ZOOLOGY LAB FINAL EXAM
5.0(8)
5.0(8)
Card Sorting
1/476
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
477 Terms
1
New cards
Anatomical Position
Standard reference point in medicine that is used to increase accuracy
2
New cards
Anatomical Position
To stand erect, facing forward, arms at the side, palms and toes directed forward
3
New cards
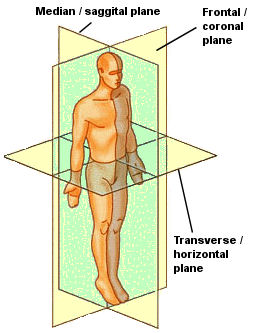
Sagittal Plane
Cardinal Plane that divides the body into left and right halves
4
New cards
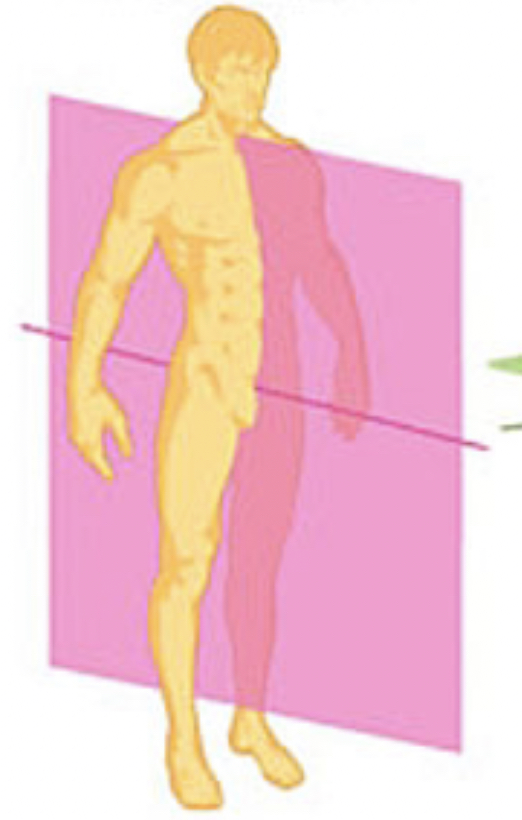
Frontal or Coronal Plane
Cardinal Plane that divides the body intro front and back halves
5
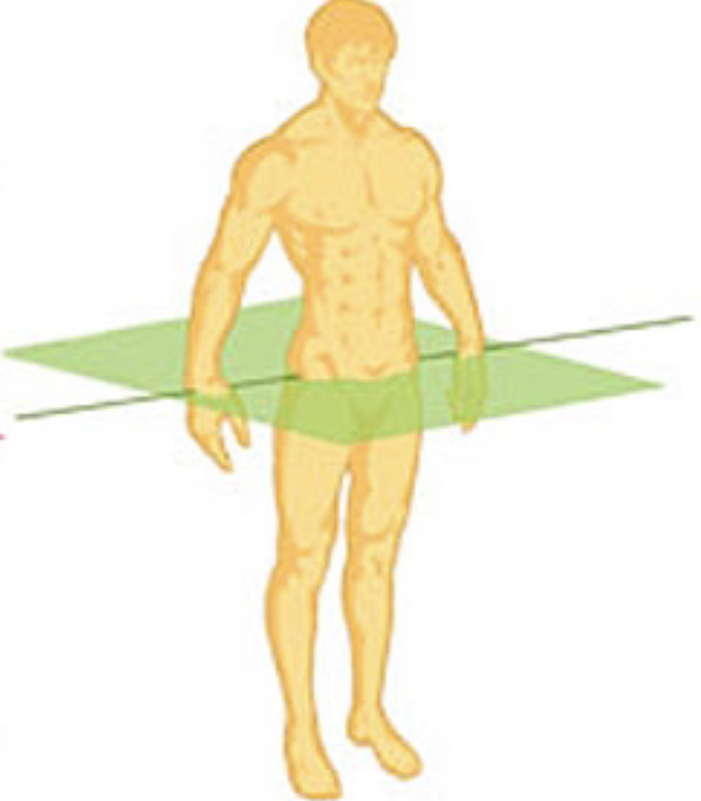
New cards
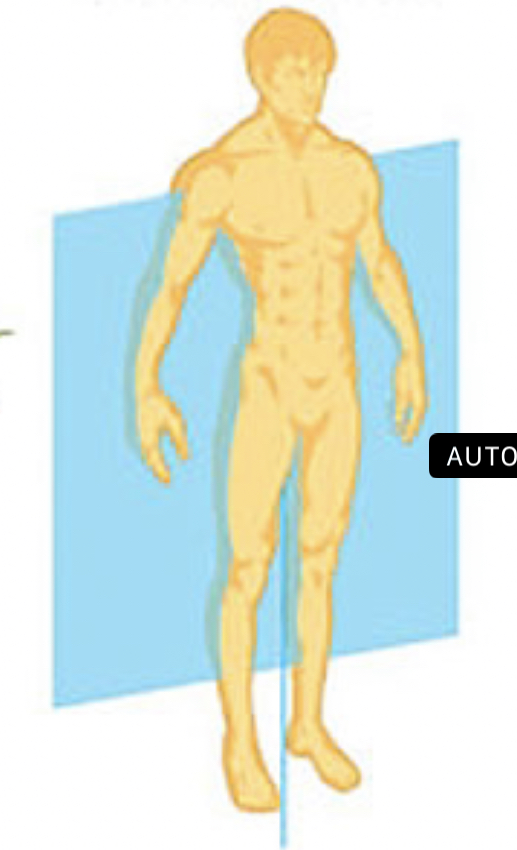
Transverse plane
Cardinal plane that divides the body into upper and lower halves
6
New cards
Claudial or inferior
Located in the tail of the body
7
New cards
Cranial or cephalic or superior
Located at the head
8
New cards
Pelvic
Located at the hips
9
New cards
Oblique Section
Cuts made diagonally
10
New cards
Pectoral
Located at the chest
11
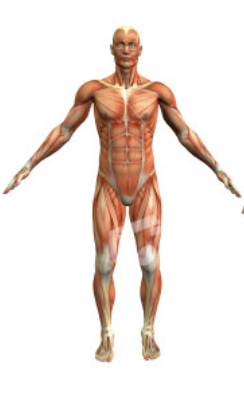
New cards
Anterior
Frontal or near the front region of the body
12
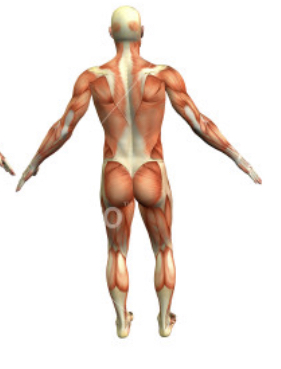
New cards
Posterior
hind or near the hind region of the body
13
New cards
Dorsal
Toward the back or near the back region of the body
14
New cards
Ventral
toward the belly or near the belly region of the body
15
New cards
Lateral
Located at the side or near the side relative to the center of the body
16
New cards
Medial or central
located or towards the middle part of the body relative to its center
17
New cards
Proximal
near the origin or point of attachment in the body
18
New cards
Distal
Far from the origin or point of attachment in the body
