UTA 3366 Patho Exam #2
1/502
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
503 Terms
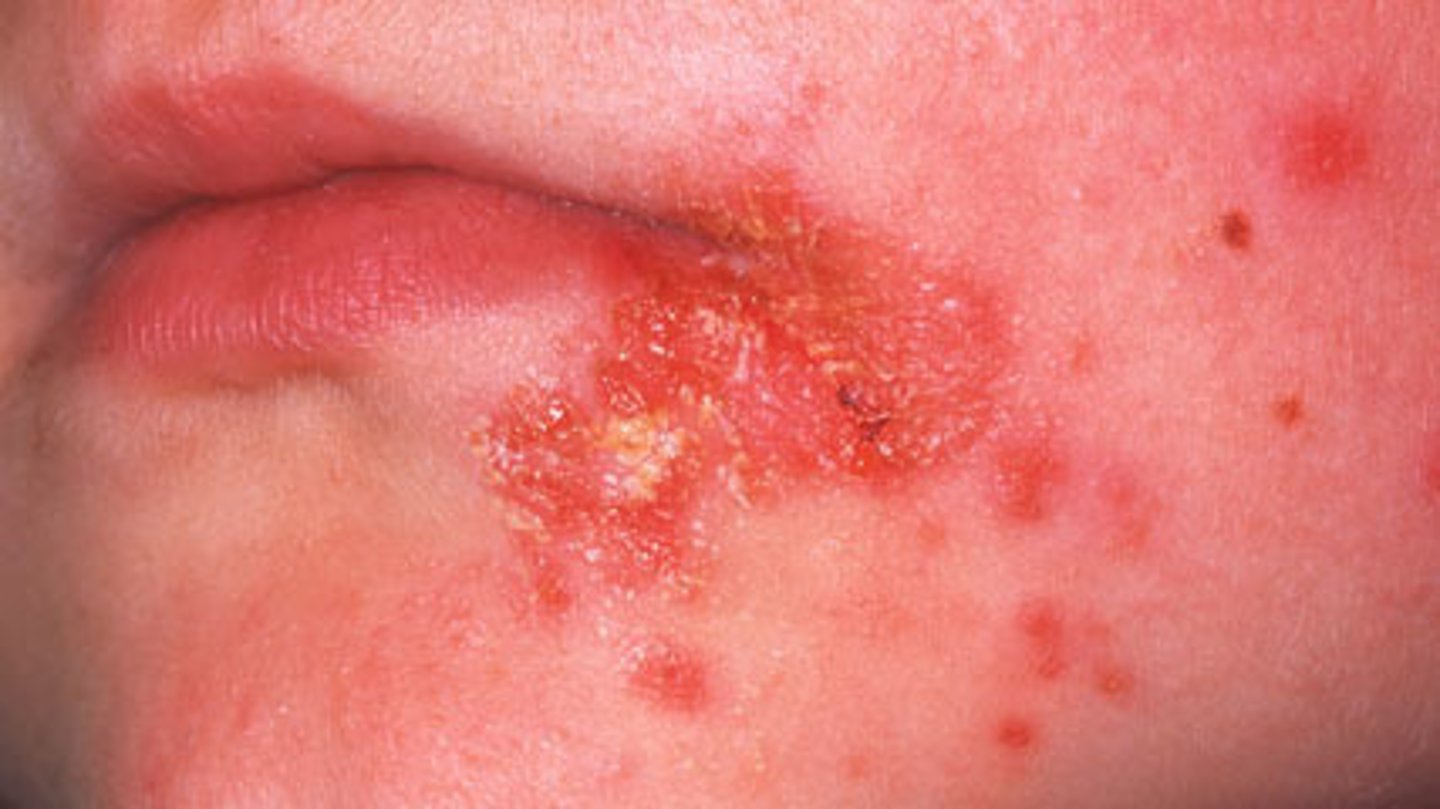
Impetigo
an eruption of blisters usually around nose & mouth that are itchy, crusty, and contagious
Innate Resistance
AKA "natural", defense mechanisms we are born with
1st Line Of Defense
the body's physical barriers which are immediate and non-specific
2nd Line Of Defense
inflammation, also immediate and non-specific
Acquired Immunity
AKA "adaptive", being able to resist certain diseases or conditions due to immunocyte involvement
Acquired Immunity is
delayed and specific
What is the First Line of Defense?
physical/mechanical and biochemical barrier and what breach them
What type of resistance is the First Line of Defense?
innate resistance
What are examples of the First Line of Defense?
skin and it's glands, and membranes/glands of body openings
Immunocytes are
lymphocytes (B-cells and T-cells)
Defense roles of the Skin and its glands
-protects more vulnerable areas underneath from simple hazards
-desquamation of skin(shedding of skin cells therefore bacteria too)
-glands secrete sweat which has antibacterial and antifungal properties
Antibacterial and antifungal properties of sweat
-attack cell walls of certain bacteria
-contribute to making the skin actually acidic making it inhospitable to most bacteria
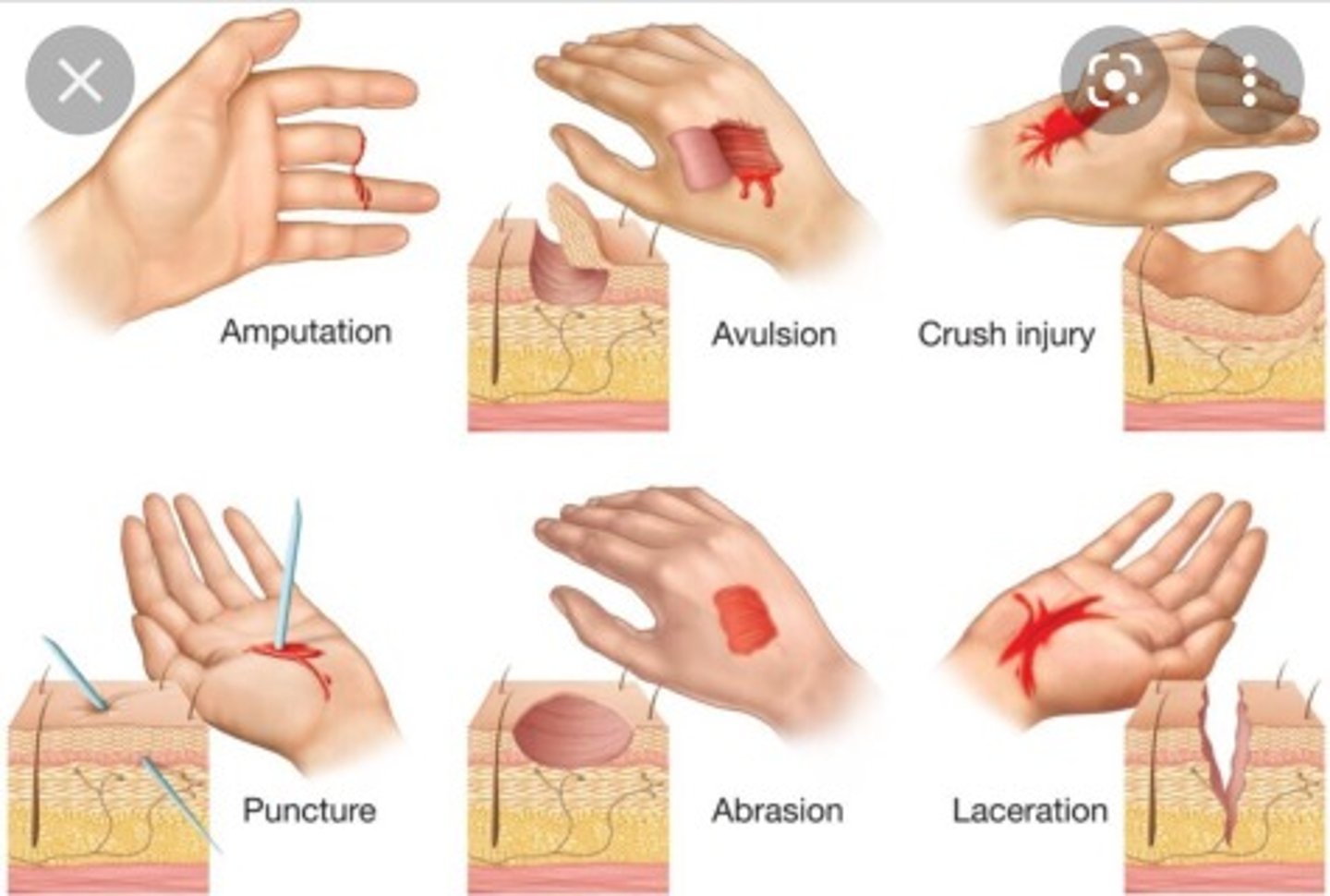
Stressors that can breach the 1st Line of Defense
lacerations, abrasions, punctures, etc.
