Final Exam Chem 131
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/184
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
1
New cards
Organic compound
\-always contains C and H sometimes N,O,P,S, or halogens
\-NO metal atoms, covalent bonds
\-low melting and boiling points
\-flammable
\-not soluble in eater if no polar (hydrophobic)
\-NO metal atoms, covalent bonds
\-low melting and boiling points
\-flammable
\-not soluble in eater if no polar (hydrophobic)
2
New cards
methyl
CH3-
3
New cards
ethyl
CH3-CH2-
4
New cards
propyl
CH3-CH2-CH2
5
New cards
isopropyl
CH3-CH2-CH3
|
|
6
New cards
butyl
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-
7
New cards
isobutyl
CH3-CH-CH2-
|
CH3
|
CH3
8
New cards
sec-butyl
CH3-CH-CH2-CH3
|
|
9
New cards
tert-butyl
CH3
|
CH2-C-CH3
|
|
CH2-C-CH3
|
10
New cards
fluoro
F-
11
New cards
chlorophyll
Cl-
12
New cards
bromo
Br-
13
New cards
iodo
I-Pre
14
New cards
prefixes
1 = mono-
2= di-
3= tri-
4= tetra-
5= penta-
6= hexa-
7= hepta-
8= octa
9= nona-
10= deca-
2= di-
3= tri-
4= tetra-
5= penta-
6= hexa-
7= hepta-
8= octa
9= nona-
10= deca-
15
New cards
methane
CH4
16
New cards
Ethane
CH3-CH3
17
New cards
Propane
CH3-CH2-CH3
18
New cards
Butane
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3
19
New cards
Pentane
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3
20
New cards
Hexane
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3
21
New cards
Heptane
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3
22
New cards
Octane
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3
23
New cards
Nonane
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3
24
New cards
Decane
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3
25
New cards
IUPAC name with cycloalkanes
\-no number for single alkyl group or halogen atoms
26
New cards
IUPAC name with alikanes and substituents
\-muliple sub of same name use greek prefix (never mono)
27
New cards
Alkanes
\-lowest melitng/boiling point, weak disperson forces
\-Branched alkanes lower boiling point than straight-chain isomer
\-longer chain more disperson force (more carbons)
\-CYCLOalkanes high boiling point than striaght-chain isomer
\-Branched alkanes lower boiling point than straight-chain isomer
\-longer chain more disperson force (more carbons)
\-CYCLOalkanes high boiling point than striaght-chain isomer
28
New cards
Alkenes and cycloalkenes
