CHEM 262 FINAL
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:57 PM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
1
New cards
Melting point
the point where the solid is in equilibrium with the liquid (precise)
2
New cards
melting range
span of temperatures where the solid just becomes a liquid to when it is fully liquid (narrow)
3
New cards
How do impurities affect the melting point?
they can lower the melting point and broaden the melting range
4
New cards
What does the critical point refer to?
It's where the boundary between the liquid and gas disappears
5
New cards
What does the triple point refer to?
Refers to the point at which the compound will do all these things (sublimation, deposition, vaporization, condensation, melting, and freezing) at the same time.
6
New cards
What happens when a compound changes states (ex: from a solid to a liquid)?
It breaks the IMF (dipole dipole, H bonding, and London Dispersion)
7
New cards
What is the eutectic composition?
Unique for a mixture of two compounds and is the lowest possible melting point for a mixture. It's a sharp melting point
8
New cards
Will impure compounds have higher melting points than the pure compound and the eutectic composition?
Impure compounds have lower melting points than pure compounds and higher than eutectic composition
9
New cards
What is the purpose of a mixed melting point?
Since melting point is a characteristic of a compound, oftentimes it can be used to identify an unknown. However, many compounds have the same melting point, so by using a mixed melting point, we can ascertain the identity of unknown compounds.
10
New cards
Orientation melting point
An approximation of the melting point
11
New cards
Sublimation
Solid to a vapor
12
New cards
Why is recrystallization done for a compound that is solid at room temperature?
It's a method of purifying the compound (sharp melting point)
13
New cards
How is solubility of a compound affected with increasing temperature?
Solubility increases
14
New cards
How is solubility of a compound affected as the solution cools down?
Solubility decreases, leading to crystals
15
New cards
How do you choose a solvent to dissolve a compound in?
Like dissolves like. The boiling point of the solvent also has to be lower than the melting point of the compound that is being crystallized
16
New cards
When does the compound oil out?
When the boiling point of the solvent is greater than the melting point of the compound since the compound is insoluble above the melting point in the solvent
17
New cards
For insoluble impurities, what method would need to be used?
Gravity filtration?
18
New cards
How to remove colored impurities?
Activated carbon is used
19
New cards
What happens if a lot of activated carbon (charcoal) is used?
It would remove a lot of the pure product
20
New cards
What type of filter paper is used for filtration of insoluble impurities?
Fluted filter paper has a higher surface area, which maximizes the filtration
21
New cards
How can crystallization be induced?
By scratching
22
New cards
What is a Büchner funnel used for?
To recover crystals
23
New cards
% recovery formula
(mass of final/mass of initial) x 100%
24
New cards
What is distillation used for?
Purifying a compound
25
New cards
Does being a volatile liquid affect boiling points and how?
Being a volatile liquid lowers the boiling point, causing higher vapor pressures
26
New cards
Materials used for distillation: pot
where the liquid is boiled
27
New cards
Materials used for distillation: water-cooled condenser
Liquefies the vapor produced by boiling
28
New cards
Materials used for distillation: receiver
Collects the liquefied compound called the distillate
29
New cards
When does evaporation occur in relation to the boiling point?
It occurs below the boiling point
30
New cards
When is conversion of a liquid to vapor faster?
It's faster with boiling than just evaporation
31
New cards
What does increasing the heating do at the boiling point?
Doesn't change the temperature, only the rate at which the vapor is produced increases
32
New cards
Raoult's law
Ptotal = Pa + Pb (ideal mixture)
Pa: xaPa (where xa is mol fraction)
Pa: xaPa (where xa is mol fraction)
33
New cards
When do two liquids form a homogenous mixture?
When they are completely miscible
34
New cards
In the vapor form of a homogenous mixture, how is the composition different from the liquid composition?
The vapor has more of the volatile component
35
New cards
Where is the boiling point of a miscible mixture in comparison to pure liquids?
Between the boiling points of the pure liquids
36
New cards
When would you use simple distillation over fractional distillation?
If one component is significantly more volatile than the other and is a single vaporization step
37
New cards
When would you use fractional distillation over simple distillation?
Used if the boiling points have a difference greater than 40C and involves many simple distillations via a fractionating column
38
New cards
How do boiling chips work?
They agitate the liquid, helping the air expand, creating the bubbles
39
New cards
Why can't boiling chips be reused?
The pores inside the boiling chips become filled with liquid on cooling
40
New cards
What is done in solvent extraction?
Separation technique that dissolves one or more compounds in a solvent. The solution is called an extract
41
New cards
Why is solvent extraction used?
