DSA16 - Pathology of the Cervix, Vulva, and Vagina
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Transformation Zone (TZ)
Where might you find immature squamous metaplasia/95% of cancers in the Cervix?
HPV/Cervical Dysplasia
Define Cervical Condition:
Caused by non-enveloped circular dsDNA virus
-Hx/Path: Very Common infex - usually from intimate skin-to-skin contact
> May be d/t vaginal, anal, oral sex w/ someone who has virus
> RARELY vertical transmission (mother to baby)
> MC LOW RISK = Types 6 & 11
> MC HIGH RISK (Cancer) = Types 16 & 18, 31, 33
-Path (Infex): Virus enters immature basal epithelial cells (trauma, immature squamous metaplasia at TZ) --> Replication in MATURING Squamous cells (G1 phase) ==> Persistent Infex = Risk of Precursor Lesions (Cervical Dysplasia) and Carcinoma))
-Tx: Usually Transient Infex (cleared by immune system)
-Prog:
> Duration of Infex depends on Type (HIGH > LOW)
> Causes 99.7% of cervical cancer
> Other cancers = Vaginal, Vulvar, Anal, Penile, Oropharyngeal SCC (mouth, throat)
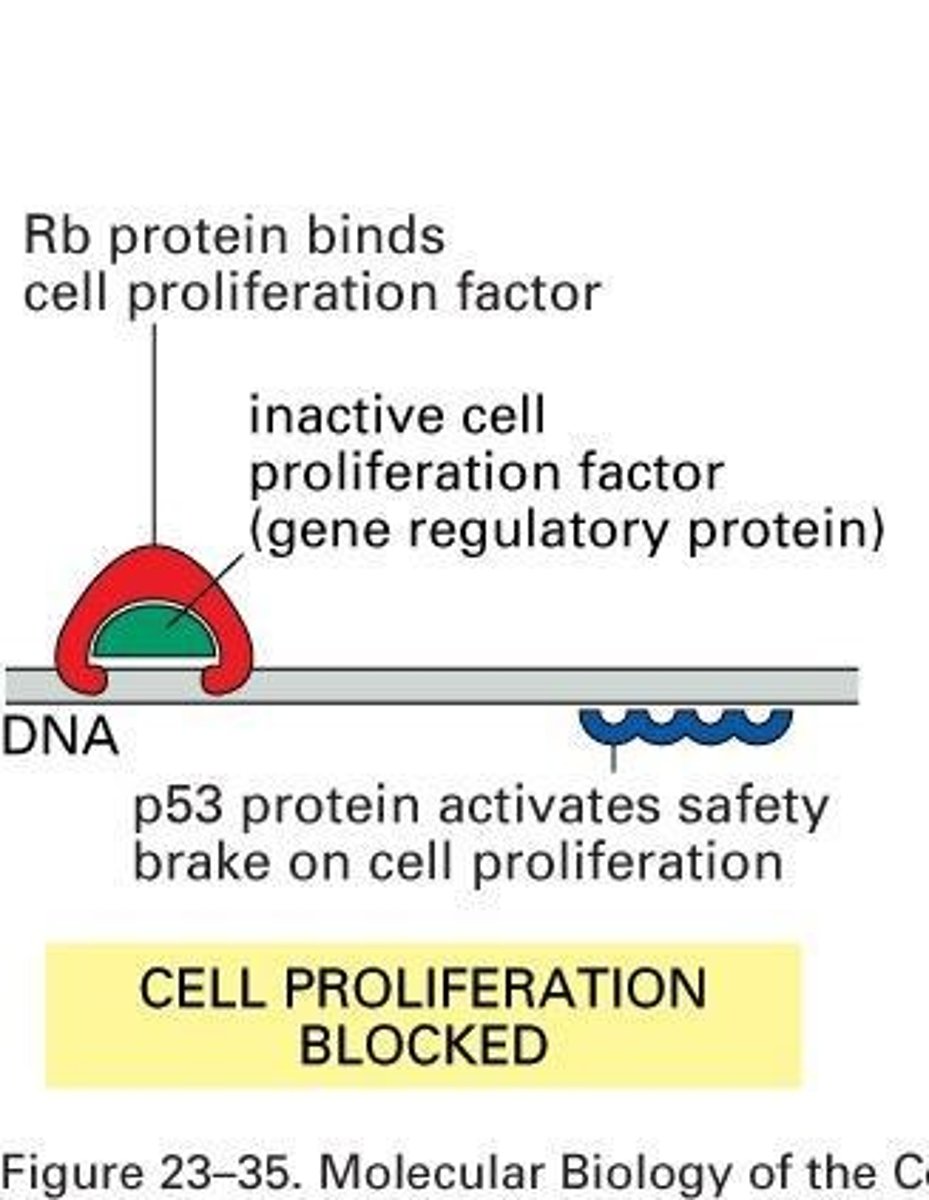
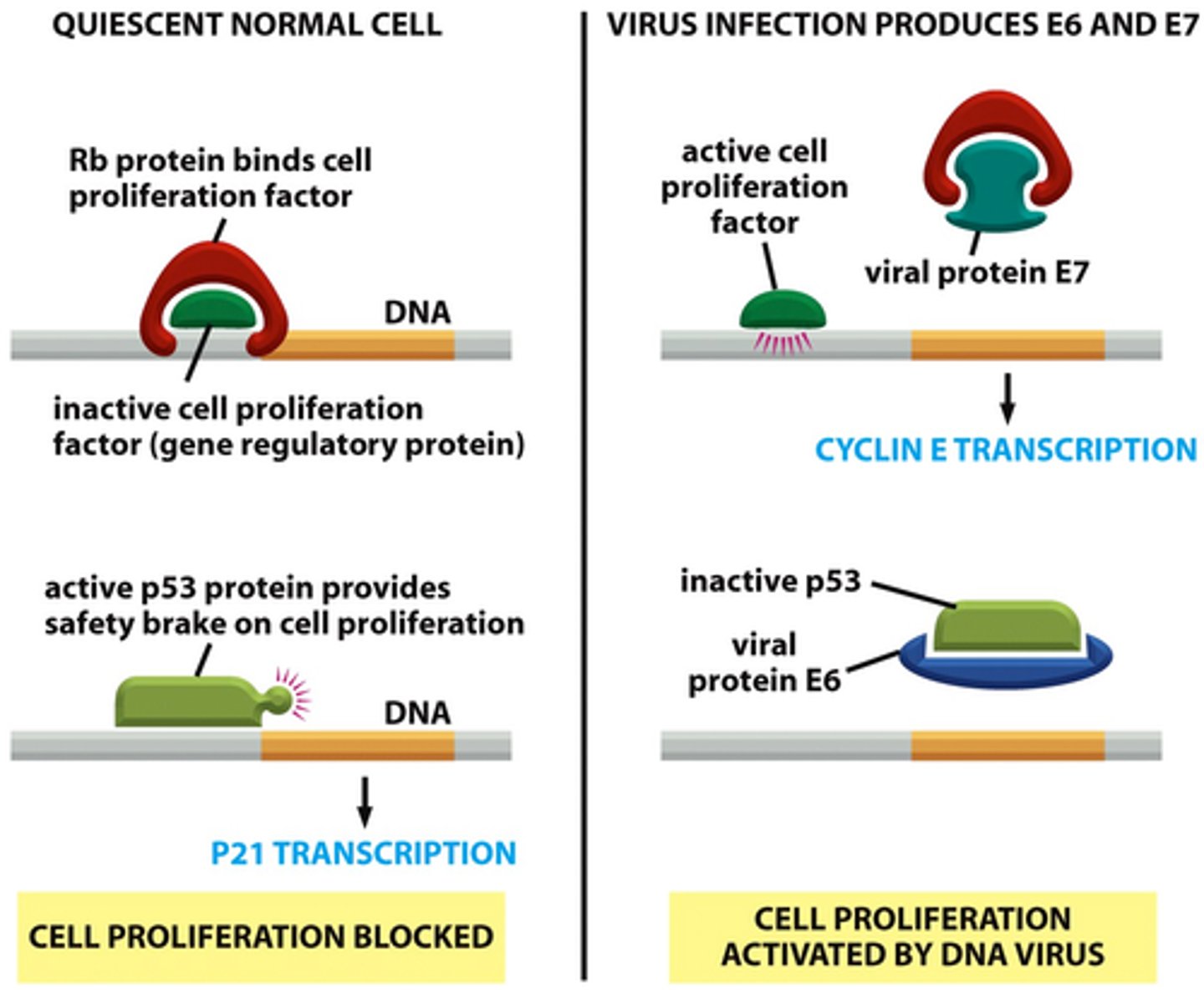
-Viral E6 protein binds/degrades p53 (high-risk HPV ↑affinity)
> p53 protein: controls cell cycle G1 to S phase progression
> Inhibited p53 -> uncontrolled growth
There are 2 key HPV viral proteins, E6 & E7 - what is the pathology behind E6 in HPV Oncogenesis?