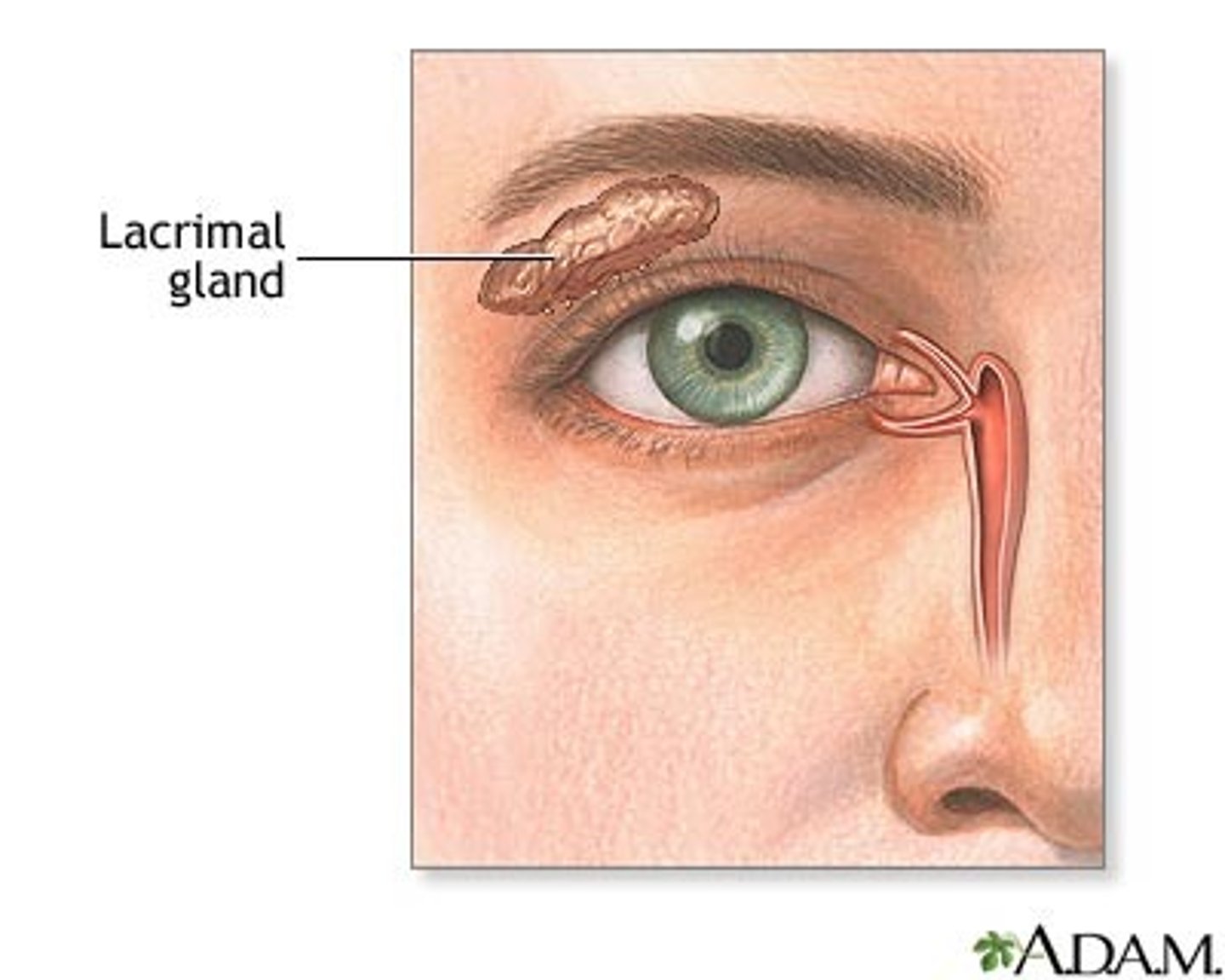
Eyes Defense Mechanism
-Tears: blinking causes lacrimal glands to spread tears over eyes=washing eye regularly
-Eyelashes
Stressors the can breach the Eye's Defense
-dry eye syndrome
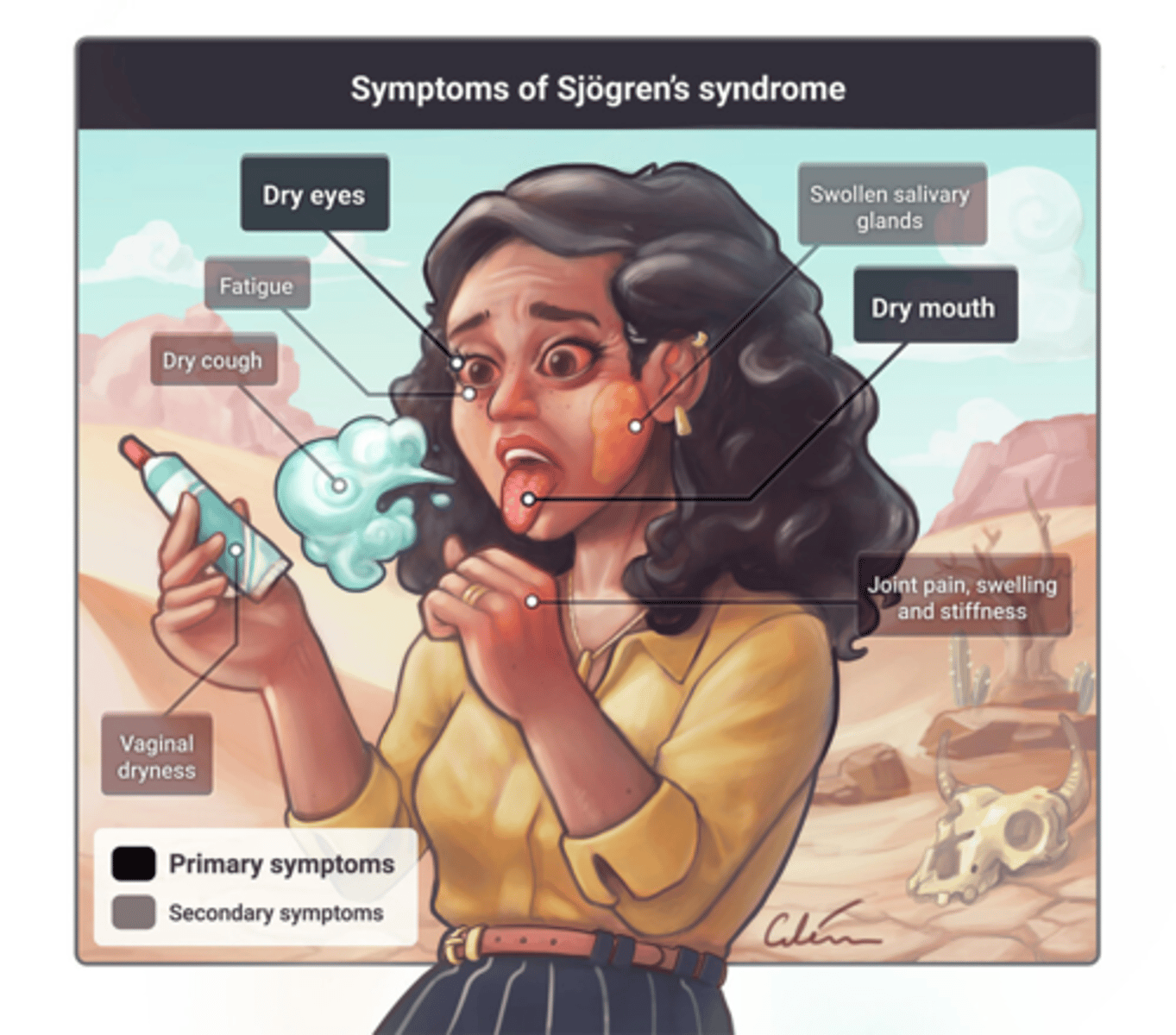
-Sjorgren's syndrome
Dry Eye Syndrome
manufacturing of tears slows down' happens to some degree to almost everyone as they age
Sjorgren's Syndrome
autoimmune disease that dries up all lubricating fluids in the body
Respiratory System Defenses
-viscosity of mucus in nose
-hair traps bacteria
-cilia of cells sweep away foreign bodies
-cough reflex: foreign body inhaled reaches the carina>cough reflex stimulated
Stressors that can breach the Respiratory System Defenses
-cigarette smoking changes bronchial cells- no more cilia (metaplasia)
-cough reflex suppression such as in head injury or stroke

Gastrointestinal (GI) System Defenses
-saliva contains protective enzymes
-stomach: HCl destroys most microbes
-gag reflex/vomiting rids of injurious agents
-bowels (good gut flora and defecation)
Normal bowel are referred to as "good flora" because
they are microbes that live in harmony with us by keeping out malicious microbes by competing for food in the gut
Defecation
gets rid of injurious agents such as harmful bacteria

Stressors that can breach the Gastrointestinal (GI) System
-Sjorgren's: dry up saliva=less protection in mouth
-anything that changes bowel flora (ex: antibiotics)
Genitourinary System Defenses
-flow of urine washes away microbes
-vaginal secretions slightly acidic-kills bacteria
Stressors that can breach the Genitourinary System (GU) Defenses
-decreased urine flow (ex: kidney stones/failure)
-anything changing vaginal acidity such as douching
Expected manifestations of 2nd Line of Defense
Swelling, Heat, Erythema, and Pain (SHEP)
Because inflammation is an uncomfortable process it is often mistakenly though of as
an abnormal state
A normal inflammatory process is usually
acute and short-lived
Purpose of Inflammatory Response
