AP Physics C Mutiple Choice Practice - CofM & Momentum
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
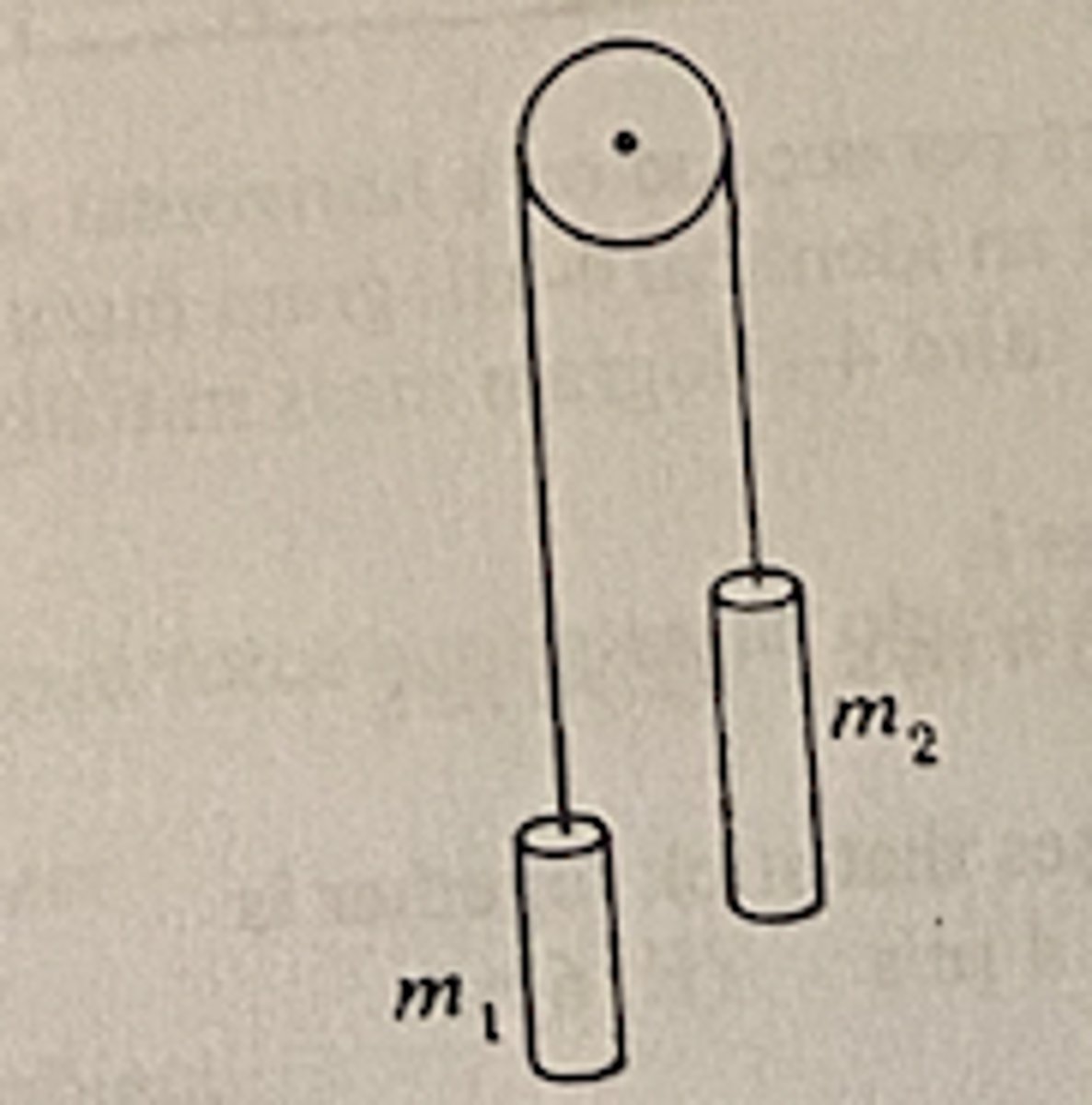
A system consists of two object having masses m1 and m2 (m1
B (m2 -m1)V
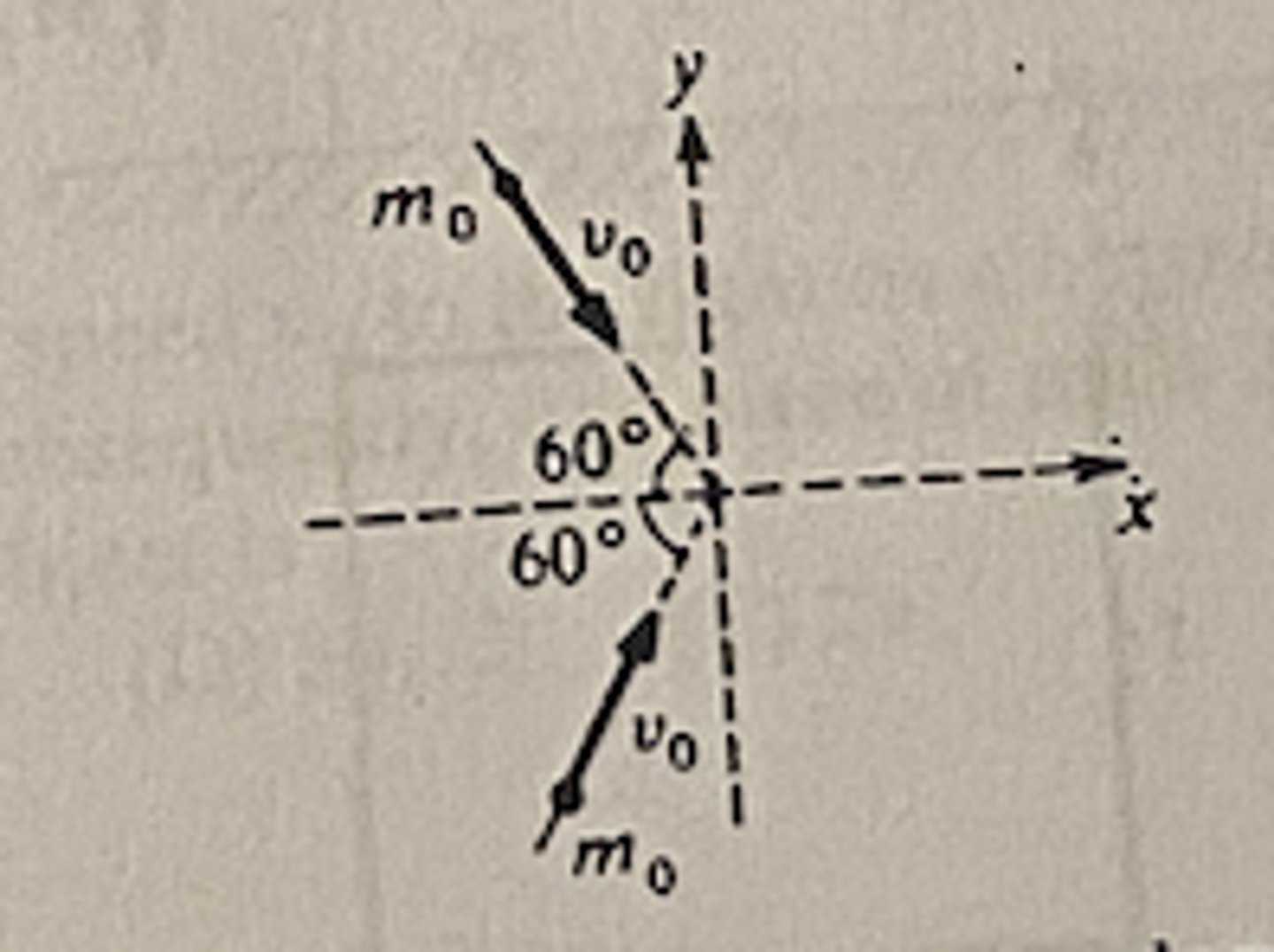
Two particles of equal mass m8, moving with equal speeds v* along paths inclined at 60 degrees to the x-axis, as shown above, collide and stick together. Their velocity after the collision has magnitude
B v*/ 2
The center of mass of a uniform wire, bent in the shape shown above, is located closest to point
B (B)
Mass M1 is moving with speed v toward stationary mass M2. The speed of the center of mass of the system is
E (M1/ M1+ M2)