-Viral E7 protein binds/inhibits RB protein (high-risk HPV ↑affinity)
> RB protein inactivates E2F transcription factor
> Inhibited RB -> E2F activation -> uncontrolled growth
There are 2 key HPV viral proteins, E6 & E7 - what is the pathology behind E7 in HPV Oncogenesis?
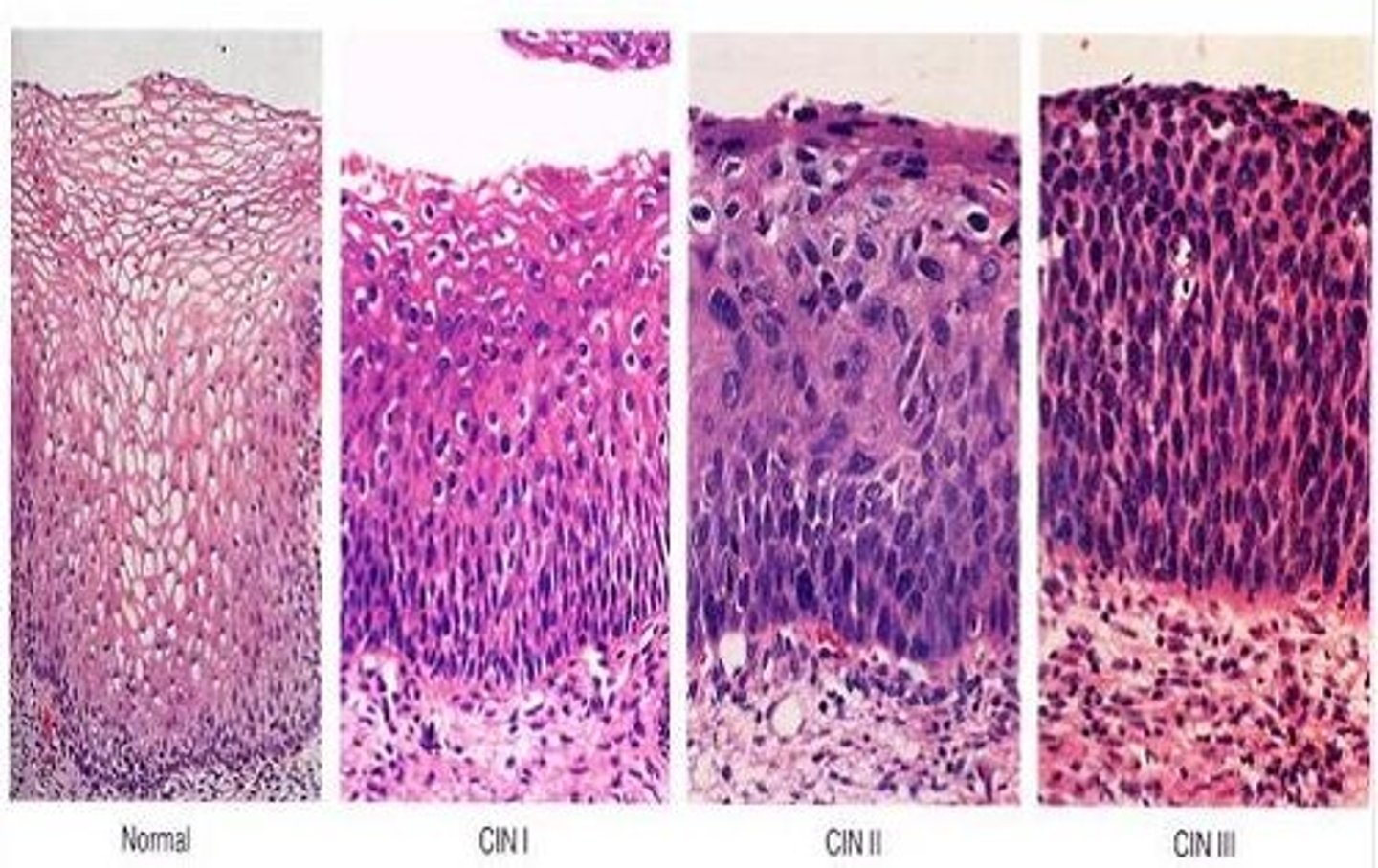
MILD DYSPLASIA in LOWER 1/3 of EPITHELIUM:
-60% regress; few progress to malignancy
-HIGH VIRAL REPLICATION, mild alterations in host cells
-Much more common than HSIL
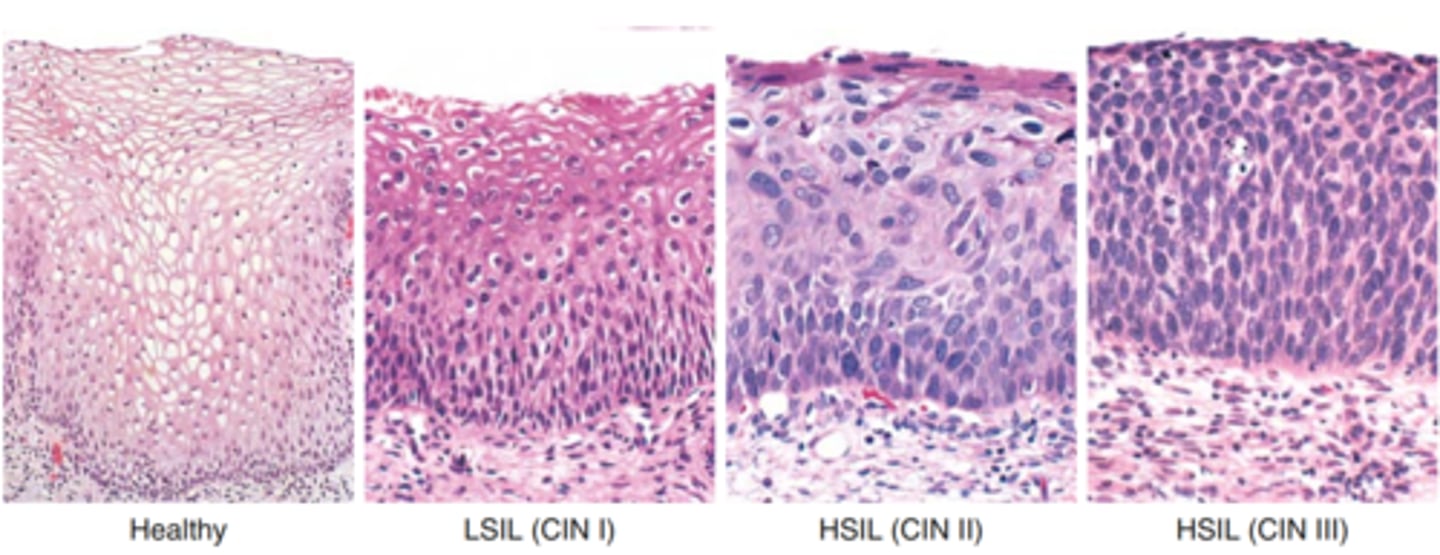
Define Low Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions/Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia 1 (LSIL/CIN1)
Observation
What is the Tx for LSIL/CIN1?
