Magnetism (scary)
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hey pooks idk if eberything is right but oh well soo la voo
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
If you cut a bar magnet in half, what happens to the poles?
the two resulting magnets are still magnets with 2 poles (magnetic monopoles DO NOT exist). when the magnet is cut in half, there are still domains, therefore there are polarized ends
what is the main source of magnetism in materials?
electron spin (charges in motion; if a charge is not moving, there is no magnetic field)
why are some objects not magnetic?
electron spins cancel out (electrons are almost always in pairs unless there is an odd amount of them)
domains
small areas/regions of aligned spins → alignment of these domains gives ferromagnetic materials their magnetic properties
magnetic domain
local region within material in which all unpaired electrons are oriented the same way
Ferromagnetism
occurs when magnetic field produce spins that do not cancel out completely in certain materials (e.g. iron, cobalt, nickel)
Paramagnetic
material weakly interacts with external field and temporarily lines up some of their domains. when field removes, domains assume random ordering.
Diamagnetic
uncommon; domains line up opposite to the external field; materials with this property are repelled by a magnet
how can magnetized items become unmagnetized
unalign domains by heating, cooling, or hitting
if there is magnetic force, then there is also…
magnetic field
where do magnetic fields start/end?
lines start at north and end at south OUTSIDE of bar magnet → start at south and end at north INSIDE bar magnet. forms a never-ending loop.
where is the Earth’s magnetic south pole located?
at geographic north
what does the range of the magnetic field depend on?
the object’s size
magnetic flux
the number of field lines that cross a certain area at right angles to that area; in Weber (Wb)
maximum and minimum flux
maximum flux when angle between magnetic field lines and area vector is zero (cos0 = 1)
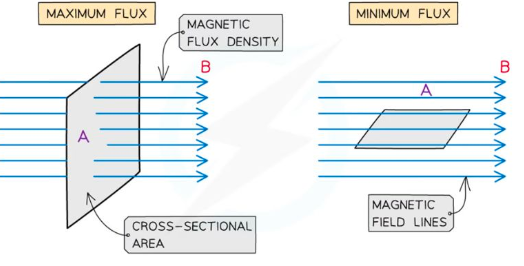
When the coil is rotated between the pole pieces of a magnet as shown, during one complete rotation of the coil, how often will the magnetic flux linked with the coil be maximum and minimum?
maximum twice, minimum twice
(initially plane of coil is perpendicular to B field lines since the coils face the poles of the magnet → coil is flush to the magnetic poles kind of like holding a book flat in your hand, so it’s parallel → perpendicular → parallel)
what do current carrying wires produce
induced magnetic field
what type of shaped magnetic field does a long, straight current carrying wire create?
a cylindrical magnetic field
B relationship with distance
inversely proportional
B relationship with current
directly proportional
what is the curly right hand rule?
used to find direction of magnetic field → point your right thumb in the direction of the current in the wire and curl fingers
value of permeability of free space
measure of ability for magnetic field to propagate through a vacuum → 4π * 10-7
symbol for out the page (towards you)
circle with dot in the middle
symbol for in the page (away from you)
circle with x in middle
solenoid
wire coiled into several different loops → creates strong magnetic field by combining several loops
solenoids create B fields that look like
bar magnet
magnetic field of solenoid is proportional to
current in wire + number of loops/turns of wire per unit length
What is the shape of the magnetic field produced by a straight current carrying wire
circle
does light need magnetism to exist?
yes, bc it is an electromagnetic wave
when the electric current flows INTO the page, the B field is
clockwise
when the electric current flows right, the magnetic field is
out of the page and into the page
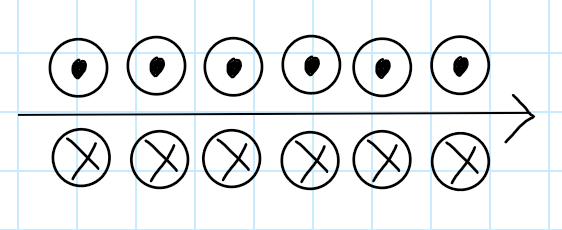
An electric current flows in a counterclockwise direction around a circular loop of wire. What is the direction of the magnetic field?
out the page
What is the direction of the magnetic field at point P due to the current flowing into the page?
tangential to the circle, kind of in the clockwise direction
What is the direction of the magnetic field at the origin due to two current-carrying wires of equal magnitude? The currents are separated from the origin by the same distance, r.
up and right from origin
A long, straight wire carries an electric current I. What is the direction of the magnetic field at point P?
into the page
two long, straight wires carry equal currents directed into the page. What is the direction of the magnetic field at the midpoint between the wires?