\-C=C bond
29
New cards
Alkynes ad cycloalkanes
* Triple bond carbon- carbon
30
New cards
cis-trans isomers
\-cis:larger groups on the same side of the double bond
\-trans:larger group on the opposite side of double bond
\-trans:larger group on the opposite side of double bond
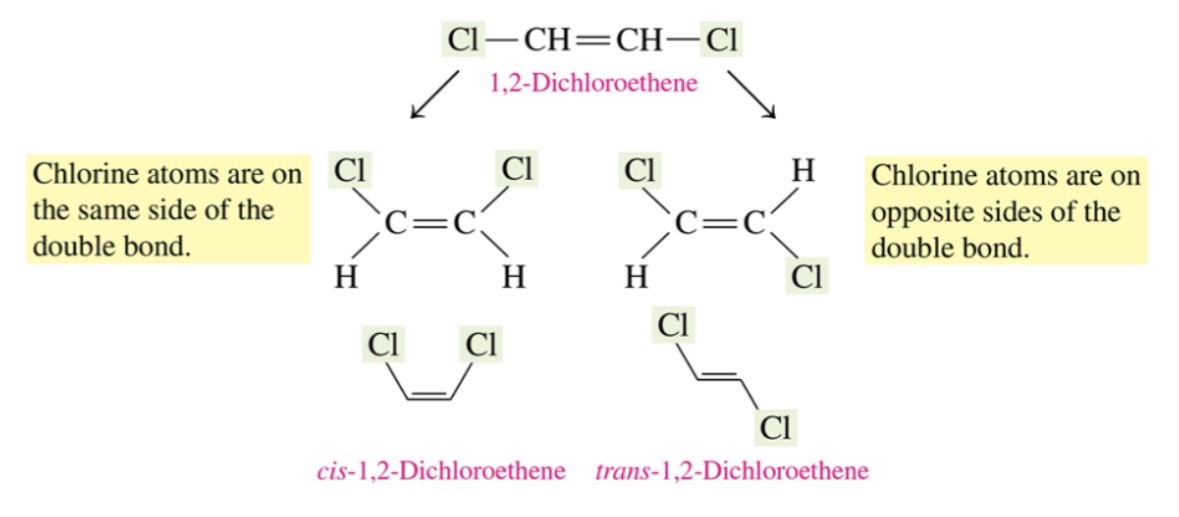
31
New cards
bonding benzenes
\-ring with 3 alternating double bonds
\-use circle in middle for drawing line angle and three lines for condensed structure
\-use circle in middle for drawing line angle and three lines for condensed structure
32
New cards
Aromatic Copounds
Step 1: write name for aromatic compound. aromatic base with one of the common names instead of benzene
Step 2: if tow or more substituents, give lowest values to substituends
Step 3: name each substituent include common and put in alphabetical order
Step 2: if tow or more substituents, give lowest values to substituends
Step 3: name each substituent include common and put in alphabetical order
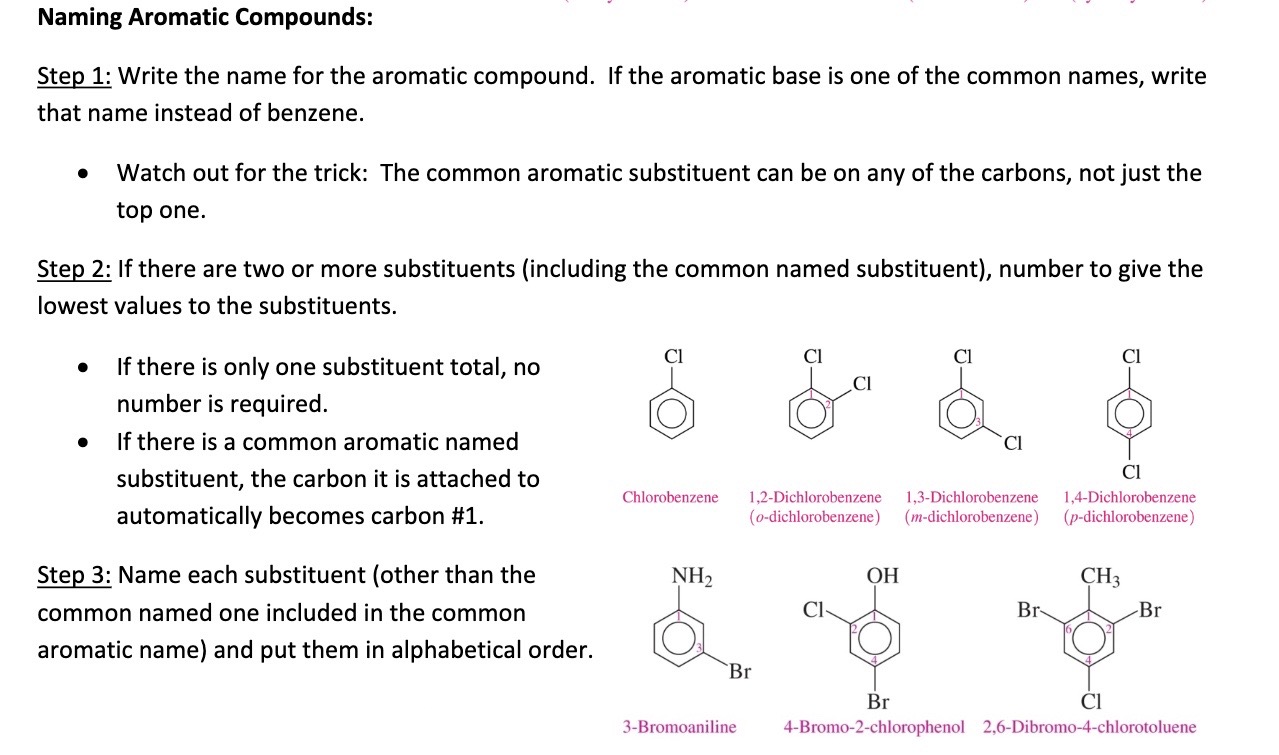
33
New cards
Common name for alcohols
\-name of alkyl gorup follwed by alcohol( methyl alchohol,cyclohexyl alcohol)
34
New cards
common name for phenols
\-methylphenal is called cresol
35
New cards
alcohol, phenol, thiol draw-
\-alchohol has a-OH attacted to carbon
\-phenol has a-OH attached to benzene ring
\-thiol has a-SH attached to catbon
\-S or O always attached, never H
\-phenol has a-OH attached to benzene ring
\-thiol has a-SH attached to catbon
\-S or O always attached, never H
36
New cards
Common name for ethers
\-two alkyl or aromatic group written in alphabetical order
\-end name is ether
\-end name is ether
37
New cards
drawing ether
\-oxygen atom attached by two single bonds to two carbon groups
\-two carbon groups will alwys be alkyl group or aromatic group
\-two carbon groups will alwys be alkyl group or aromatic group
38
New cards
Classification of alchohols
\
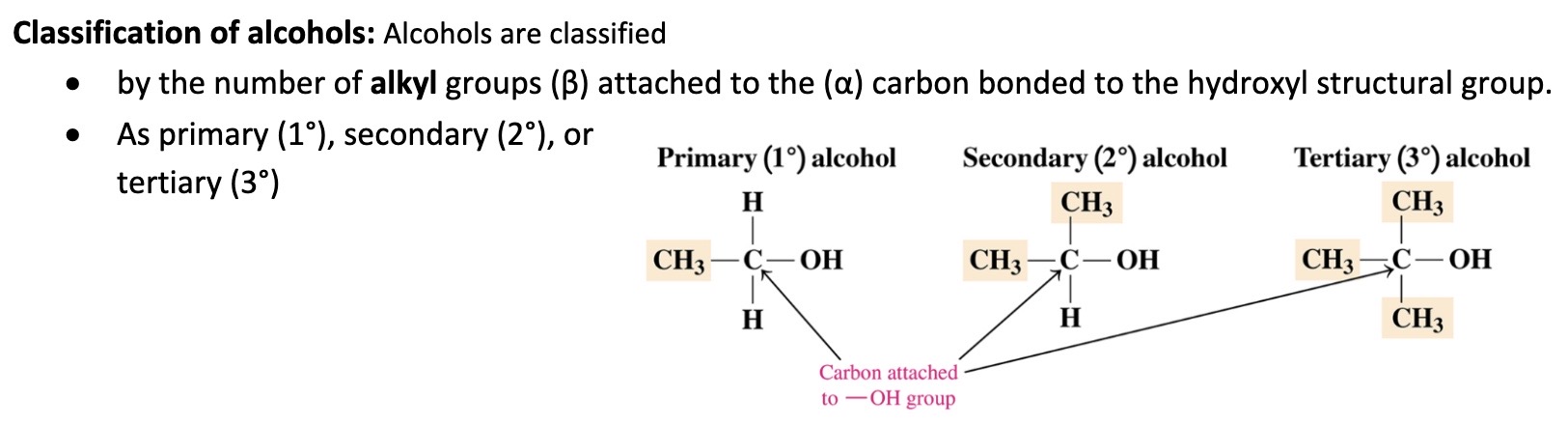
39
New cards
boiling point of alcohols and ethers
\-alcohol and ether boiling point increases as carbons are added
\-ether has lower boiling point thann alcohol becasue it doesn’t intiate hydrogen bonding
\-ether has lower boiling point thann alcohol becasue it doesn’t intiate hydrogen bonding
40
New cards
solubility of alcohols phenols and ethers
\-alcohols 1-3 carbons soluble in water 4 carbons slightly soluble
