17.1 - Gross Anatomy of the Brain and Cranial Nerves
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
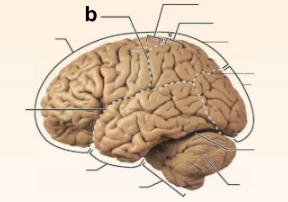
Identify the structure labeled “b” in the image.
Central culcus
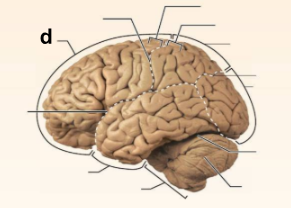
Identify the structure labeled “d” in the image.
Frontal lobe
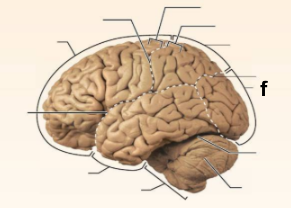
Identify the structure labeled “f” in the image.
Occipital lobe
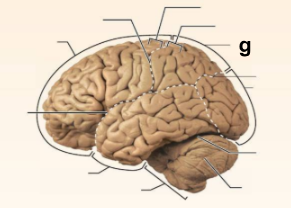
Identify the structure labeled “g” in the image.
Parietal lobe
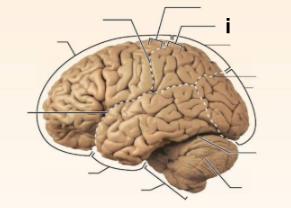
Identify the structure labeled “i” in the image.
Postcentral gyrus
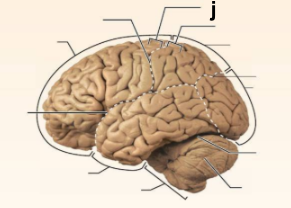
Identify the structure labeled “j” in the image.
Precentral gyrus
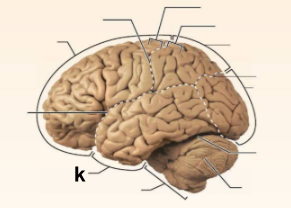
Identify the structure labeled “k” in the image.
Temporal lobe
In which of the cerebral lobes is the primary auditory cortex found?
Temporal lobe
In which of the cerebral lobes is the primary motor cortex found?
Frontal lobe
In which of the cerebral lobes is the primary somatosensory cortex found?
Parietal lobe
In which of the cerebral lobes is the olfactory cortex found?
Temporal lobe
In which of the cerebral lobes is the primary visual cortex found?
Occipital lobe
In which of the cerebral lobes is the Broca’s area found?
Frontal lobe
What is the term for an elevated ridge of cerebral tissue?
Gyrus
What is the primary function of the convolutions in the cerebrum?
Increase the surface area
What is gray matter primary composed of?
Neuron cell bodies and dendrites
What is the name of a fiber tractor that provides communication between different parts of the same cerebral hemisphere?
Association tract
What type of fiber tractor carries impulses from the cerebrum to lower CNS areas?
Projection tract
What are the caudate nucleus and putamen collectively called?
Basal nuclei / ganglia
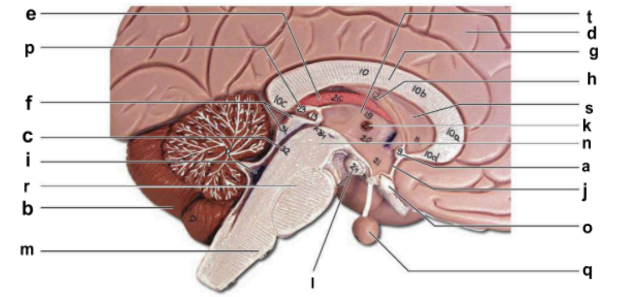
Identify the structure labeled “b” in the image.
cerebellum
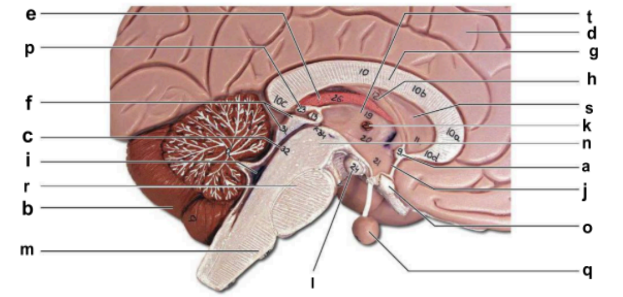
Identify the structure labeled “c” in the image.
cerebral aqueduct
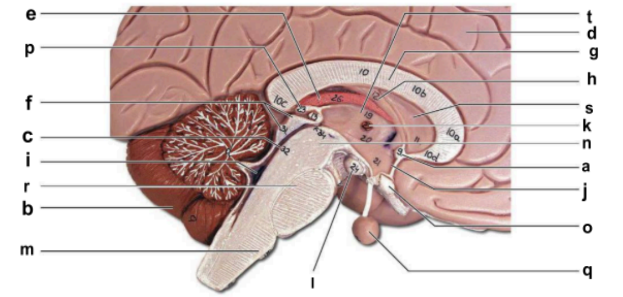
Identify the structure labeled “d” in the image.