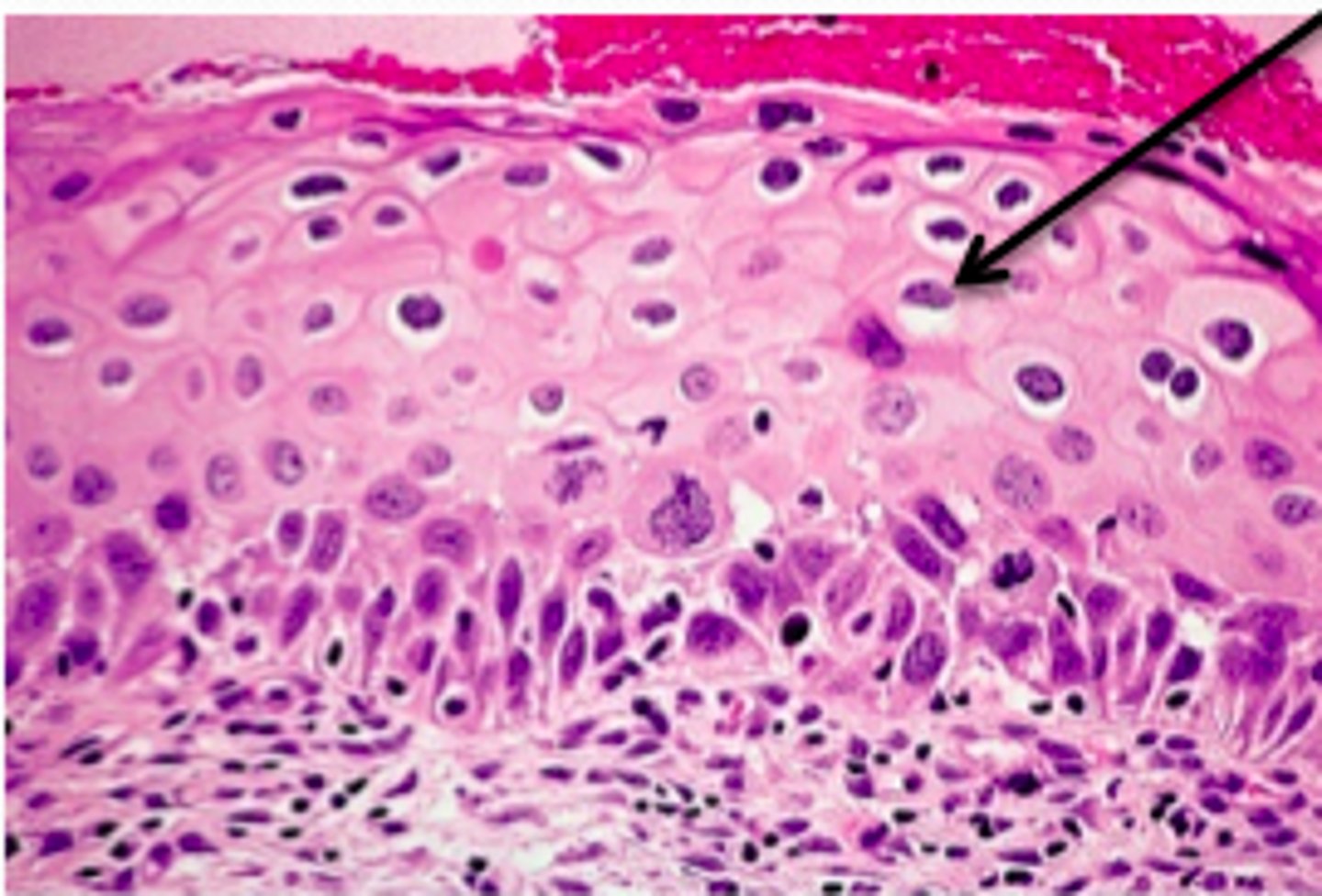
Koilocytic atypia = dysplastic nuclei (enlarged, hyperchromatic, nuclei with irregular nuclei membranes (“raisinoid”)) + perinuclear halos
How do cervical cells appear d/t HPV infex?
MOD to SEVERE DYSPLASIA (in Lower 2/3 to FULL LAYER of EPITHELIUM)
-DYSPLASTIC CELLS HAVE HIGH N:C RATIO
-↑risk of progression to malignancy
-↑deregulation of cell cycle, ↓cell maturation -> ↓viral replication
-Most develop from LSIL (20% develop de novo)
Define High Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions/Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia 2-3 (HSIL/CIN2-3)
higher
CIN 2 has a (higher/lower) regression rate than CIN 3
Cone biopsy, loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP), cryotherapy
What is the Tx for HSIL/CIN2-3?
Better for fertility
What is a benefit of LEEP/Cone Biopsy?
Preterm Delivery
What is a risk of LEEP/Cone Biopsy?
Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Define Cervical Condition:
Malignant tumor arising from cervical squamous epithelium
-Hx:
> Usually in Women in 40s-50s
> D/t High Risk HPV Type 16 (60%) or HPV Type 18 (10%)
-Path: 70-80%
> HPV-related = Early sexual activity, multiple partners, Hx of STDs
> Non-HPV related = Immunosuppression, Cigarette smoking, Lower socioeconomic status
-Sx/PE:
> Most Asx
> Postcoital Bleeding
-Dx:
> Gross = Fungating (Exophytic), ulcerated, or infiltrating mass
> Micro = Keratinizing/Nonkeratinizing invasive squamous cells
-Prog: Depends on TUMOR STAGE
> Advanced tumor may invade anterior uterine wall into bladder (blocks uterus) --> Hydronephrosis w/ postrenal failure = Common Cause of Death if Advanced
-Tx/Screen:
> Pap Smear (GOLD Standard for Screen) = brush exfoliates cells at the cervical TZ and are evaluated for cytologic atypia -> detect early/precursor lesions
> HPV DNA on Pap Smear Test
> HPV Vaccines
Endocervical Adenocarcinoma
Define Cervical Condition:
Malignant proliferation of endocervical glands
-Hx:
> D/t High Risk HPV Type 18 (50%)
> Precursor = AIS
-Path: 15-25%
> HPV-related = Early sexual activity, multiple partners, Hx of STDs
> Non-HPV related = Immunosuppression, Cigarette smoking, Lower socioeconomic status
-Sx/PE: Usually Asx
-Dx:
> Gross = Exophytic, ulcerated, flat, barrel cervix
> Micro = Invasive malignant glands
-Prog: Depends on TUMOR STAGE
-Tx/Screen:
> Pap Smear (GOLD Standard for Screen) = brush exfoliates cells at the cervical TZ and are evaluated for cytologic atypia -> detect early/precursor lesions
> HPV DNA on Pap Smear Test
> HPV Vaccines
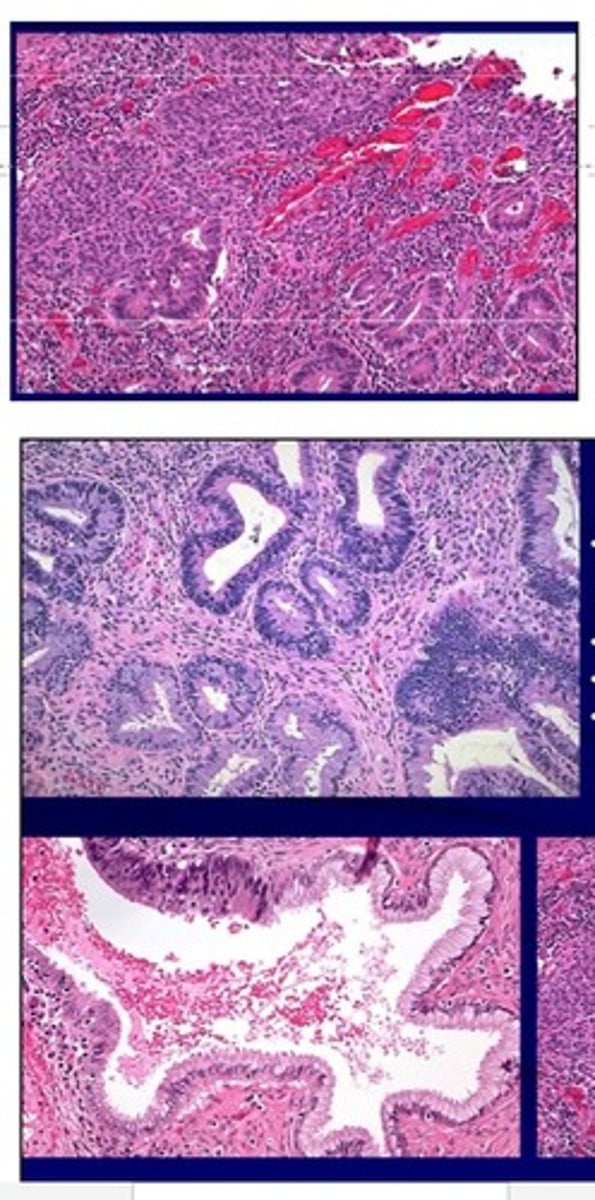
Vaginal Adenosis
Define Vaginal Condition:
Focal persistence of columnar epithelium; BENIGN/NON-NEOPLASTIC Lesion
-Hx: A/w in utero diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure)
> Exposed to Hormones
> Trauma
> Inflammation
-Path: During development, squamous epithelium from the lower 1/3 of the vagina (derived from the urogenital sinus) grows UPWARD to replace the columnar epithelium lining of the upper 2/3 of the vagina (derived from the Müllerian ducts)
-Sx/PE:
> MC Found in UPPER VAGINA
> Usually Asx
> Vaginal Discharge
> Postcoital bleeding
> Dyspareunia
-Dx:
> Gross: Vaginal mucosa displays red granular spots or patches
> Histo: cluster of benign glands in vaginal stroma
-Prog: Clear Cell Carcinoma!