\-ethers 2-4 carbons slightly soluble in water 5 carbons insoluble
\-phenol slightly soluble in water
\-ethers 2-4 carbons slightly soluble in water 5 carbons insoluble
\-phenol slightly soluble in water
41
New cards
dehydration reaction for alcohol
\-alkene(2 double bonned c)+ water
\-loses -H and -OH from adjacent carbon atoms of the same alcohol
\-loses -H and -OH from adjacent carbon atoms of the same alcohol
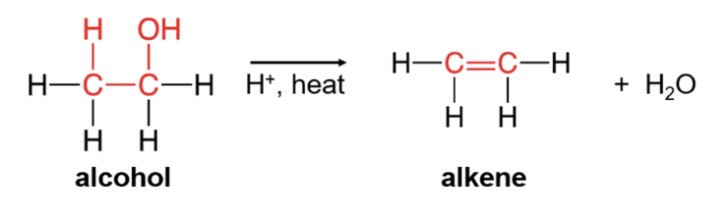
42
New cards
oxidation reaction for primary alcohol
\-primary oxidize to produce aldehyle (double doned c-c and h)
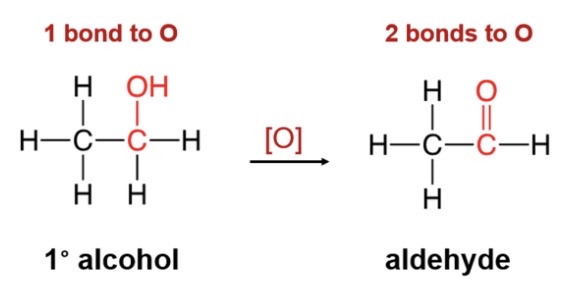
43
New cards
oxidation of secondary alcohol
\-secondary alcohols oxiixe to produce a ketone( double bonded c-c and c)
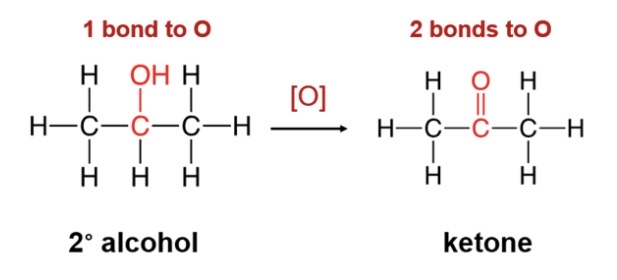
44
New cards
oxidation of tertiary alcohols
\-can’t oxide because there si no H on the a-carbon
45
New cards
Oxidation of aldehydes
\-aldehydes oxidize to produce carboxylic acid (H turns into OH)
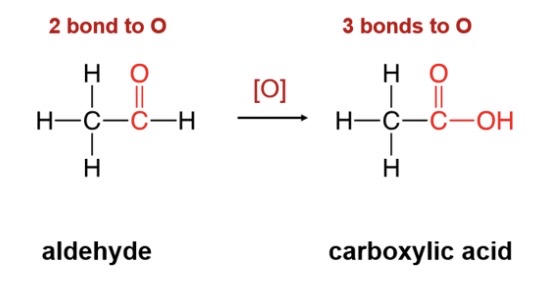
46
New cards
catalyst for different reactions
\-oxidation \[O\]
\-reduction: pt, ni, or pd
\-dehydration: H+, heat
\-reduction: pt, ni, or pd
\-dehydration: H+, heat
47
New cards
compounds with carbonyl groups as aldehydes and ketones
\-O=C
\-aldehyde is -CHO
\-ketoen is -CO-
\-aldehyde is -CHO
\-ketoen is -CO-
48
New cards
common names for aldehydes and ketones
\-greek prefix -aldehyde (acetaldehyde)
\-1C= form-, 2C= acet, 3C= propion, 4C= butyr
\-alkyl group bonded to carbon group are listed alphabetically -ketone (ethyl methyl ketone)
\-1C= form-, 2C= acet, 3C= propion, 4C= butyr
\-alkyl group bonded to carbon group are listed alphabetically -ketone (ethyl methyl ketone)
49
New cards
boiling point and solubility of aldehydes and ketones
\-boiling point increased as carbons increase
* 1-4 carbons soluble in water, 5 carbons slightly soluble, 6+ carbons insoluble
* -both accept hydrogen bonds, not initiate
* 1-4 carbons soluble in water, 5 carbons slightly soluble, 6+ carbons insoluble
* -both accept hydrogen bonds, not initiate
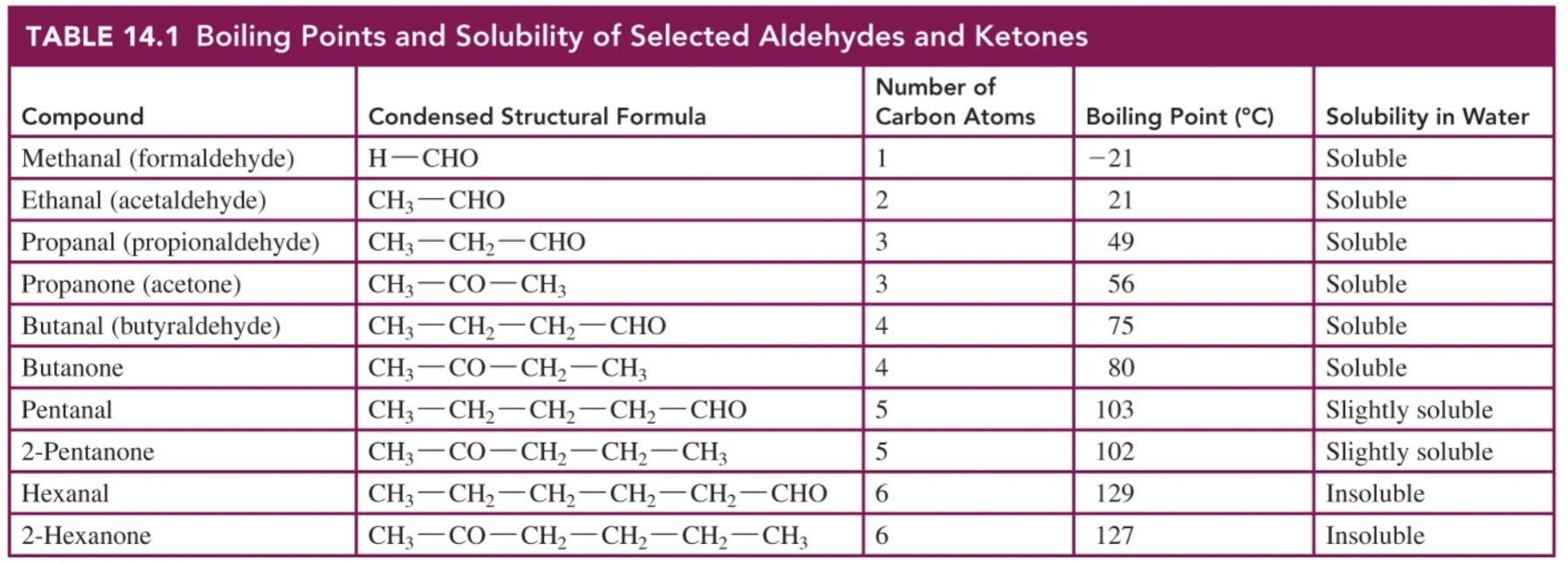
50
New cards
formulas of aldehydes and ketones
\-condense as CHO or CO
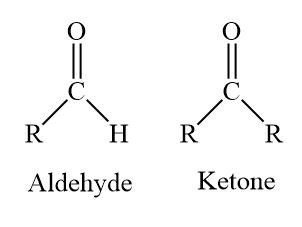
51
New cards
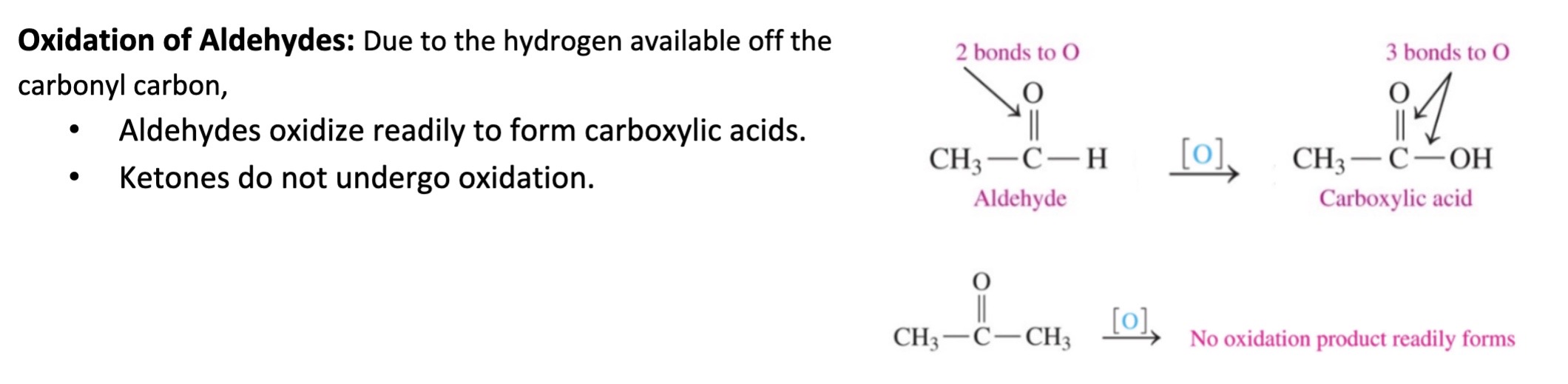
reactants and products in oxidation /reduction reactions of aldehydes and ketones
\-aldehydes oxidize into carboxylic acid