19
New cards
Superficial
Surface of the body
20
New cards
Deep
Within the body
21
New cards
Ipsilateral
On the same side
22
New cards
Contralateral
On opposite sides
23
New cards
Flexion
Movement of the body that refers to decreasing joint angle
24
New cards
Extension
Movement of the body that refers to Increasing joint angle
25
New cards
Abduction
Movement of the body that refers to Moving away from the midline
26
New cards
Adduction
Movement of the body that refers to moving toward the midline
27
New cards
Hyperflexion
Movement of the body that refers to flexion beyond normal range
28
New cards
Hyperextension
Movement of the body that refers to extension beyond normal range
29
New cards
Hyperabduction
Movement of the body that refers to Abduction past 180 degrees point
30
New cards
Hyperadduction
Movement of the body that refers to Adduction past 0 degree point
31
New cards
Circumduction
Movement in a conic fashion
32
New cards
Plantarflexion
Movement of the body that refers to increasing angle between foot and shank
33
New cards
Dorsiflexion
Movement of the body that refers to decreasing angle between foot and shank
34
New cards
Inversion
Movement of the body that refers to lifting the medial edge of foot
35
New cards
Eversion
Movement of the body that refers to lifting the lateral edge of foot
36
New cards
Median Rotation
Internal or inward rotation
37
New cards
Lateral Rotation
External or outward rotation
38
New cards
Midsagittal Plane
Sagittal plane that lies on the midline
39
New cards
Integumentary system
Set of organs that forms the external covering of the body and protects it from external environment
40
New cards
Integumentum
Latin word that means "to cover"