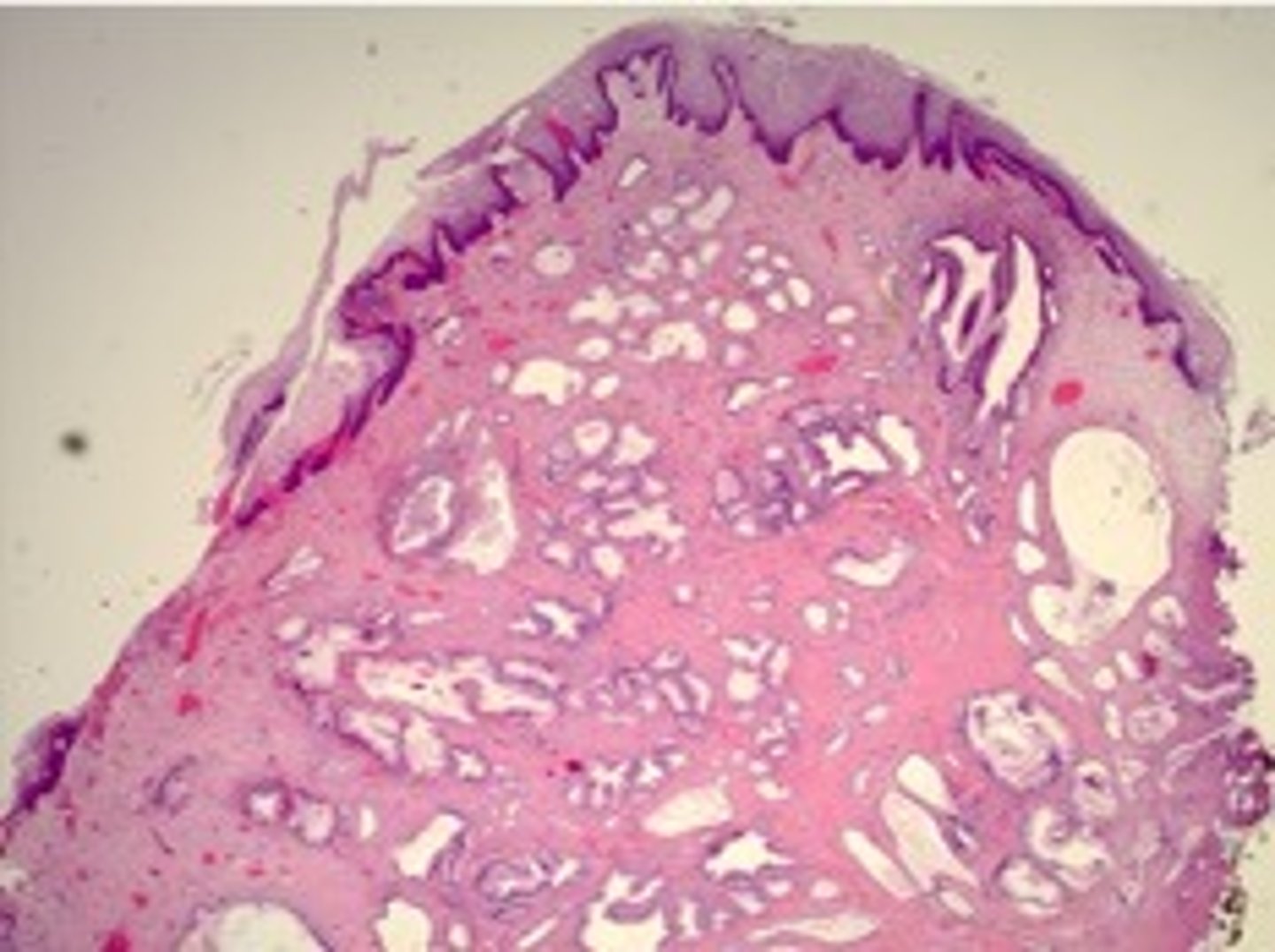
Vaginal Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma
Define Vaginal Condition:
Malignant proliferation of glands with clear cytoplasm
-Hx: Rare, complication of DES-associated vaginal adenosis
-Dx: Histo: Tumor cells have distinct cell membranes, are large with moderate to abundant clear cytoplasm
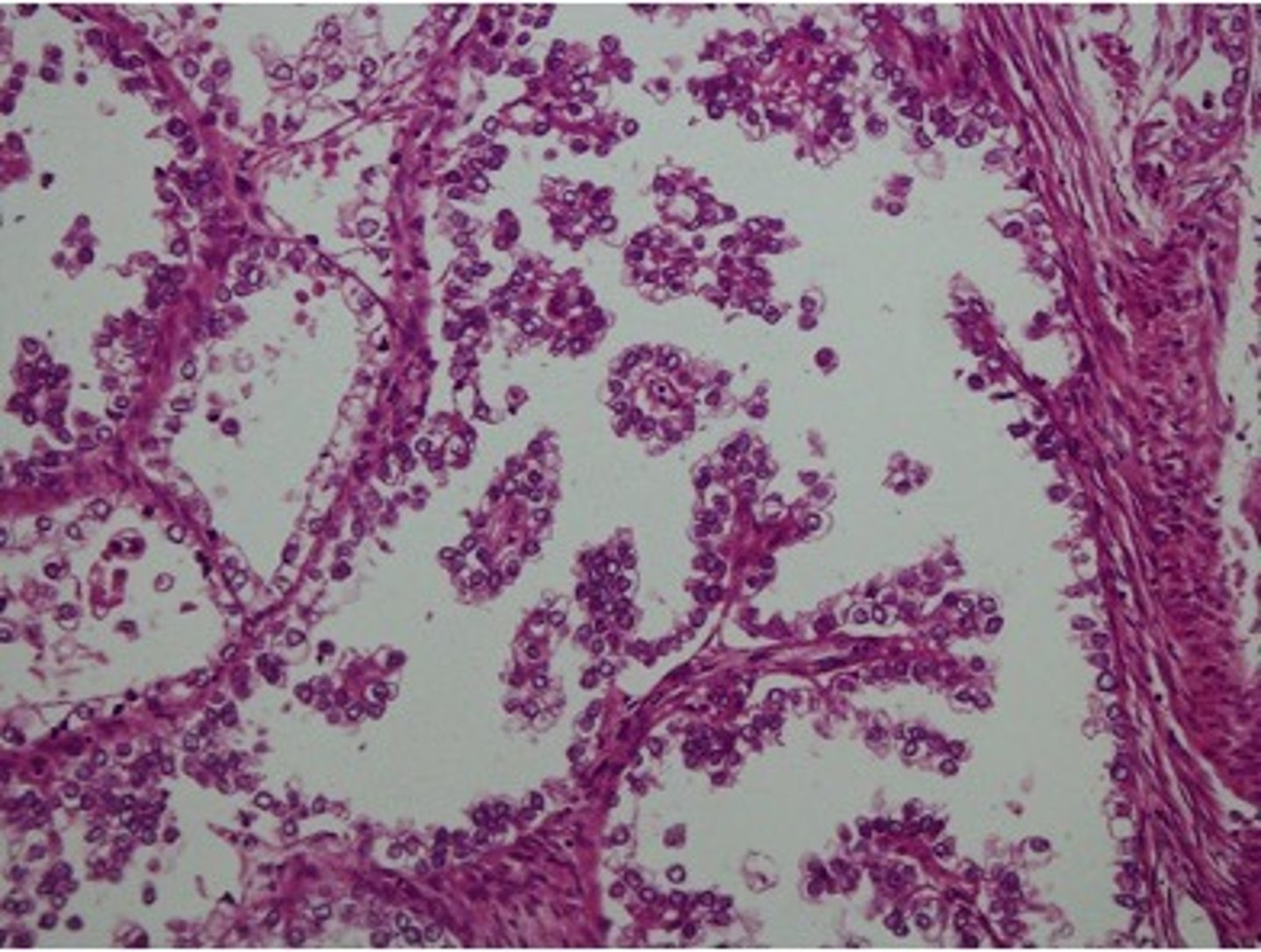
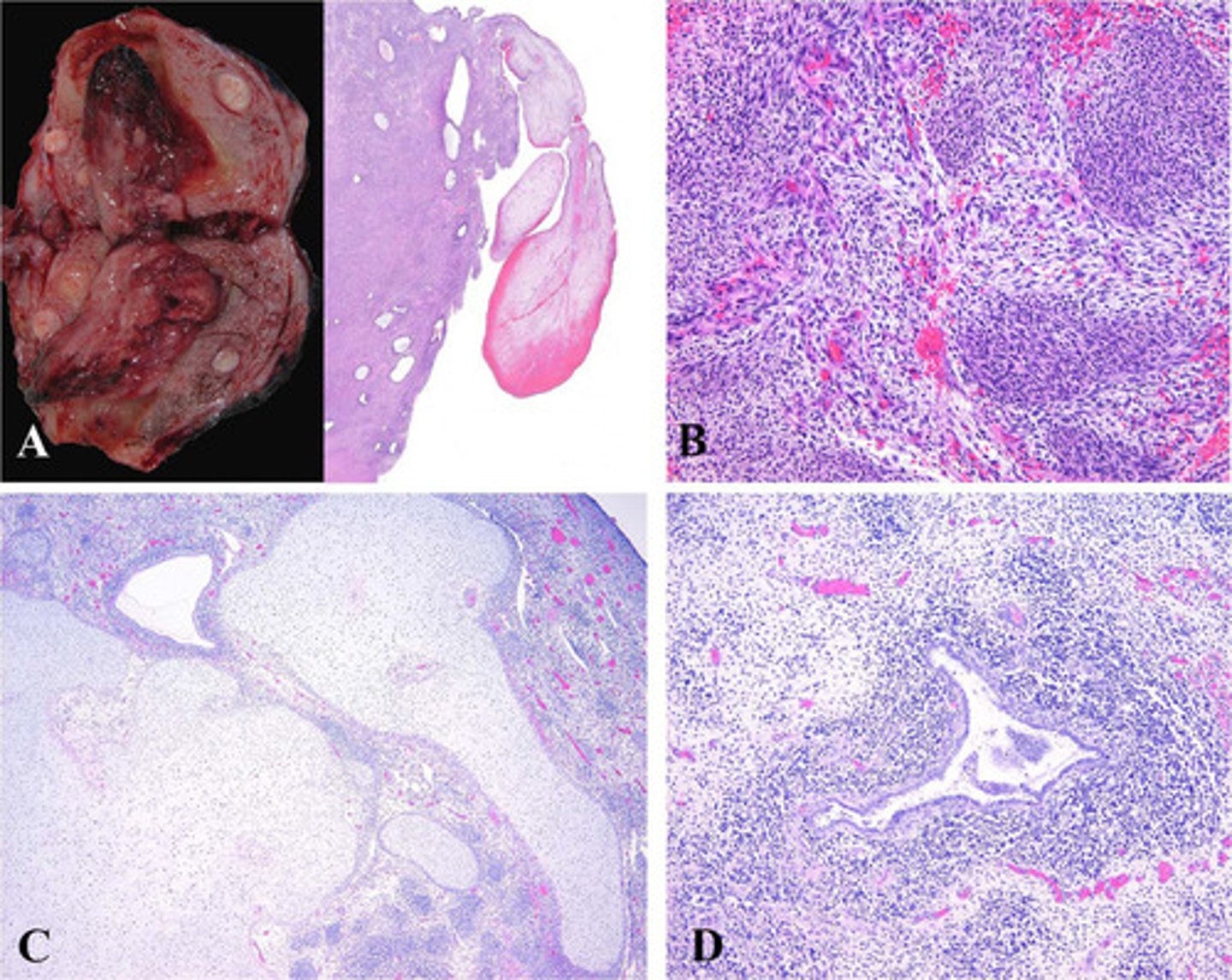
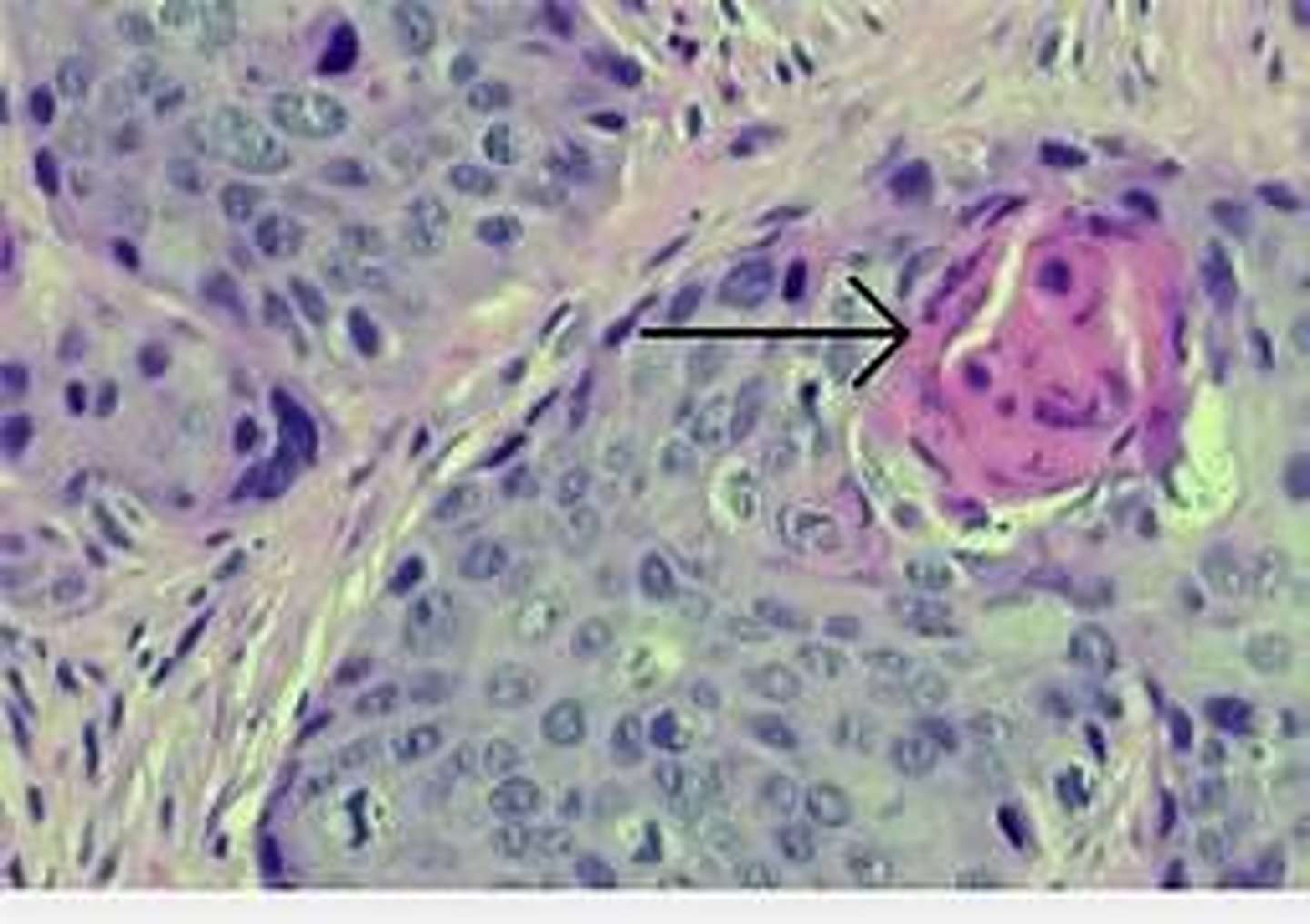
Vaginal Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
Define Vaginal Condition:
Rare, malignant mesenchymal proliferation of immature skeletal muscle
Sarcoma Botyroides
Define Vaginal Condition:
Rhabdomyosarcoma variant
-Hx: Infants or children < 5 y/o
-Dx:
> Gross: Clear, polypoid grape-like mass growing from vagina
> Histo: Tumor consists of small round blue cells and rhabdomyoblasts (pink spindled cells with cytoplasmic cross-striations) and positive immunohistochemical staining for desmin and myogenin (muscle cell markers)