\-ketones don’t oxidize because they don’t have a hydrogen
\-ketones don’t oxidize because they don’t have a hydrogen
52
New cards
Oxidation of Aldehydes
\-aldehydes reduce into primary alcohols
\-ketones reduce into secondary alcohols
\-ketones reduce into secondary alcohols
53
New cards
reduction of aldehydes and ketones
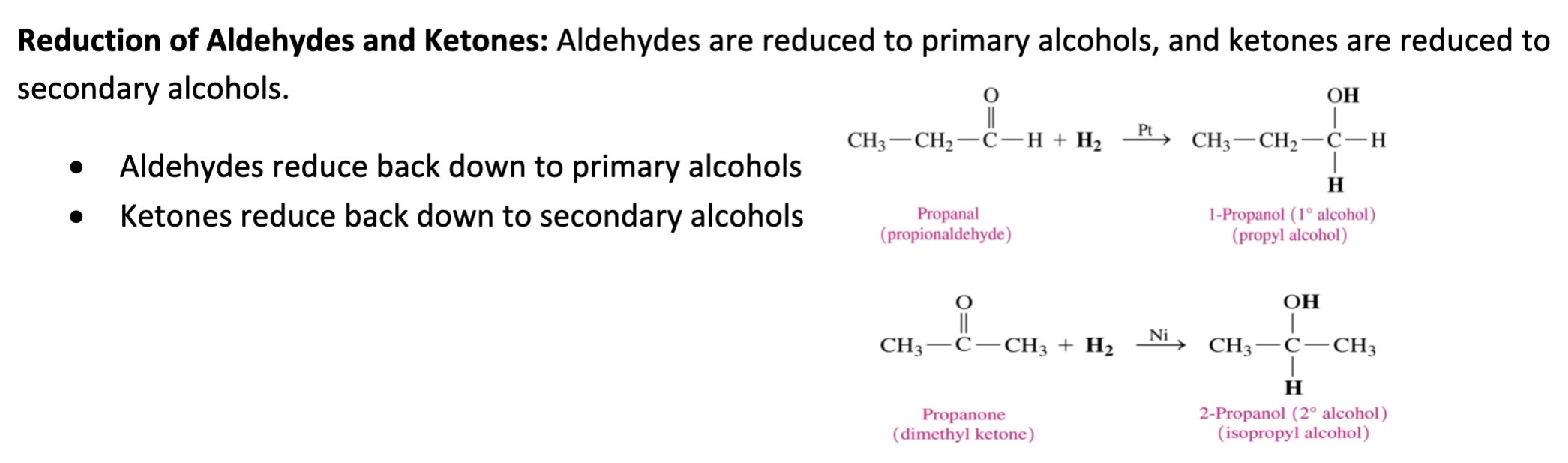
54
New cards
difference between tollen and benedict’s test
\-tollens oxidizes aldehydes and forms a silver mirror but not ketones (negative for ketones
\-benedict turns brick red when reacting with aldehyde
\-benedict turns brick red when reacting with aldehyde
55
New cards
hemiacetals and acetals
\-meniacetals contain an -OH and -OR group on the same carbons atoms
\-acetals contain two -OR groups on the same carbons
\-acetals contain two -OR groups on the same carbons
56
New cards
monosaccharides as aldose or ketose
\-alsoses have a H-C+O (aldehyde) group at the top in the Fischer structures
\-ketoses have CH2OH-C=O (ketone) group at the top of fisher strctures
\-ketoses have CH2OH-C=O (ketone) group at the top of fisher strctures
57
New cards
Number of carbons in monosaccharides
\-triose (3 carbons atoms)
\-tetrose (4 carbon atoms)
\-pentose (5 carbon atoms)
\-hexose (6 carbon atoms)
\-tetrose (4 carbon atoms)
\-pentose (5 carbon atoms)
\-hexose (6 carbon atoms)
58
New cards
chiral and a-chiral in organic molecules
\-carbon atoms are chiral if they have four different atoms or groups
59
New cards
D or L enontiomers of monosaccharides with fisher projections
\-D= right Oh on the last chiral carbon
\-L= left HO on last chiral carbon
\-L= left HO on last chiral carbon
60
New cards
common monosaccharides based on thier structures and functions
\-D-glucose: blood sugar) aldohexose
\-D-galactose (found in milk) aldohexose
\-D-Fructose (fruit sugar) ketohexose
\-D-galactose (found in milk) aldohexose
\-D-Fructose (fruit sugar) ketohexose
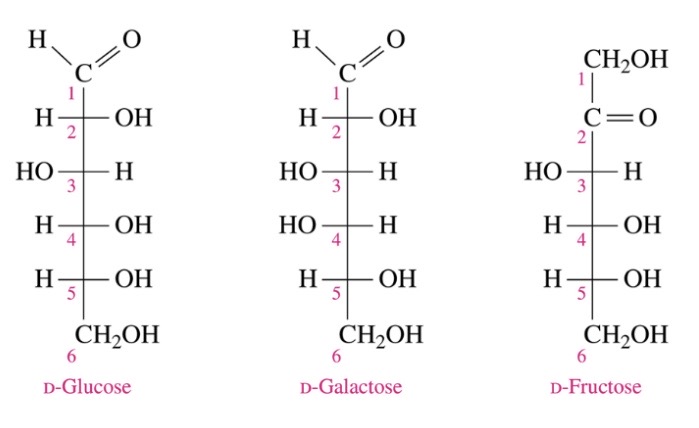
61
New cards
haworth stuctures for monosaccharides
\-turn figher projection 90 clockwise, bond O on carbon 5 to carbon 1, draw Oh on carbon 1 accround to the isomer
\-pentagon if fructose or ketohexose
\-a isomers hav -OH below carbon 1
\-B isomer have -Oh above carbon 1
\-pentagon if fructose or ketohexose
\-a isomers hav -OH below carbon 1
\-B isomer have -Oh above carbon 1
62
New cards