A 4-kilogram mass has a speed of 6 meters per second on a horizontal frictionless surface, as shown above. The mass collides head-on and elastically with an identical 4-kilogram mass initially at rest. The second 4-kilogram mass then collides head-on and sticks to a third 4-kilogram mass initially at rest. The final speed of the first 4-kilogram mass is
A (0 m/s)
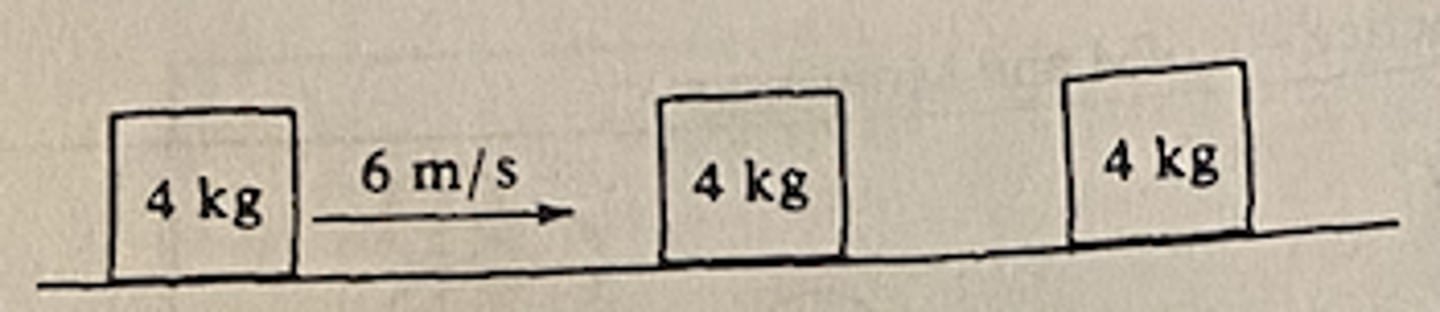
A 4-kilogram mass has a speed of 6 meters per second on a horizontal frictionless surface, as shown above. The mass collides head-on and elastically with an identical 4-kilogram mass initially at rest. The second 4-kilogram mass then collides head-on and sticks to a third 4-kilogram mass initially at rest.