-Prog: May invade peritoneum --> Obstruct bladder
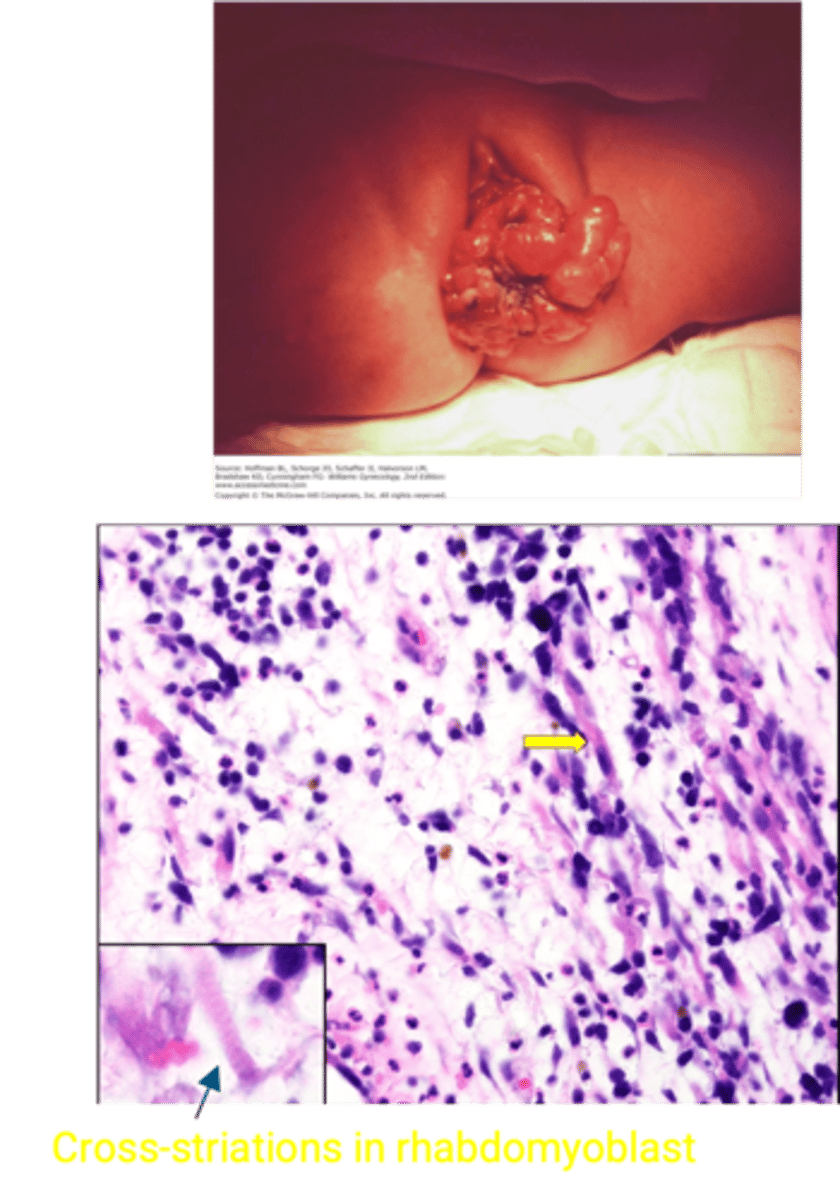
Vaginal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Define Vaginal Condition:
Malignant tumor arising from squamous epithelium
-Hx: Usually involves high-risk HPV; MC Secondary to extension of cervical SCC
> Usually in Women in 40s-50s
> D/t High Risk HPV Type 16 (60%) or HPV Type 18 (10%)
-Path:
> Primary tumor RARE
> Precursor = Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia (VaIN), LSIL, HSIL
> LN metastasis
>> Inguinal Nodes = cancer from lower 1/3 vagina (from urogenital)
>> Regional Iliac Nodes = cancer from upper 2/3 vagina (from Mullerian ducts)
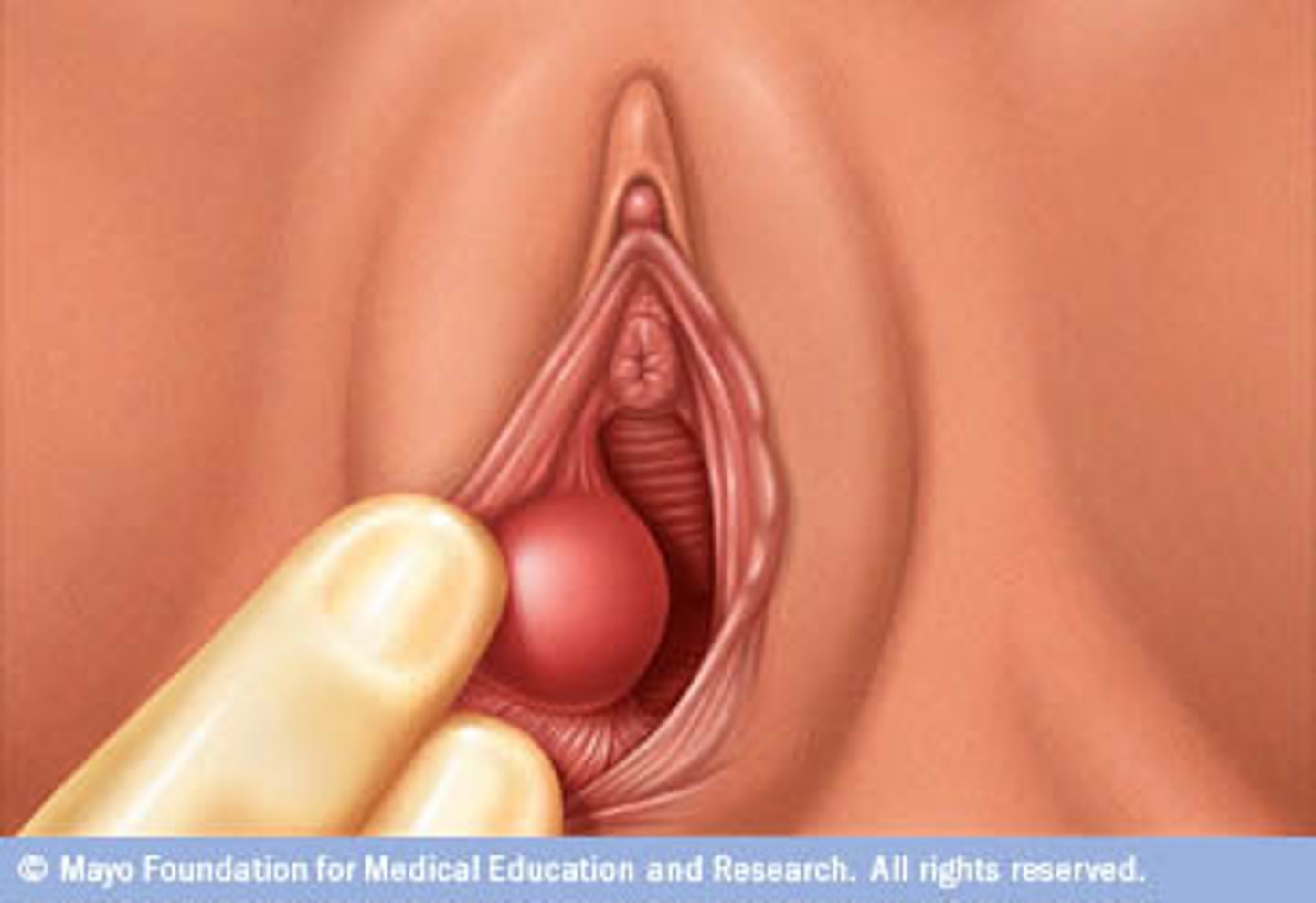
Bartholin Cyst/Abscess
Define Vulvar Condition:
Inflammation and obstruction of Bartholin gland duct (normally secretes mucus-like fluid draining into lower vestibule to lubricate vagina) -> accumulation of fluid -> cystic dilation of Bartholin gland ==> Infex = ABSCESS
-Hx: Reproductive females
-Sx/PE: Tender/painful bump at a 4- or 8-o’clock position on the vulva