oxidation or reduction of monosaccharides
\-oxidation converts top form H-C+O to HO-C=o
\-oxidation renames -ose ending to -onic acid
\-reduction converts top from H-C-O to CH2OH
\-reduction renames -ose ending to -itol
\-oxidation renames -ose ending to -onic acid
\-reduction converts top from H-C-O to CH2OH
\-reduction renames -ose ending to -itol
63
New cards
carbohydrate is a reducing sugar
\-all aldoses are reducing sufars that can oxidize to carboxylic acids
\-all ketoses are reducting sufars due to rearrangement
\-all ketoses are reducting sufars due to rearrangement
64
New cards
monosaccharides in disaccharides
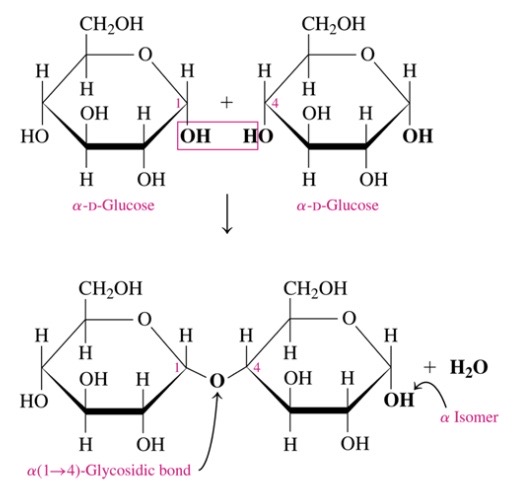
\-glucose+glucose = maltose
\-a-1,4 glycosidic bond
\-glucose_galatose = lactose
\-B-1,4 glycosidic bond
\-glucose+fructose = sucrose
\-a,B- 1,2 glycosidic bonds
\-a-1,4 glycosidic bond
\-glucose_galatose = lactose
\-B-1,4 glycosidic bond
\-glucose+fructose = sucrose
\-a,B- 1,2 glycosidic bonds
65
New cards
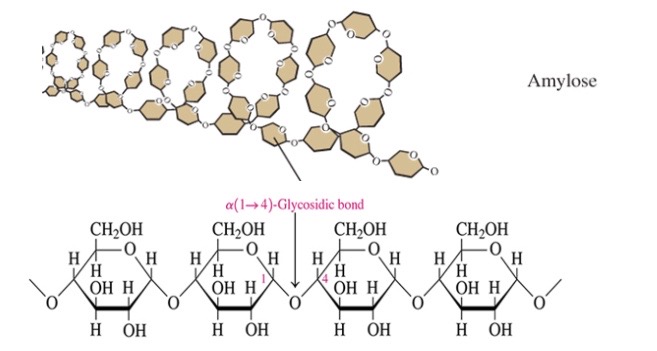
Amylose
\-20% of starch: storage form of glucose in plants
\-glucose molecules connected by a-1,4 glycosidic bonds
\-glucose molecules connected by a-1,4 glycosidic bonds
66
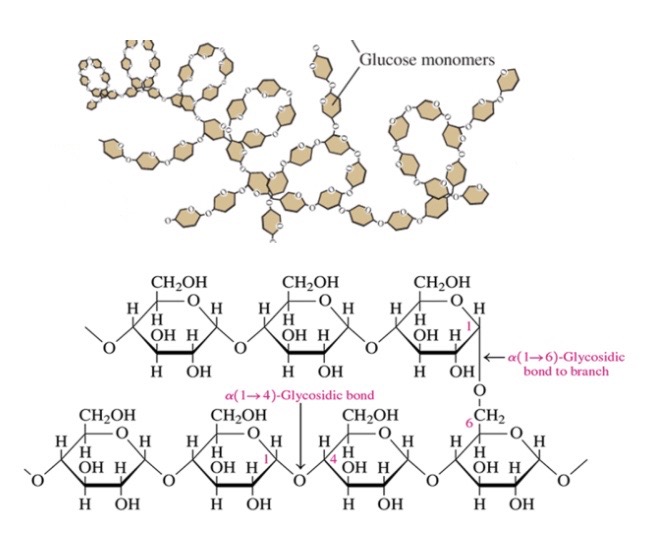
New cards
Amylopectin
\-80% of starch
\-glucose molecules connected by a-1,4 and a-1,6 glycosidic bonds
\-glucose molecules connected by a-1,4 and a-1,6 glycosidic bonds
67
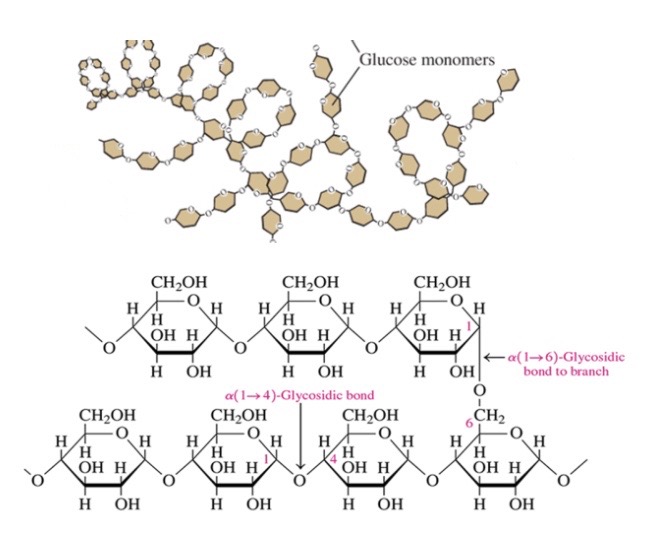
New cards
Glycogen
\-glucose stored in liver and muscle to provide energy between meals
\-glucose molecules connected by a-1,4 glycosidic bonds with branches attached by a-1,6 glycosidic bonds
\-like amylopectin but more highly branched
\-glucose molecules connected by a-1,4 glycosidic bonds with branches attached by a-1,6 glycosidic bonds
\-like amylopectin but more highly branched
68
New cards
Cellulose
\-structural unit of woods and plants
\-unbranched chain of B-1.4 glycosidic bonds
\-can’t be digested by humans
\-unbranched chain of B-1.4 glycosidic bonds
\-can’t be digested by humans
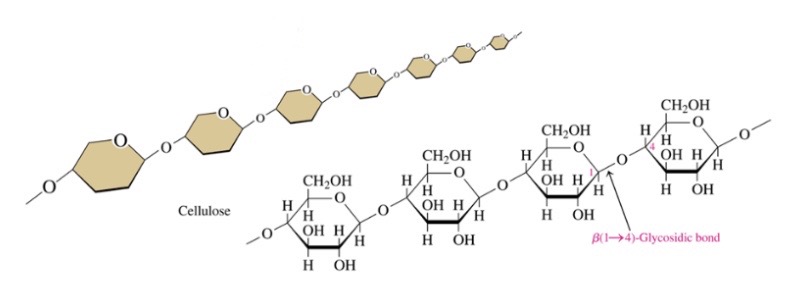
69
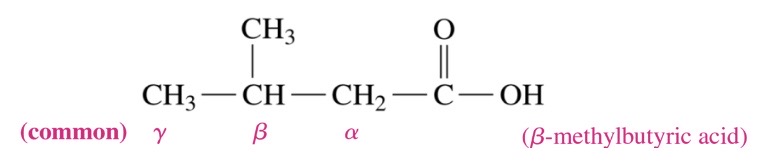
New cards
carboxylic acid
\-prefix for carbon is ic acid
\-substituted carboxylic acids, the carbon next to COOH is called a and followed by B, y, and delta
\-substituted carboxylic acids, the carbon next to COOH is called a and followed by B, y, and delta
70