The final speed of the two 4-kilogram masses that stick together is
C (3 m/s)
A projectile os mass M1 is fired horizontally from a spring gun that is initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The combined mass of the gun and projectile is M2. If the kinetic energy of the projectile after firing is K, the gun will recoil with a kinetic energy equal to
D (M1/ M2 - M1)
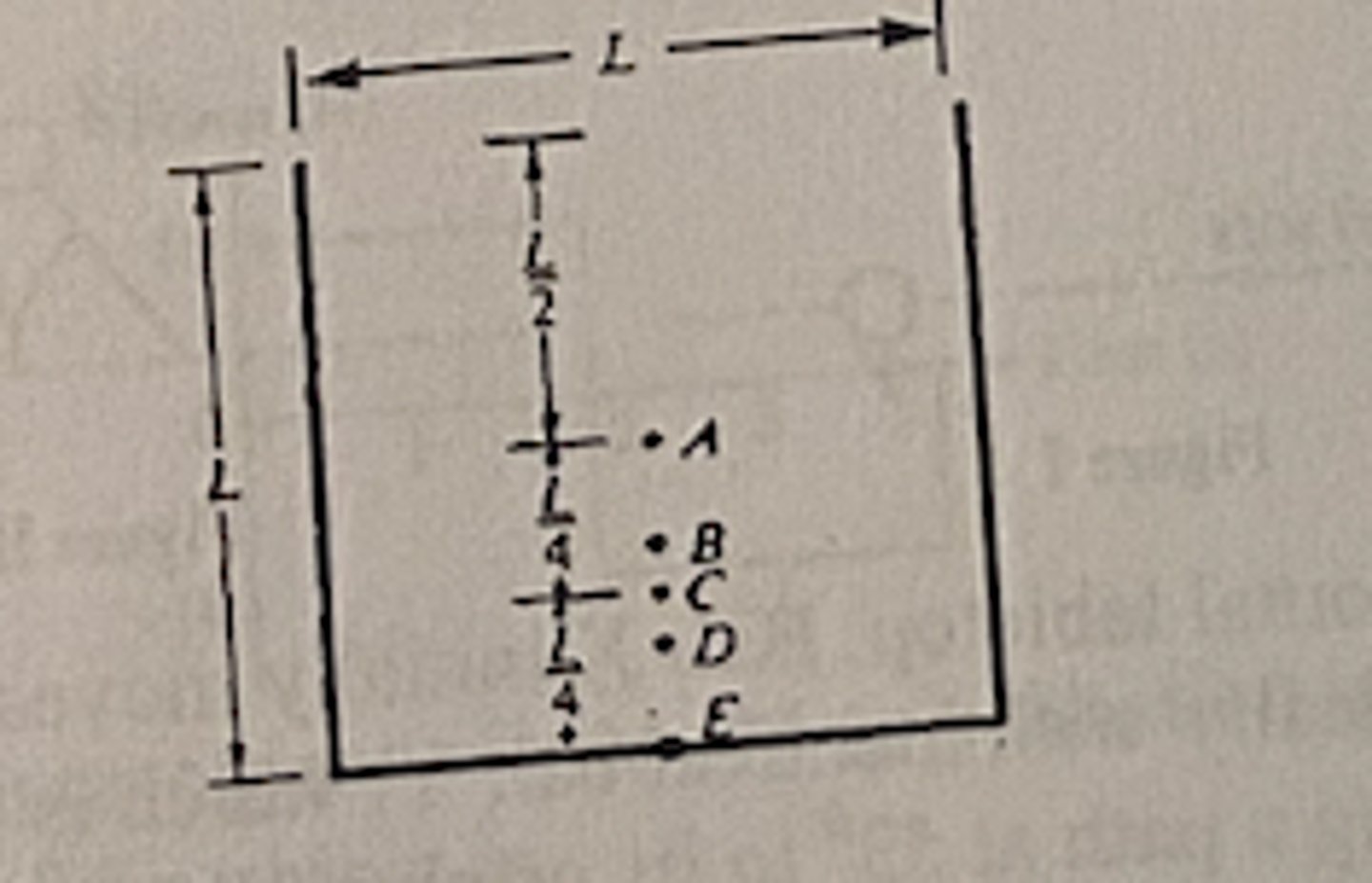
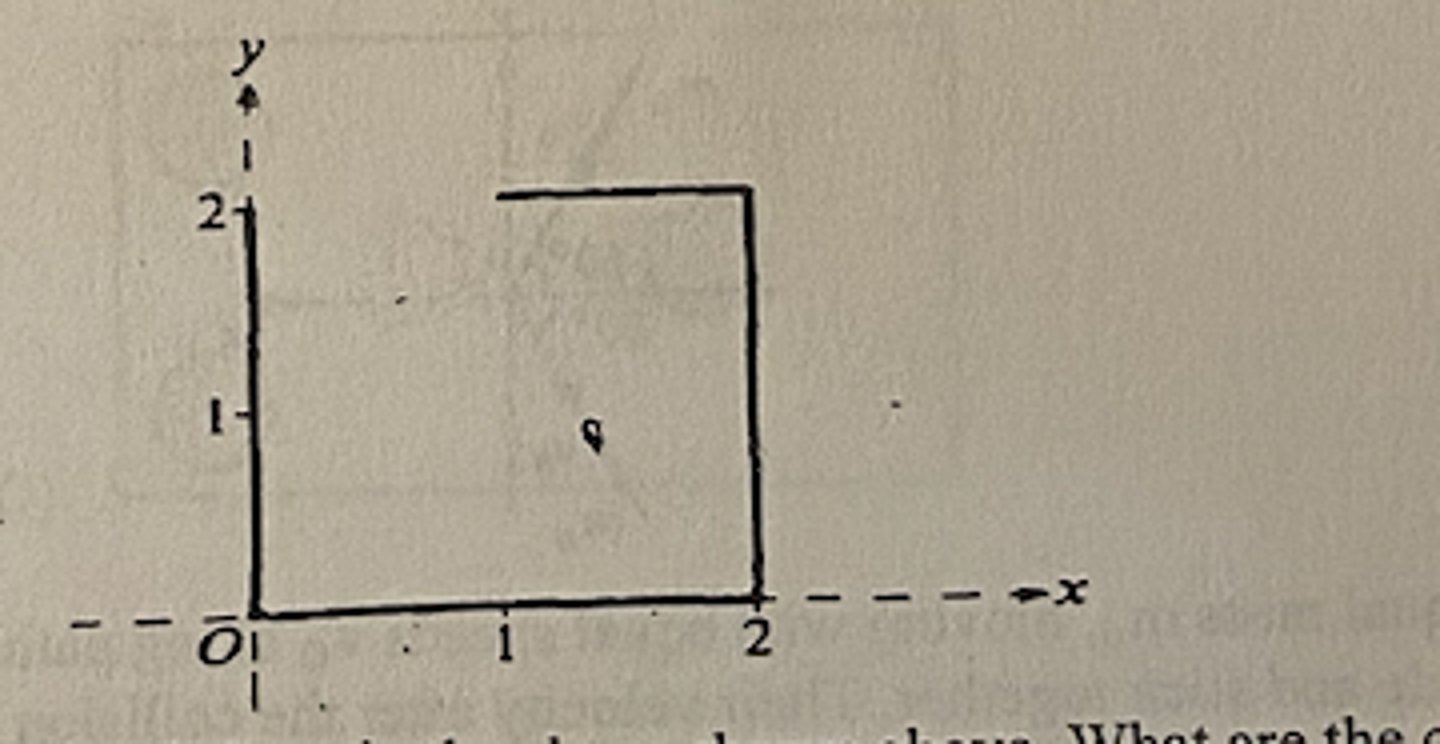
A piece of wire of uniform cross section is bent in the shape shown above. What are the coordinates (x,y) of the center of mass?
