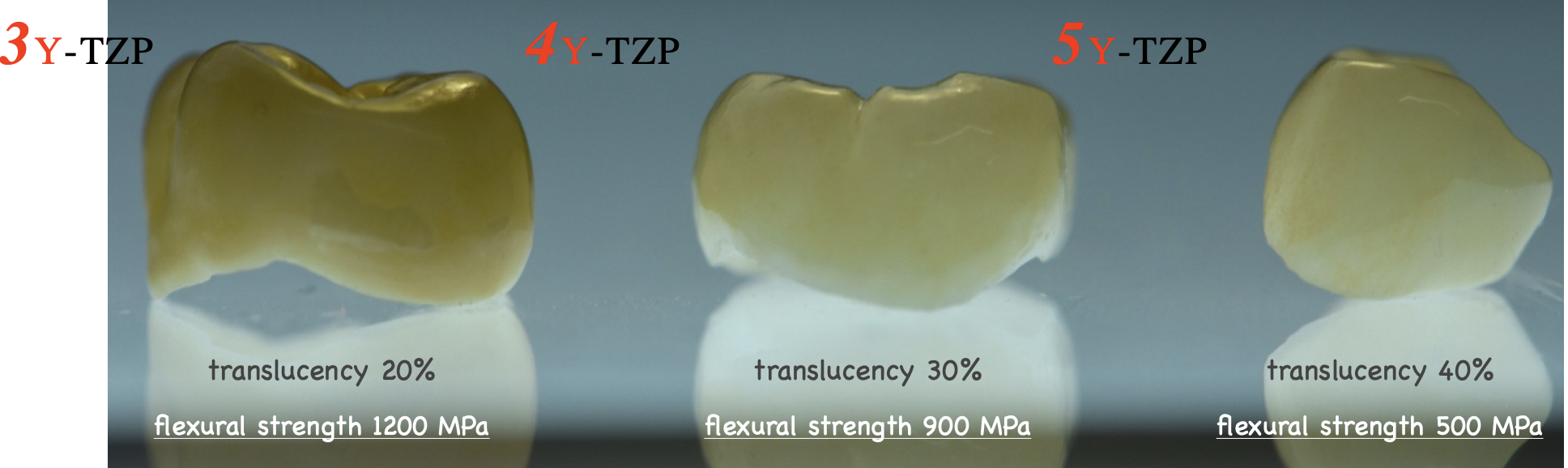
what is 3Y-TZP and what are its properties
yttria-stabalized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal
first generation zirconia
very opaque
strongest material of all zirconia

clinical indications for 3Y-TZP
crown copings
bridge frameworks
implant abutments
talk about the coefficient of thermal expansion under compression vs tension
good compression, poor tension
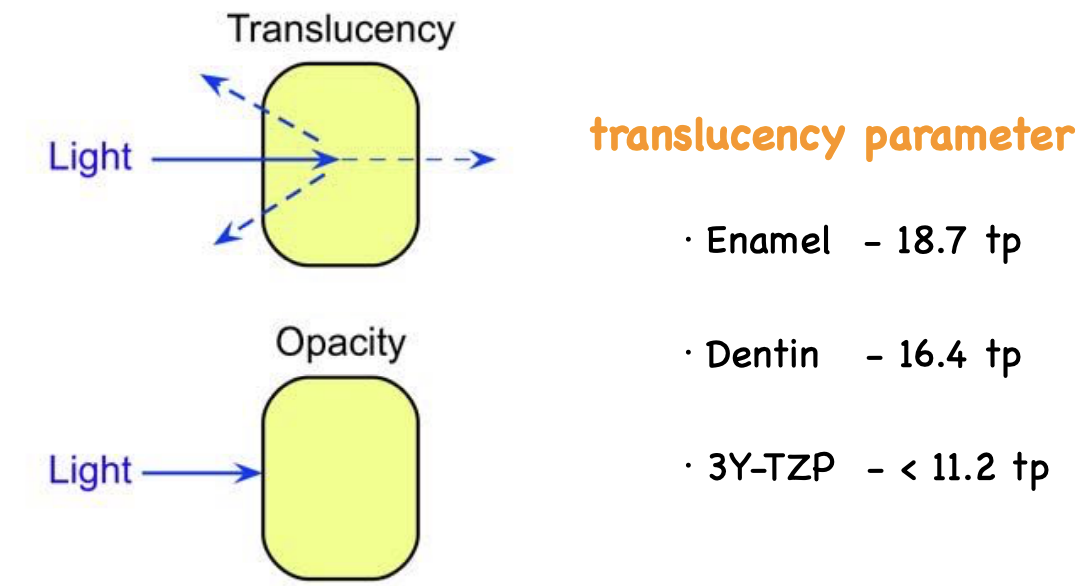
translucency parameters of enamel vs dentin vs 3Y-TZP
enamel: 18.7 tp
dentin: 16.4 to
3Y-TZP: < 11.2 tp (v opaque)
3Y-TZP → 5Y-TZP what happens to the properties (midterm q!!)