to facilitate shifting of substances from blood into injured/irritated tissue
Inflammatory mediators
a subset of biochemical mediators- substances that act on the body in a variety of ways
2nd Line of Defense: Step 1 (way 1)
irritated/injured cells undergo disruption to metabolic pathway=loss of cell membrane integrity=leakage of fluid/other substances from all injured cells in the area
2nd Line of Defense: Step 1 (way 2)
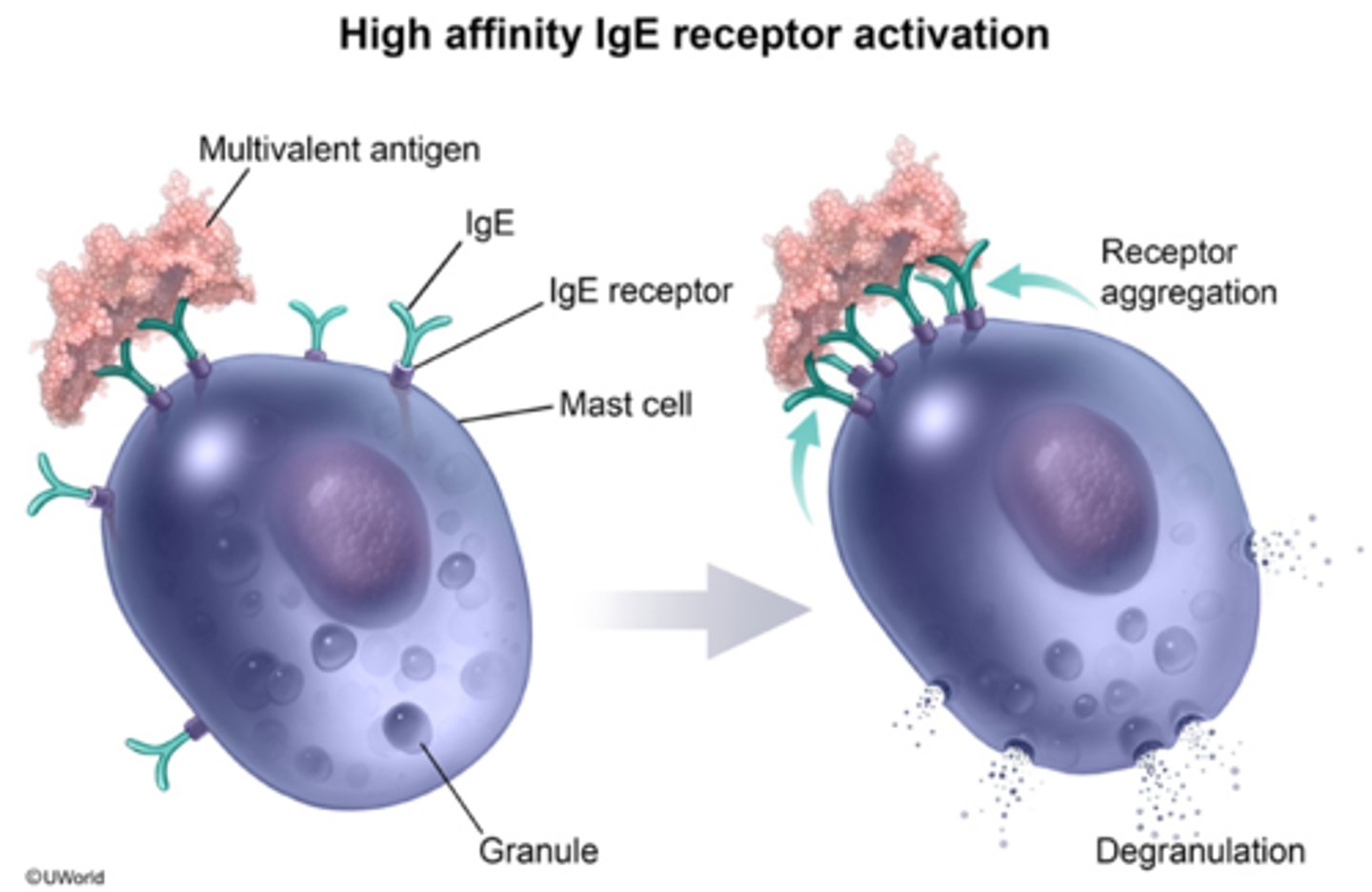
Mast Cell Degranulation Occurs
specialized cell (Mast Cells) are stimulated by an irritant/injury and degranulate (leak) HLP (histamine, leukotriene, and prostaglandins)
2nd Line of Defense: Step 1 (way 3)
HLP causes vasodilation leading to the capillary becoming more permeable then "leaks" plasma containing neutrophils, clotting factors and fibrin
If MORE inflammation is needed, what comes the the affected area?
SYSTEMIC inflammatory mediators (acute phase reactants)
What are the Systemic Inflammatory Mediators?
Acute Phase Reactants (C-reactive protein, complement, circulating prostaglandins)
2nd Line of Defense: Step 2
neutrophils(phagocytic WBCs from the blood) and macrophages(phagocytic cells in the tissue) phagocytize any dirt, debris, dying tissue, and/or microbes they might find in the tissue area
Examples of Acute Phase Reactants (APR)
C-reactive protein (CRP), circulating prostaglandins, kinins, cytokines, complement, and more clotting elements like factors
If inflammation is occurring, there is always going to be a degree of
vasodilation and increased capillary permeability "leakiness"
Mast Cells
WBCs that are found in tissue instead of blood
Macrophages
-start life as circulating monocytes, and end up in the tissues as their home
-another type of
permanent" WBC of the tissue
-phagocytize microbes and other duties
Neutrophils
circulating phagocytes- kill microorganisms in blood and tissue
Lymphocytes
T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes; AKA the immunocytes
Exudate
combination of plasma, phagocytes, dead tissue cells, bacteria, fibrin, etc.