To remove soluble materials from insoluble ones (they have to be immiscible)
42
New cards
How can you tell whether the upper layer is aqueous or organic solvent?
The organic solvent is more dense, so the upper layer is aqueous
43
New cards
Washing technique
The impurities are removed in a second solvent, leaving the desired compound in the first
44
New cards
What is used for larger scale extractions?
Separatory funnel
45
New cards
What is an emulsion?
Fine dispersion of small droplets of one liquid in another where it is not soluble/miscible
46
New cards
When can an emulsion occur?
During an extraction when the solvents are not miscible
47
New cards
What does emulsion look like?
Small droplets of one solvent in the other, but they can often be mistaken for a third layer since they are opaque/cloudy
48
New cards
Ways to get rid of the emulsion "layer"
gentle swirling, addition of brine, addition of some ethanol, addition of more solvent, filtration
49
New cards
What is brine?
saturated solution of NaCl in water.
50
New cards
What is salting out?
Addition of NaCl
51
New cards
What is salting out used for?
When organic compounds are polar enough to be soluble in water, they become hard to extract. By adding NaCl (water soluble), it reduces the solubility of the organic compound in water and forces the organic compound to dissolve in the organic solvent
52
New cards
What can acidic compounds be converted into?
Acidic compounds (carboxylic acids and phenols) can be converted into the conjugate bases. Carboxylic acids have lower pKa than phenols (more acidic)
53
New cards
Converting carboxylic acids into carboxylate
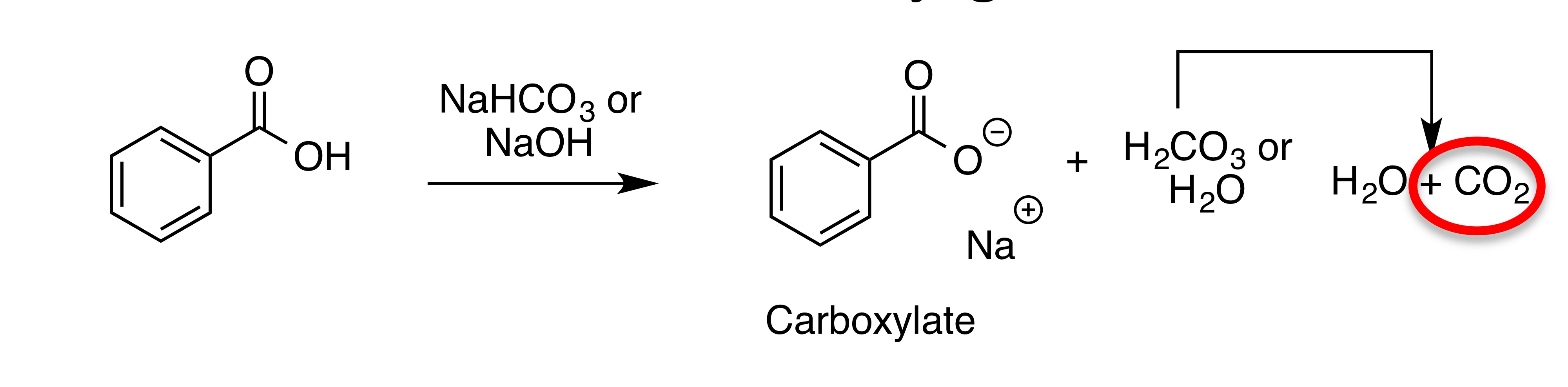
54
New cards
Converting phenol into phenoxide
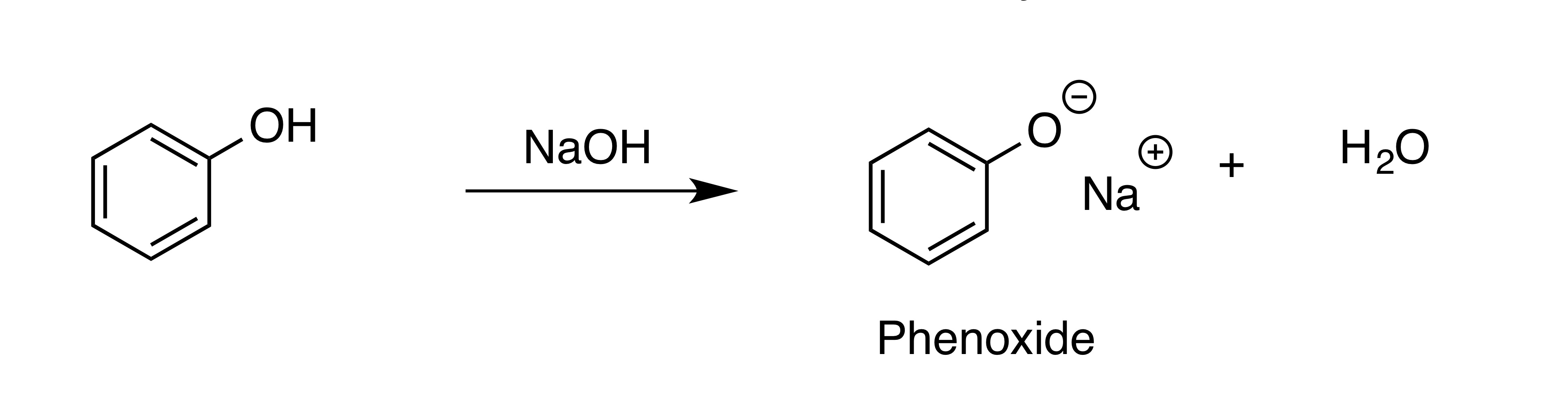
55
New cards
Converting amines to the salts, the conjugate acids
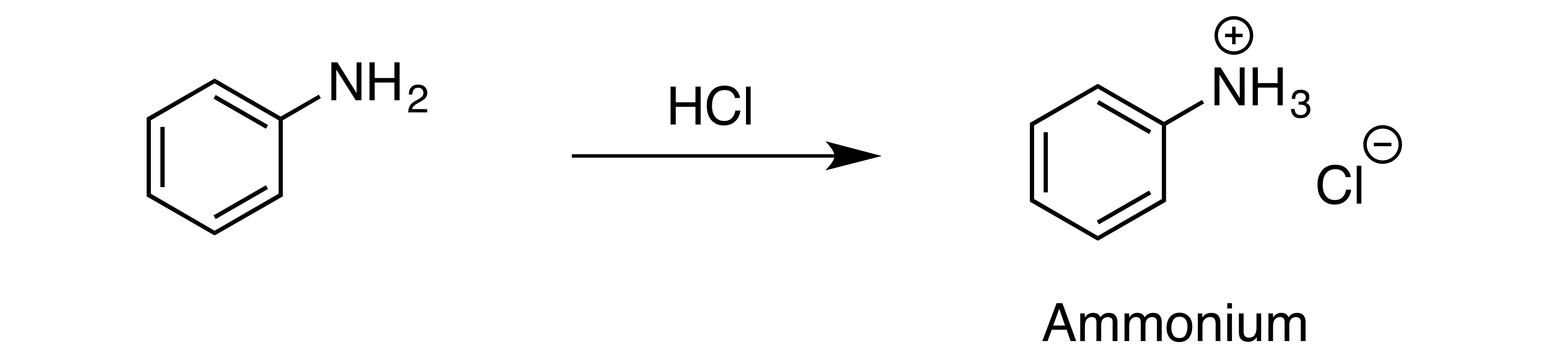
56
New cards