phase of tetragonal dec and will transform to cubic phase to become more translucent
trade off is dec strength
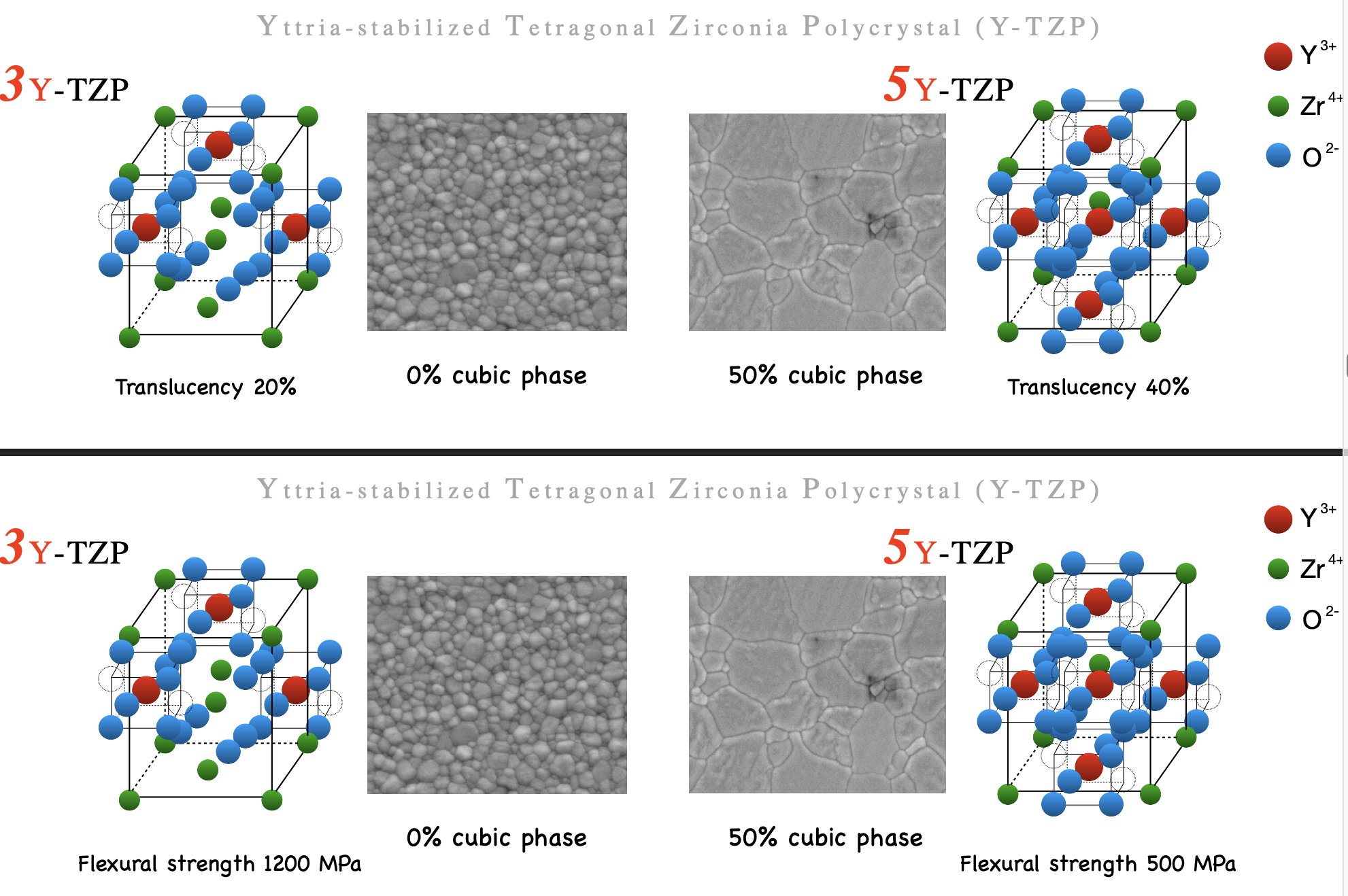
what is 5Y-TZP and what are its properties
5 ytrria-stabalized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal
second generation (maybe third??)