41
New cards
Skin
Main organ of the integumentary system
42
New cards
36 degrees celsius
Normal temperature of human body
43
New cards
presence of vocal sacs
size of the body
shape of snout or head
enlarge innermost digit
presence of dark spots in the neck or throat
size of the body
shape of snout or head
enlarge innermost digit
presence of dark spots in the neck or throat
Differences of male and female frogs
44
New cards
Rana vittigera
Scientific name of frog
45
New cards
Parts are similar to man
they are small, can be easily handles
they are readily available and cheaper
they have a well documented life cycle
they are small, can be easily handles
they are readily available and cheaper
they have a well documented life cycle
Reasons why frogs are used as representative sample in zoology
46
New cards
Rainy season
Breeding season of frogs
47
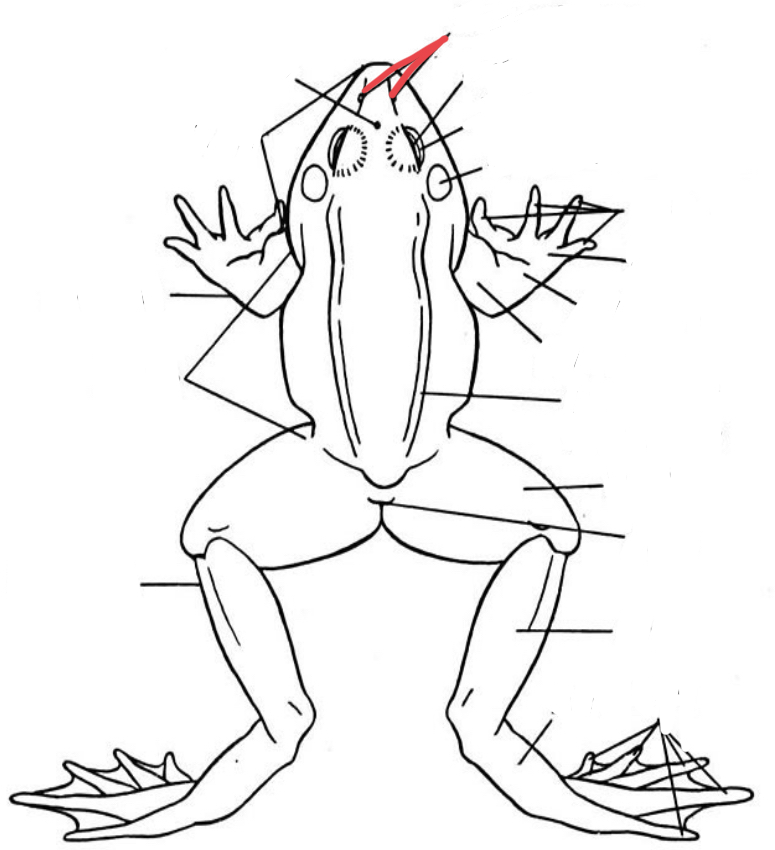
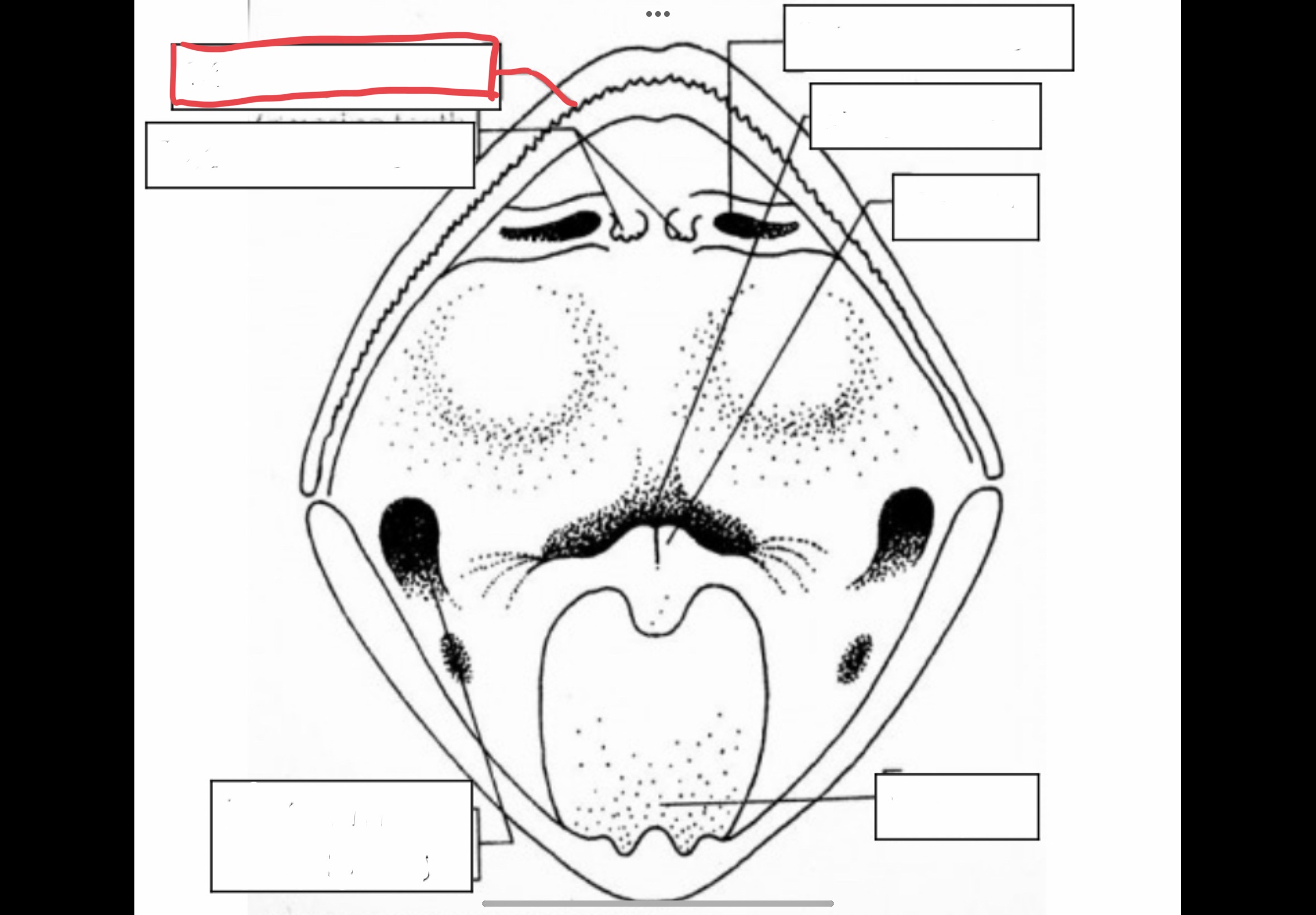
New cards
Snout
Most anterior border of the head of the frog
48
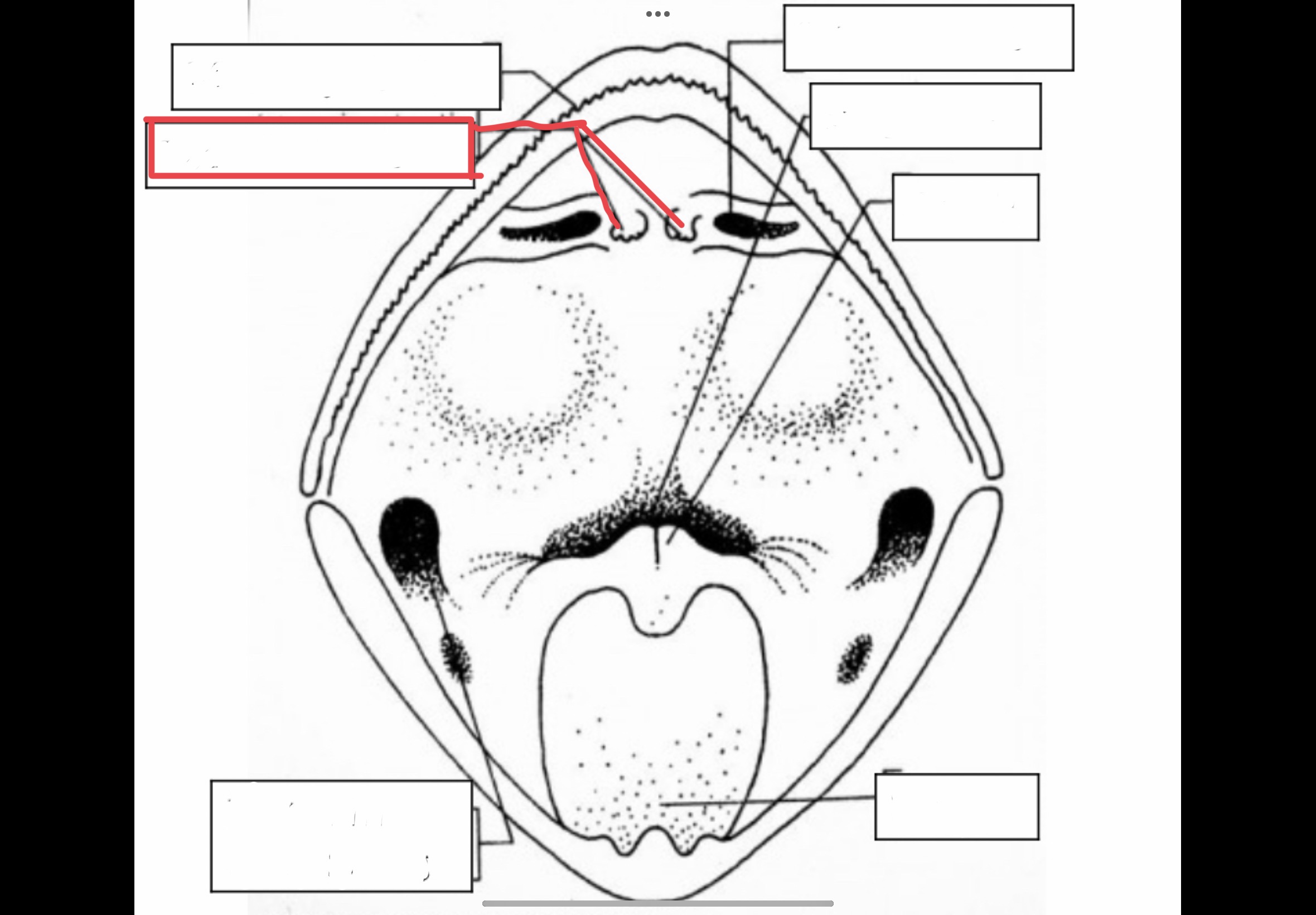
New cards
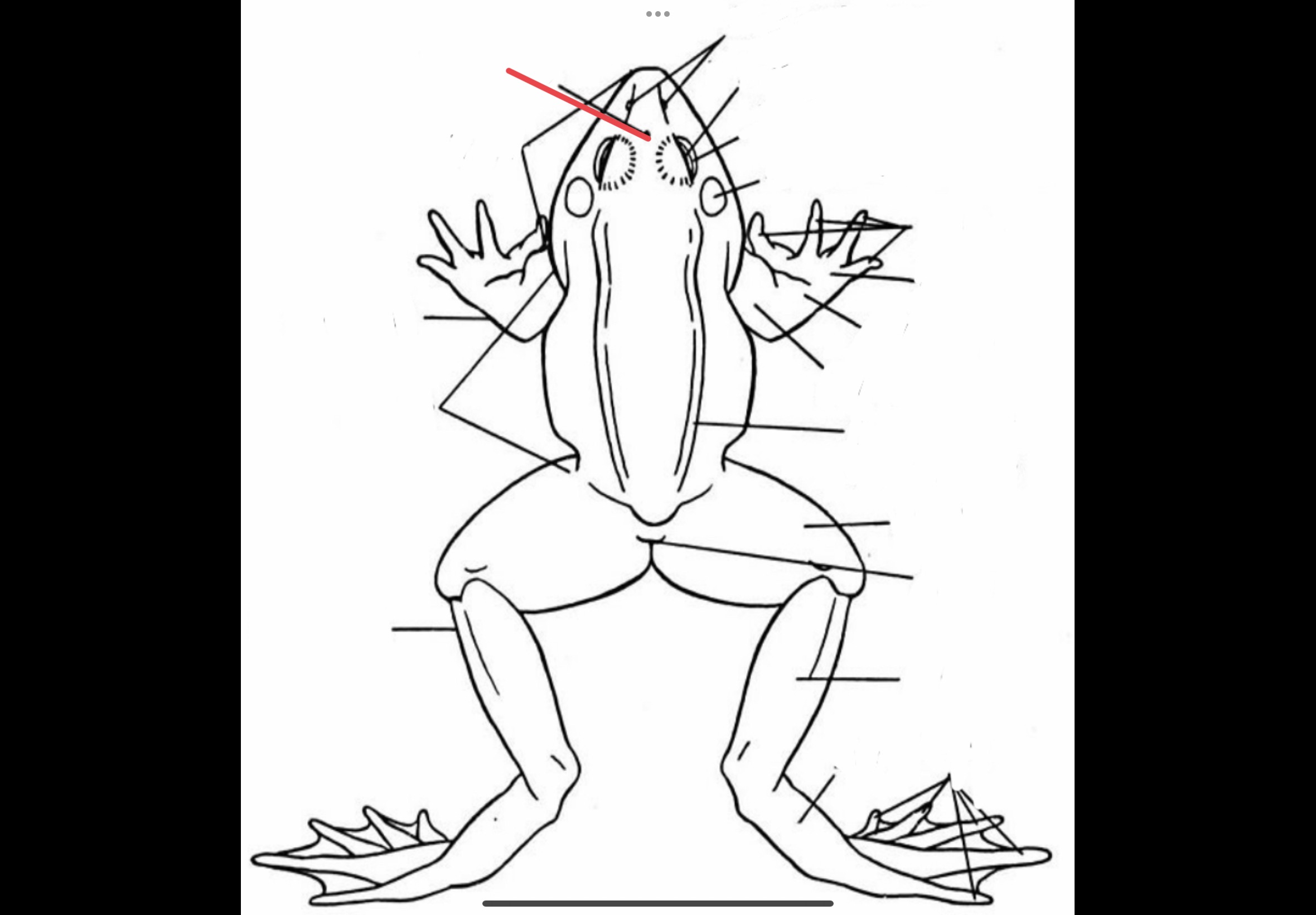
Browspot
Vestigial eye located between the eyeballs
49
New cards
Eyes
Bulging structures which consists of three eyelids
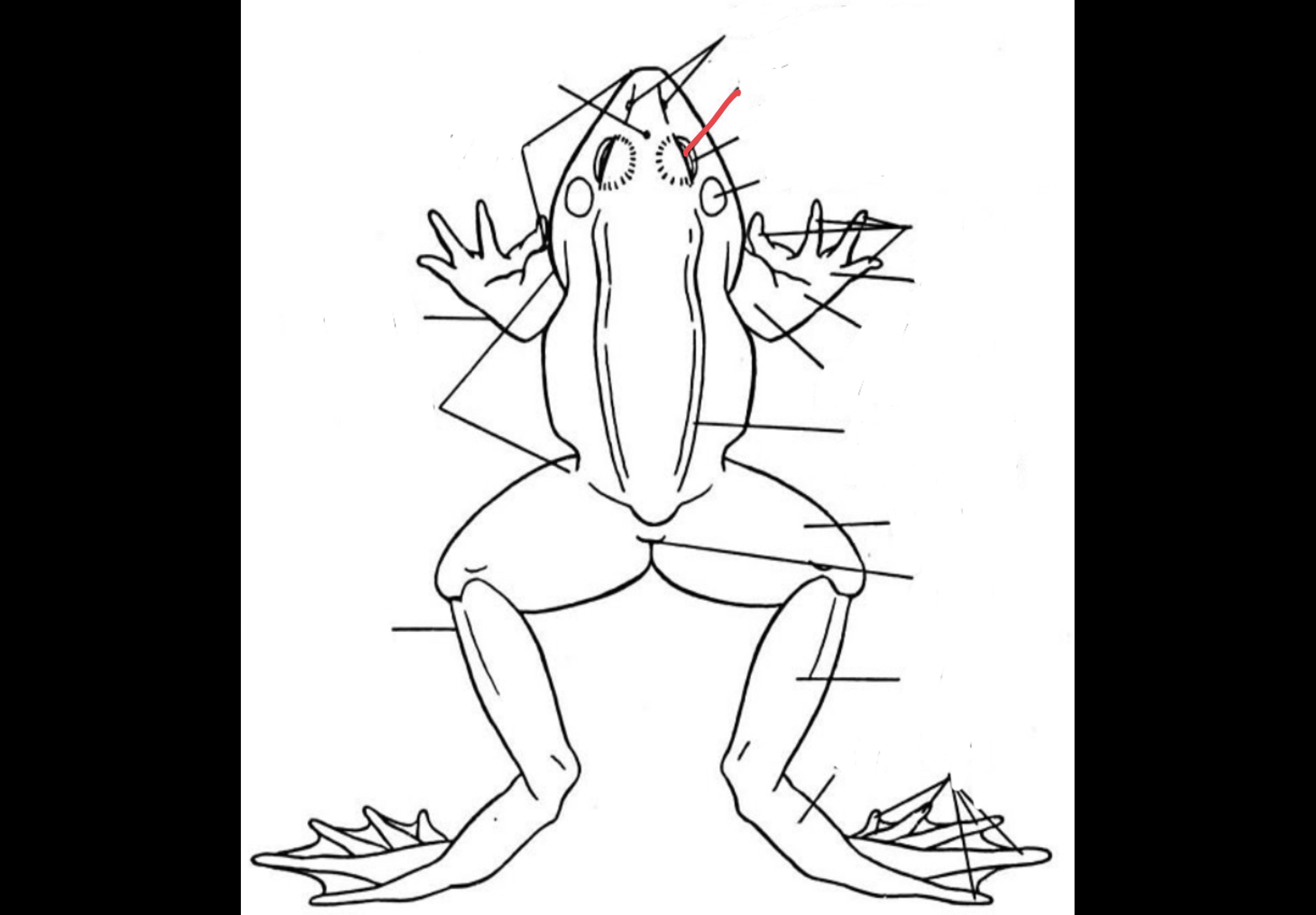
50
New cards
Nictitating membrane
Transparent structure that covers the eye to protect it and keep it moist
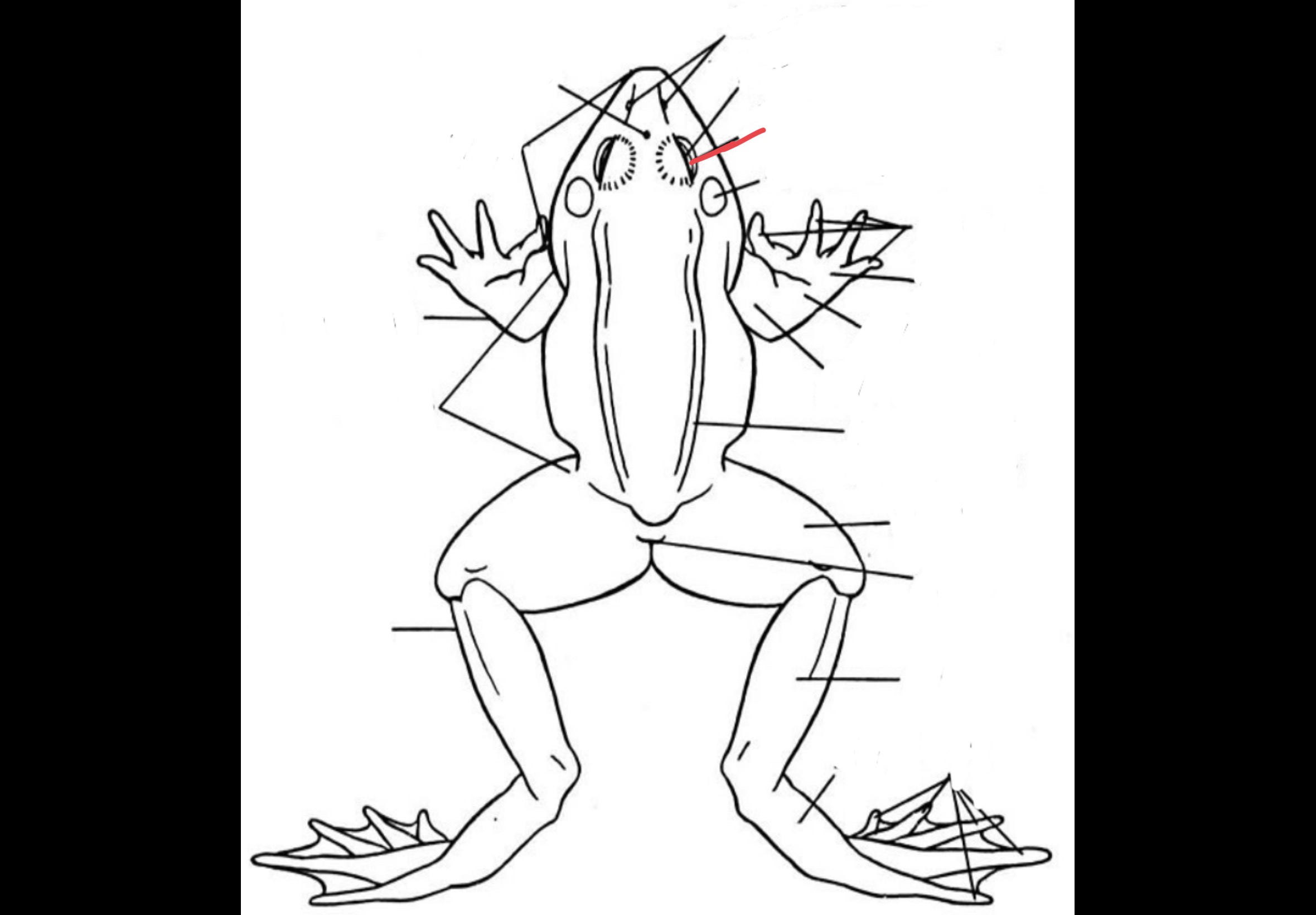
51
New cards
External Nares
Two openings which are anteriorly located that serves as an entry and exit way of air
52
New cards
Tympanic Membrane
Two flat and rounded structures located laterally behind the eyeballs that receives sound waves
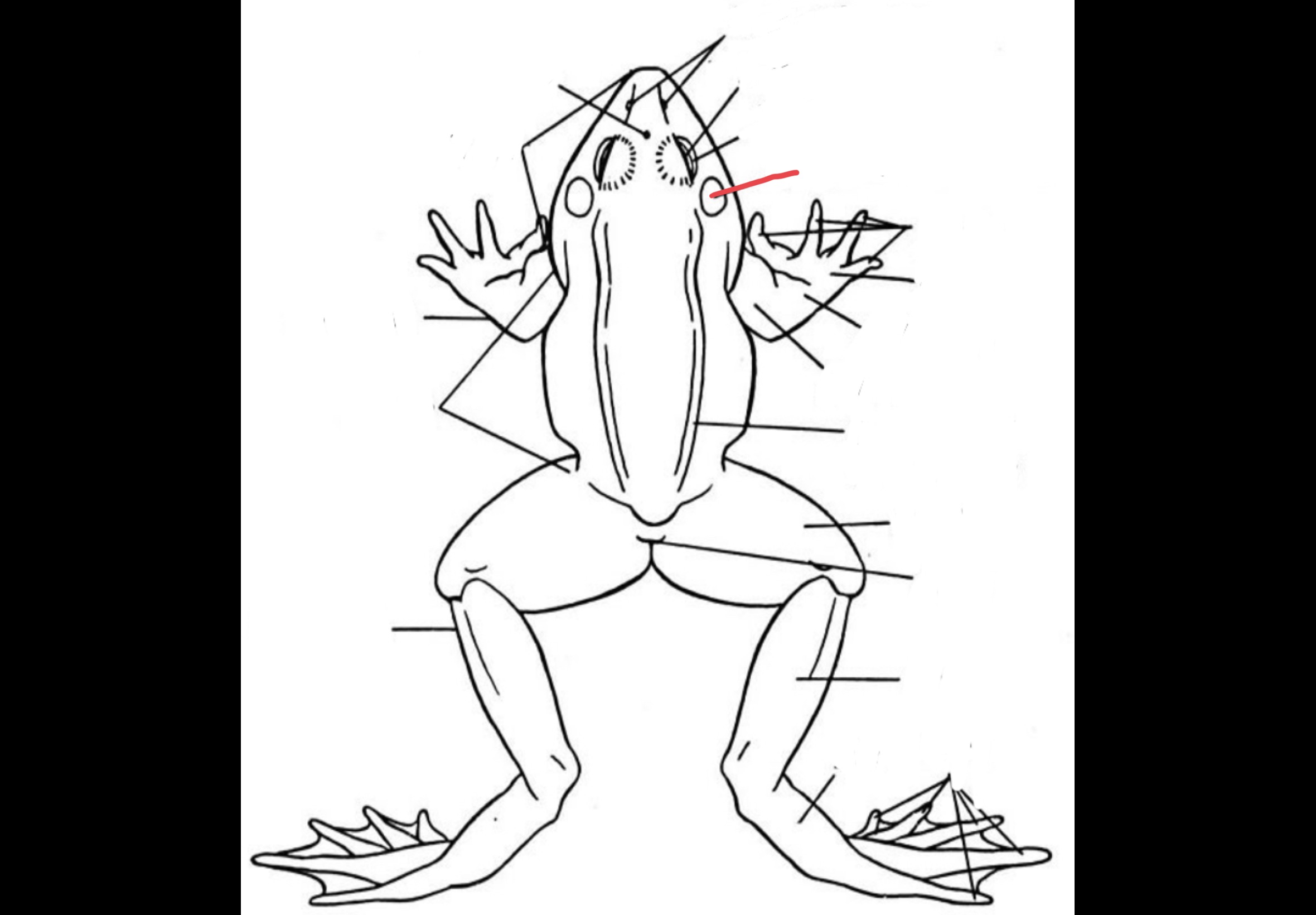
53
New cards
Trunk
main mass of the body