A (15/14, 6/7)
Two balls are on a frictionless horizontal tabletop. Ball X initially moves at 10 meters per second, as shown in Figure 1 above. It then collides elastically with identical ball Y. which is initially at rest. After the collision, ball X moves at 6 meters per second along a path at 53 degrees to its original direction, as shown in Figure II above. Which of the following diagrams best represents the motion of ball Y after the collision?
D (graph)
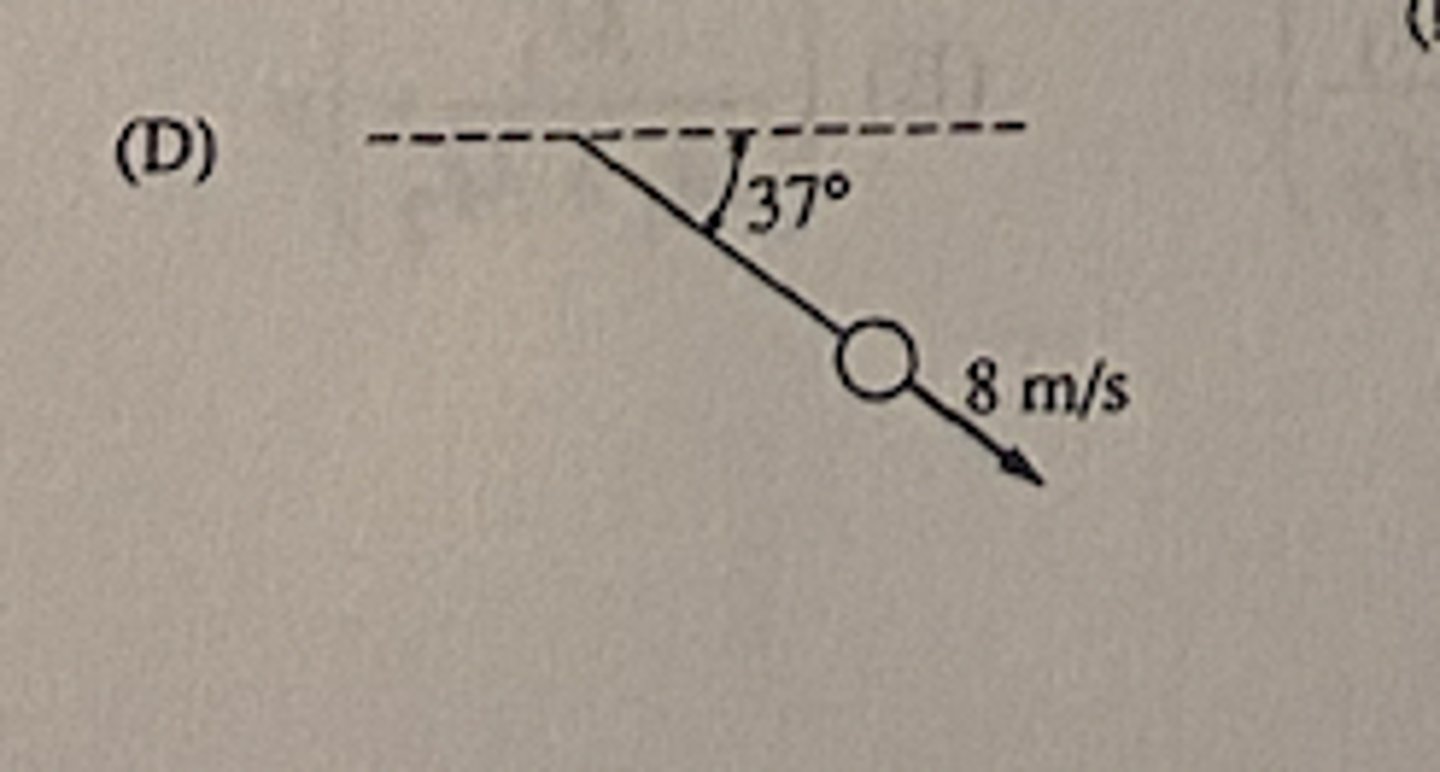
A balloon of mass M is floating motionless in the air. A person of mass less than M is on a rope ladder hanging from the ballon. The person begins to climb the ladder at a uniform speed V relative to the ground. How does the balloon move relative to the ground?
D (Down with a speed less than V)
If one knows only the constant resultant force acting on an object and the time during which this force acts, one can determine the
A (change in momentum of the object)
An object of mass m is moving with speed v to the right on a horizontal frictionless surface, as shown above, when it explodes into two pieces. Subsequently, one piece of mass 2/5 m moves with a speed v/2 to the left. The speed of the other piece of the object is
E (2v*)
A 5-kilogram sphere is connected to a 10-kilogram sphere by a ridged rod of negligible mass, as shown above. Which of the five lettered points represents the center of mass of the sphere-rod combination?