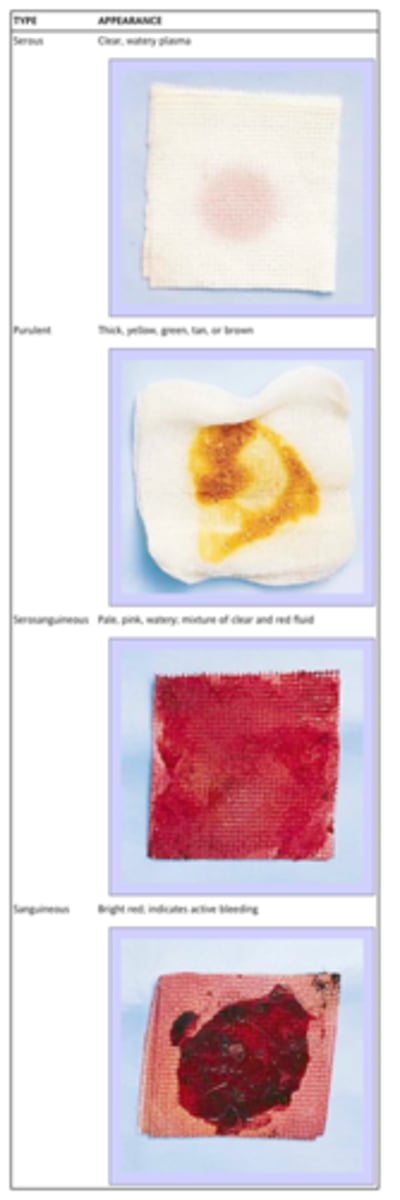
Serous Exudate
little microbe involvement, clear gold color
Serosanguinous Exudate
serous exudate with some blood

Purulent Exudate
AKA pus, microbe and WBC involvement, thick and whitish/yellowish
2nd Line of Defense: Step 3
if bacteria, viruses, or other microbes are a part of the serous exudate, macrophages will have phagocytized and processed them and now need help from the 3rd line of defense (the lymphocytes) to help kill the microbes but also create memory of the microbe
To involve the lymphocytes, the macrophages will
-secrete chemotactic substances to "call immunocytes (usually T cell/CD4 cell lymphocytes) to come to the are via the bloodstream
-display remnants of the microbes on their cell membranes as a guide to the T-lymphocytes
Chemotactic substances
biochemical mediators that summon OTHER substances to a certain area, or to increase in amount
2nd Line of Defense: Step 4
clotting factors, platelets, and fibrin come together in various ways in the area to create healing, granulating tissue
Degranulation
breaking apart of mast cells with spillage of granules of biochemical mediators into tissue
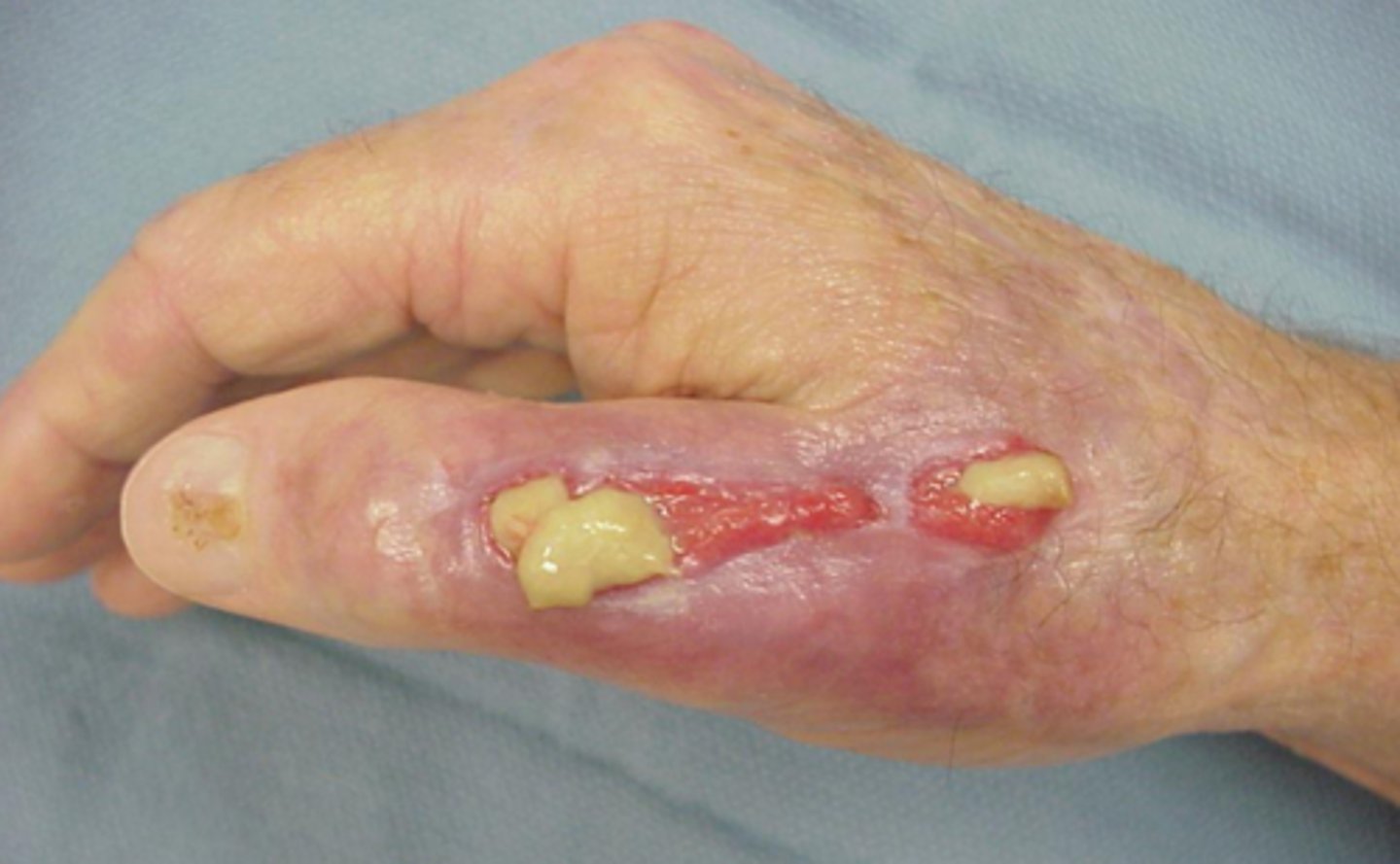
Granulating
tissue-pink, healthy, healing tissue
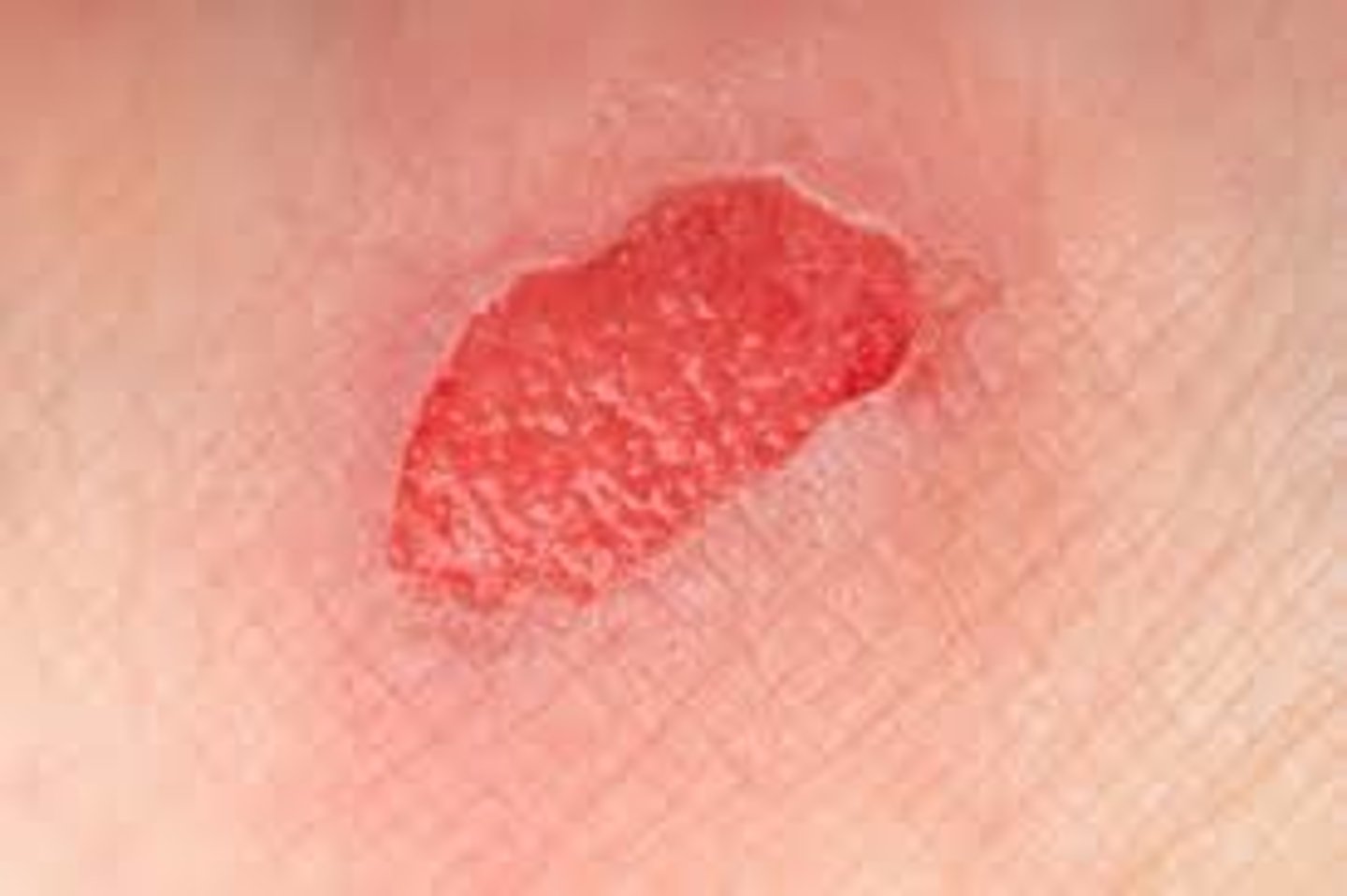
Granuloma
a hunk of tissue that has been chronically inflamed and is now essentially just scar tissue
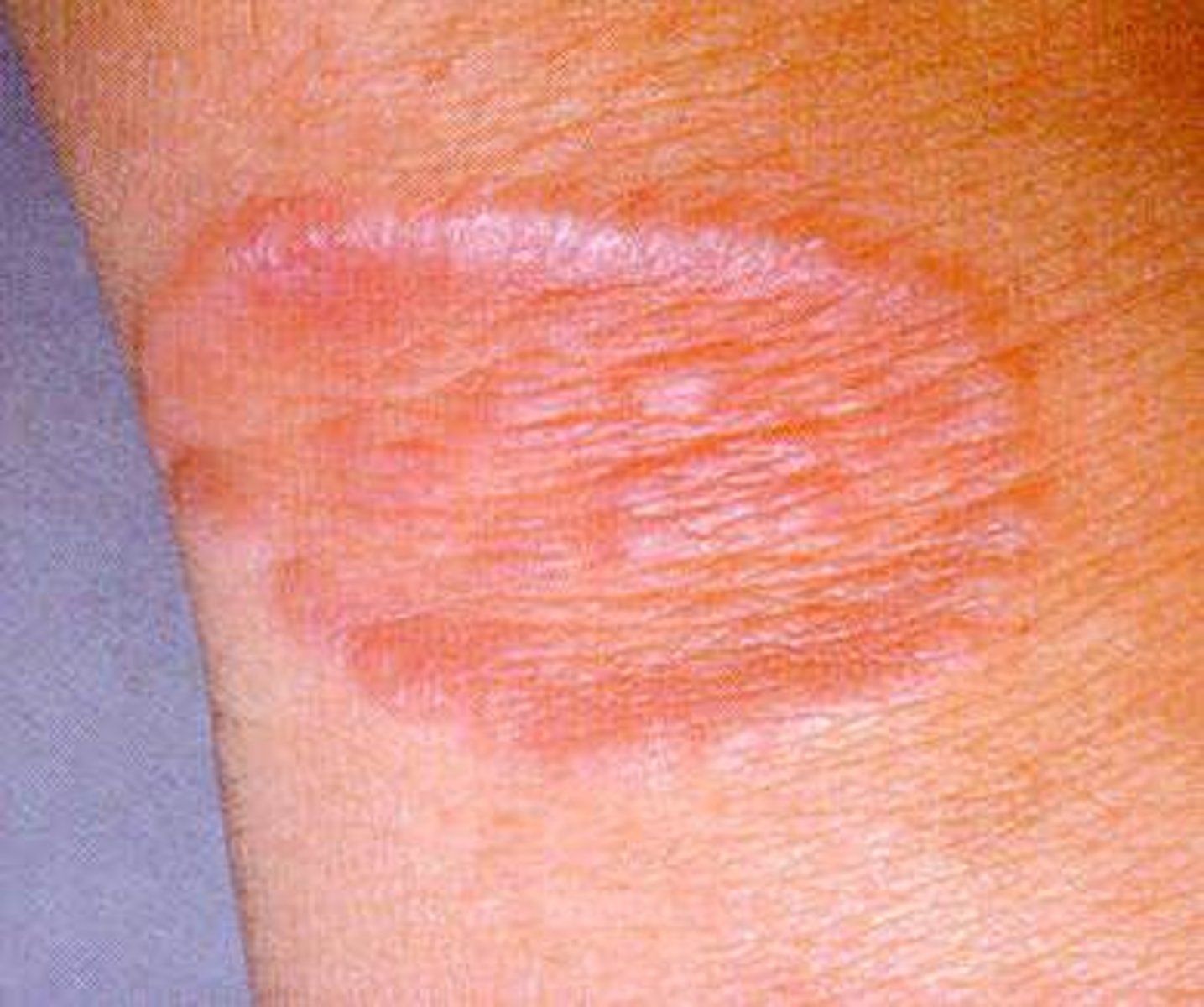
The inflammatory response can be either
local or systemic