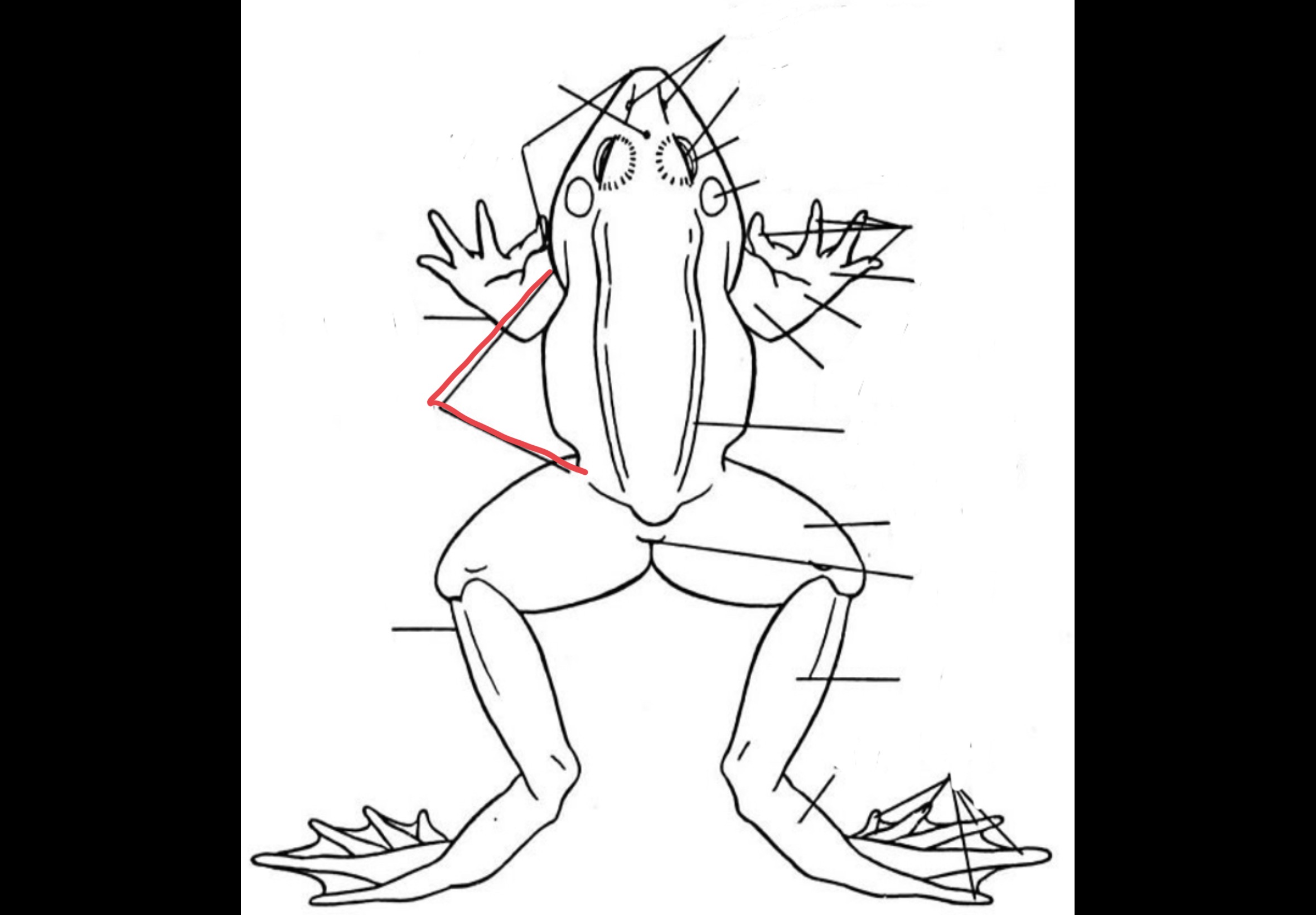
54
New cards
Forelimb
composed of the upper arm, lower arm, carpus, and manus
55
New cards
Mouth
Anterior opening of the frog's body
56
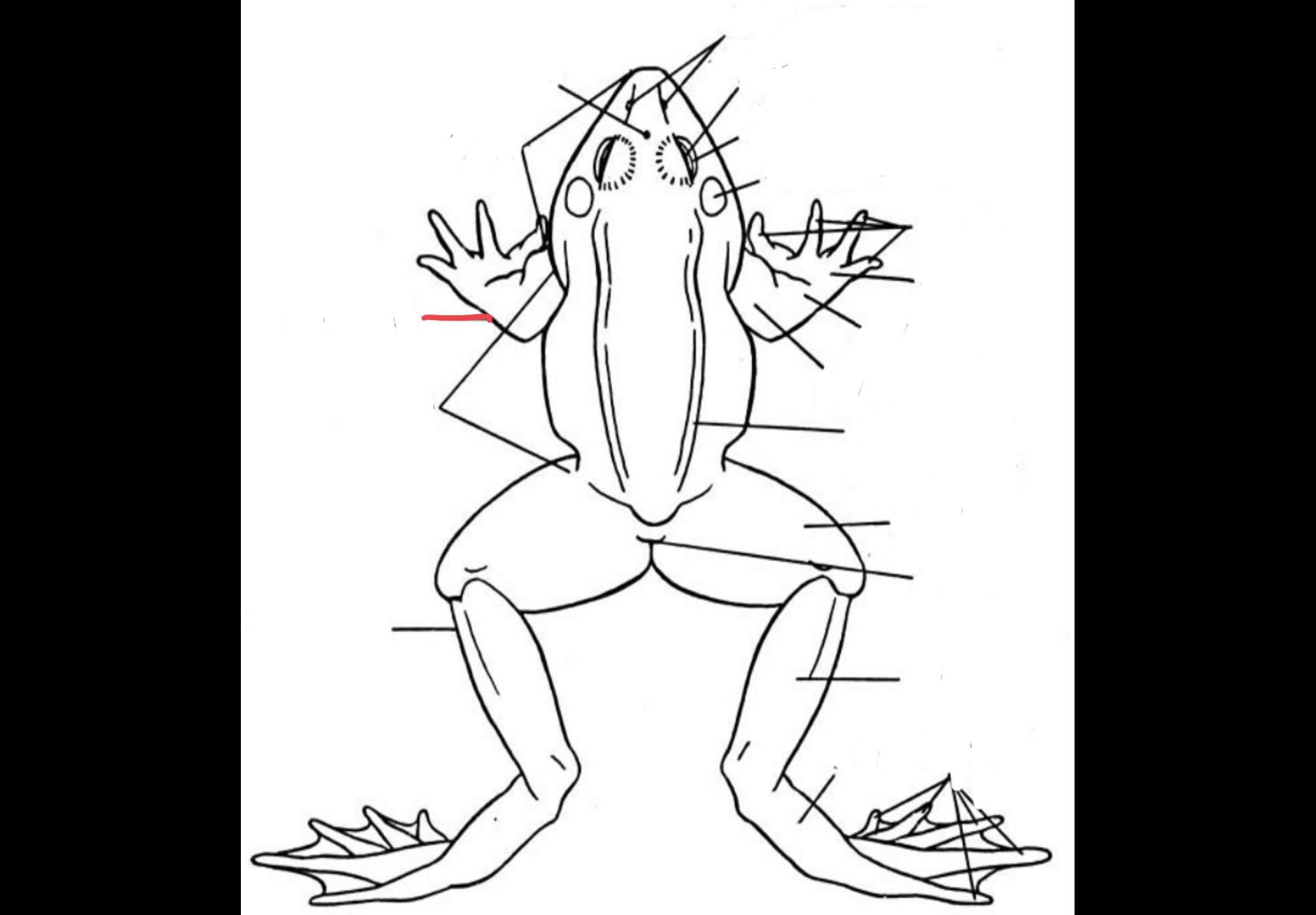
New cards
Hindlimb
Made up of the thigh, shanks, tarsus, and pes
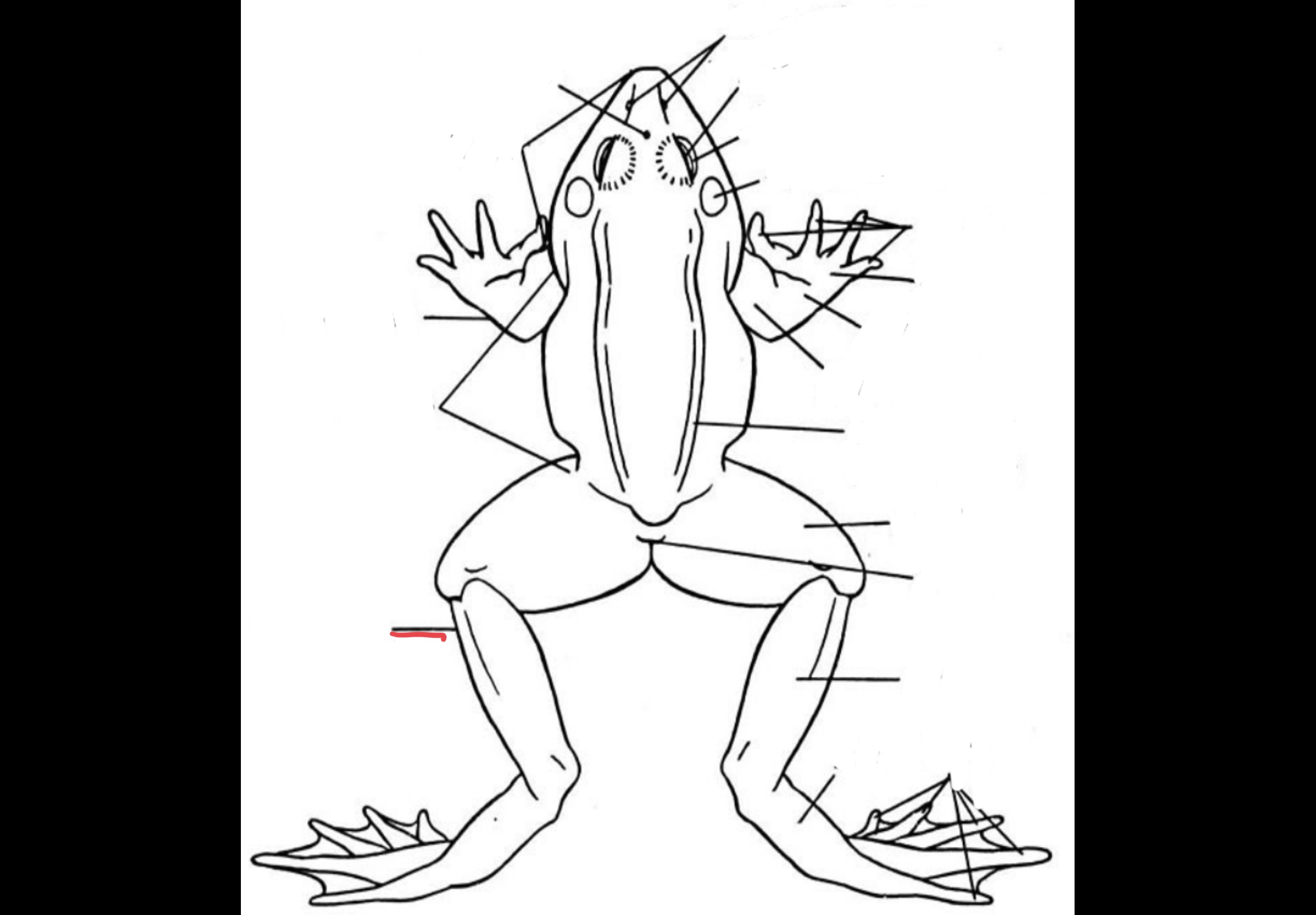
57
New cards
Pes
Feet of the frog
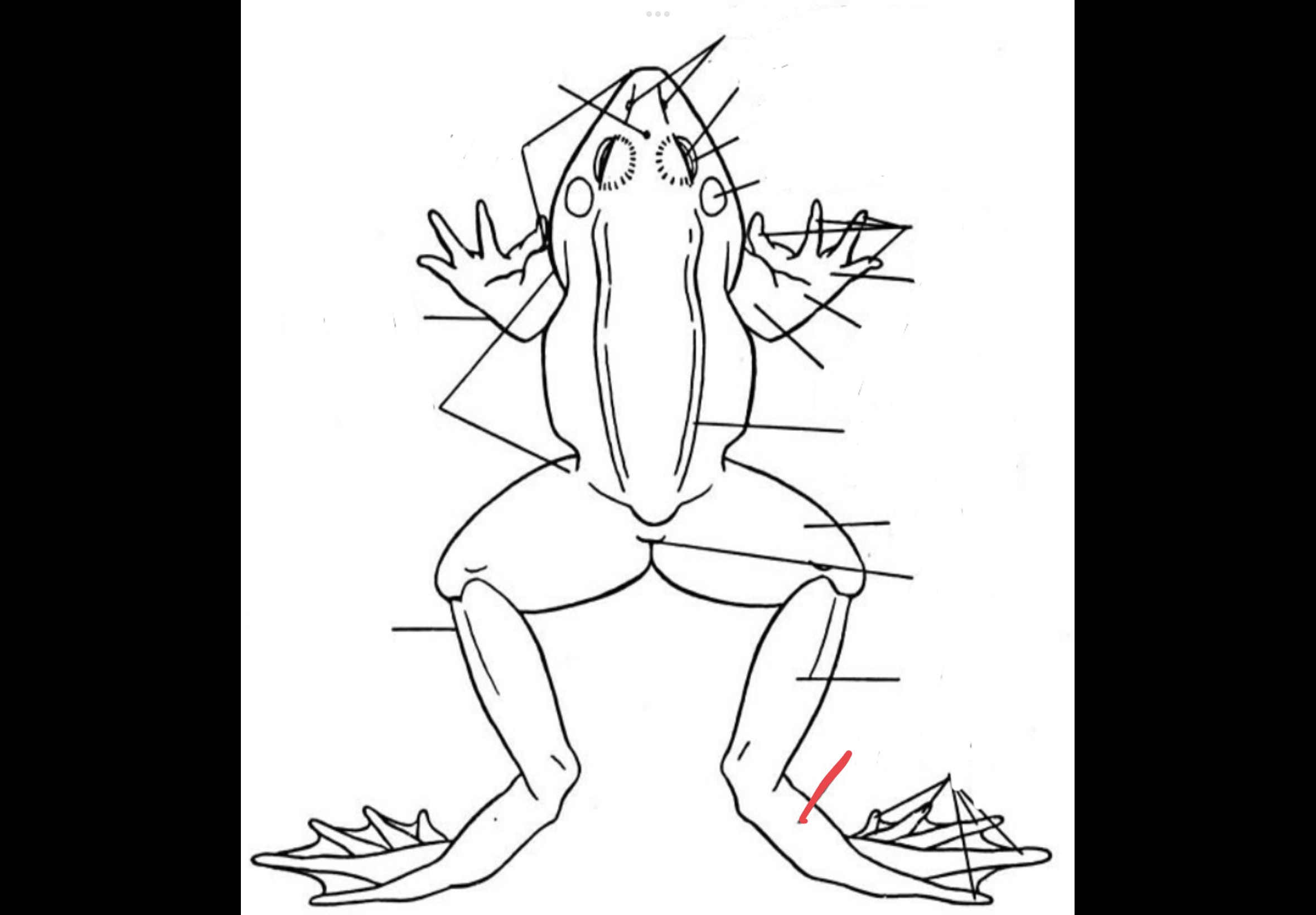
58
New cards
Tarsus
Ankle of the frog
59
New cards
Carpus
Wrist of the frog
60
New cards
Manus
Hand of the frog
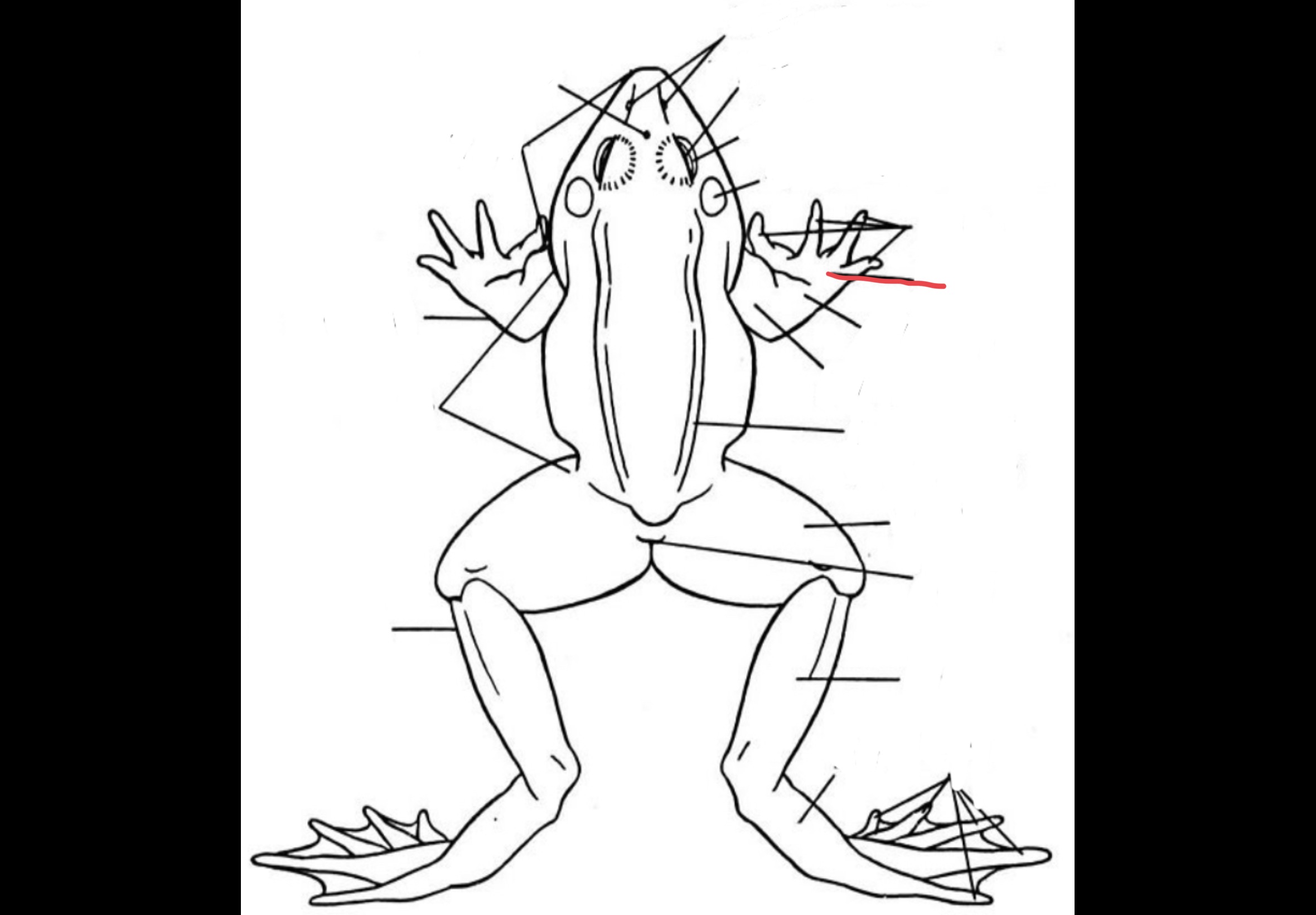
61
New cards
Digits
Fingers and toes of the frog
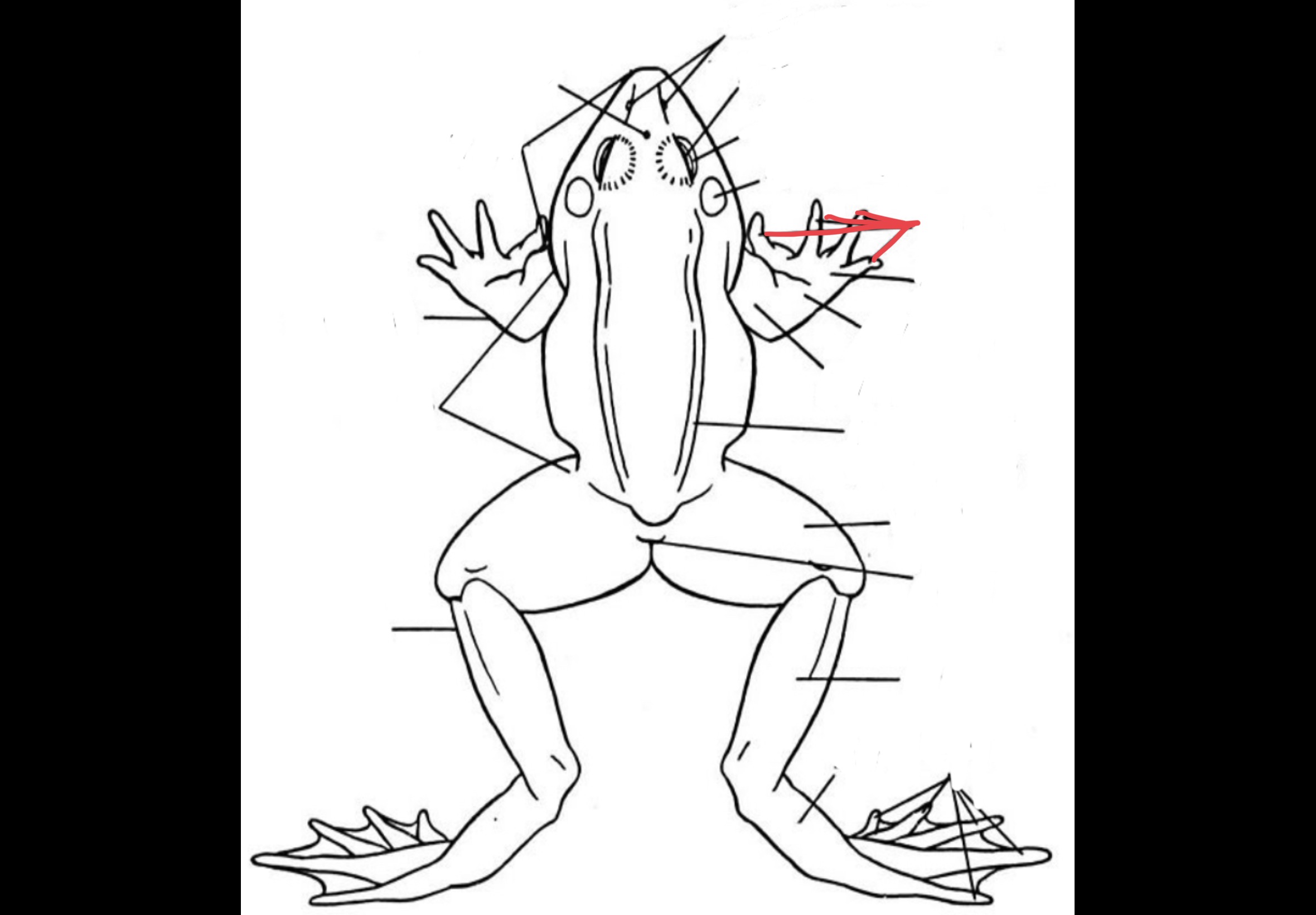
62
New cards
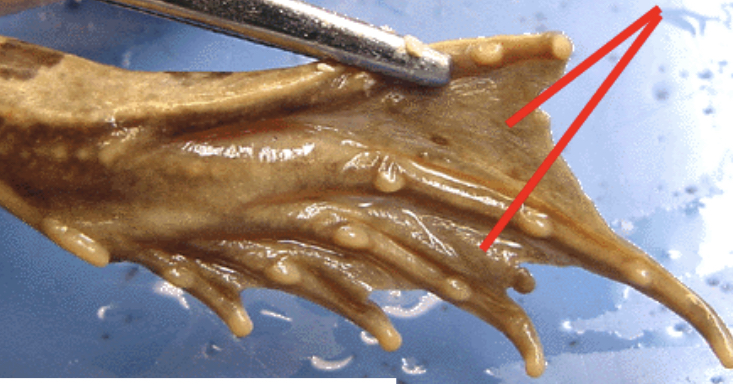
Web
Located in between the digits in the hindlimb which allows them to push themselves in the water for swimming
63
New cards
Esophagus
Tube that connects the mouth and the stomach
64
New cards
Glottis
opening from the mouth in the respiratory system, to the vocal cord or lungs
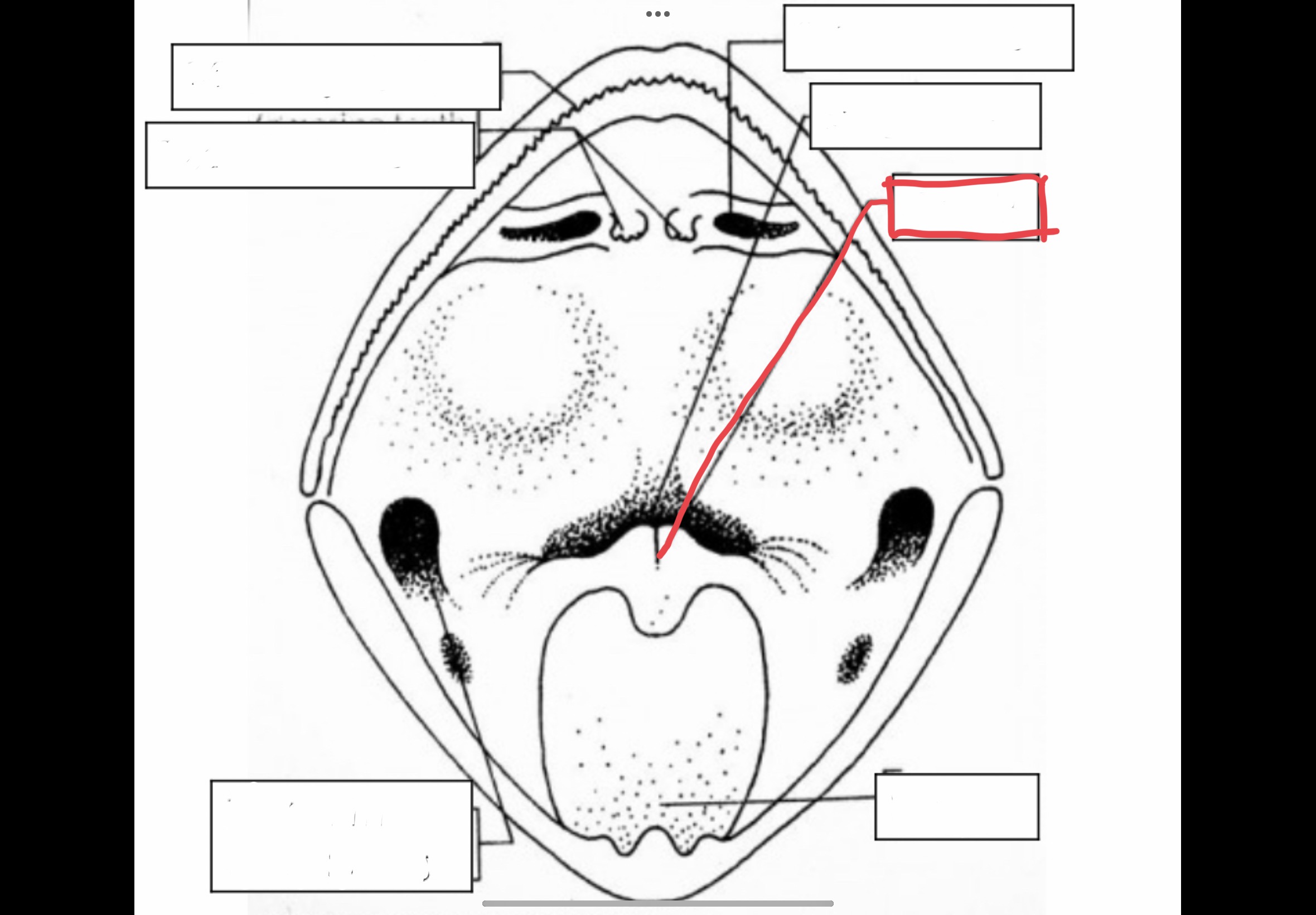
65
New cards
Tongue
Muscular structure attached tot he front of the mouth which can be extended
66
New cards
Maxillary Teeth
Sharp teeth in the maxillary that holds captured prey
67
New cards
Vomerine Teeth
Small projections in the top of a frog's mouth that holds captured prey
68
New cards
Eustachian Tube Opening
Mouth openings that lead to tubes that connect to the middle ear to equalize air pressure
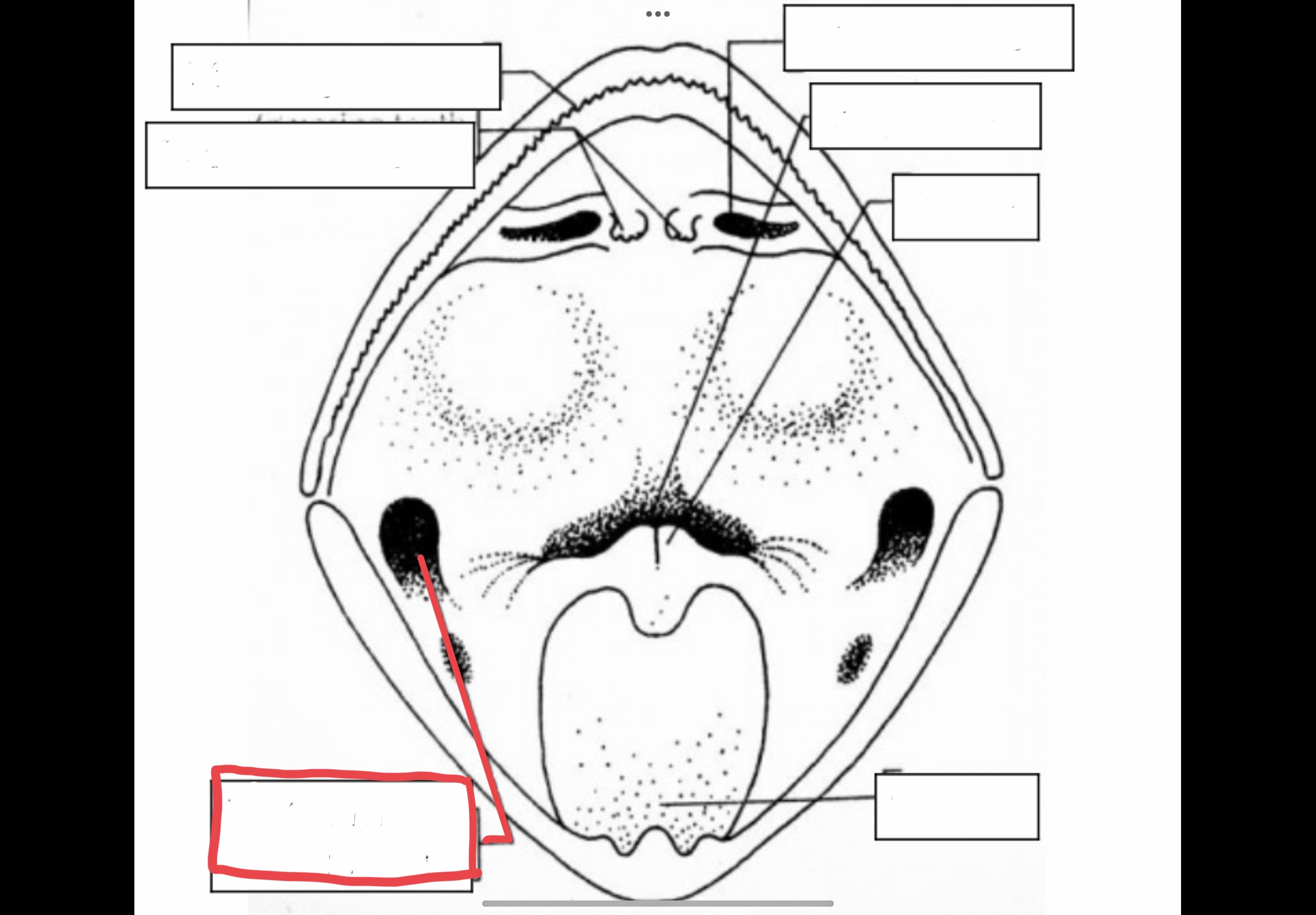
69
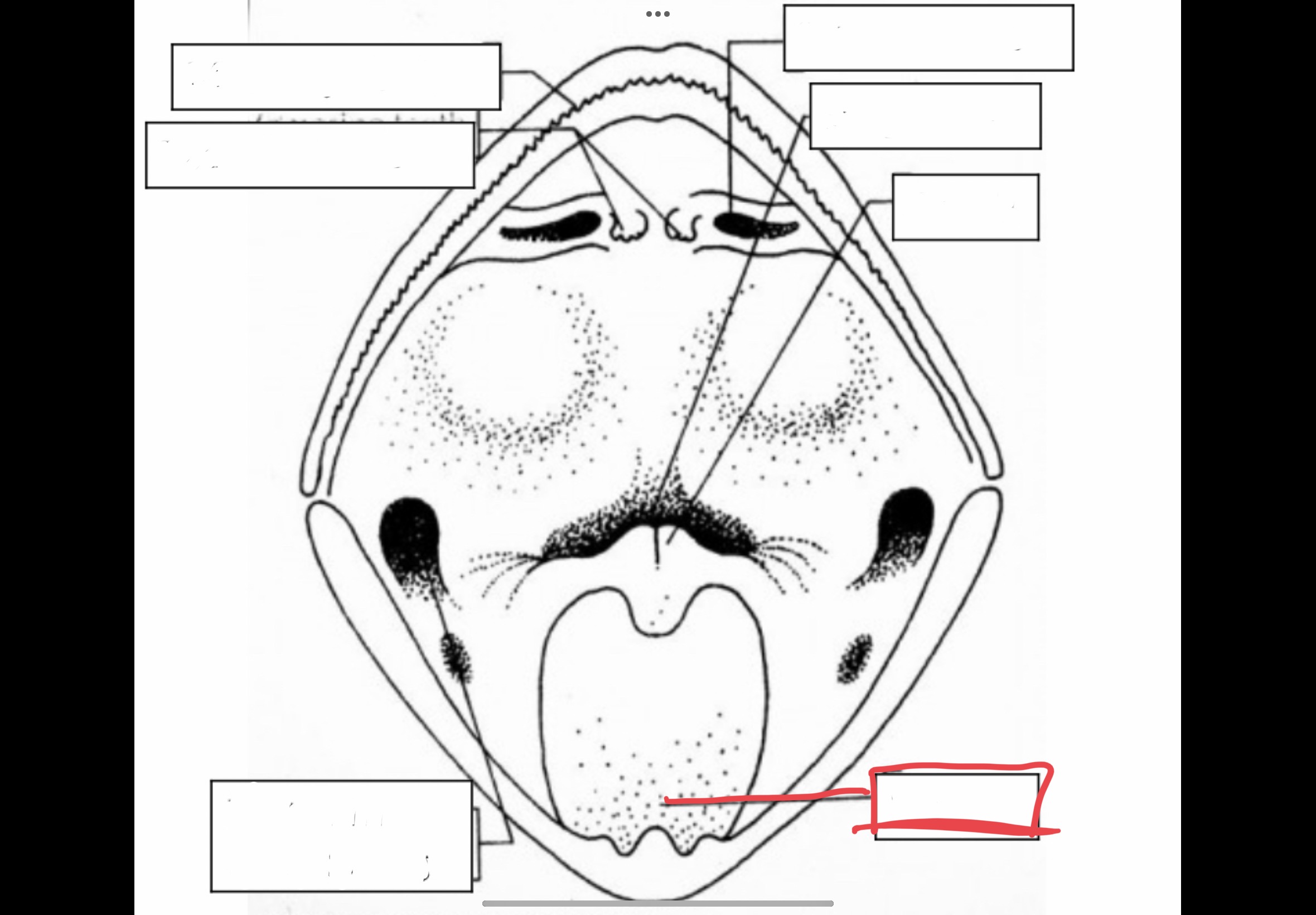
New cards
Cloacal Opening
Opening of cloaca through which indigested food, urine, and sperm are passed
70
New cards
Vocal Sacs
Flexible membrane of skin that is used for amplification of a male's mating call