B (B)
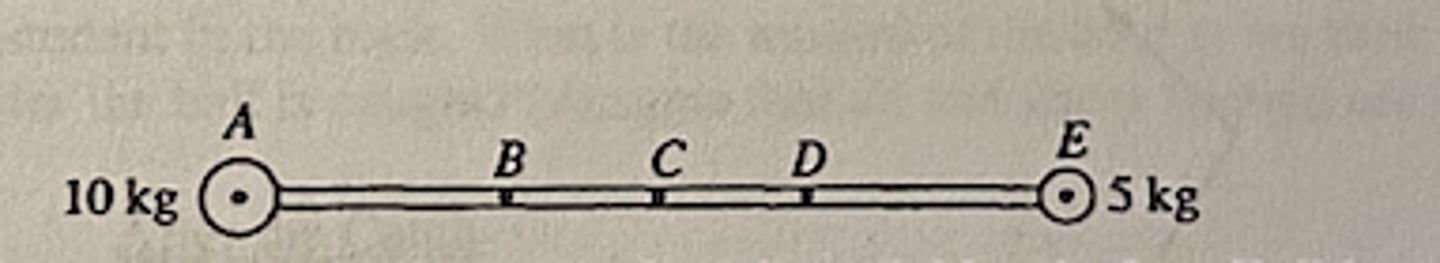
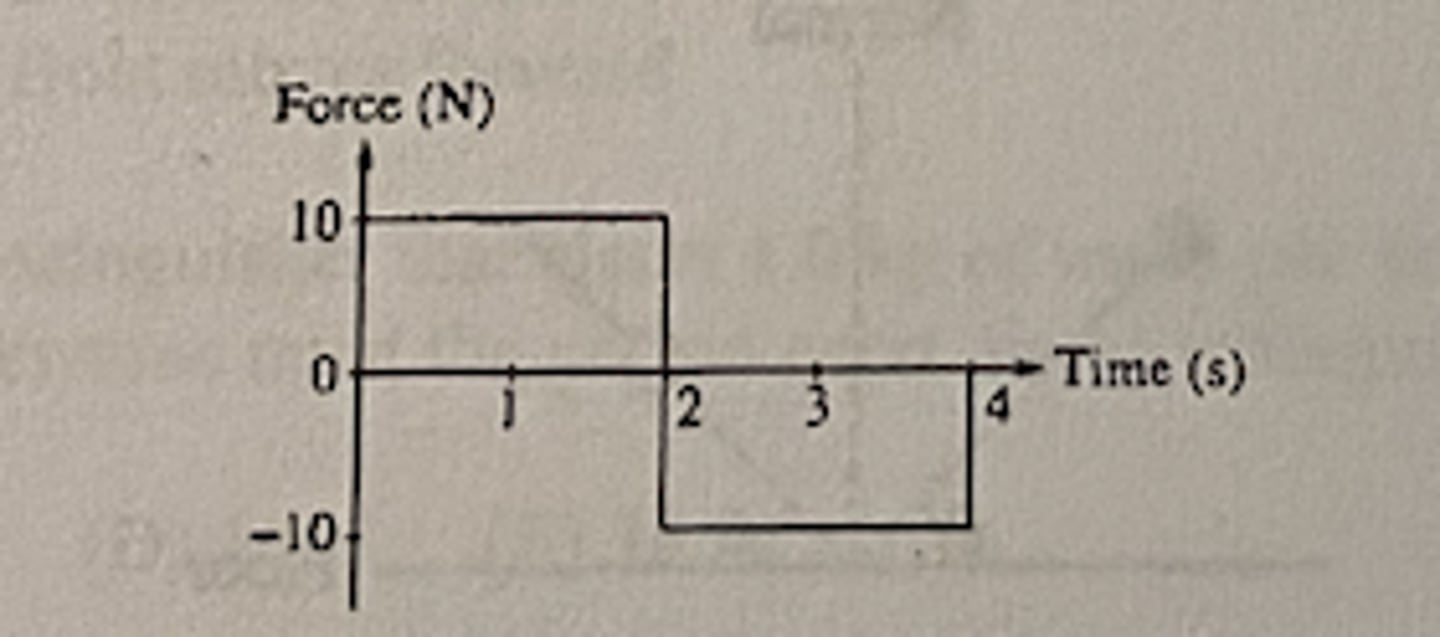
The graph above shows the force on an object of ass M as a function of time. For the time intevcal 0 to 4 s, the total change in the momentum of the object is
C (0 kg m /s)
As shown in the top view above, a disc of mass m is moving horizontally to the right with speed v on the table with negligible friction when it collides with a second disc of mass 2m. The second disc is moving horizontally to the right with speed v/2 at the moment of impact. The two discs stick together upon impact. The speed of the composite body immediately after the collision is
C (2v/3)

Two people are initially standing still on frictionless ice. They push on each other so that one person, of mass 120 kg, moves to the left at 2 m/s, while the other person, of mass 80 kg, moves to the right at 3 m/s. What is the velocity of their center of mass.
A (Zero)
An object having an initial momentum that may be represented by the vector above strikes an object that is initially at rest. Which of the following sets of vectors may represent the momenta of the two objects after the collision?