The magnetic field is 0 (they cancel out)
when is magnetic force on a moving charged particle at max value
when a charged particle is moving perpendicular to the field
can magnetic force change the speed of the particle
NO → velocity and force are set quantities; only direction is changing
Right Hand Rule
thumb → velocity
fingers → B field direction
palm → force direction if charge is positive
back of hand → force direction if charge is negative
shape of path of charge moving through B field
circular
What is the magnetic force on the electron that is moving out of the page?
there is no magnetic force acting on the electron
Observe that the stream of electrons in a cathode ray tube interacts with a bar magnet. Why might the stream of electrons change direction when the magnet is held nearby?
due to interactions between moving electrons and B field of magnet → deflected from their og path
An electron moving to the right at 4.5*104 m/s enters a 1.0 mT magnetic field pointed upward. What would the force be if the particle were a neutron?
0 N → neutrons don’t have a charge
mass spectrometer
device that is used to separate out atoms and molecules based on their mass - and is used to analyze the physical makeup of substances in terms of their relative concentrations of their constituent parts
velocity selector
device that consists of perpendicular electric (curves up) and magnetic (curves down) fields and is used against charged particles
How to calculate velocity of the particles that go straight through the velocity selector
Fe = Fb → qE = qvB → E/B = v
what type of particles can pass through a velocity selector?
particles with specific velocity of v = E/B
when in B field, field exerts force perpendicular to motion that makes charges move in circle. all start w/ same velocity bc of velocity selector
the movement of proton is depicted in the picture
electrons would go the other way and curve more since electrons are lighter
various masses separate out along diameter of mass selector. can find mass once you find r.
solve for the mass of particles
Fb = mv2/r
qvB = mv2/r
m = qBr/v
solving for radius
Fb = mv2/r
qvB = mv2/r
r = mv/qB
What describes the behavior of a charged particle that is injected into an area that just has a magnetic field?
speed remains the same (B field can change direction, but cannot change speed → force is perpendicular to velocity of particle)
right hand rule for current carrying wire
thumb → direction of current
fingers → B field direction
palm → force direction if charge is positive
back of hand → force direction if charge is negative
What is the direction of the magnetic force on the current carrying wire (green) in the magnetic field (red)?
current and B field are parallel → no force (A)
right hand rule to find B force on two current carrying wires
use curly RHR to find direction of B field on other wire
use RHR to figure out direction of force on that wire
wires w/ current going in same direction attract
wires w/ currents going in different direction repel
An electron moving North encounters a uniform magnetic field. If the magnetic field points East, what is the direction of the magnetic force on the electron?
out of the page
Two parallel wires have charges moving in the same direction. Is the force between them attractive or repulsive?
attractive
what is necessary to induce a current from magnetic field?
motion bc magnetic field needs to be changing (either circuit or magnet can move). magnetic flux through coil/loop changes → B field changes
where is induced emf the strongest? where is it weakest?
greatest when there is a lot of field lines
least at center of bar magnet
ways to induce current
Circuit moved into or out of the magnetic field
Circuit is rotated in the magnetic field
Intensity and/or direction of magnetic field is varied
A bar magnet is moved towards a circular conducting loop. what happens to the B field and current flow?
B field in loop increases (more field lines going through loop) and a current flows through loop
what will generate an emf in a conducting loop
emf in a conducting loop will be generated when magnet moves towards surface of loop
Lenz’s Law
magnetic field of the induced current is in a direction to produce a field that opposes the change causing it
(if the external field gets weaker, the induced current tries to replace the "missing" external field by generating a magnetic field to "replace" it. If the external field gets stronger, the induced current opposes the "extra" external field by generating a magnetic field opposing the change.)
apply Lenz’s Law
losing B field, need to add to field
induced current moves CCW
apply Lenz’s Law
adding B field, need to oppose it
induced current moves CW
A coil of wire is sitting on a table top. A magnet is held above it with the North Pole pointing downwards. The magnet is then pushed down towards the coil. What is the direction of the induced current in the coil of wire?