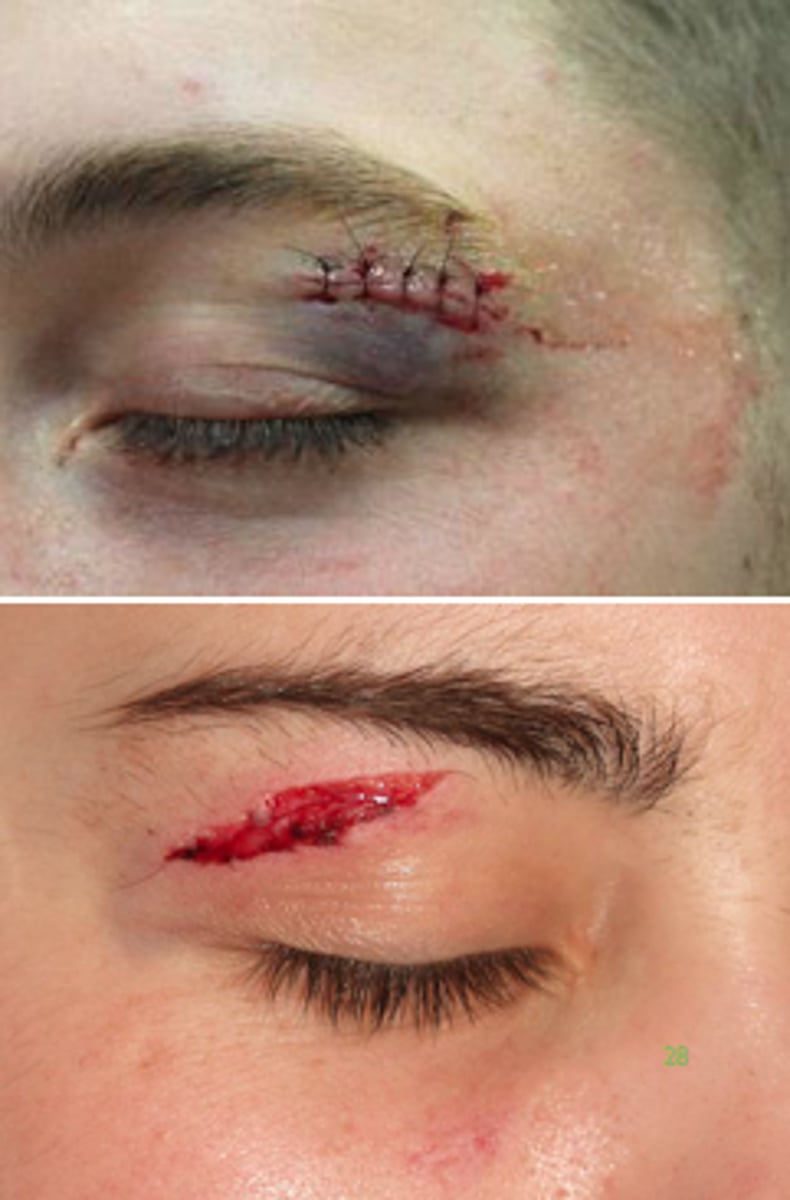
Local External Inflammatory Response Example
laceration or abrasion to skin
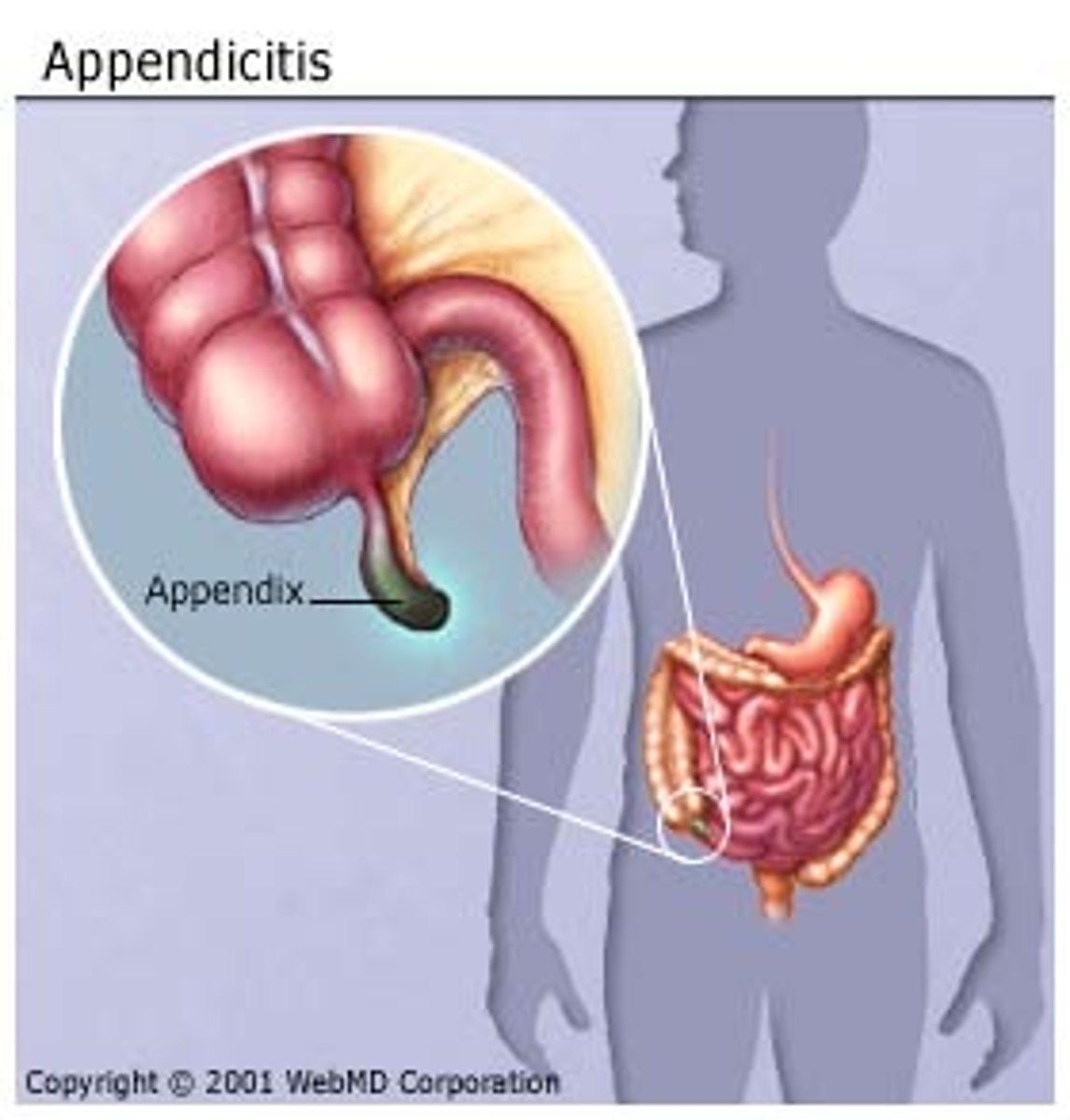
Local Internal Inflammatory Response Example: Appendicitis
appendix gets irritated by a piece of food or microbe>normal inflammation responds to the irritation>appendicitis
Local Internal Inflammatory Response Example: Pleuritis
inflammation of pleura when irritated by, for example, a lung cancer cell
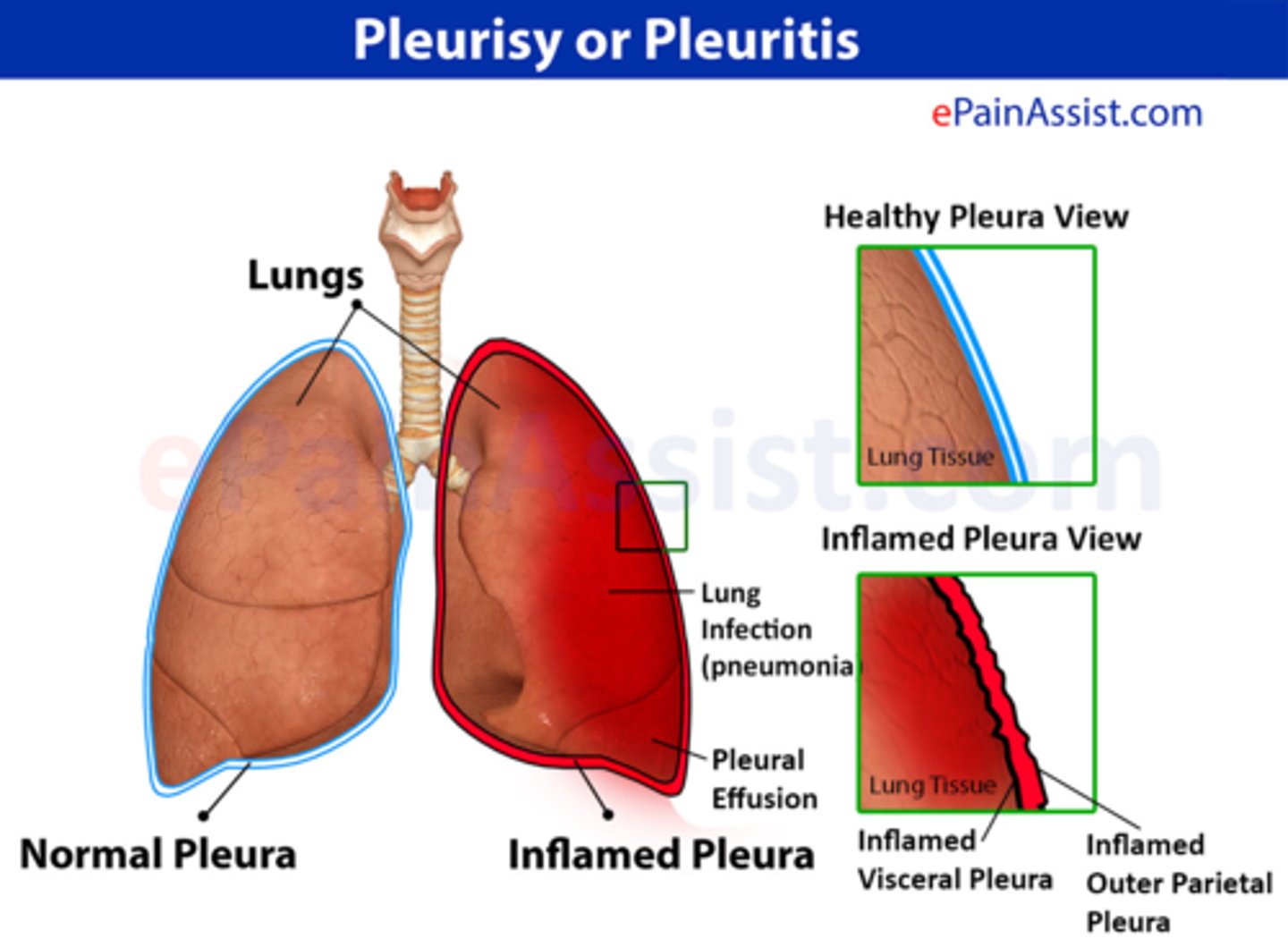
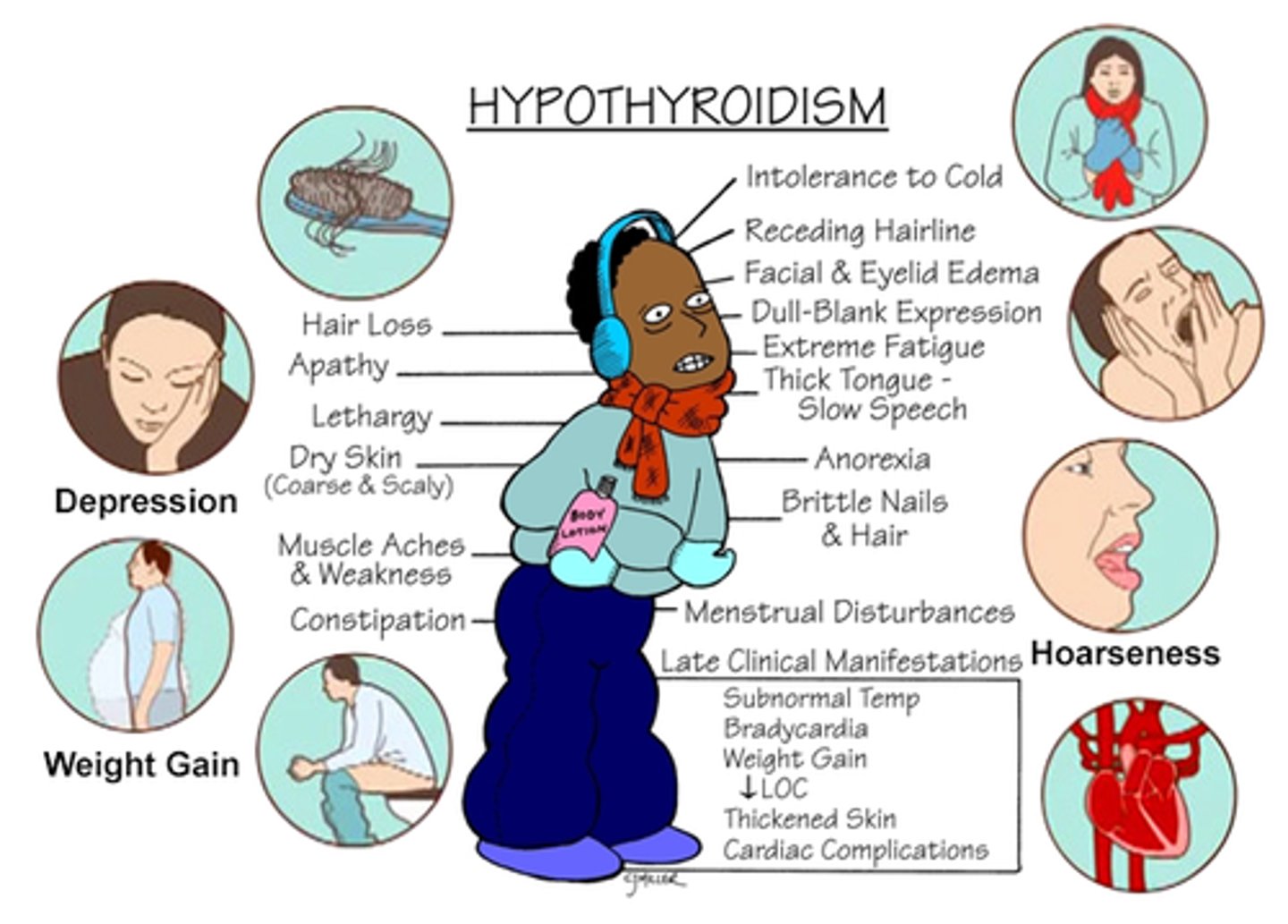
Local Internal Inflammatory Response Example: Thyroiditis
thyroid is inflamed because of an autoimmune attack
When tissues get irritated/injured, local cells leak and mast cell
degranulate biochemical mediators (Histamine, Leukotriene, and Prostaglandins)
HLP causes capillaries to
vasodilate and "LEAK"
Capillaries vasodilating and leaking allows phagocytes (mostly neutrophils) and coagulatory substances to
leak out and reach the injured area of tissue to help begin the healing process
Normal Systemic Inflammatory Response
same as local, but without a specific focus
S&S of Systemic Inflammation
-malaise, aches, and pains
-fever (from response to increased prostaglandins & acute phase reactants)

Purpose of Fever
has beneficial effect of directly killing some microorganisms but can also have deleterious effects
Deleterious effects of fevers
-can dilate blood vessels too much resulting in low blood pressure
-increases metabolic rate which may cause decompensation in very ill, debilitates, and/or elderly patients