E (graph)
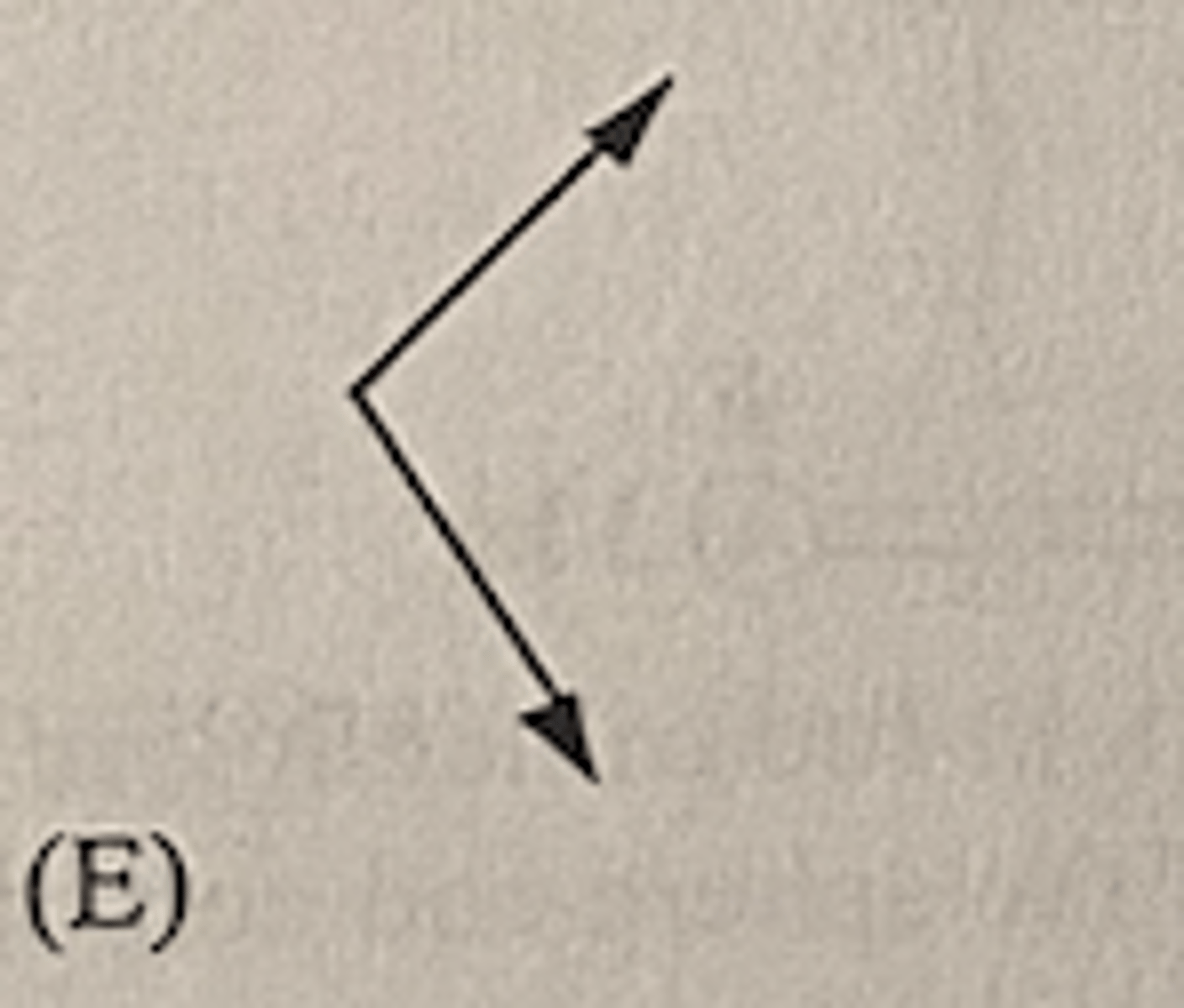
A 2 kg ball collides with the floor at an angle x and rebound at the same angle and speed as shown above. Which of the following vectors represents the impulse exerted on the ball by the floor?
E (graph)

The momentum P of a moving object as a function of time T is given by the expression P = kT^3, where k is a constant. The force causing this motion is given by the expression
A (3kt^2)
Two pucks moving on a frictionless air table are about to collide, as shown above. The 1.5 kg puck is moving directly east at 2.0 m/s. The 4.0 kg puck is moving directly north at 1.0 m/s.
What is the total kinetic energy of the two-puck system before the collision?
B (5.0 J)
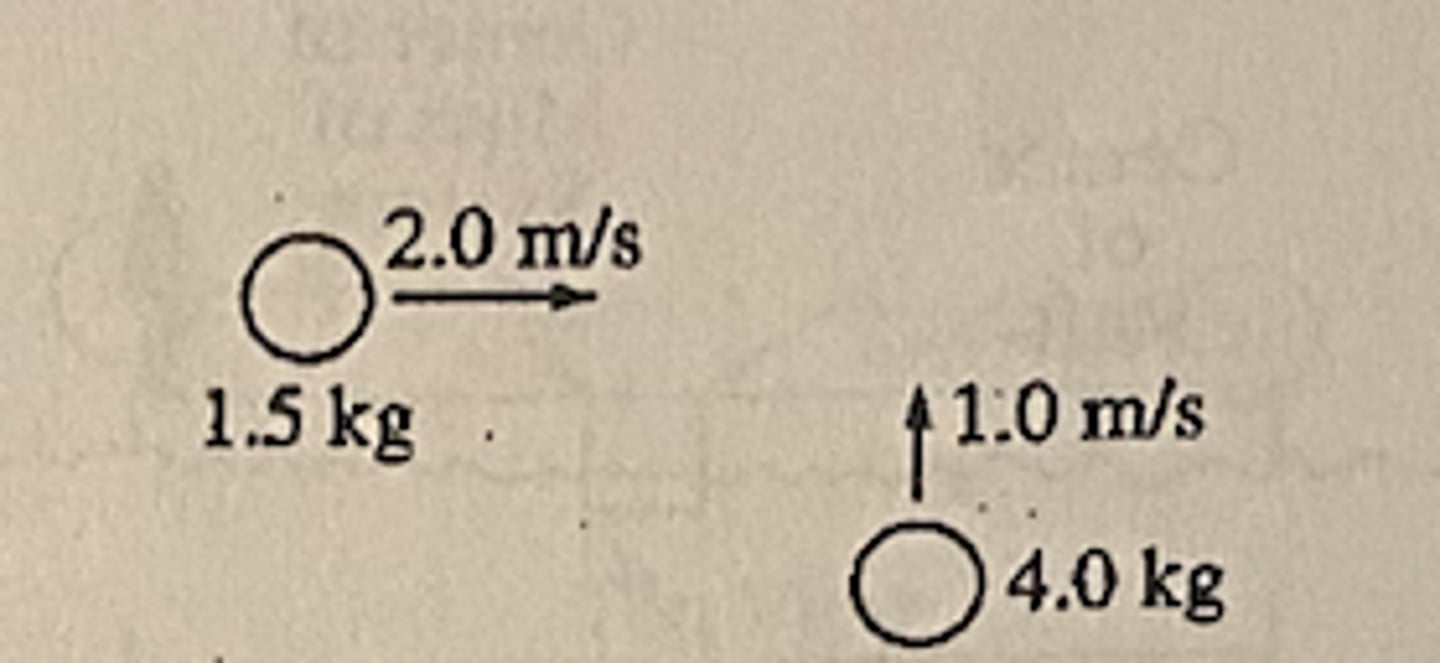
Two pucks moving on a frictionless air table are about to collide, as shown above. The 1.5 kg puck is moving directly east at 2.0 m/s. The 4.0 kg puck is moving directly north at 1.0 m/s.