71
New cards
Muscular System
Organ system that is responsible for the movement of the body; made out of muscle fibers
72
New cards
Skeletal muscle tissue
A type of muscle tissue that has striations and is involved in voluntary movements
73
New cards
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
A type of muscle tissue that has striations and is involved in involuntary movements like propelling blood in circulation
74
New cards
Smooth Muscle Tissue
A type of muscle tissue that does not have striations and is involved in involuntary movements like giving birth
75
New cards
40%
Percentage of muscles to our body weight
76
New cards
Gluteus maximus
largest muscle in the body
77
New cards
Ear
Part of the body that contains the smallest muscle and bone
78
New cards
Masseter
Strongest muscle by weight, located in the jaw
79
New cards
Cardiac Muscle
the hardest-working muscle in the body
80
New cards
Myology
the study of the structure and functions of muscles
81
New cards
Fascia
connective tissue membrane lining the outer surface of the muscles, dense fibrous, connective tissue
82
New cards
Tendon
Formed by fascia
83
New cards
Aponeuroses
flat tendons
84
New cards
Protractor
pushes a part away from the base
85
New cards
Supinator
rotator that turns a part upward
86
New cards
Pronator
rotator the turns a part downward
87
New cards
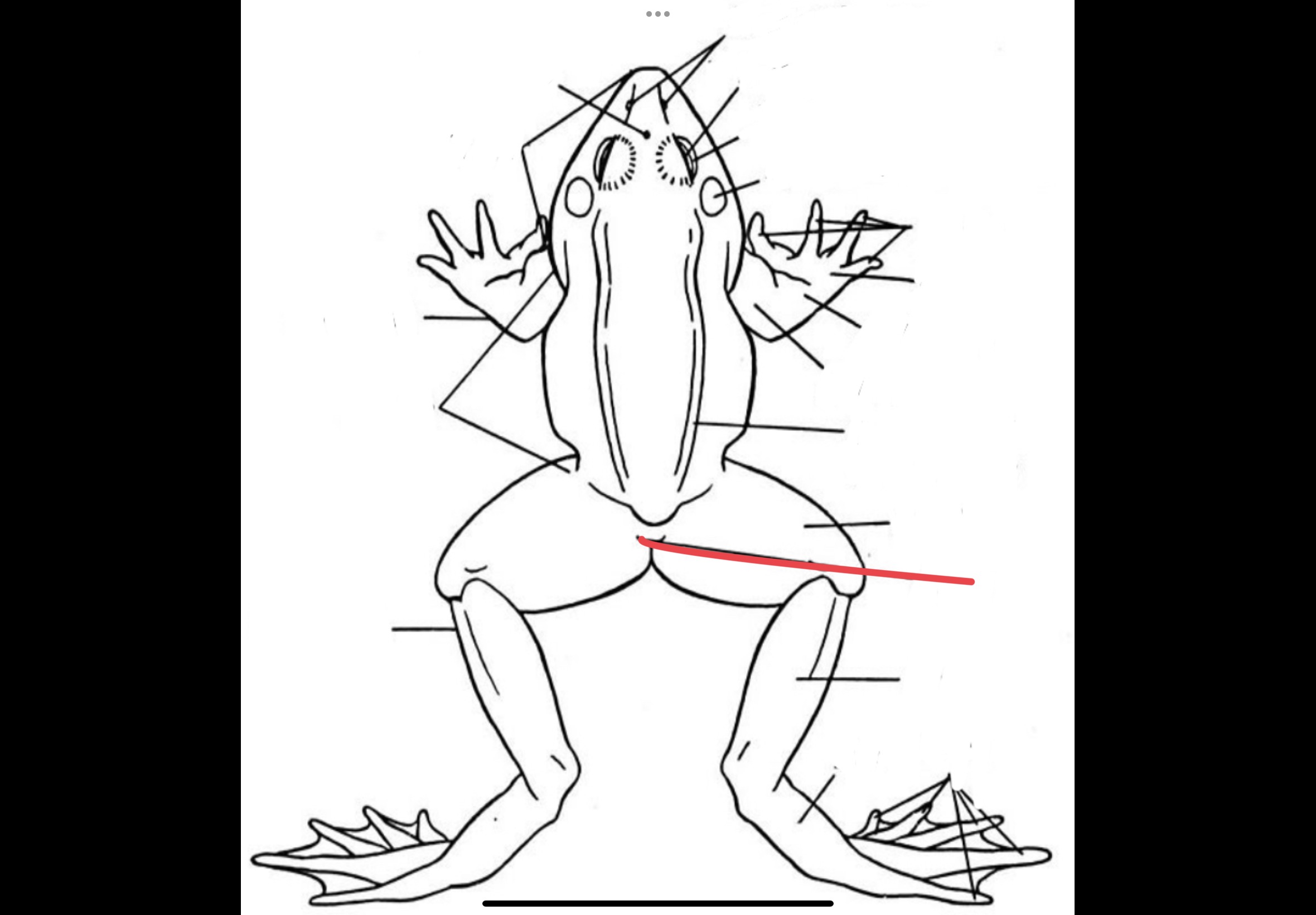
Temporalis
broad muscle posterior to the eye and on the same level as the tympanum
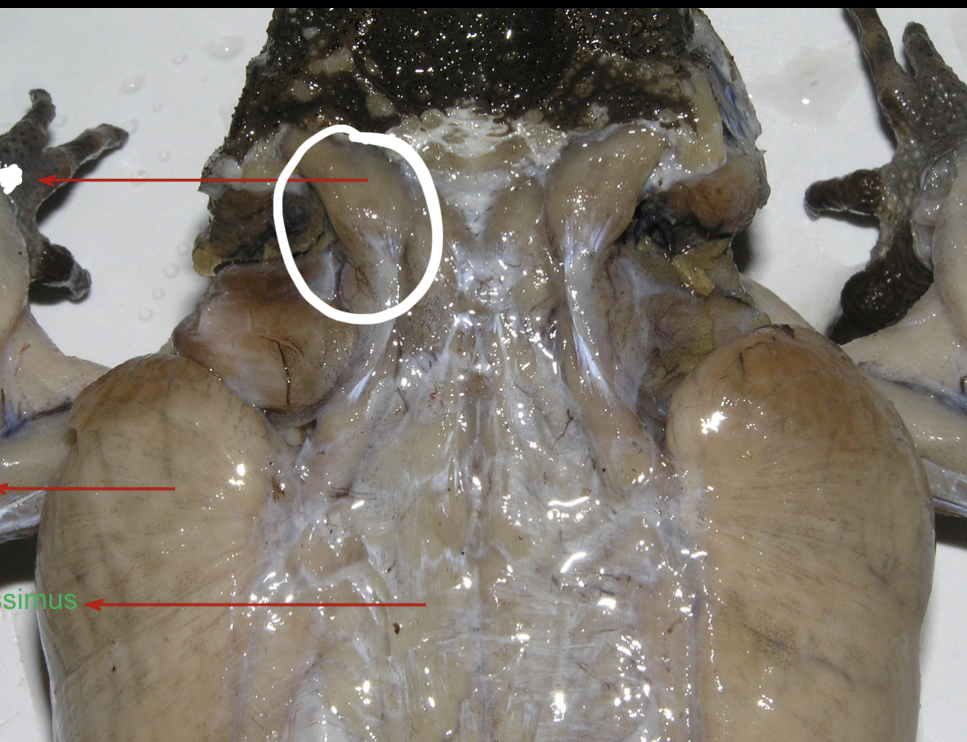
88
New cards
Depressor Mandibulae
flat fan shaped muscles posterior to the temporalis that originates from the tough fascia in the middorsal line. It inserts into the lower jaw and serves as a jaw depressor.