cerebral hemisphere
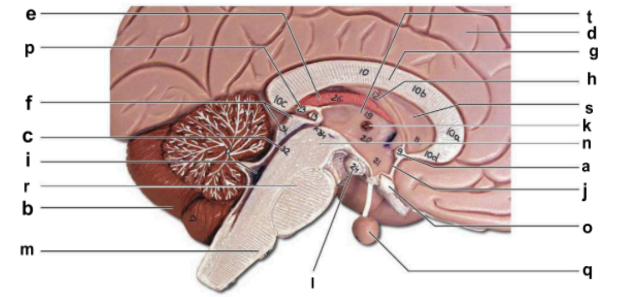
Identify the structure labeled “e” in the image.
choroid plexus
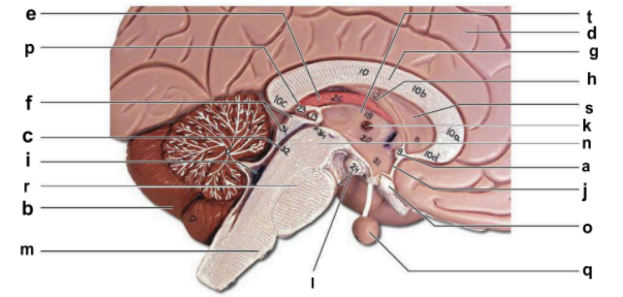
Identify the structure labeled “g” in the image.
corpos callosum
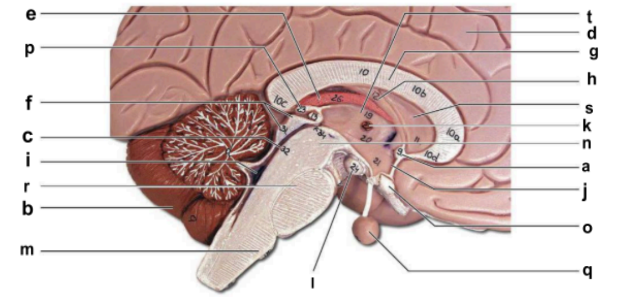
Identify the structure labeled “j” in the image.
hypothalamus
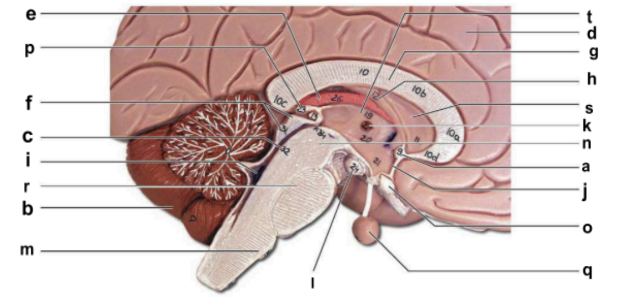
Identify the structure labeled “m” in the image.
medulla oblongata
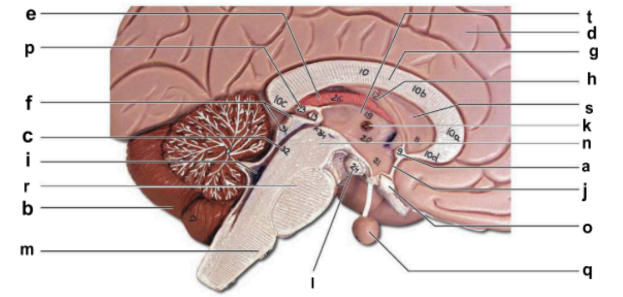
Identify the structure labeled “n” in the image.
midbrain
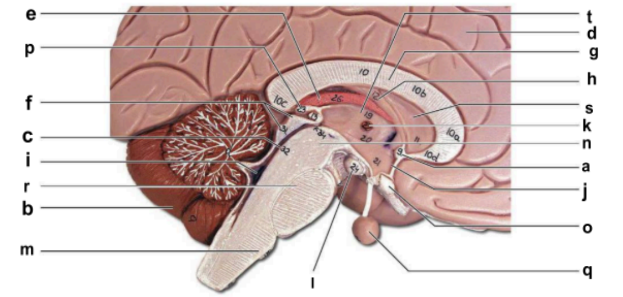
Identify the structure labeled “o” in the image.
optic chiasma
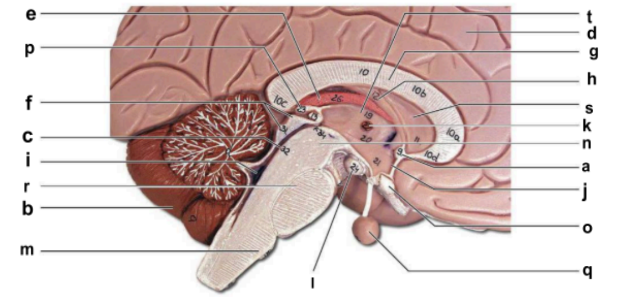
Identify the structure labeled “q” in the image.