What is the magnitude of the total momentum of the two-puck system after the collision?
C (=.0 kg*m/s)
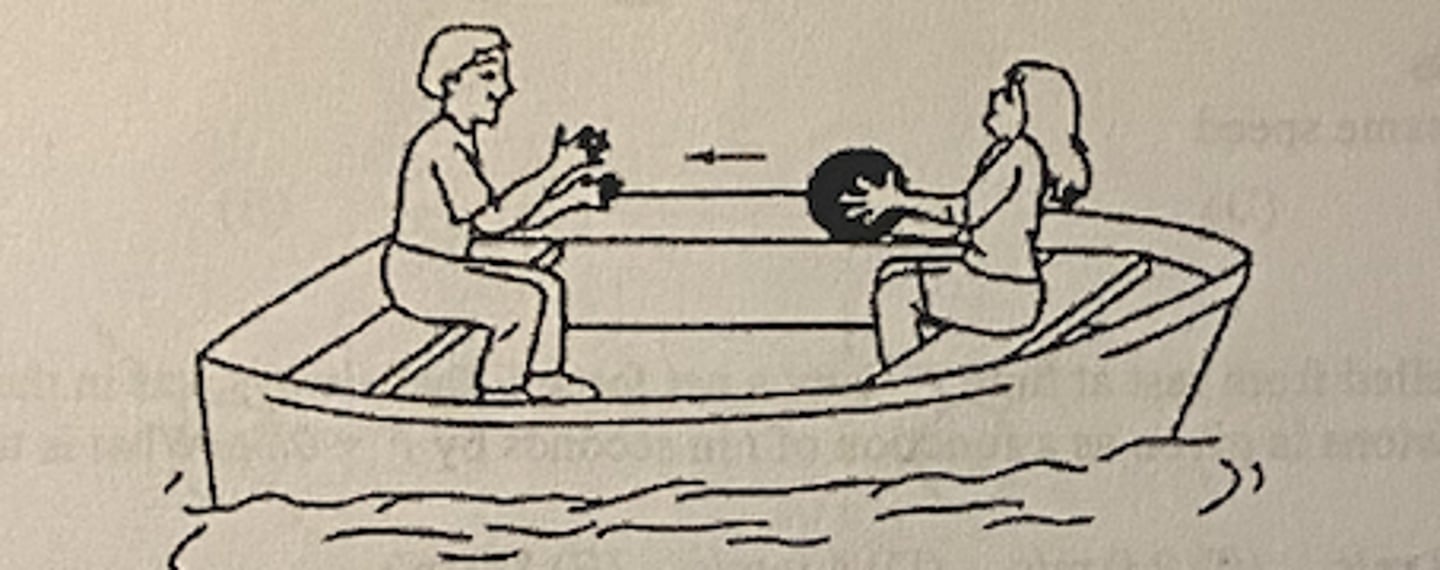
As shown above, two students sit at opposite ends of a boat that is initially at rest. The student in the front throws a heavy ball to the student in the back. What is the motion of the boat at the time immediately after the ball is thrown and, later, after the ball is caught? (Assume that air and water friction are negligible.)
Immediately
C
After the Throw
Boat moves forward
After the Catch
Boat does not move
A person holds a portable fire extinguisher that ejects 1.0 kg of water per second horizontally at a speed of 6.0 m/s, What horizontal force in newtons must the person exert on the extinguisher in order to prevent it from accelerating?
B (6 N)
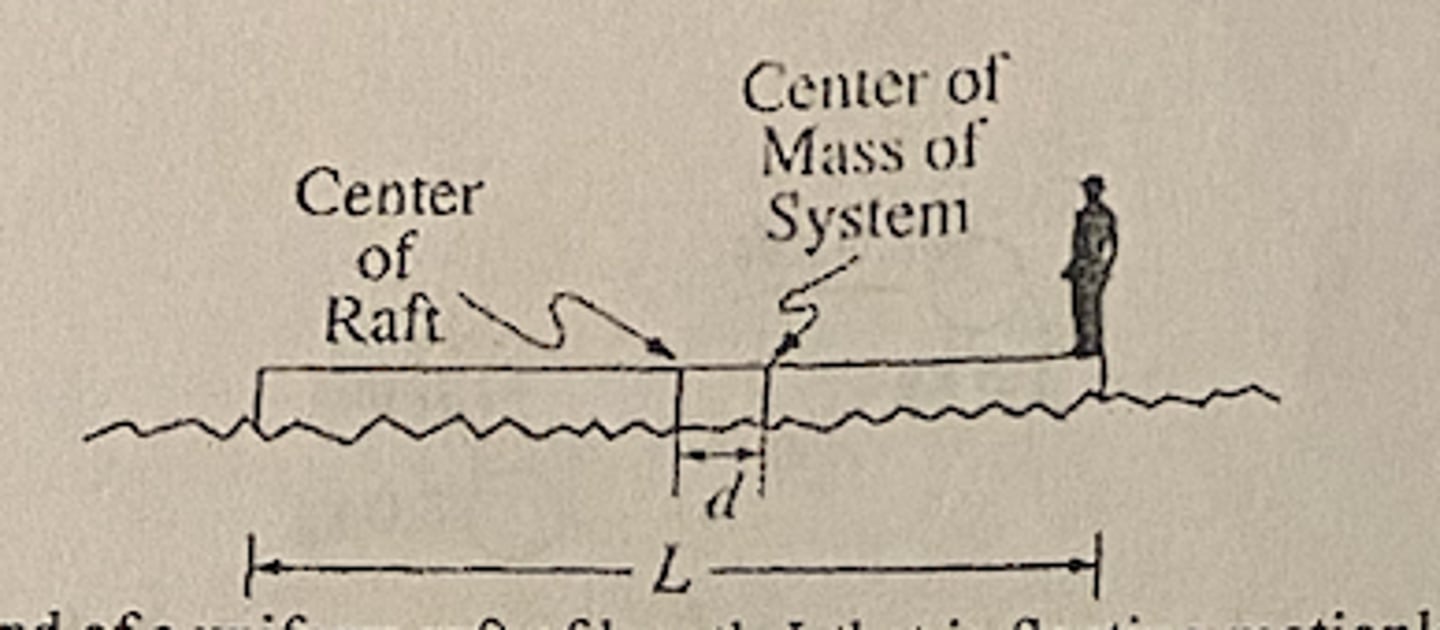
A person is standing at one end of a uniform raft of length L that is floating motionless on water, as shown above. The center of mass of the personal-raft system is a distance d from the center of the raft. The person then walks to the other end of the raft. If friction between the raft and the water is negligible, ow far does the raft move relative to the water?