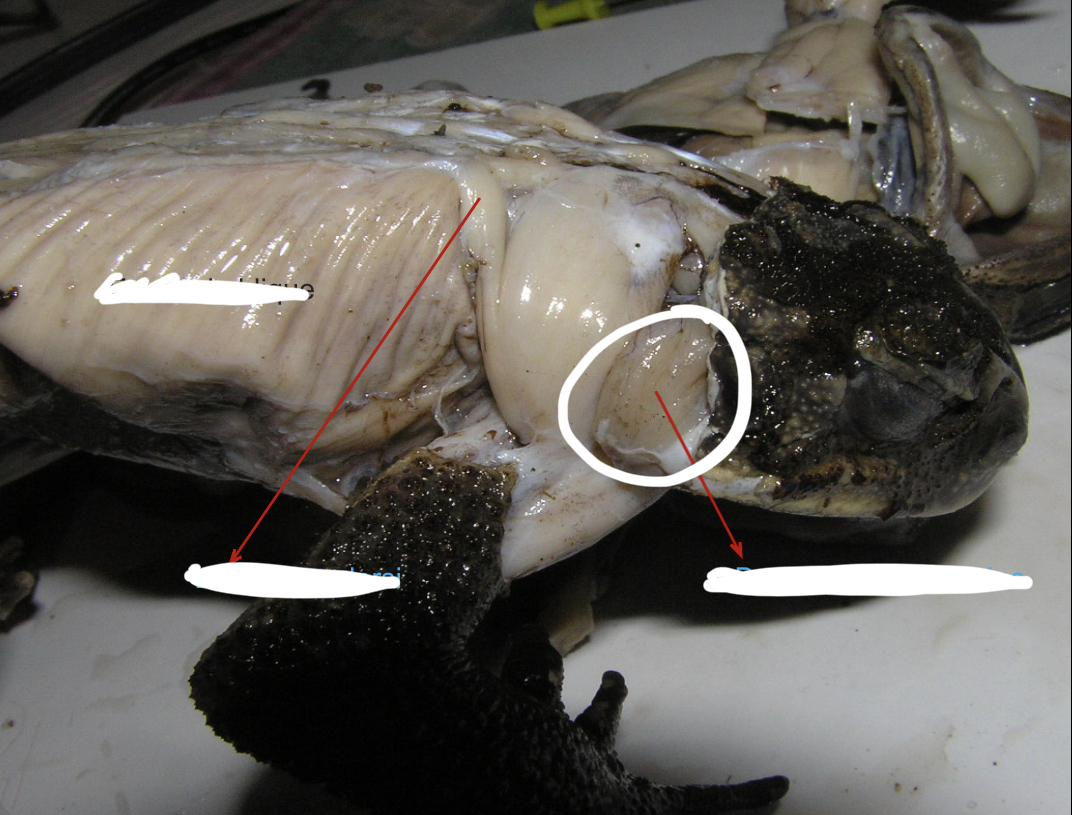
89
New cards
Latissimus dorsi
Broad muscles posterior to and partly covered by the depressor mandibulae
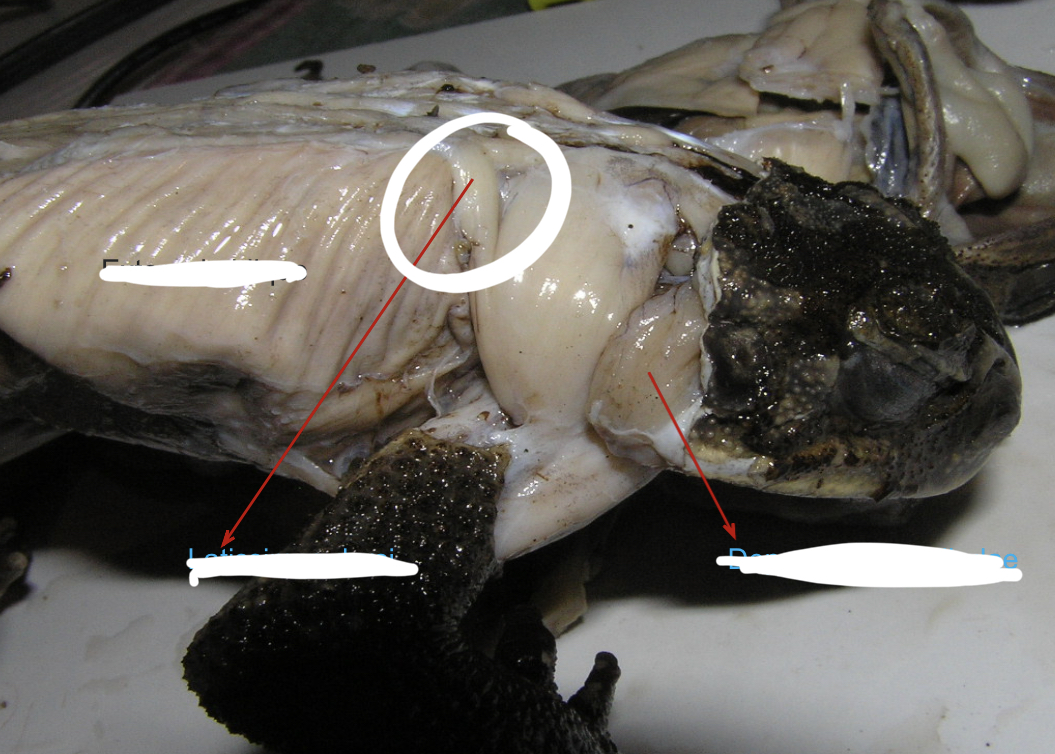
90
New cards
Longissimus Dorsi
Posterior to the latissimus dorsi these muscles are attached to the anterior third of the urostyle and skull. They are inserted along the vertebral column and they serve as extensor of the back and levator of the head.
91
New cards
Coccygeosacralis
A pair of narrow V – shaped muscles posterior to the longissimus dorsi
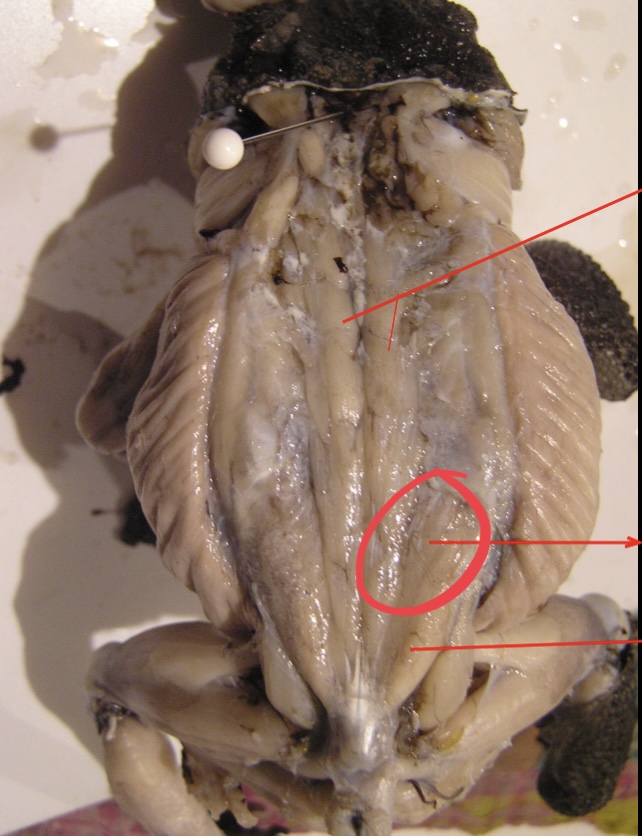
92
New cards
Coccygeoilliacus
A pair of broad V shaped muscles posterior to coccygeo sacralis.
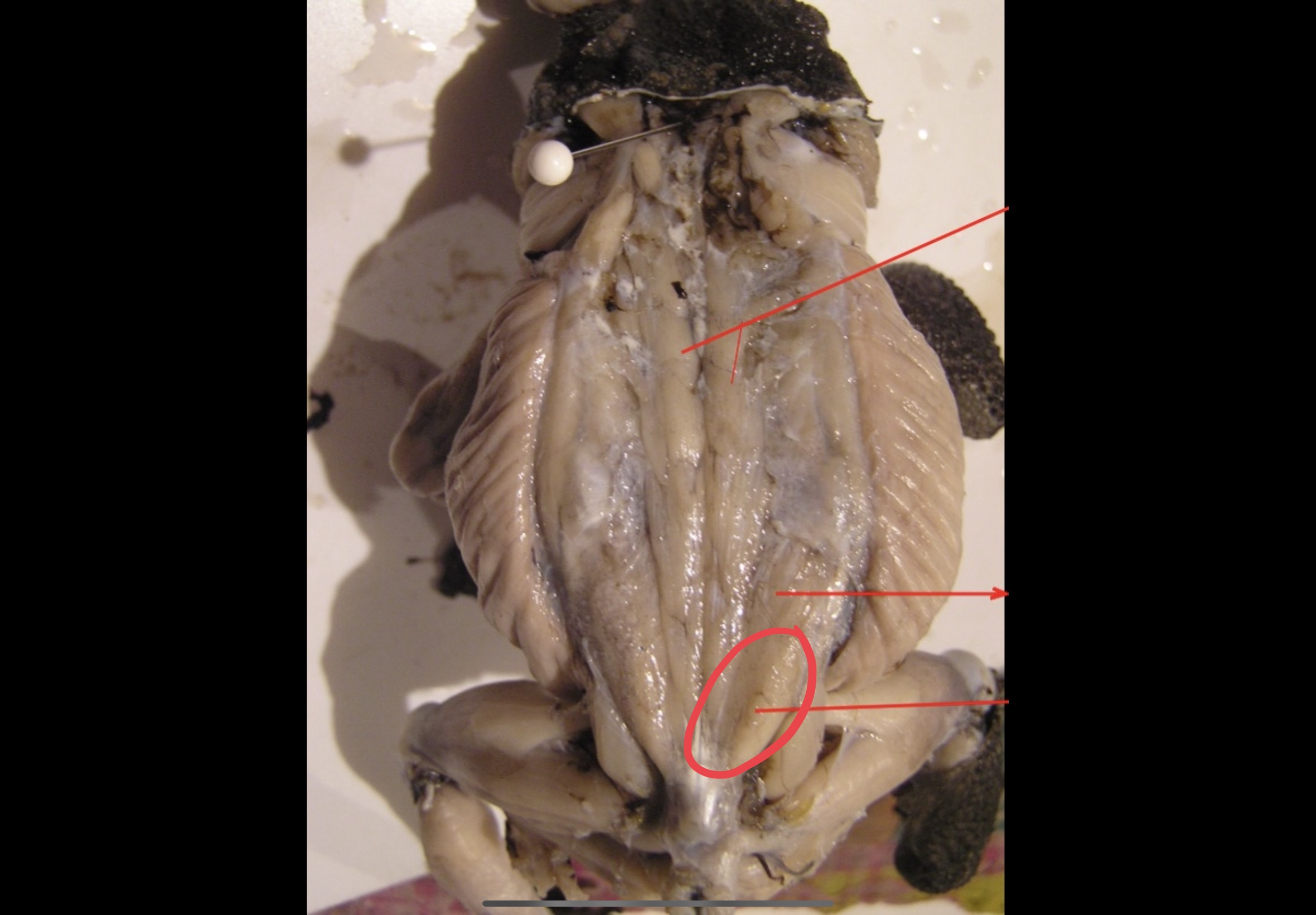
93