What are common drying agents?
Na2SO4, MgSO4, CaCl2
57
New cards
What is the purpose of chromatography?
separating compounds
58
New cards
What is chromatography?
A method of separating compounds that involves equilibrium of the compound/compounds between two phases
59
New cards
What are the two phases in chromatography?
Stationary and mobile phases
60
New cards
In column chromatography, what is the stationary phase?
A solid or contains another liquid
61
New cards
In column chromatography, what is the mobile phase?
Liquid or gas
62
New cards
How does the compound move in column chromatography?
It's carried by the liquid or gas (mobile phase) over the stationary phase
63
New cards
How can you separate compounds in a mixture with column chromatography?
In a mixture, two compounds can interact different with each phase and compounds that interact more strongly with the mobile phase end up moving faster than those that interact strongly with the stationary phase
64
New cards
What is the solid adsorbent used in column chromatography?
usually silica gel (SiO2.xH2O) or alumina
65
New cards
What is the organic solvent used as a mobile phase in column chromatography known as?
Eluent
66
New cards
Column chromatography: Dry packing method
glass wool/cotton to plug the bottom, then sand to provide a level base on top, dry adsorbent, sample-adsorbent powder (ferrocene/acetylferrocene), dry adsorbent (silica gel). the eluting solvent is poured ontop
67
New cards
Column chromatography: slurry packing/wet packing method
glass wool/cotton to plug the bottom, sand to provide a level base, solvent, slurry of adsorbent in the eluent
68
New cards
How do the compounds move in column chromatography?
As bands
69
New cards
What is the stationary phase in GC?
non-volatile liquid
70
New cards
What is a non-volatile liquid?
a polymer with a high boiling point
71
New cards
What is the mobile phase in GC?