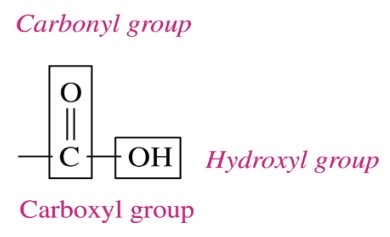
New cards
draw corboxylic acid
\-carboxylic acid contains a carboxyl grou consists fo hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the carbon in carbonyl group (C=O)
\-con carbon in carboxyl group as first carbon
\-con carbon in carboxyl group as first carbon
71
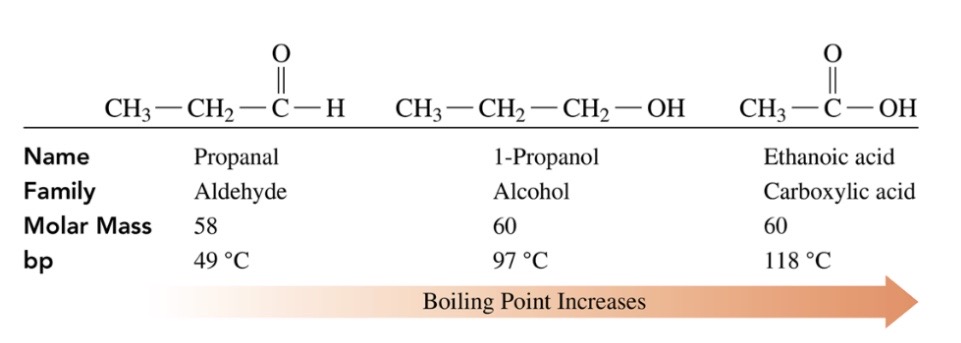
New cards
Boiling points and solubility of carboxylic acids
\-polar carboxyl group allows carboxylic acid to form multiple hydrogen bonds with carboxylic acids wihc gives the carboxylic acid a higher boiling point than alcohols,ketones, and aldehydes of similar molar mass
\-carboxylic acids with 1-5 carbon atoms are very soluanlt n water, 6+ are slightly soluble
\-carboxylic acids with 1-5 carbon atoms are very soluanlt n water, 6+ are slightly soluble
72
New cards
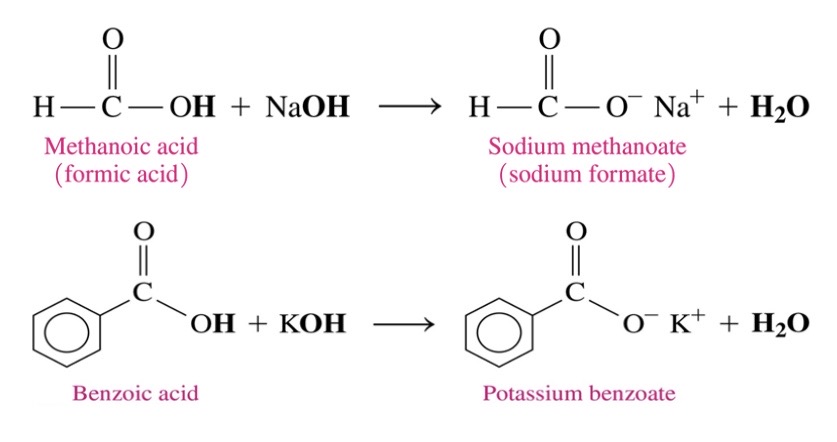
Neutralization reactions of carboxylic acids
\-carboxylate salts are a products of neautralization of carboxylic acids with strong base like NaOH or KOH
\-carboxylate ion is named by replacing ic acid ending with ate
\-carboxylate ion is named by replacing ic acid ending with ate
73
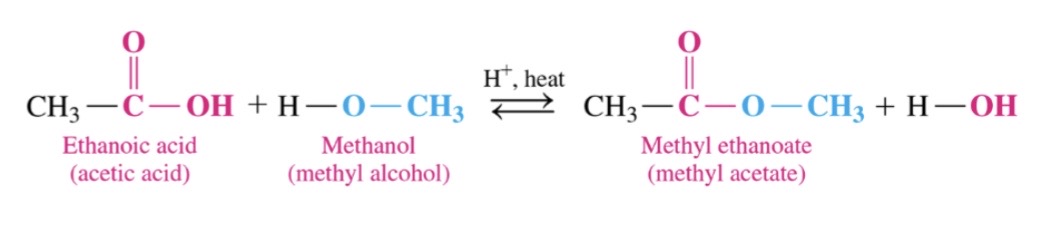
New cards
Esterfication
\-equalibrium reaction of a carbocylic avid and alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst and heat to produce an ester
74
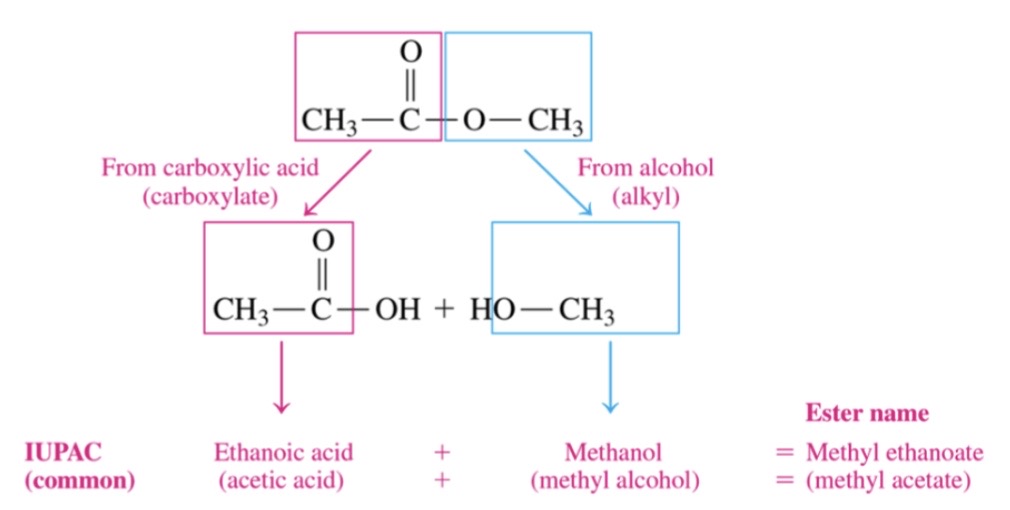
New cards
common names for esters
\-first word indicated alkyl part from alcohol
\-sec word carboxylate from carboxylic acid
\-sec word carboxylate from carboxylic acid
75
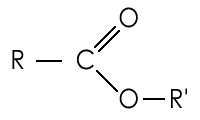
New cards
Ester structure
76
New cards
Products form base hydrolysis of esters
\-ester reaction with strong base to produce carboxylate salt and alcohol
\-heat requried
\-heat requried
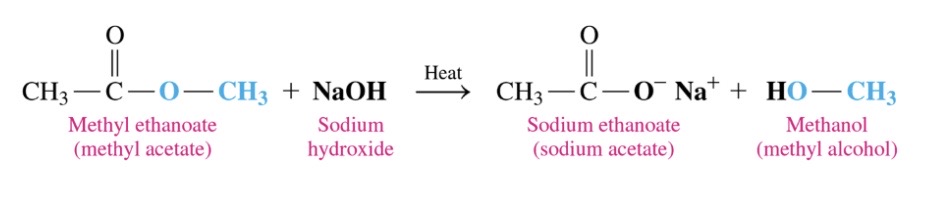
77
New cards
Boling point and solubility of esters
\-boiling point higher than alkanes and ethers, lower than alcohols and carboxylic acids
\-ester don’t have hydroxyl groups so they can’t hydrogen bond to each other
\-esters with 2-5 carbons are soluble
\-ester don’t have hydroxyl groups so they can’t hydrogen bond to each other
\-esters with 2-5 carbons are soluble
78
New cards
Summary of reactions

79
New cards
lipids
\-steriods
\-fatty acids
\-fatty acids
80
New cards
fatty acids
\-long unbranched carbon chains with a carboxylic acid group at the end.