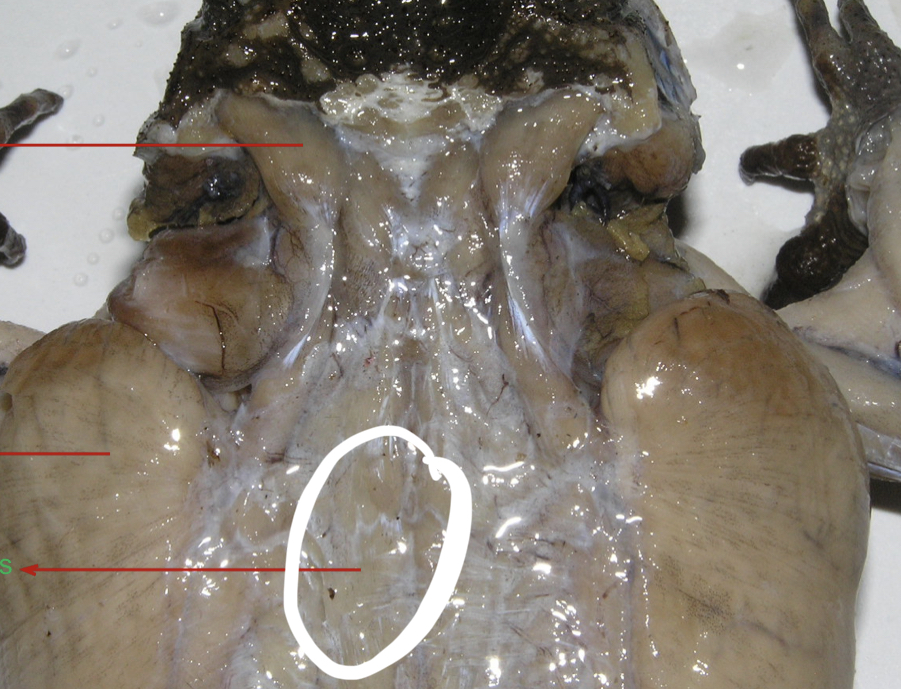
New cards
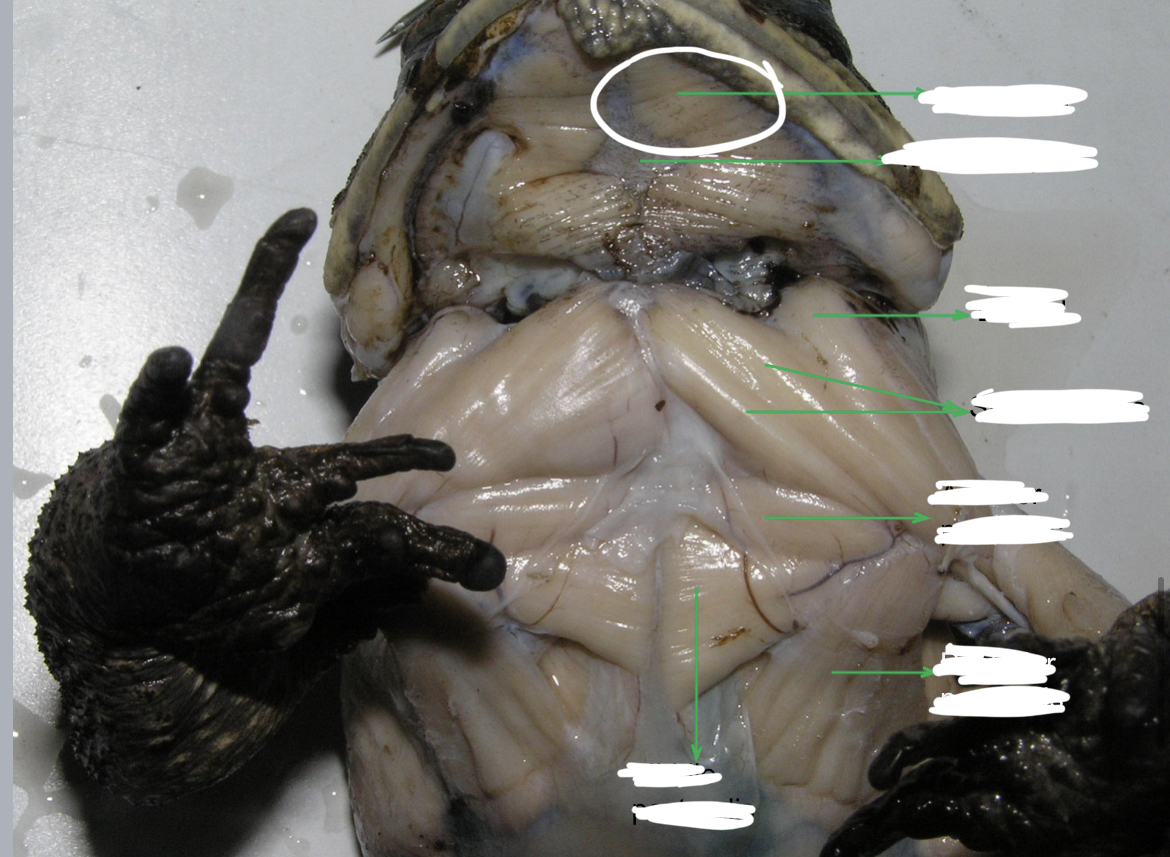
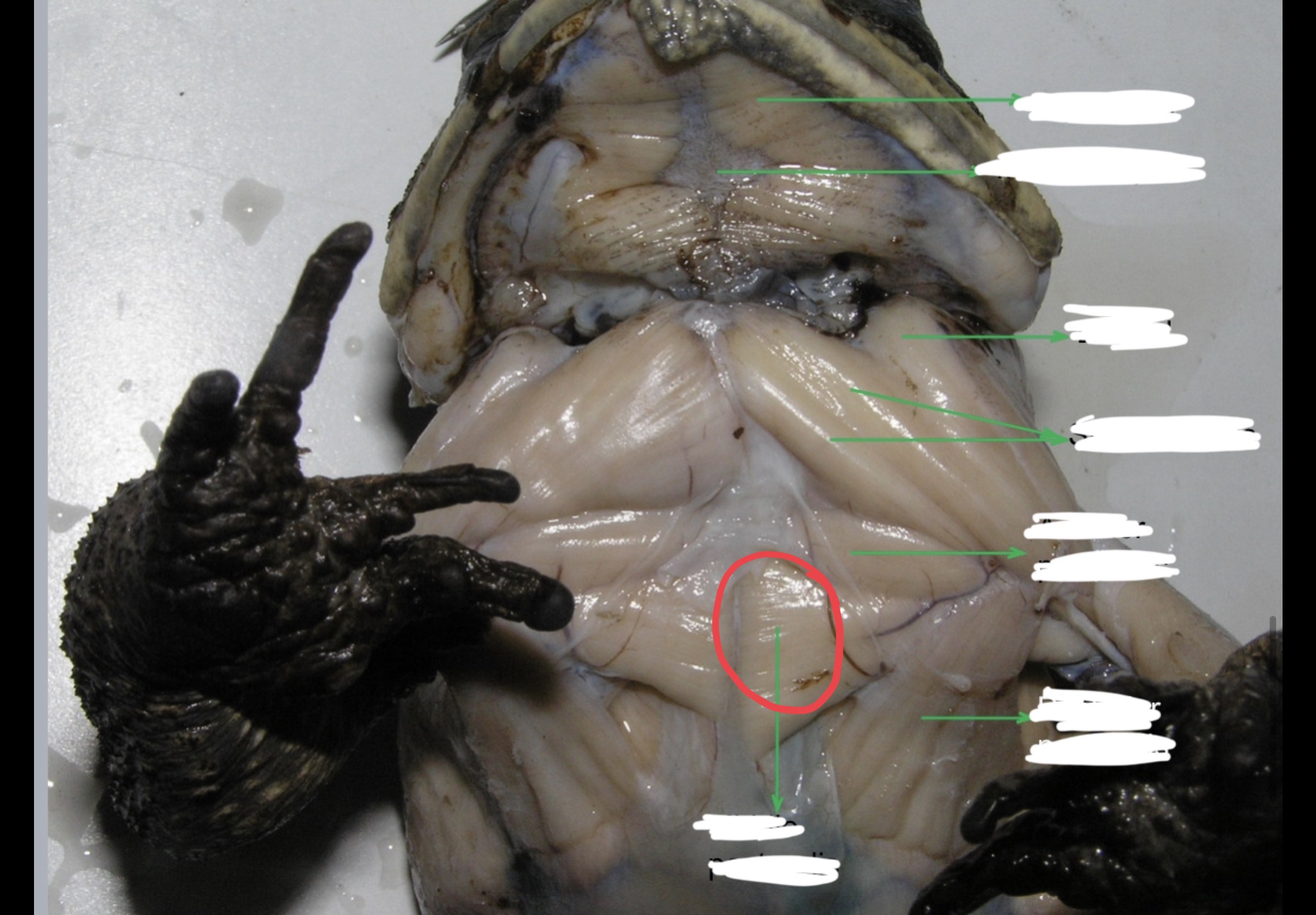
Mylohyoid
A large transverse muscle on the ventral surface of the mouth floor this muscle
94
New cards
Median Raphe
A midventral connective tissue partition that divides the mylohyoid into left and right portions
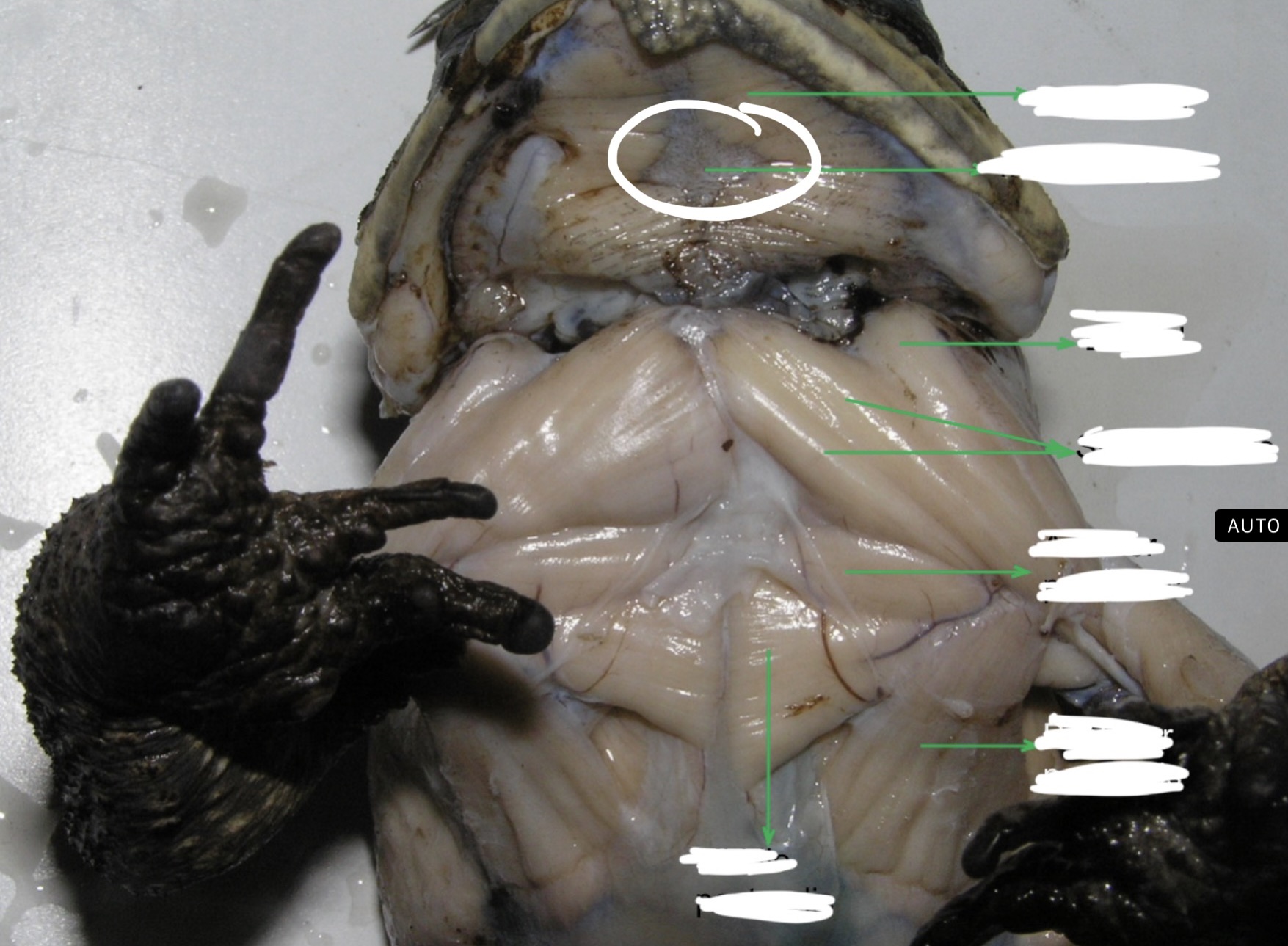
95
New cards
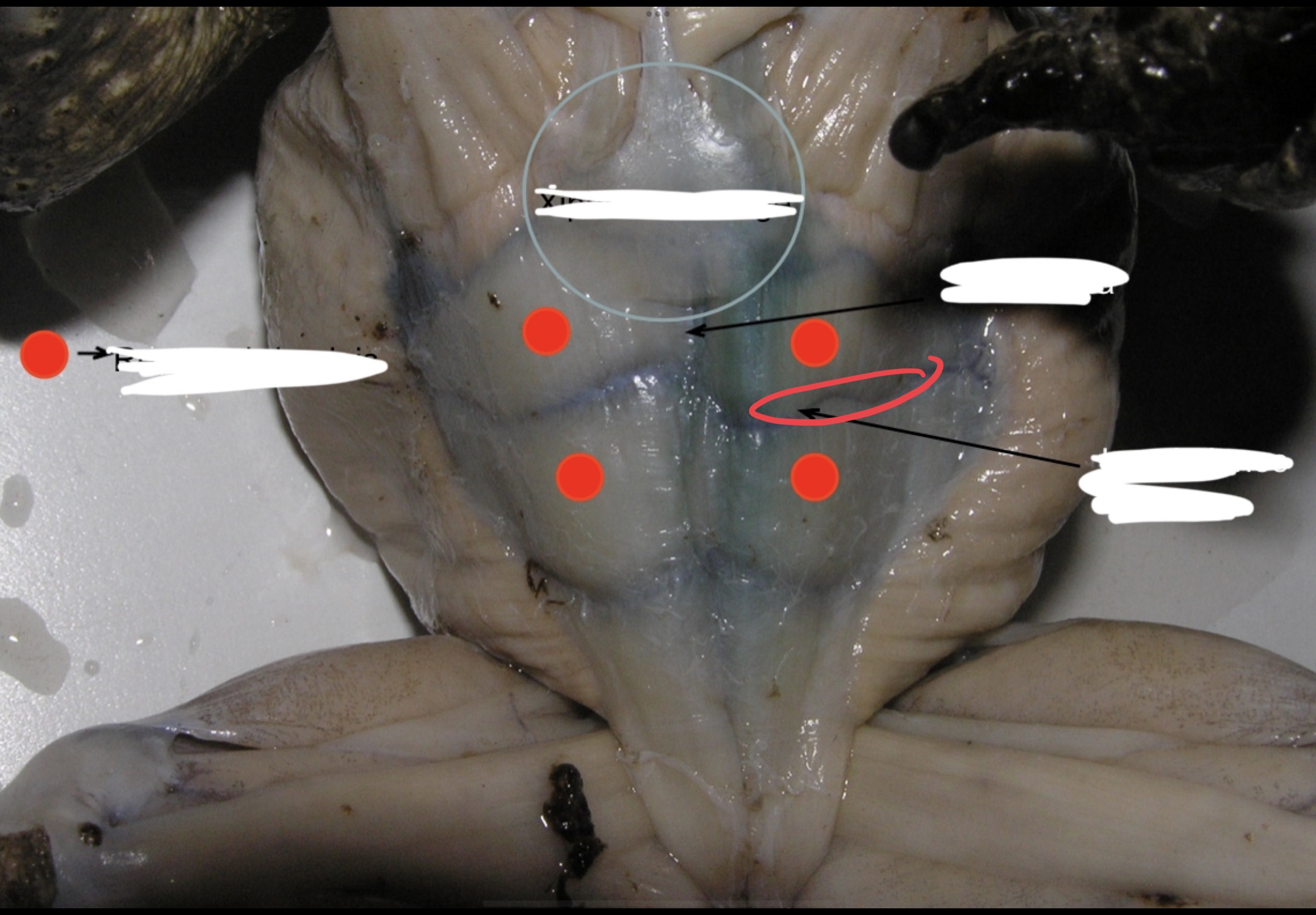
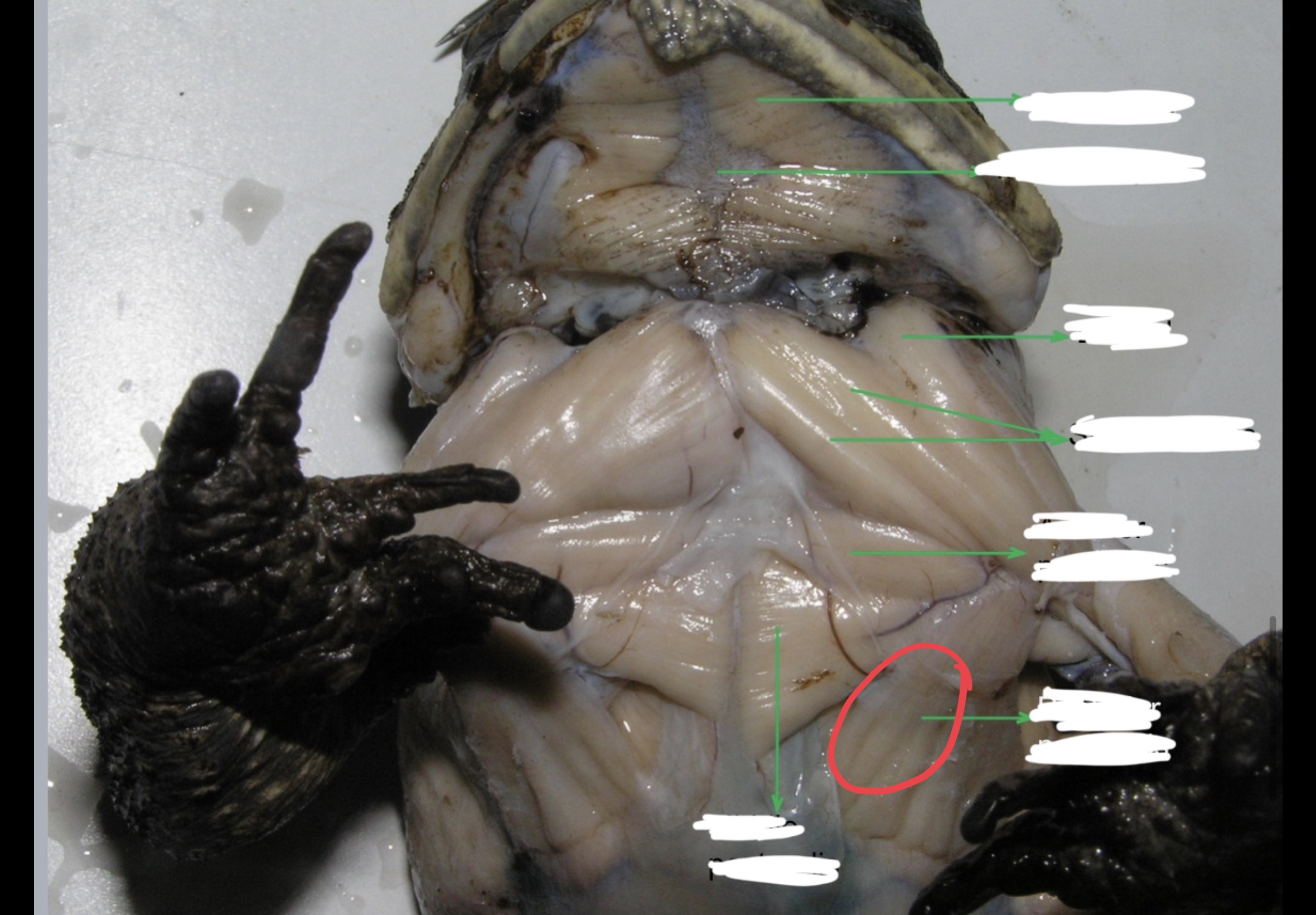
Anterior Pectoralis
This muscle lies immediately posterior to the strenoradialis and the most anterior of the chest muscle. It originates from the epicoracoidea and it is inserted into the deltoid ridge; it acts as adductor and rotator of the arm.