inc volume of yttrium
inc the cubic phase > tetragonal
more translucent →
little less strength

clinical indications for 5Y-TZP
monolithic veneers
monolithic anterior crown
5Y-TZP has the same translucency and strength as what other material
lithium disilicate
between 5Y-TZP and lithium disilicate which has better bonding properties
lithium disilicate; bc can be etched → better bonding
properties of 4Y-TZP
stronger than 3Y
700-800 MPa
little more translucent than 3Y
better for posterior crowns
what is used more in labs now

clinical indication for 4Y-TZP
monolithic crowns
monolithic short-span bridges
how translucency and strength changes between 3Y- 4Y amd 5Y-TZP
inc translucency but dec strength
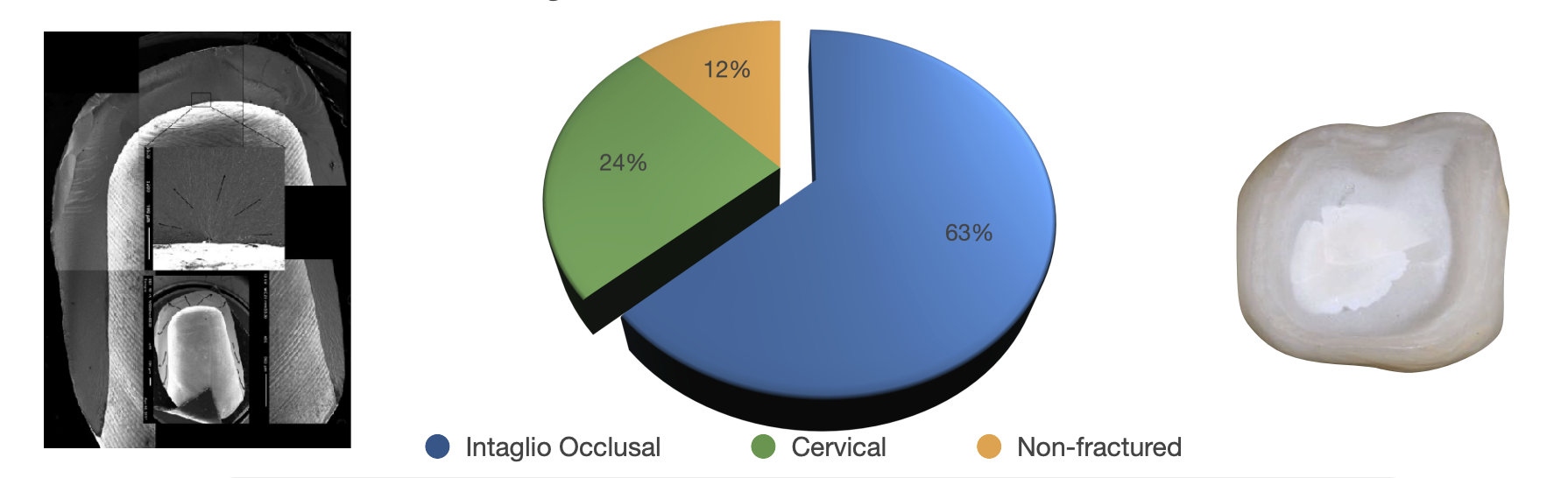
rank these origin sof fx from most common cause to least of fx of monolithic zirocnia
intaglio occlusal
cervical
non-fx

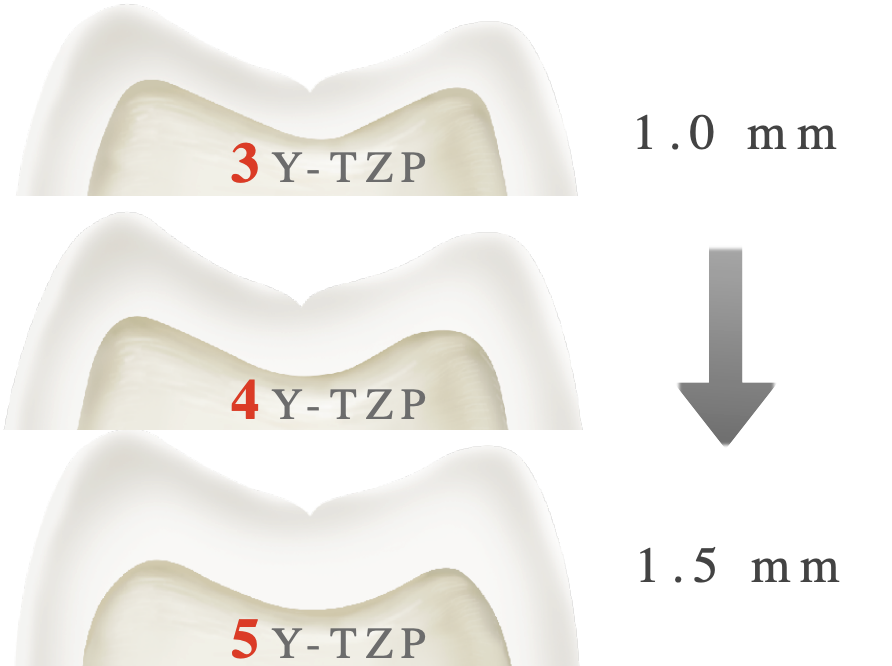
rank the amount of occlusal reduction required from least to most of 3Y- 4Y- and 5Y-TZP