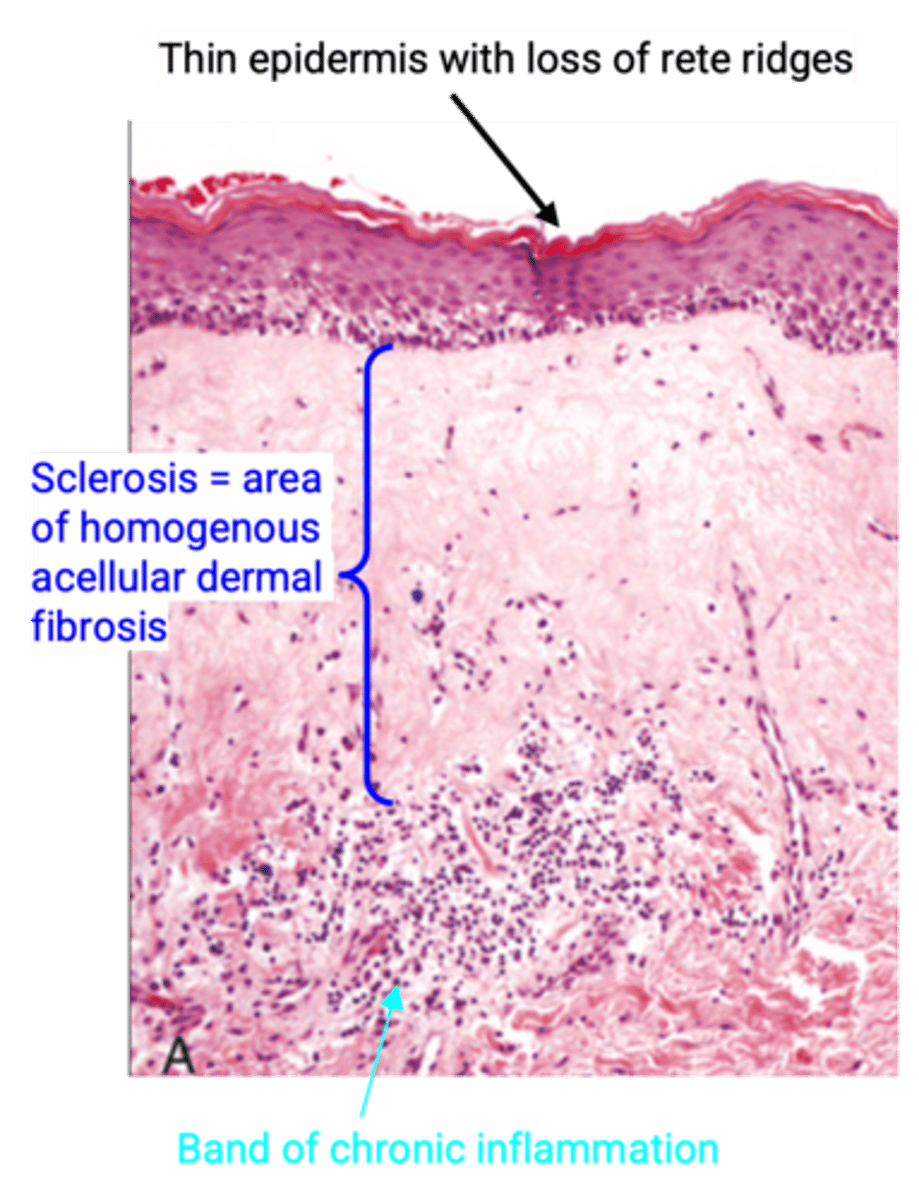
Lichen Sclerosus (LS)
Define Vulvar Condition:
Chronic inflammatory skin disorder that most often affects genital and perianal areas
-Hx: Any age, but MC in Peri/Postmenopausal females
-Path: A/w Other Autoimmune disorders
-Sx/PE: INTENSE PRURITUS
-Dx:
> Gross: white patch (leukoplakia) with parchment-like vulvar skin
> Histo: Epithelial thinning/Atrophic epidermis, dermal fibrosis (aka SCLEROSIS), and a band of chronic inflammation
-Prog: Benign, but slight risk of SCC
Lichen Simplex Chronicus
Define Vulvar Condition:
Chronic, itchy skin disorder
-Hx: (These CAUSE it)
> Chronic Irritation
> Scratching
-Dx:
> Gross: Leukoplakia with thick, leathery vulvar skin
> Histo: squamous hyperplasia of the vulvar epithelium, hyperkeratosis
-Prog: Benign, but NO RISK OF SCC
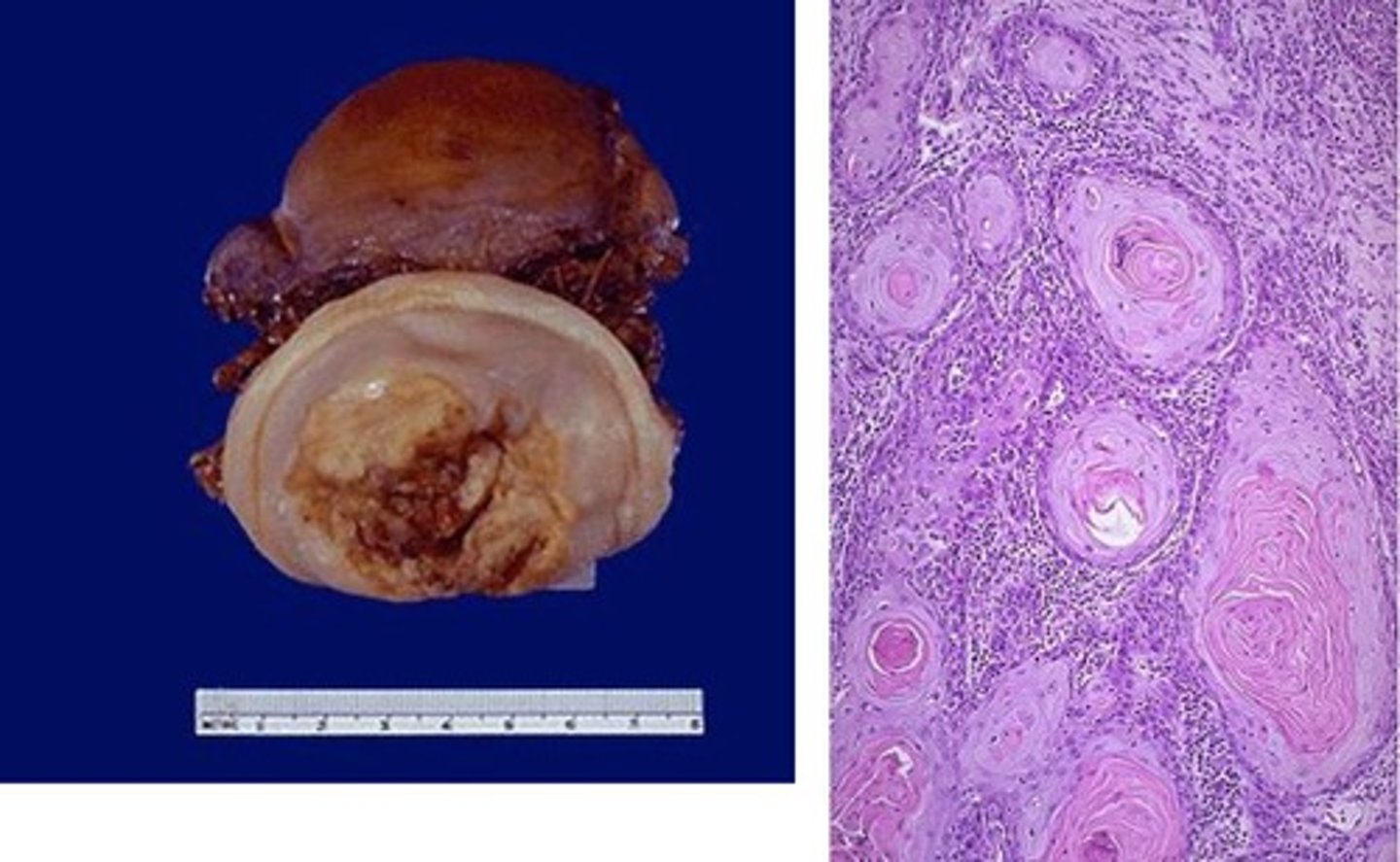
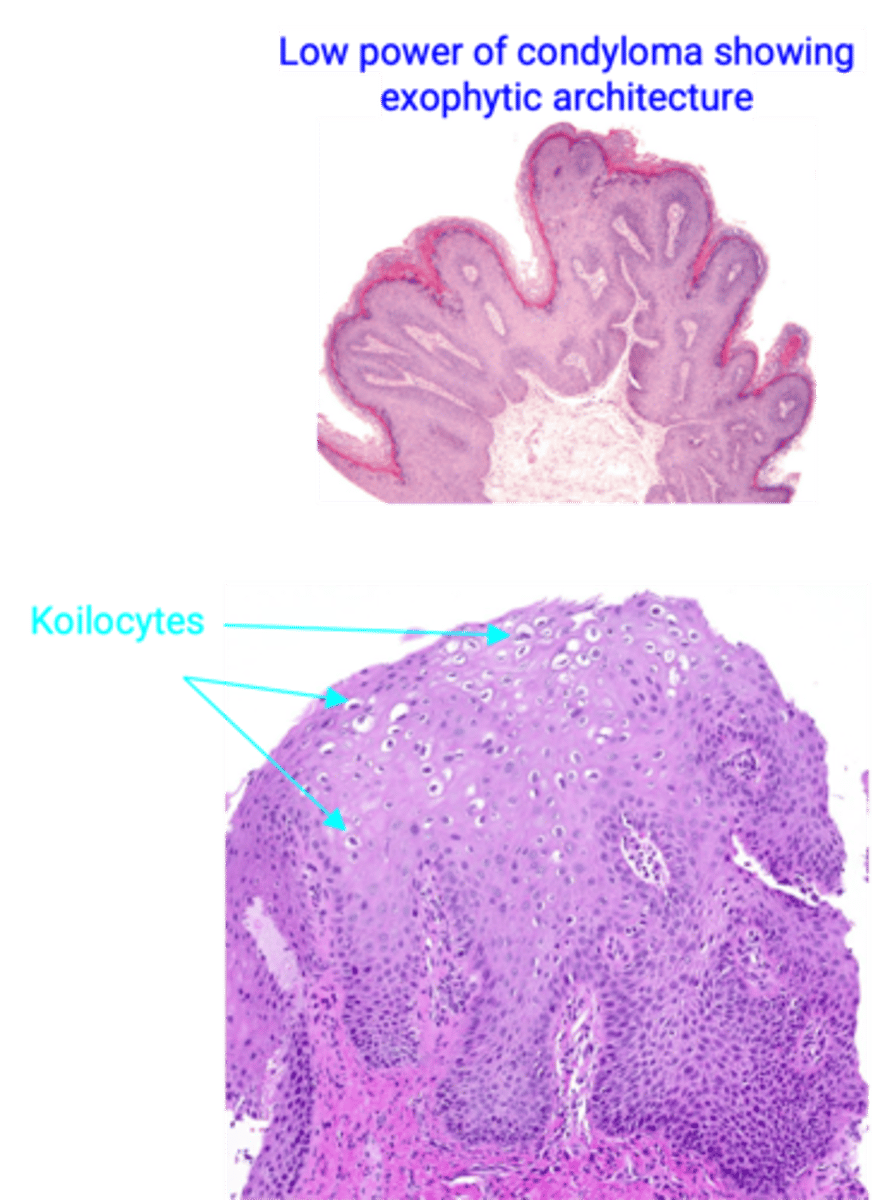
Condyloma Acuminatum (Genital Warts)
Define Vulvar Condition:
Warty neoplasm of vulvar skin, often large