E (2d)
Objects 1 and 2 have the same momentum. Object 1 can have more kinetic energy than object 2 if, compared with object 2, it
E (is moving faster)
A 5 kg object is propelled from rest at time t = 0 by a net force F that always acts in the same direction. The magnitude of F in newtons is given asa function of t in seconds by F = 0.5t. What is the speed of the object at t = 4 s?
B (0.8 m/s)
Two balls with masses m and 2m approach each other with equal speeds v on a horizontal a frictionless table, as shown in the top view above. Which of the following shows possible velocities of the balls for a time soon after the ball collide?
D (graph)
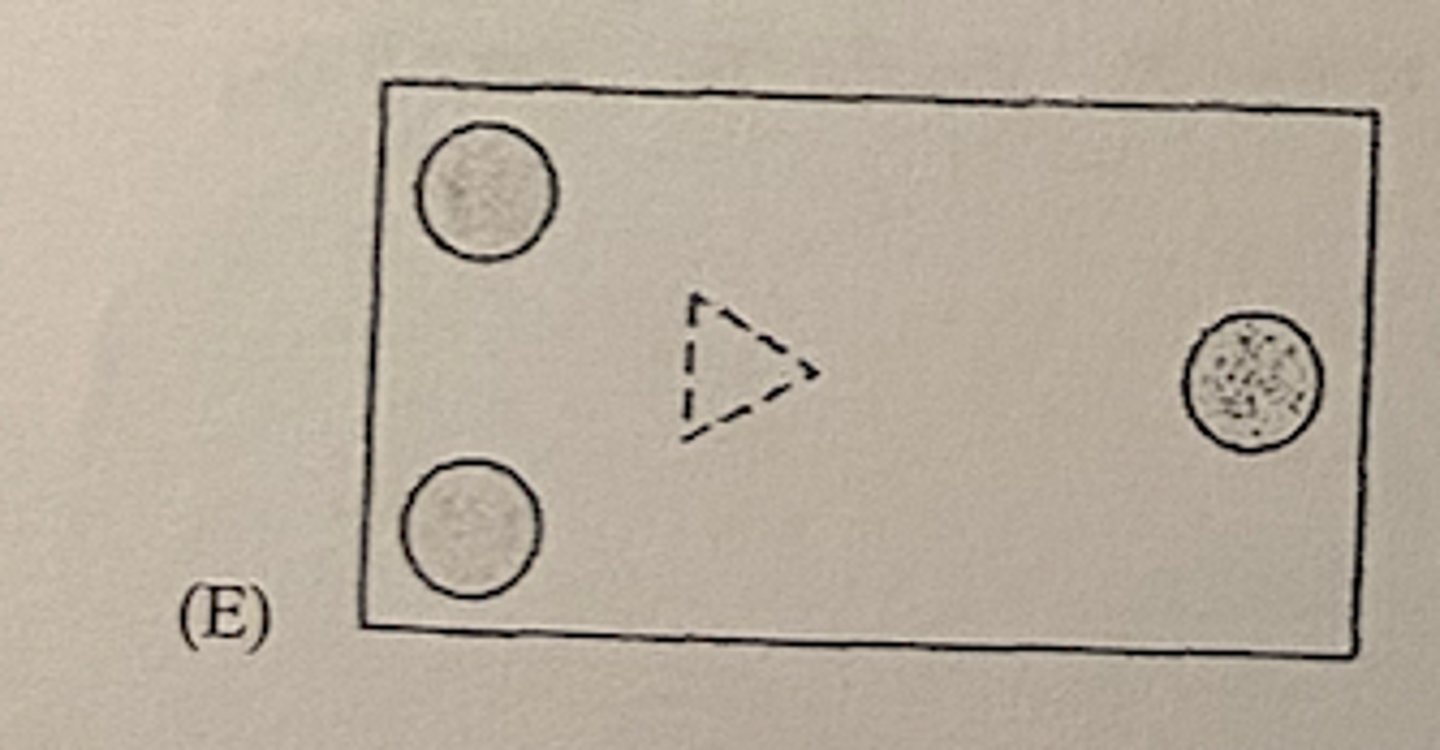
Three identical disk are initially at rest on a frictionless, horizontal table with their edges touching to form a triangle, as shown in the top view above. An explosion occurs within the triangle, propelling the disks horizontally along the surface. Which of the following diagrams shows a possible position of the disks at a later time? (In these diagrams the triangle is shown in its original position.)
E (graph)