3Y < 4Y < 5Y
(more translucent material → more occlusal reduction)
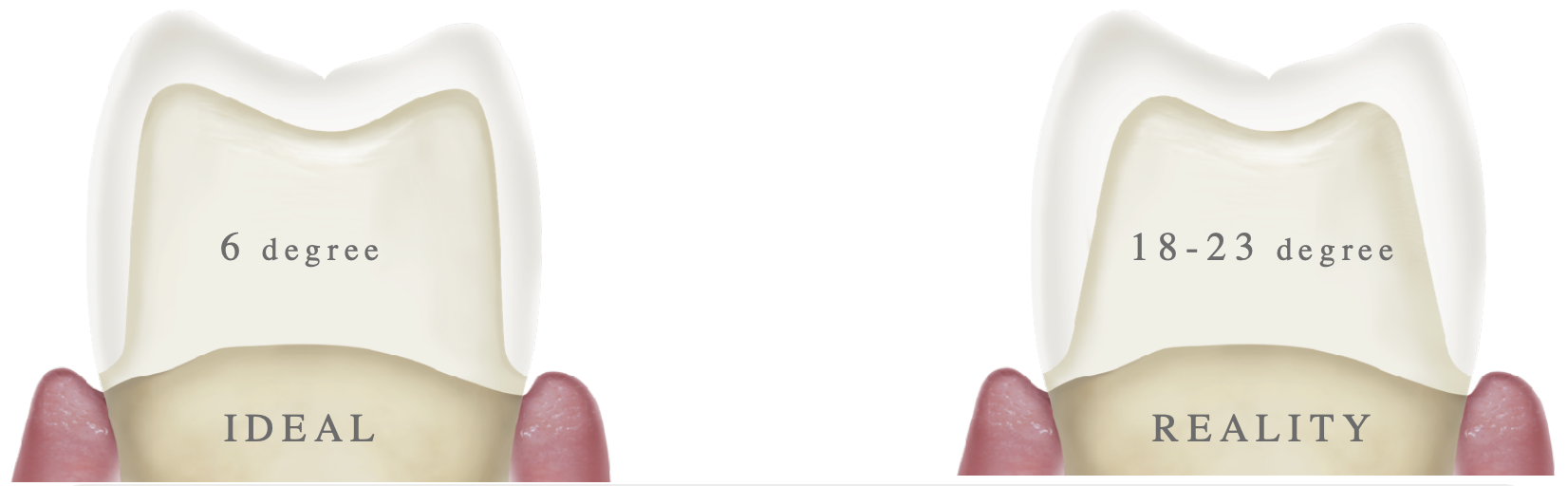
ideal vs reality of total occlusal convergence
ideal: 6 degrees
reality: 18-23 degrees

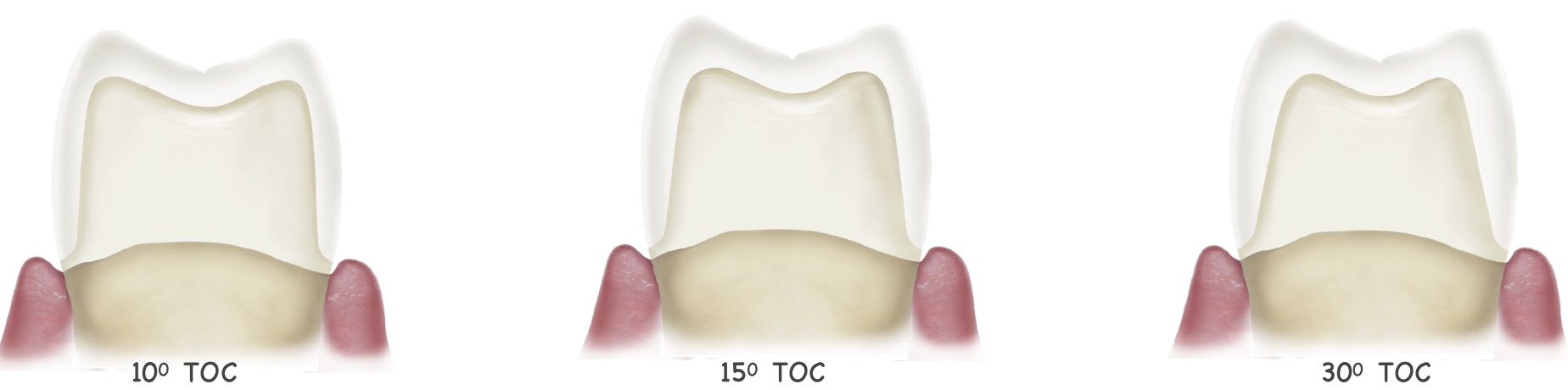
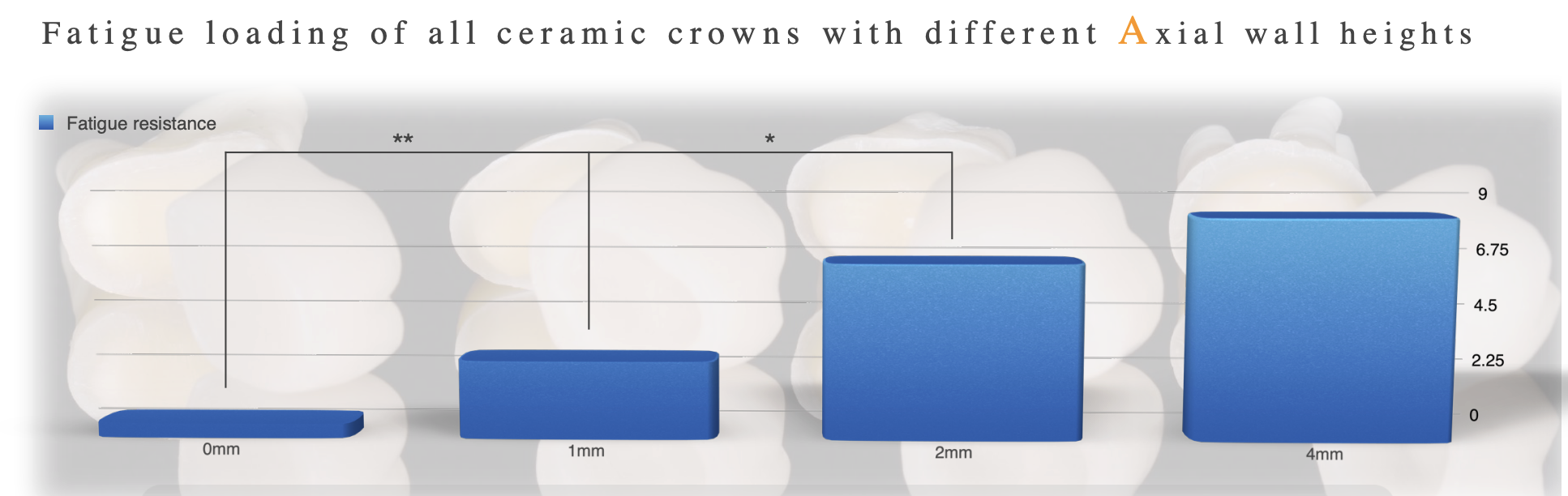
fx resistance of monolithic zirconia crowns w different total occlusal convergence of 10 vs 15 vs 30 degree
15 degree
10 degree
30 degree
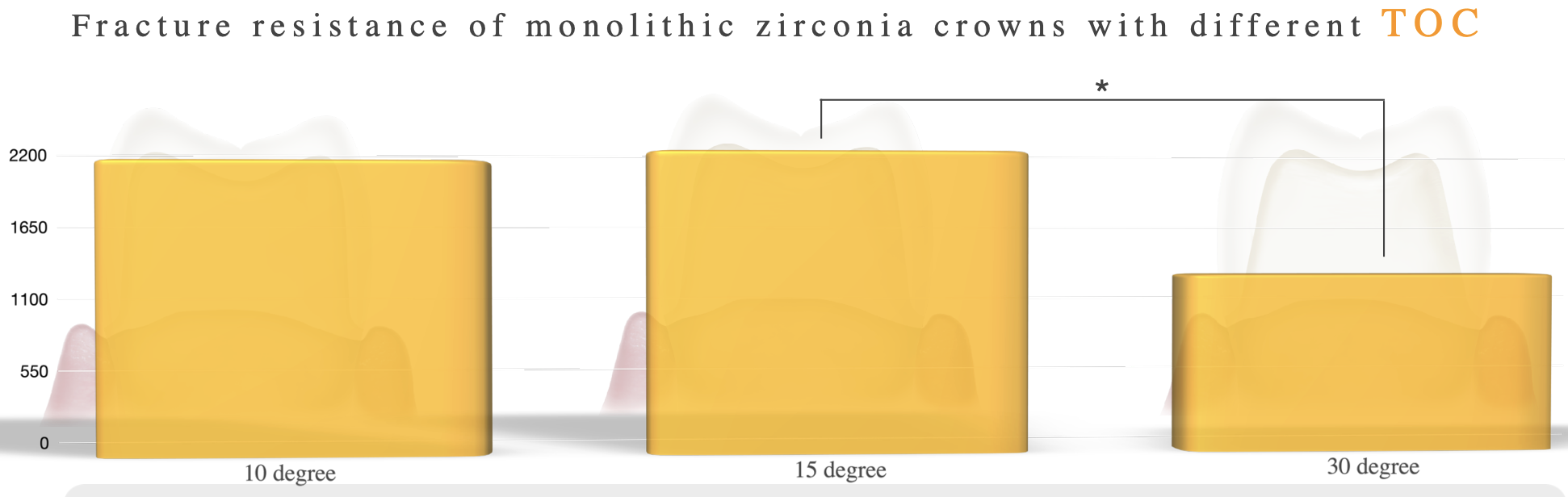