Inert gas/carrier gas
72
New cards
What is used in the inert gas/carrier gas?
Helium or Nitrogen
73
New cards
Which compounds are retained longer in the GC?
Compounds that interact more strongly with the stationary phase
74
New cards
What is the relationship between retention time and interaction with the stationary phase?
Longer retention time, more stronger interaction with the stationary phase
75
New cards
What can affect retention time?
Structure of the compounds, type of stationary phase, column temperature, length of the column, rate of flow of carrier gas
76
New cards
How to determine area under peaks: Triangulation method
area = h x w1/2
h=height of peak
w1/2 = width at half height of peak
h=height of peak
w1/2 = width at half height of peak
77
New cards
% of compound A
(Area of compound a/ sum of all areas) x100
78
New cards
What can be used to measure column efficiency?
Number of theoretical plates
79
New cards
What is the number of theoretical plates? (formula)
N = 16 (tR/w)^2
where tR is equal to the height of the peak and w is the width of the peak
where tR is equal to the height of the peak and w is the width of the peak
80
New cards
What is resolution? (Definition)
separation between the two peaks
81
New cards
What is resolution? (formula)
R= (tB-tA) / (Wa + Wb/2)
where tB is height of peak B and WB is the width of peak B
where tB is height of peak B and WB is the width of peak B
82
New cards
What is the stationary phase in TLC?
Adsorbent (silica gel/alumina) on a backing/sheet of plastic, glass, or aluminum
83
New cards
What is the mobile phase called in TLC?
The eluent/eluting solvent
84
New cards
Which compounds are retained longer on a TLC plate?
Compounds that interact more strongly with the stationary phase are retained longer
85
New cards
What is TLC used for?
Identifying compounds, determining how many compounds are in a mixture, monitoring course of reactions, finding suitable solvents for column chromatography, separating and isolating compounds
86
New cards
What are the steps in performing TLC?
Spotting a TLC plate, developing a TLC plate, visualizing the spots on a TLC plate, calculating Rf values
87
New cards
How to calculate Rf (retention factor)
Distance moved by compound/distance moved by solvent front
88
New cards
Which types of compounds have higher Rf vaues?
Less polar compounds have higher Rf values (interact less with the stationary phase)
89
New cards
Which compounds will have a greater distance moved by the compound?
The least polar since they interact less with the stationary phase)
90
New cards
What type of dihalides are produced when alkenes react rapidly with Br2 and Cl2?
Vicinal dihalides
91
New cards
How do alkenes react with I2 and F2?
I2 generally reacts sluggishly and F2 reacts explosively
92
New cards
What type of reaction happens when alkenes are brominated?
Electrophilic addition reaction
93
New cards
How to calculate the number of stereoisomers
2^n
where n = number of chiral centers
where n = number of chiral centers
94
New cards
What is the chemical structure of PBP (pyridinium tribromide or pyridinium bromine perbromide)?
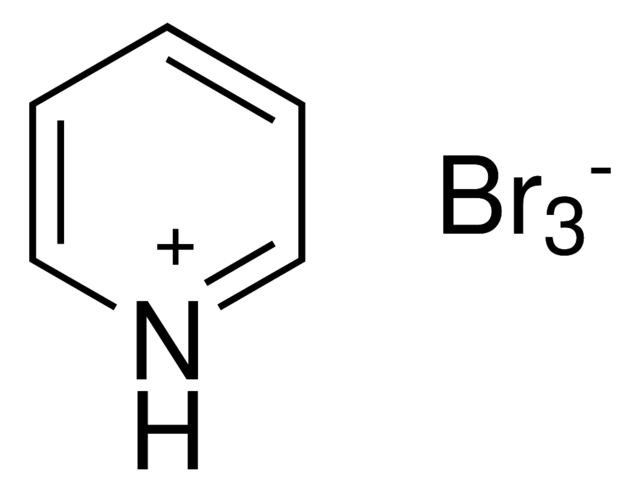
95
New cards
How can you test the presence of alkyl Cl or Br atoms?
Using an ethanolic solution of AgNO3 (silver nitrate)
96
New cards
From left to right on the infrared spectroscopy, how does frequency and wavelength change?
Frequency increases and shorter wavelengths
97
New cards
From left to right on IR spectroscopy, what are the waves?
Radiowaves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays
98
New cards
What is the range for IR radiation?
400-4000 cm-1
99
New cards
What is the output for IR?
A graph with wavenumber (v) in cm-1 in the x-axis and % transmittance on the y-axis
100
New cards
What are specific adsorption bands diagnostic of?
Specific functional groups, giving structural information