-Hx/Path: Most commonly due to Low-risk HPV types 6 & 11
-Dx:
> Gross: exophytic lesion, “cauliflower-like”
> Histo: exophytic lesion covered with thickened squamous epithelium and viral cytopathic changes (koilocytic atypia or LSIL)
>> Koilocytes - squamous cells with enlarged, hyperchromatic, wrinkled nuclei with perinuclear halos
-Prog: Low risk of carcinoma
HPV-Related Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Define Vulvar Condition:
Carcinoma arising from the vulvar epithelium
-Hx: RARE
> HPV exposure
> Multiple Sexual Partners
> Early Intercourse
> Women of Reproductive age
-Path: Due to high-risk HPV (type 16)
> Arises from HPV-associated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), a dysplastic precursor lesion characterized by koilocytic change, disordered cellular maturation, nuclear atypia, and increased mitotic activity
-Sx/PE: Leukoplakia
-Dx: Biopsy = nests and sheets of pleomorphic squamous cells +/- keratinization
HPV-Independent Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Define Vulvar Condition:
Carcinoma arising from the vulvar epithelium
-Hx: RARE
> Elderly Women (> 70)
-Path: Arises, most often, from long-standing lichen sclerosus
> Chronic Inflammation & Irritation --> Carcinoma
> Precursor lesion is differentiated vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (dVIN) - can be seen adjacent -Sx/PE: Leukoplakia
-Dx: Biopsy = nests and sheets of pleomorphic squamous cells +/- keratinization
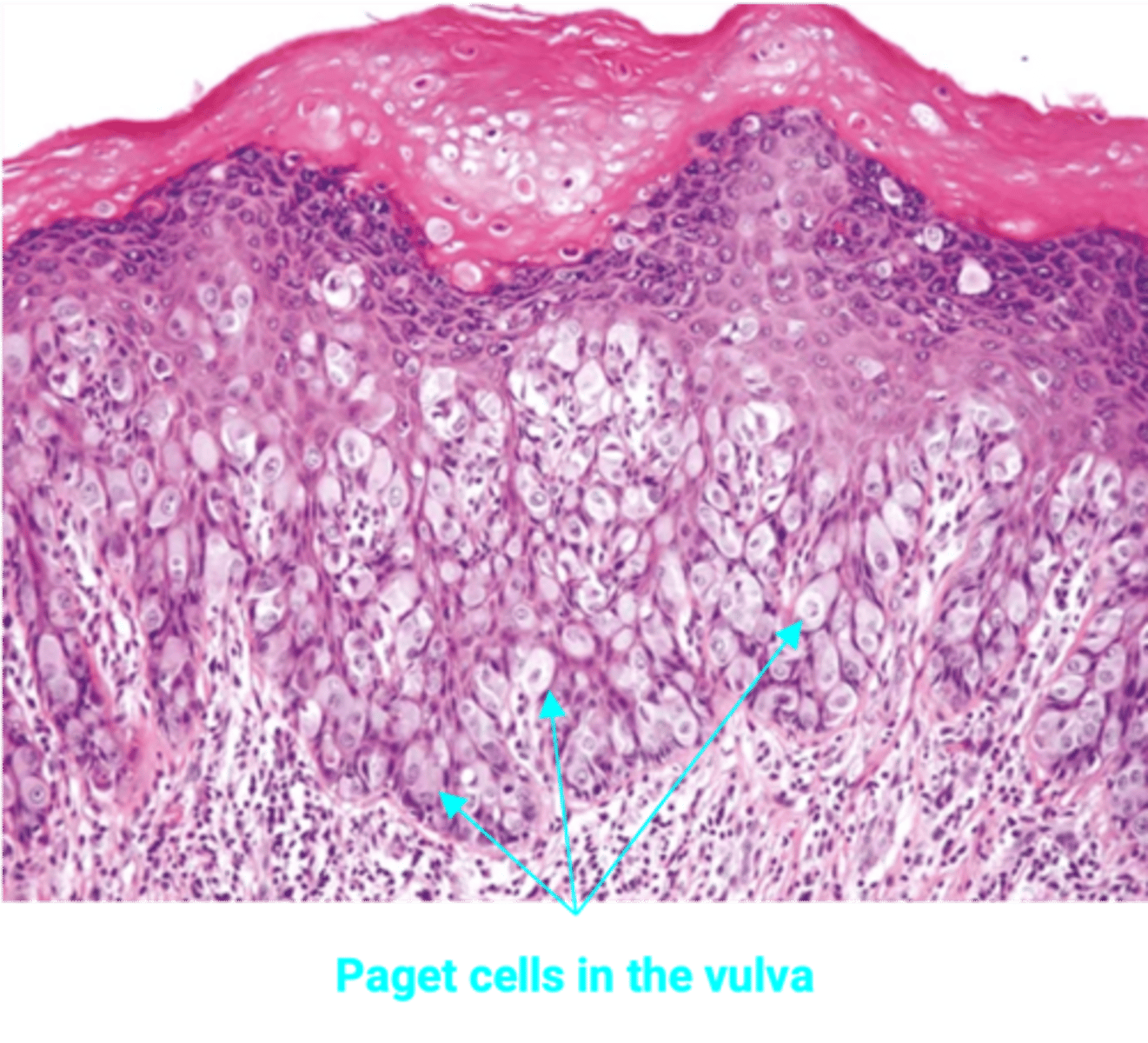
Extramammary Paget Disease
Define Vulvar Condition:
Malignant epithelial cells in the epidermis of the vulva
-Path: Represents adenocarcinoma in situ, usually with NO underlying carcinoma
-Sx/PE: Erythematous, pruritic, ulcerated vulvar skin
-Dx:
> Biopsy = Paget cells: enlarged, polygonal epithelial cells with abundant pale cytoplasm, large nuclei; frequently has intracytoplasmic mucin (clusters and single pale vacuolated cells/mucin in the epidermis)
> Markers
>> Paget = PAS+ (mucin), Cytokeratin+ (Epithelial), S-100-
>> Melanoma = PAS-, Keratin-, S-100+