taper affects __________ and __________
retention and strength of retoration (more taper → less retention/strength)
what is the poisson effect
when you reduce enamel → your prep is getting more tapered → more dentin exposed → dentin is more flexible than enamel → occlusal force under no enamel and hard material over dentin → force will go to cervical area bc this is the weak point → cervical crack propagation
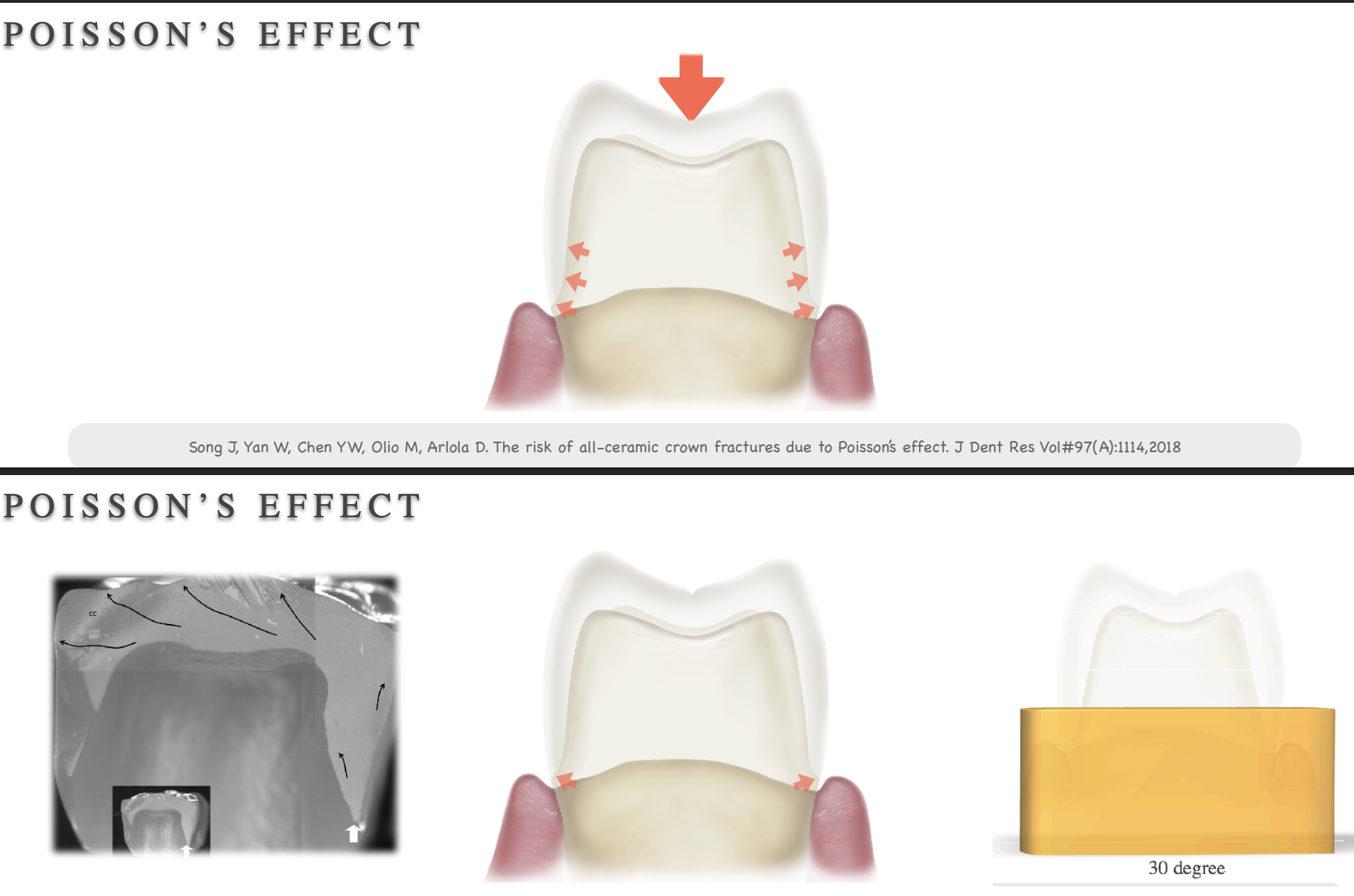
crack propagation in the cervical area is related to…