\-insoluble in water becasue of long chain
\-insoluble in water becasue of long chain
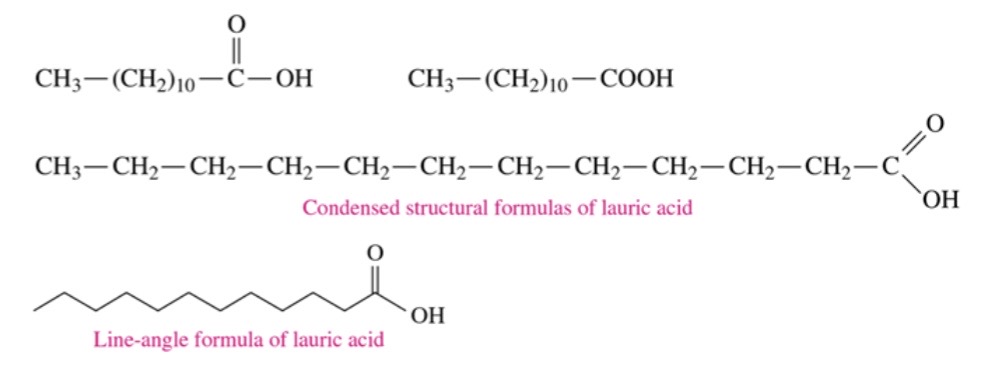
81
New cards
Fatty acids as saturated or unsaturated
\-saturated when theyhave single c-c bond in carbon chain
\-unsaturated when they have c=c bond in carbon chain
\-unsaturated when they have c=c bond in carbon chain
82
New cards
wax produced by reaction of fatty acid and alcohol or glycerol
\-wax is a ester of long chain fatty acid and alcohol, with 14-30 carbon atoms
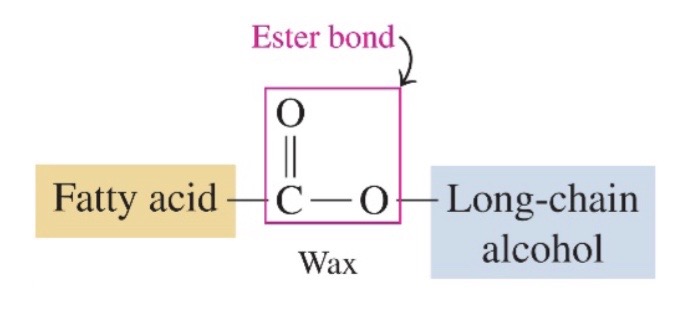
83
New cards
triacylglycerol produced by reaction of fatty acid and alcohol or glycerol
triaclyglycerols are ester of fatty acids and glycerol
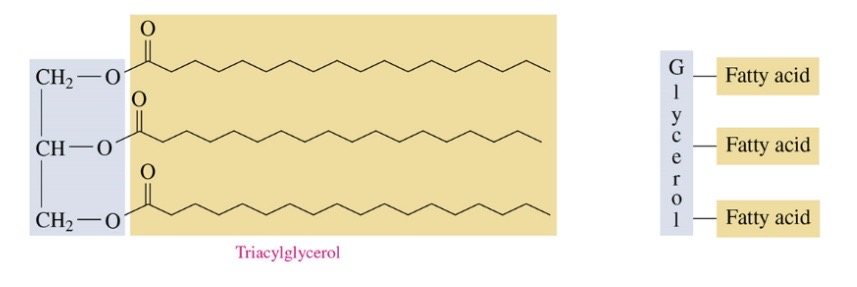
84
New cards
Triacylglycerol that undergoes hydrogenation
\-Double bonds in unstaruated fatty acids react with hydrogen gas to produce c-c bond
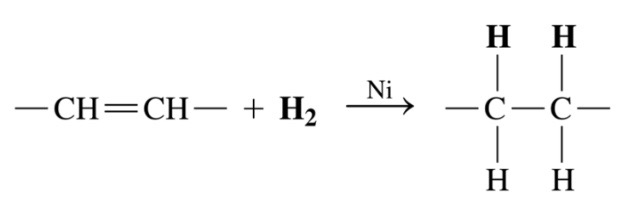
85
New cards
Triacylglycerol that undergoes hydrolysis
\-triacylglycerols are hydrolyzed (split by water) to produce glycerol and 3 fatty acids in presence of strong acids
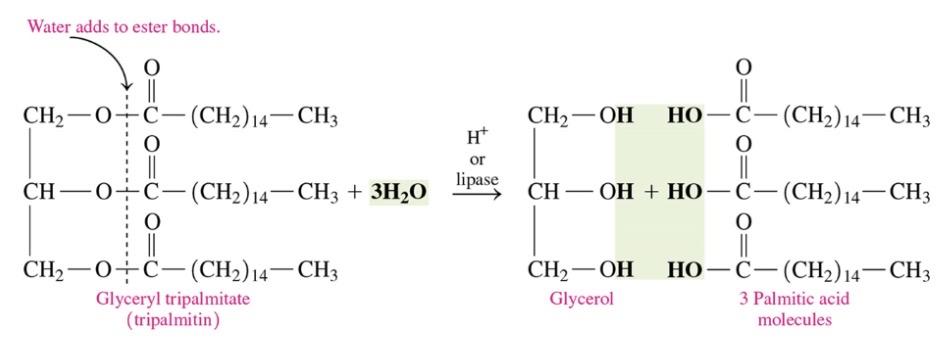
86
New cards
Triacylglycerol that undergoes saponification
\-A fat and strong base react to produce glycerol and the soaps in presence of heat
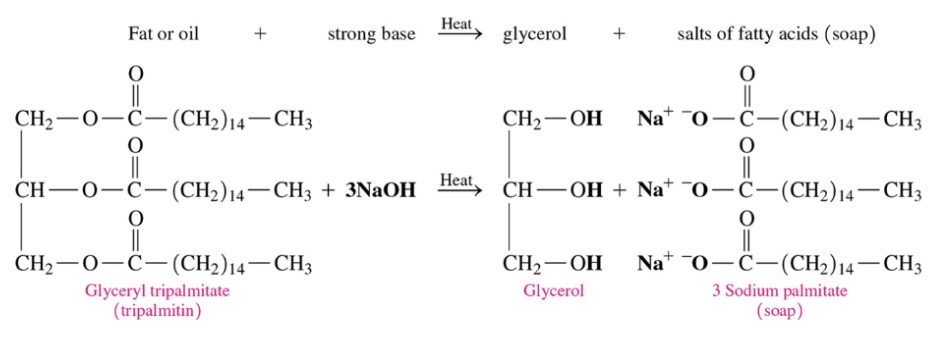
87
New cards
Glycerophospholipids
\-Glycerol 2fatty acids, phosphoric acid and amino alcohol
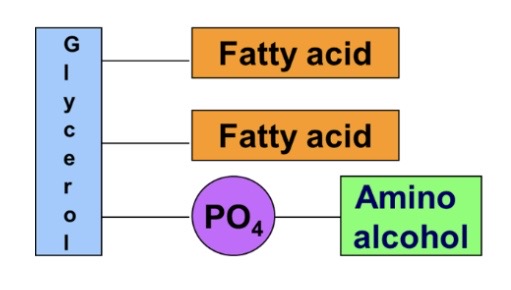
88
New cards
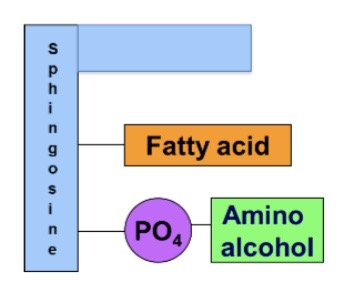
Sphingomyelin
sphingosine, fatty acid, phosphate, amino acid
\*Amino Alcohols in glycerophospholipids are choline, serine, and ethanol amine
\*Amino Alcohols in glycerophospholipids are choline, serine, and ethanol amine
89
New cards
Steriod Nucleus
\-3 cyclohexane rings and 1 cyclopentane ring fused together
90
New cards
steriod compounds
\-cholesterol: synthesized in liver needed to make brain and nerve tussue, steriod hormones, vitamin D, bile salts
\-bile salts: emulsify fat globules, allowing fat to easily digester, synthesized in liver, sotred in gallbladder, help absorb cholesterol
\-steroid hormones: aldosterone and cortisone, regulate water balance and glucose levels in cells
\-bile salts: emulsify fat globules, allowing fat to easily digester, synthesized in liver, sotred in gallbladder, help absorb cholesterol
\-steroid hormones: aldosterone and cortisone, regulate water balance and glucose levels in cells
91
New cards
Lipoprotiens
* surround nonpolar lipids with polr lipids and protiedn for transport to cells
* primary function to transport triglycerides and cholesterol around the body
* LDL bad lipoprotien transports cholesterol to make cell membranes and deposits excess into arteries
* HDL good lipoprotein transprots cholesterol from tissues to liver to make bile salts that can be eliminated
* primary function to transport triglycerides and cholesterol around the body
* LDL bad lipoprotien transports cholesterol to make cell membranes and deposits excess into arteries
* HDL good lipoprotein transprots cholesterol from tissues to liver to make bile salts that can be eliminated