Typical Systemic Inflammation Lab Tests
-CBC shows increased WBCs (leukocytosis)
-usually most increased is neutrophils (neutrophilia)
Lab Report showing Leukocytosis/Neutrophilia
total WBCs count= 15,000 K/ul (norm~5-10,000)
percentage of neutrophils=88%
(norm~50-75%)
Serum CRP will often be elevated during systemic inflammation because
it is an acute phase reactant (fuel on fire)
Anyone with not enough inflammation will be
extra susceptible to infections
Examples of "Not enough" inflammation include
defects in phagocytic functions and complement deficiencies
The 2 types of defects in phagocytic functions are
quantitative and qualitative
Quantitative defect in phagocytic functions (example from chemotherapy)
leukopenia (deficiency in WBCs) and neutropenia (deficiency in neutrophils)
Quantitative defect in phagocytic functions
-stem from genetic defect in synthesis of complement proteins
-pt's who have defects in these problems have problems that are very similar to those seen in pt's with antibody deficiencies (will be extra susceptible to infections)
Examples of inflammation going into overdrive (too much inflammation)
-SIRS
-Sepsis
-Septic shock
-chronic inflammation disorders
Shock
low BP that causes S&S; usually lower than 80 or 90 systolic
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)
-occurs when normal systemic inflammatory response goes into overdrive
-contributes to widespread impaired tissue function and organ damage