taper and margin thickness
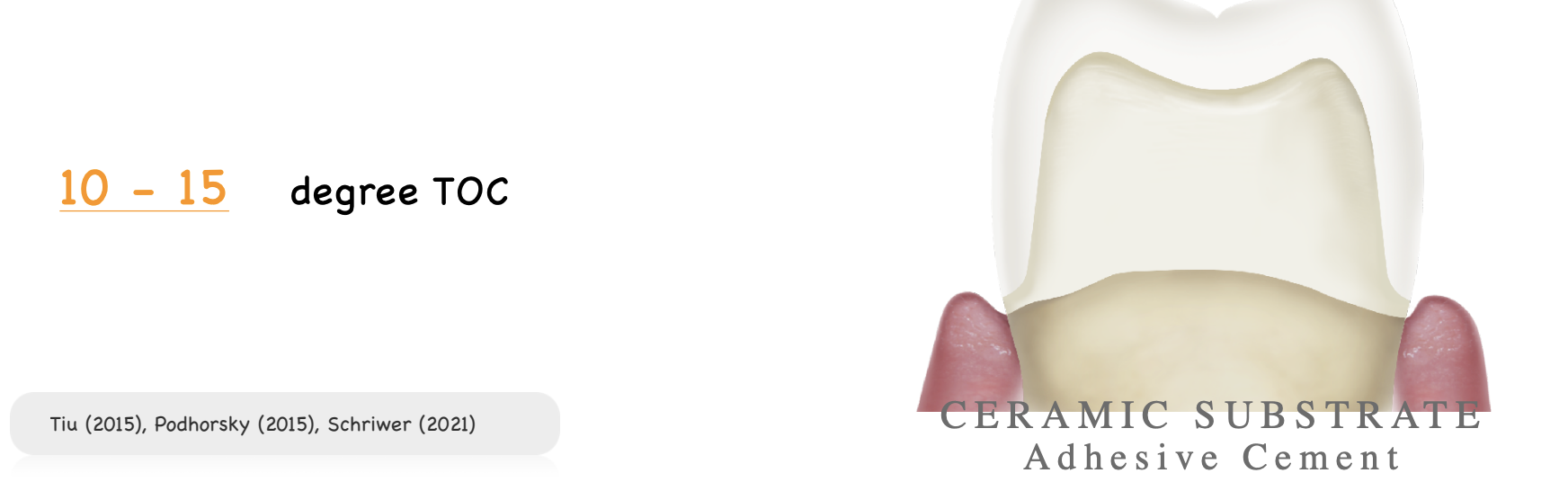
for our prep in school what total oclcusal convergence are we aiming for
10-15 degrees

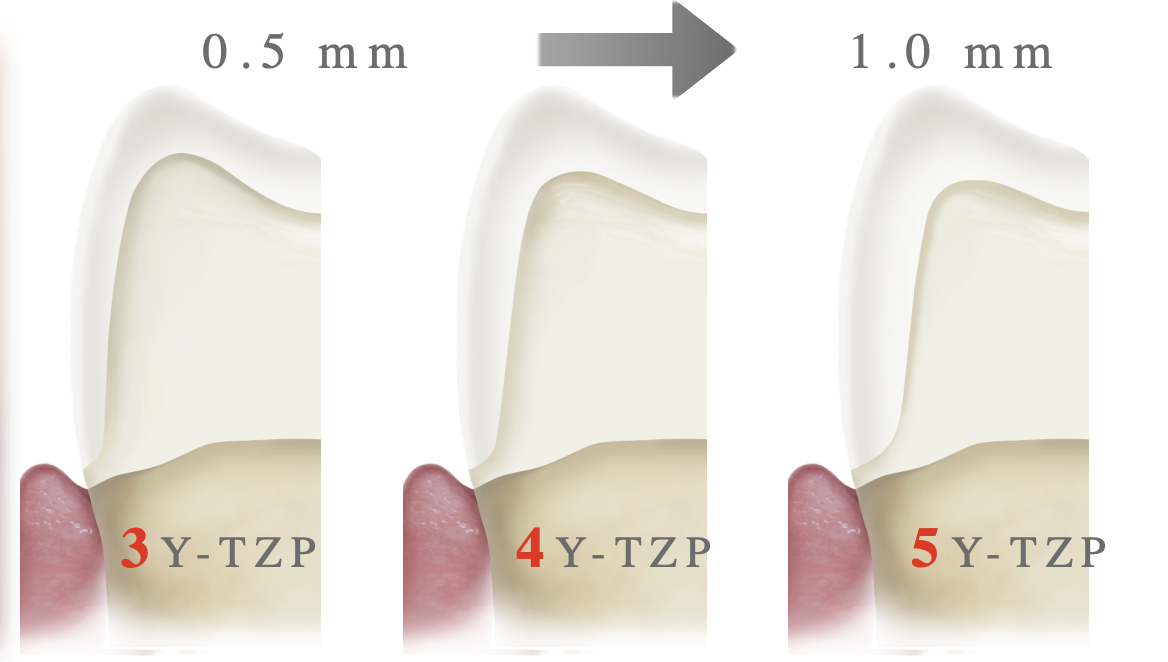
3Y-TZP finish line design
light chamfer .5 mm

4Y-TZP finish line design
.8 mm

5Y-TZP finish line design
heavy chamfer margin

how finish line design is different as you go from 3Y- 4Y- to 5Y-TZP
will inc
from them group, which group will cause more wear
polished zirconia
glazed zirconia