92
New cards
Lipid bilayer
\-cell membranes separate cellular contents from the external environment, consists of 2 rows of phospholipids
\-barrier to molecules passing in and out of cell
\-one layer facing out and other facing in so polar on the outside and nonpolar on the inside
\-barrier to molecules passing in and out of cell
\-one layer facing out and other facing in so polar on the outside and nonpolar on the inside
93
New cards
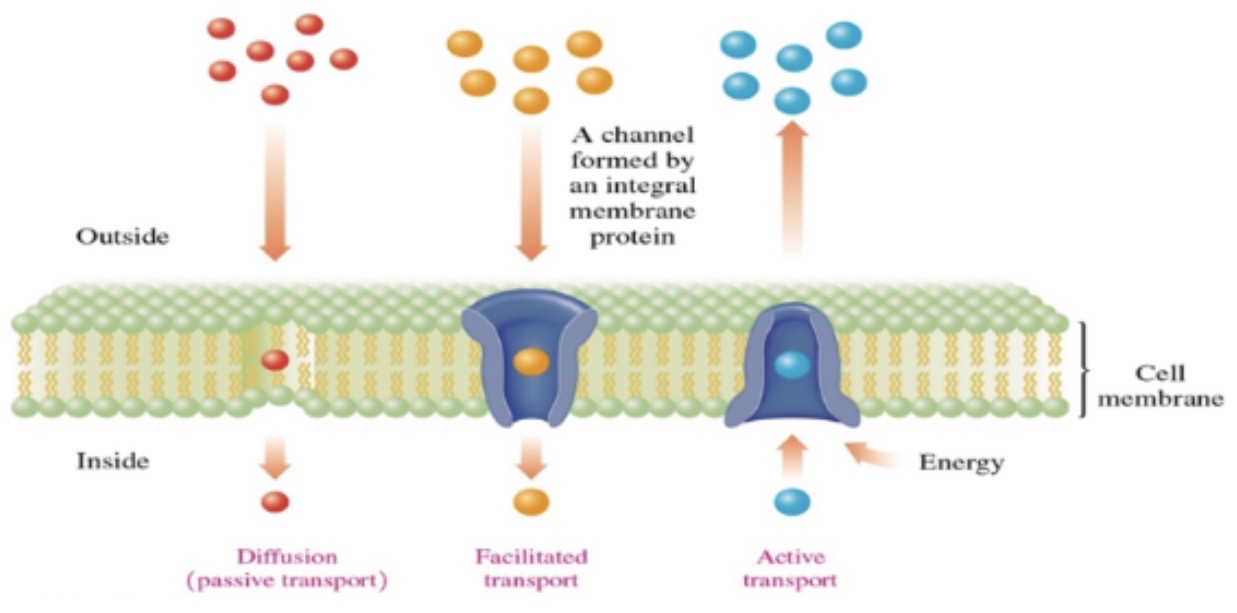
Transprot through cell membranes
\-diffusion: moves particles from higher to lower concentration
\-Facilitated transport: uses protein channels to increase the rate of diffusion
\-active transport: move ions against a concentration gradient
\-Facilitated transport: uses protein channels to increase the rate of diffusion
\-active transport: move ions against a concentration gradient
94
New cards
Amines
\-alkyl groups not branched
\-alkyl groups banded to the N atom in alphabetical order in front of amine
\-prefixes di- and tri- to identify duplicate alkyl substituents
\-amine benzene is named aniline by IUPAC
\-alkyl groups banded to the N atom in alphabetical order in front of amine
\-prefixes di- and tri- to identify duplicate alkyl substituents
\-amine benzene is named aniline by IUPAC
95
New cards
Draw amines
\-shows amine molecules with alkyl groups bonded to nitrogen atom
96
New cards
Amines as primary secondary or tertiary
\-primary 1 carbon group bonded to nitrogen
\-secondary 2 carbon groups bonded to nitrogen
\-tertiary 3 carbon groups bonded to nitrogen
\-secondary 2 carbon groups bonded to nitrogen
\-tertiary 3 carbon groups bonded to nitrogen
97
New cards
boiling points and solubility of amines
\-boiling point is higher than alkanes but lower than alcohols
\-primanry amines have higher boiling points than secondary amines becasuse they can form more hydrogen bonds
\-tertiary amines have lower boiling points than primary and secondary amines becasue they can’t form hydrogen bonds with each other
\-amines with 1-6 carbon atoms are soluble in water
\-primanry amines have higher boiling points than secondary amines becasuse they can form more hydrogen bonds
\-tertiary amines have lower boiling points than primary and secondary amines becasue they can’t form hydrogen bonds with each other
\-amines with 1-6 carbon atoms are soluble in water
98
New cards
reaction of amines with acids
\-amine + acid = ammonium salt
99
New cards
Heterocyclic amines
\-simplest 5 atoms ring is pyrrolidine
\-imines have double bonded nitrogens
\-amines have single bonded nitrogen
\-6atom ring purine is a combination of pyrimidine and imidazole
\-imines have double bonded nitrogens
\-amines have single bonded nitrogen
\-6atom ring purine is a combination of pyrimidine and imidazole
100
New cards
exciatory and inhibitoy neurotransmitters
\-excitatory increase the signal of activity in nerve cells
\-inhibitory decrease the signal of activity in nerve cells
\-inhibitory decrease the signal of activity in nerve cells