SIRS is present when 2 (usually more) of the following S&S are present
-unexplained change in mental status (confusion, not as awake/alert)
-fever of more than 100.4
-increased heart rate
-increased respiratory rate
-abnormal white blood cell count
Sepsis
known/suspected infection+SIRS
Septic Shock
sepsis+low blood pressure
high levels of systemic inflammatory mediators trigger widespread extreme vasodilation> floppy arterial tone (vasomotor tone)>blood pools in periphery instead of circulating>low blood volume reduced amount of O2 being brought to tissues as well as decreasing BP
S&S of Septic Shock
-SIRS: change in mental status, fever, increased heart rate, increased respiratory rate, abnormal white blood cells
+
-low BP (causes ischemia to organs so patient can have renal failure, respiratory failure, heart failure, or death)
Chronic Inflammation
lasts weeks or longer, regardless of cause
Histamines, Leukotrienes, & Prostaglandins contribute to
vasodilation & increased vascular permeability = SHEP
Systemic Mediators Response
-help further lysis of bacteria
-enhance opsonization (identify and destroy) of bacteria
-attract more neutrophils as needed
-activate coagulation cascade so that clots can form and fibrin mesh can be established at site of injury
-contribute to vasodilation and permeability of blood vessels
-cause more pain
-help to attract lymphocytes cells as needed (CD 4 cells specifically since they are introducer cells)
3rd LOD Primary Immune Response
Initial exposure to microbe.