pituitary gland
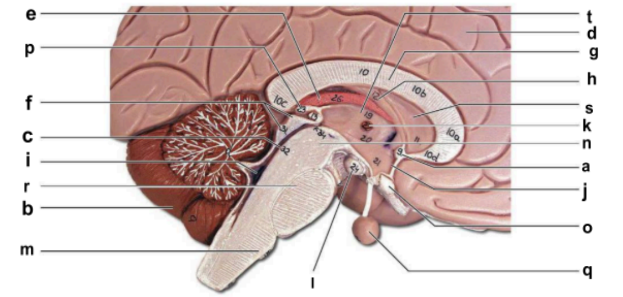
Identify the structure labeled “r” in the image.
pons
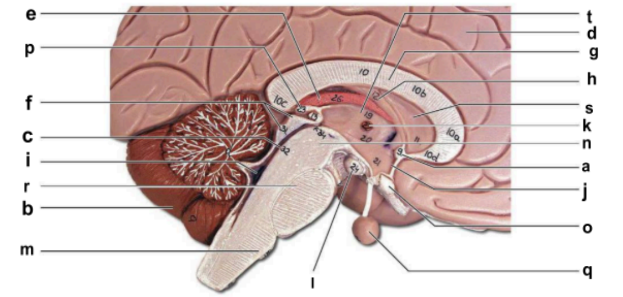
Identify the structure labeled “t” in the image.
thalamus
Site of regulation of body temperature and water balance; most important autonomic center
Hypothalamus
Site where medial fibers of the optic nerves cross
Optic chiasm
Located in the midbrain; contains reflex centers for vision and hearing
Corpora quadrigemina
Responsible for regulation of posture and coordination of complex muscular movements
Cerebellum
Important synapses site for afferent fibers traveling to the sensory cortex
Thalamus
Contains autonomic centers regulating blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rhythm, as well as coughing.
Medulla oblongata
Large fiber tract connecting the cerebral hemispheres
Corpus callosum
Relay stations for olfactory pathways
Mammilary body
Canal that connects the third and fourth ventricles
Cerebral aqueduct
Portion of the brain stem where the cerebral peduncles are located
Midbrain
Which embryonic brain region includes the thalamus, optic chiasma, and hypothalamus?
The forebrain
Which embryonic brain region includes the medulla oblongata, pons, and cerebellum?
The hindbrain
Which embryonic brain region includes the cerebral hemispheres?
The forebrain
What is the function of the basal nucei?
Regulation of voluntary motor activities
What is the outermost meninx covering the brain, composed of tough fibrous connective tissue?
Dura mater
What is the innermost meninx covering the brain, which is delicate and highly vascular?
Pia mater
Which structure produces cerebrospinal fluid?
Choroid plexus
What structures are instrumental in returning cerebrospinal fluid to the venous blood in the dural venous sinuses?
Arachnoid villi
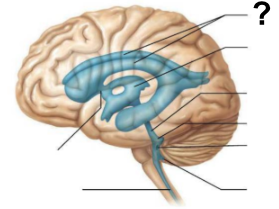
What structure, labeled “?”, is the starting point of cerebrospinal fluid circulation in the brain?
Lateral ventricle
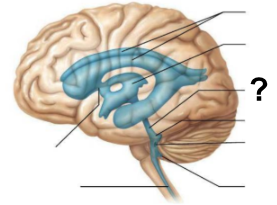
After the third ventricle, CSF flows through which narrow passage, labeled “?”, to reach the fourth ventricle?
Cerebral aqueduct
Which structure surrounds the brain and spinal cord, allowing CSF to circulate?
Subarachnoid space
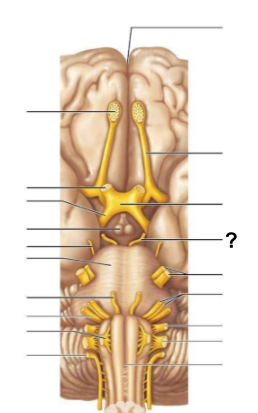
Through which structure, labeled “?”, is CSF absorbed into the venous blood?
Arachnoid villi
Into which venous system does CSF drain after passing through the arachnoid villi?
Dural venous sinuses
What is the function of the central canal in CSF circulation?
It allows CSF to flow through the spinal cord.
Which cranial nerve (name and number) is responsible for rotating the head?
Accessory nerve (XI)
Which cranial nerve (name and number) is responsible for smelling a flower?
Olfactory nerve (I)
Which cranial nerve (name and number) is responsible for raising the eyelids and pupillary constriction?
Oculomotor nerve (III)
Which cranial nerve (name and number) slows the heart and increases the motility of the digestive tract?
Vagus nerve (X)
Which cranial nerve (name and number) is responsible for chewing food?
Trigeminal nerve (V)
Which cranial nerve (name and number) is responsible for the secretion of saliva and tasting well-seasoned food?
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
Which cranial nerve (name and number) is responsible for reading the newspaper?
Optic nerve (II)
The __________ nerve (cranial nerve III) controls most of the eye’s movements, including pupil constriction
Oculomotor