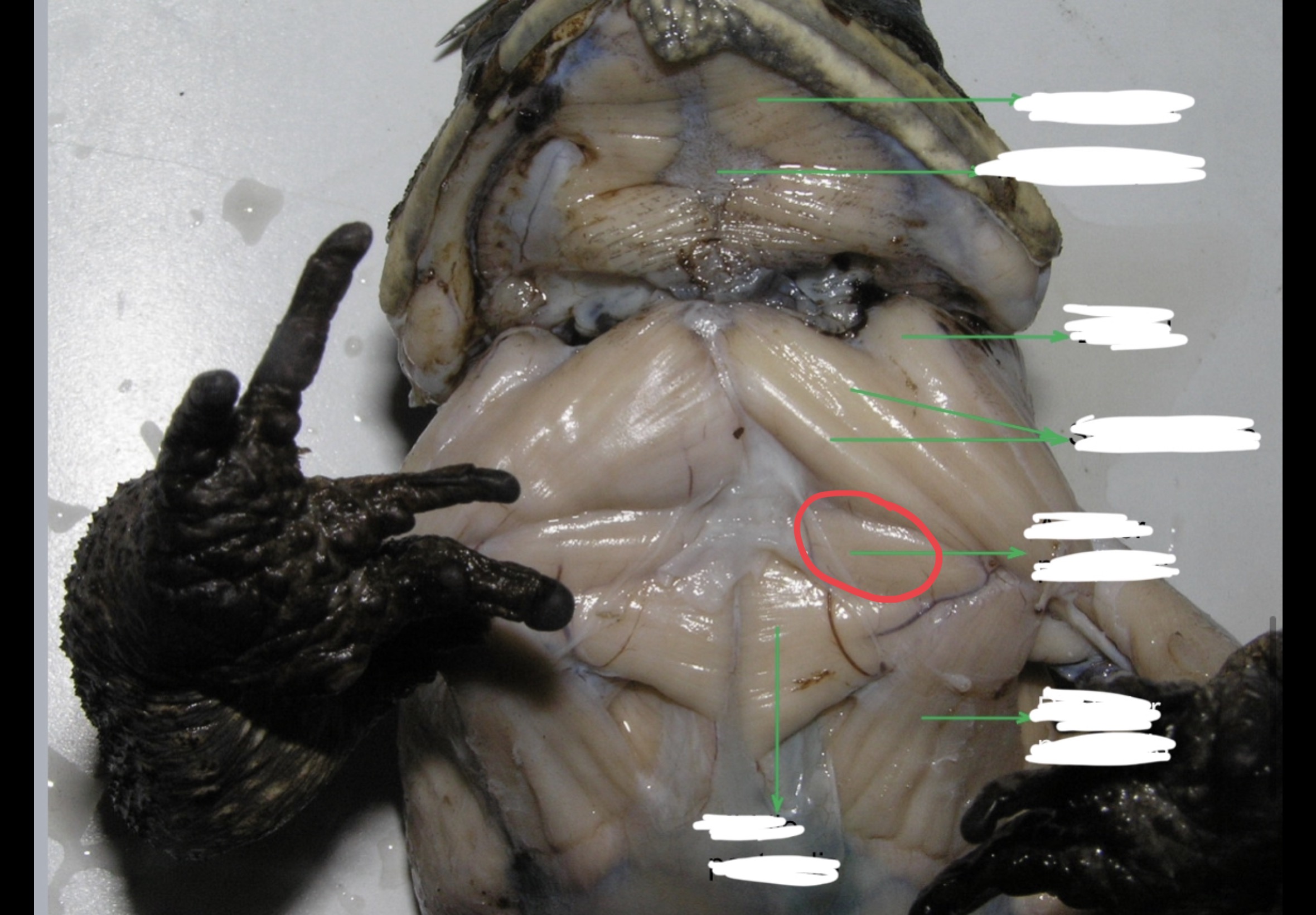
96
New cards
Middle Pectoralis
Posterior to the anterior pectoralis. this muscle takes origin from the mesosternum and xiphisternum. It is inserted into the ventral portion of the proximal end of the humerus and adducts and rotates the arm.
97
New cards
Posterior Pectoralis
Postero – lateral to the middle pectoralis. it extends to almost the entire portion of the median surface of the trunk. It is inserted into the deltoid ridge; it serves as adductor and rotator of the arm.
98
New cards
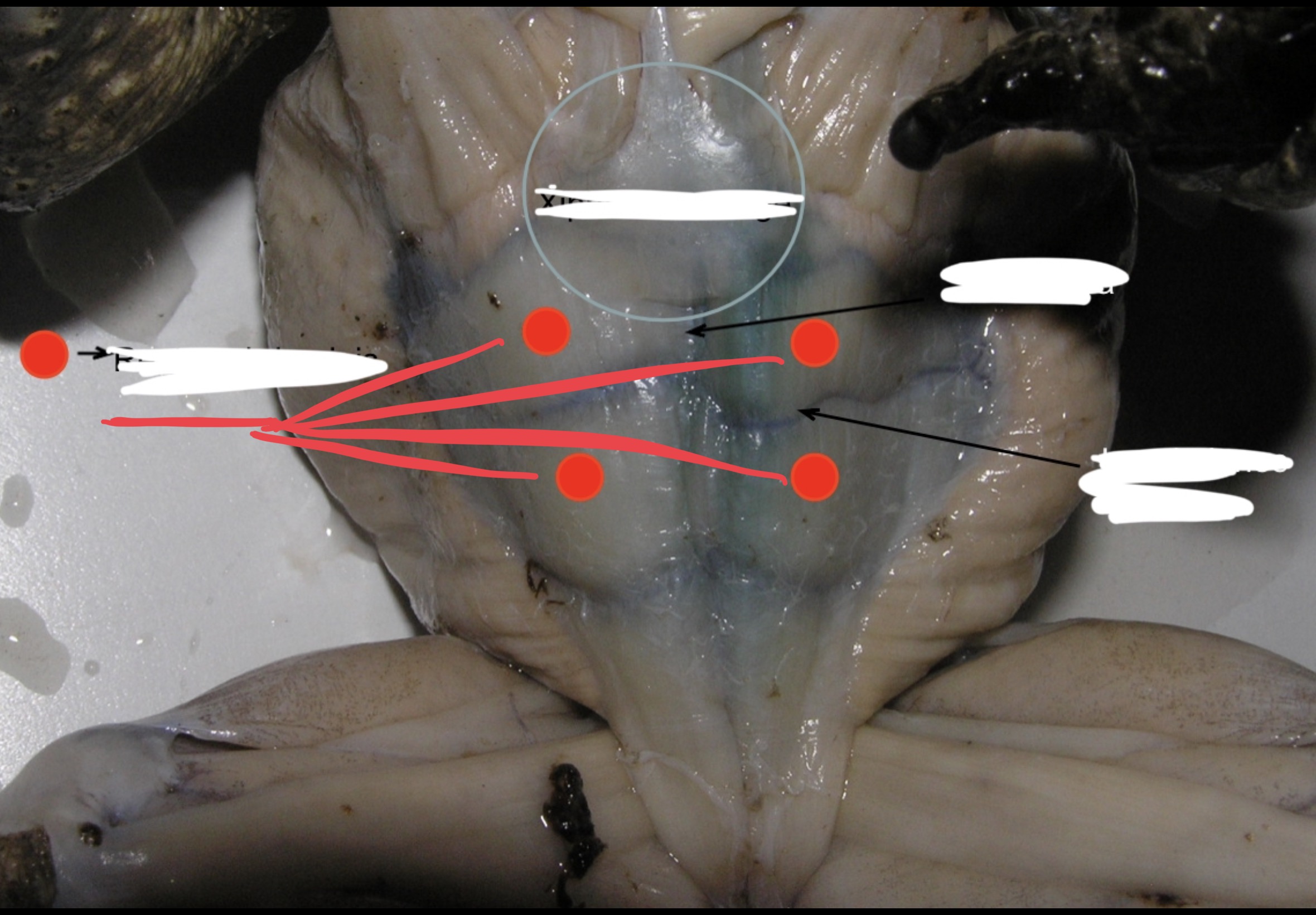
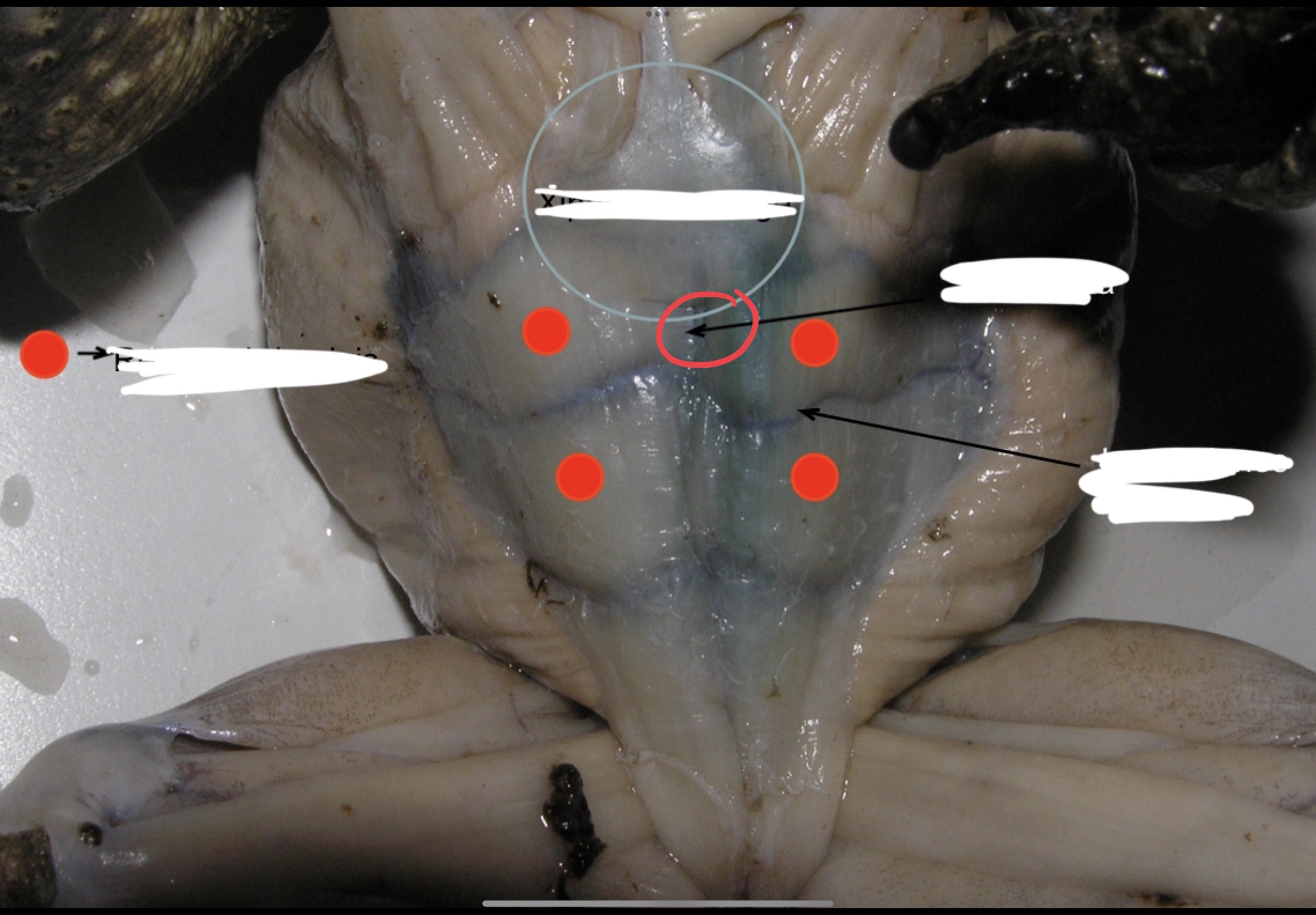
Rectus Adbominis
This longitudinal muscle extends to each side of the linea alba
99
New cards
Linea Alba
a strip of connective tissue that acts as a partition on the midventral line.
100
New cards
Inscriptiones tendinae
Divides the rectus adbominis into muscle segments.