-CD4 acts as introductory cells
-CD4 accepts phagocytized remnants of antigen from macrophages and accept remnants
-CD4 displays antigen remnants on its cell membrane and decides what is the best response to deal with this particular pathogen (cell-mediated T cell response or humoral B cell response)
3rd LOD Secondary Response
Much more rapid and effective than primary response because they have immunity to antigen now
-cell mediated (T-cell): if same virus invades body, antigen-specific memory cells will immediately recognize it and very quickly send CD8 cells to area of invasion and kill it
-humoral (B-cell): if same bacteria invades again, the antigen specific B cells will immediately recognize it & differentiate into plasma cells which very quickly send out appropriate antibodies to area of invasion and destroy bacteria
MOA of non-medicinal interventions for inflammation: Protected Ice
cold numbs pain, coolness vasoconstricts the blood vessels of the area, this swelling & pain
MOA of medicinal therapeutics: Antiinflammatoriees
suppress the effects of prostaglandins (which works well in suppressing inflammation but can result in side effects)
What are the two types of anti-inflammatory drugs?
Steroids and NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
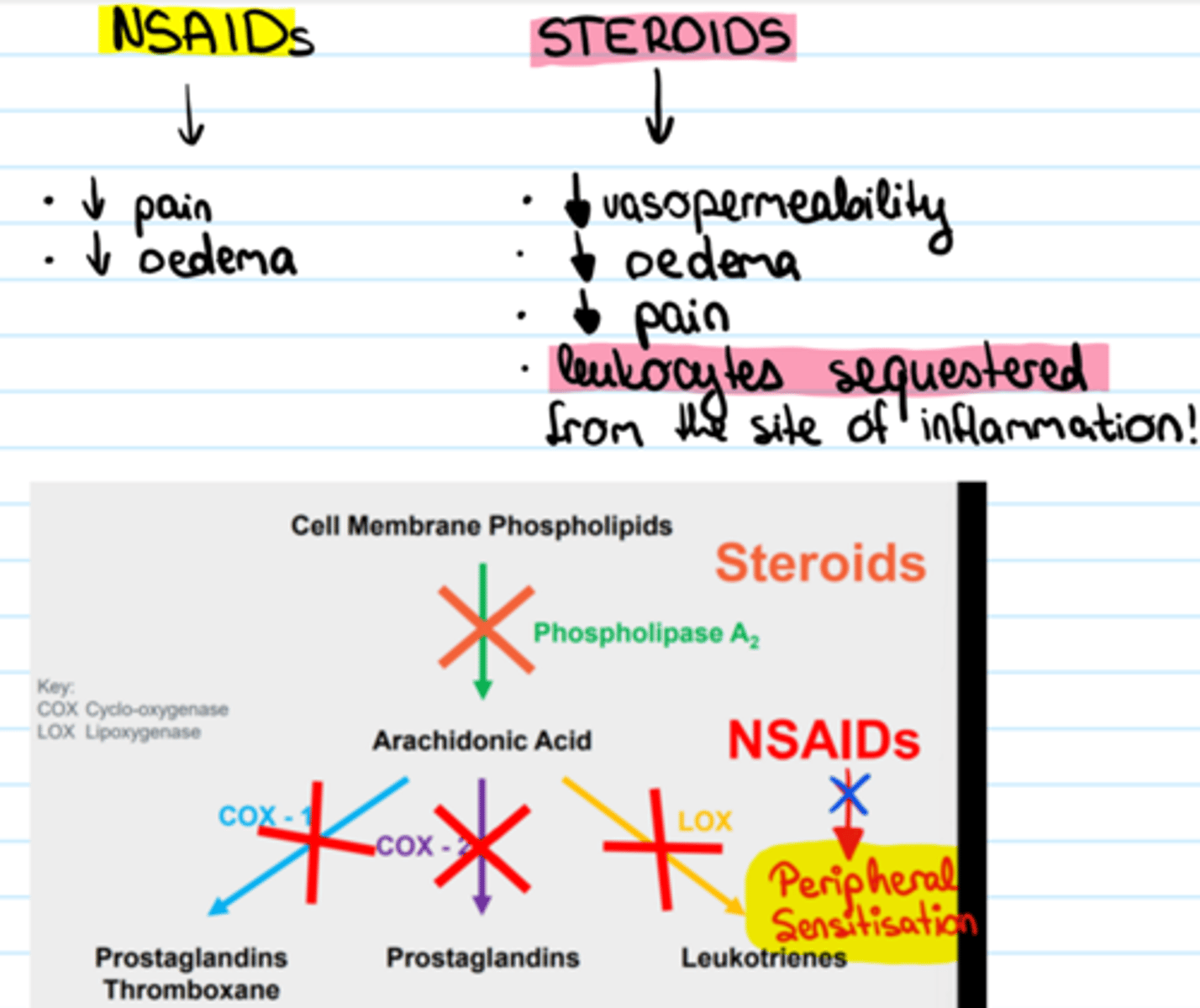
Where are prostaglandins (PGs) created in the body?
most cells
Prostaglandins (PGs) are created in a series of steps called the
Arachidonic Pathway
What are the 2 general categories of Prostaglandins?
Protective or proinflammatory
Proinflammatory Prostaglandins
stimulate further inflammation
How do pro-inflammatory PGs stimulate further inflammation?
by increasing vascular permeability and inducing fever & pain
Most side effects due to inflammatory drugs are because what type of prostaglandin being suppressed?
protective prostaglandins
What would be the ideal effect of anti inflammatory drugs?
to be specific and suppress the proinflammatory prostaglandins ONLY
Arachidonic Pathway- "Birth Pathway" of Prostaglandins
process in the cell membranes of most cells which begins with phospholipids and ends with the creation of inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins and leukotrienes
What is the enzyme that catalyzes the creation of arachidonic acid from the phospholipids of the cell membrane?
phospholipases
Where in the arachidonic pathway do steroids work?
in the cell membrane by suppressing the phospholipase enzyme
What is the most common naturally occurring steroid?
cortisol
Synthetic examples of drugs based on the structure of cortisol
prednisone & solumedrol