polish/glazed zirconia
feldspathic porcelain
enamel
porcelain/PFM
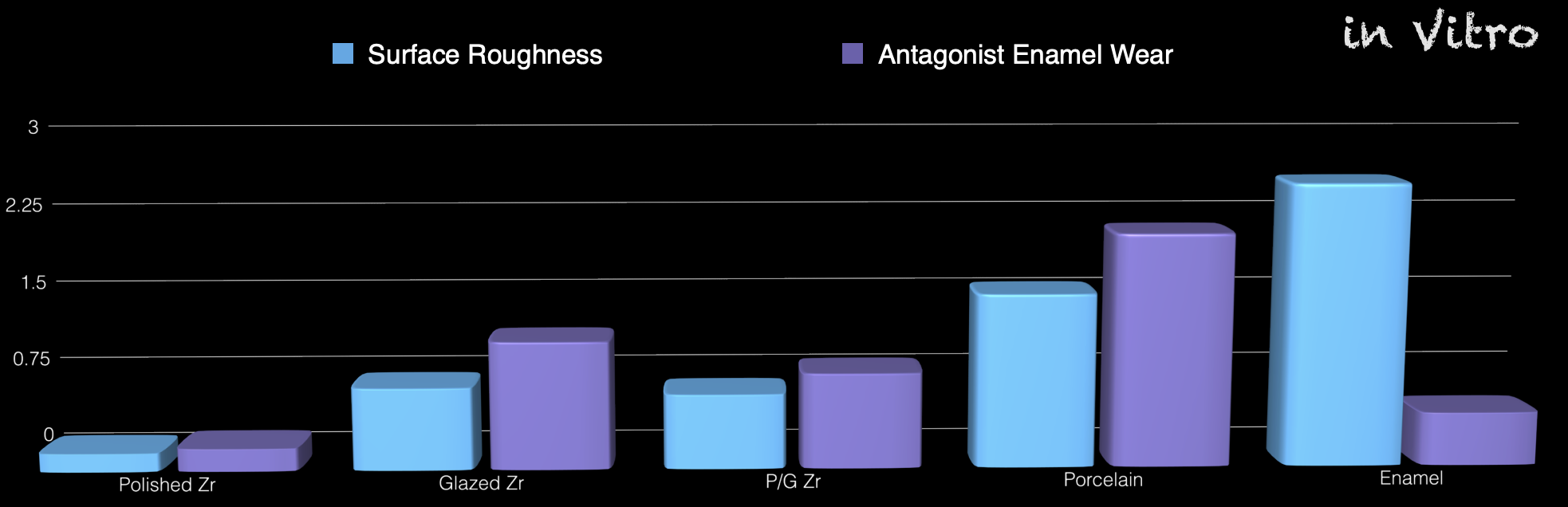
how surface roughness affects tooth wear
the more rough → the more wear it will cause on the opposing tooth (smooth/polish rather than glazed)

zirconia crowns led to ___ (less/more) wear of antagonist enamel then metal ceramic crown, but _____ (less/more) than natural teeth
zirconia crowns led to less wear of antagonist enamel then metal ceramic crown, but more than natural teeth