B field increases (in downward direction), needs to oppose it (needs something upward) → curly RHR → induced current is CCW
A coil of wire is sitting on a table top. A magnet is held above it with the North Pole pointing downwards. What is the direction of the induced current in the coil of wire?
no induced current
A permanent magnet is pushed into a stationary ring that is suspended from a vertical string. What happens to the ring? How can we use Lenz’s law to explain this experiment?
initially, ring and magnet repel since the induced current is north. as the magnet passes through the ring, the south end and ring attract
what is emf like
potential difference
units for emf
volts
how can magnetic flux be changed
The magnetic field strength
The area
The angle of orientation
generator
converts mechanical energy into electrical energy (e.g. turbine)
has constant B field
faster = greater induced emf
formula for induced emf from a generator
ε = NABωsin(ωt)
max occurs when sinωt=1
alternating current
Since the emf generated goes from positive to negative, the output of the current is changing directions as well as the coil spins.
The rate at which the coil in the generator rotates determines the maximum generated emf.
Why would we want a wire to spin?
more practical to create spinning motion + want magnetic torque
torque equation
𝜏=NIABsinθ
θ = angle between B field and area
motors
do the opposite of generators; convert electrical energy to mechanical energy
transformers
device that converts a small applied emf to a larger one, or a larger applied emf to a smaller one
has two coils of wire wrapped around a core of soft iron
primary coil: connected to the primary AC source and has N1 number of turns.
secondary coil: connected to a resistor and has N2 number of turns
step up transformer
When N2 is greater than N1 → the secondary emf is greater than the primary emf
step down transformer
When N1 is greater than N2 → the secondary emf is smaller than the primary emf
Can a magnetic field set a stationary electron in motion? If so, how?
NO
if stationary, v = 0 m/s, meaning force exerted on electron will also be zero
An electron passes through a magnetic field without being deflected. What can you conclude about the orientation between the magnetic field and the velocity of the electron?
the B field is parallel or anti-parallel to the velocity of electron (sin0 = 0)
Two straight wires are parallel to each other. If the currents in the wires are in the same direction, will the wires attract or repel each other? What if the currents are opposite?
If currents are in the same direction, wires attract. if currents in opposite directions, wires repel.
What five factors affect the magnitude of the induced emf in a coil of wire?
number of coils/turns
area
angle
B field strength
time
Does dropping a strong magnet down a long copper tube induce a current in the tube? If so, what effect will the induce current have on the magnet?
YES
as magnet falls through tube, magnetic field changes, inducing a current. the induced current will try to oppose the magnet, slowing the magnet’s speed through the tube.
A transformer is constructed so that the coil on the left has 60 turns and the coil on the right has 3 turns. If the input potential difference is across the coil on the left, what type of transformer is this?
step down transformer
Where is the north magnetic pole on the Earth?
The South pole of earth
What would happen if a positive side of a magnet is placed near the positive side of another magnet?
Repel
At what place do the magnetic field lines leave a magnet?
North pole
What is the unit of magnetic field?
Tesla
What is it called when materials can be permanently magnetized by the application of the field (all of their domains will line up in the same direction)?
Ferromagnetic
Which of the following will cause a change in flux through a loop?
I. A rotating loop within a static magnetic field
II. A static loop in a changing magnetic field
III. A loop moving parallel within a magnetic field
I and II → A rotating loop within a static magnetic field and A static loop in a changing magnetic field
A loop sits next to a current carrying wire of current I. Will rotating a loop with respect to its center of mass induce a current?
NO
rotating the loop is not changing B, N, A, or angle
A loop of wire sits perpendicular to a magnetic field pointing into the page. The magnetic field begins to decrease. What is the direction of the induced current in the loop?
CW
A magnetic field is pointing upwards through a loop when it is shut off. What is the direction of the induced current in the loop?
CCW
What direction is the magnetic force?
Toward the center of the curved path
What is the direction of the magnetic field that would cause the deflection shown for the proton beam?
into the page