Lab 3: Osteology: Joints/Articulation
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
articulations/joints
- locations in which two or more bones are joined together
- cartilage and other types of connective tissues protect bones from abrasion and sometimes allow movement in these places
synarthroses
- joints that do not allow for any movement
- ex: sutures of the skull and epiphyseal lines
amphiarthroses
- joints that allow for a little movement because of connective tissue give
- ex: ligamentous connections between tibia and fibula, pubic symphysis
diarthroses
- joints that have free movement due to joint capsules that contain synovial fluid
- aka synovial joints
synovial joints
- can be uniaxial (elbow and ankle)
- can be biaxial (metacarpophalangeal)
- can be multiaxial (shoulder and hip)
nonaxial synovial joints
- permits translational movement
- plane and gliding joints
uniaxial synovial joints
- permits movement in one plane
- hinge and pivot joints
biaxial synovial joints
- permits movement in two planes
- condylar and saddle joints
multiaxial synovial joints
- permits movement in three planes
- ball and socket joints
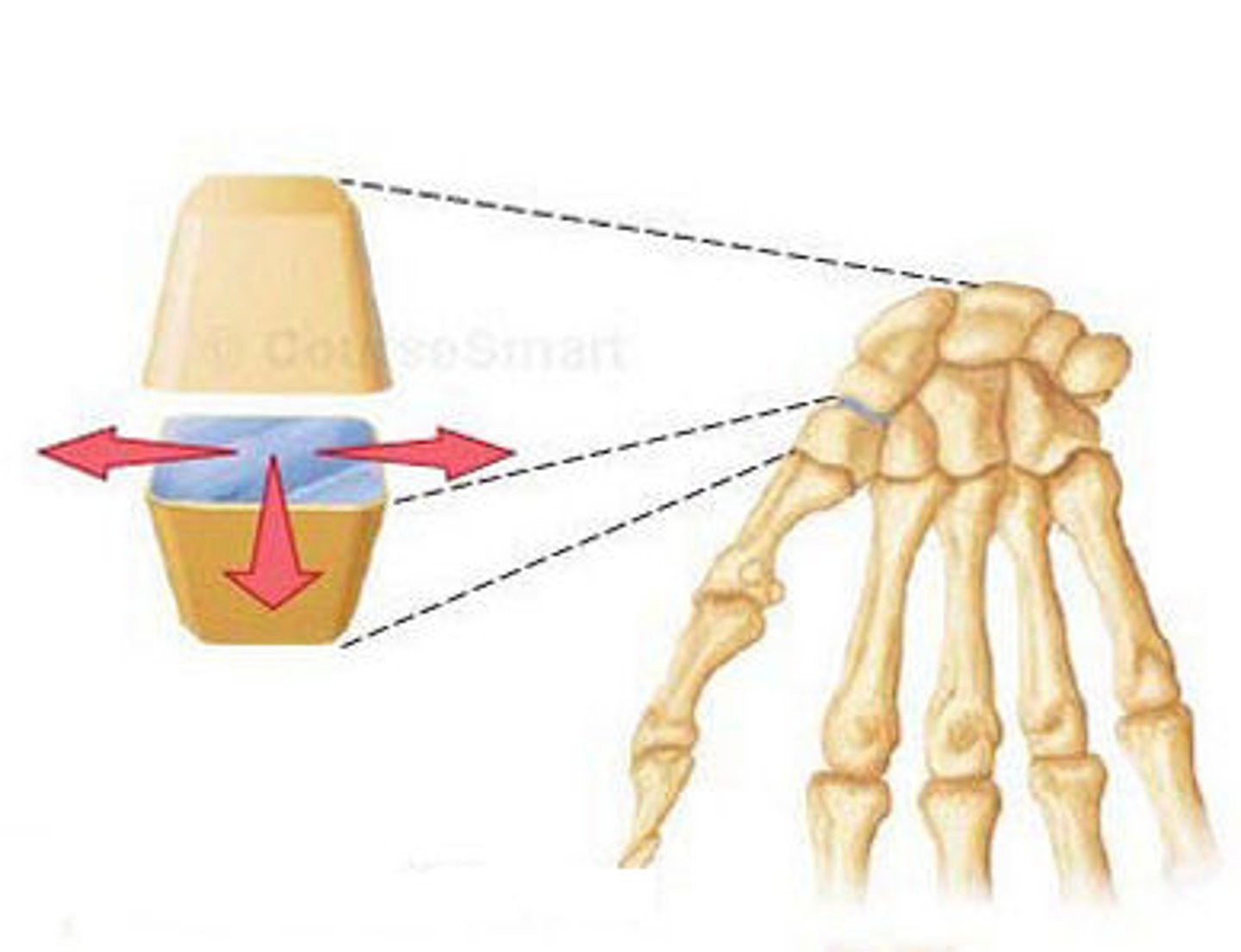
plane joints/gliding joints
- common where flat articular surfaces slide by neighboring bones
- typically nonaxial movement (limited due to supporting ligaments)
- found in wrist (in between carpals), in between the tarsals, and between vertebral articular surfaces
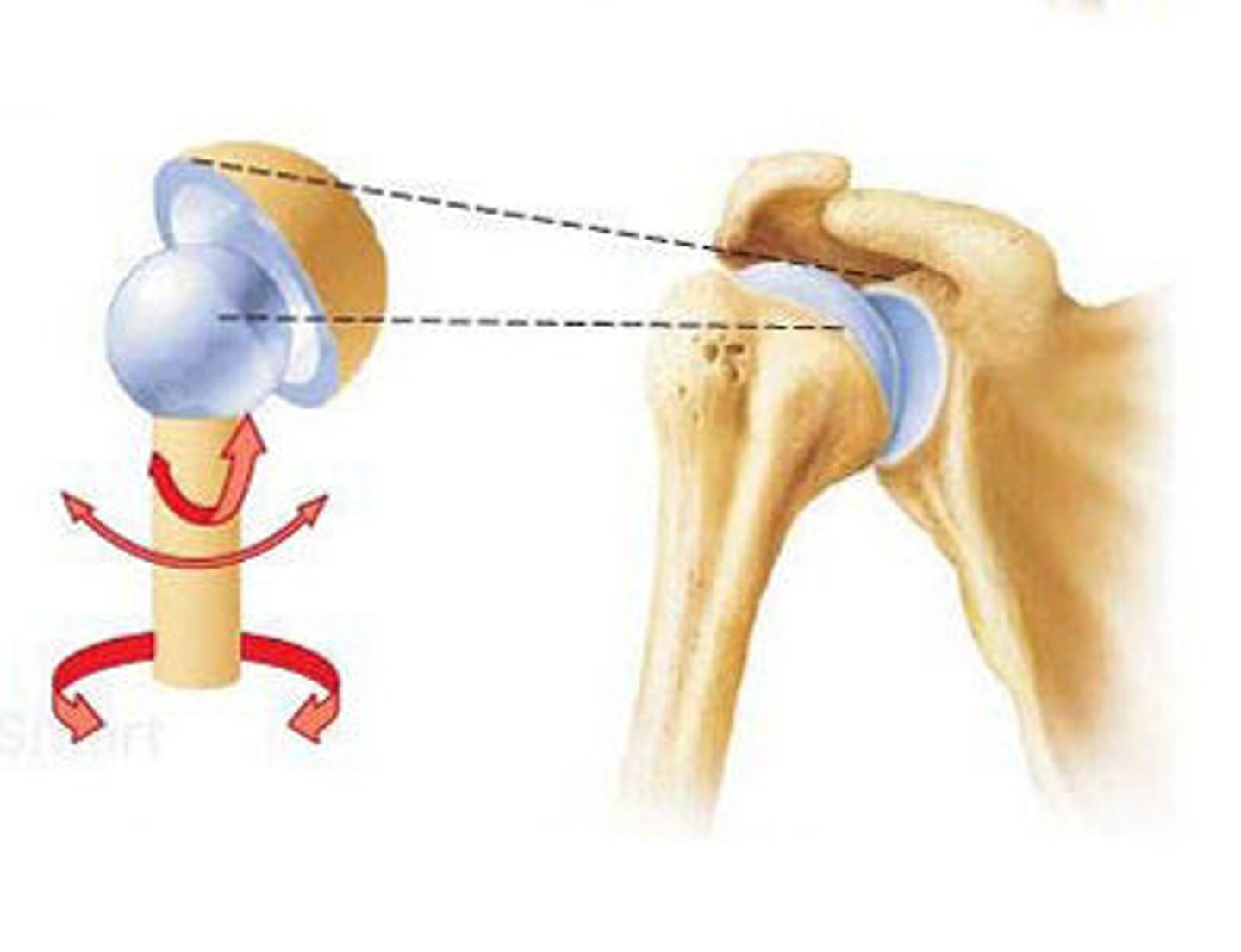
ball-and-socket joints
- occur where spherical head of one bone fits into a cup-shaped fossa of another bone
- multiaxial and permits a variety of movements including rotation along the long axis (also flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, etc.)
- found in the shoulder and hip
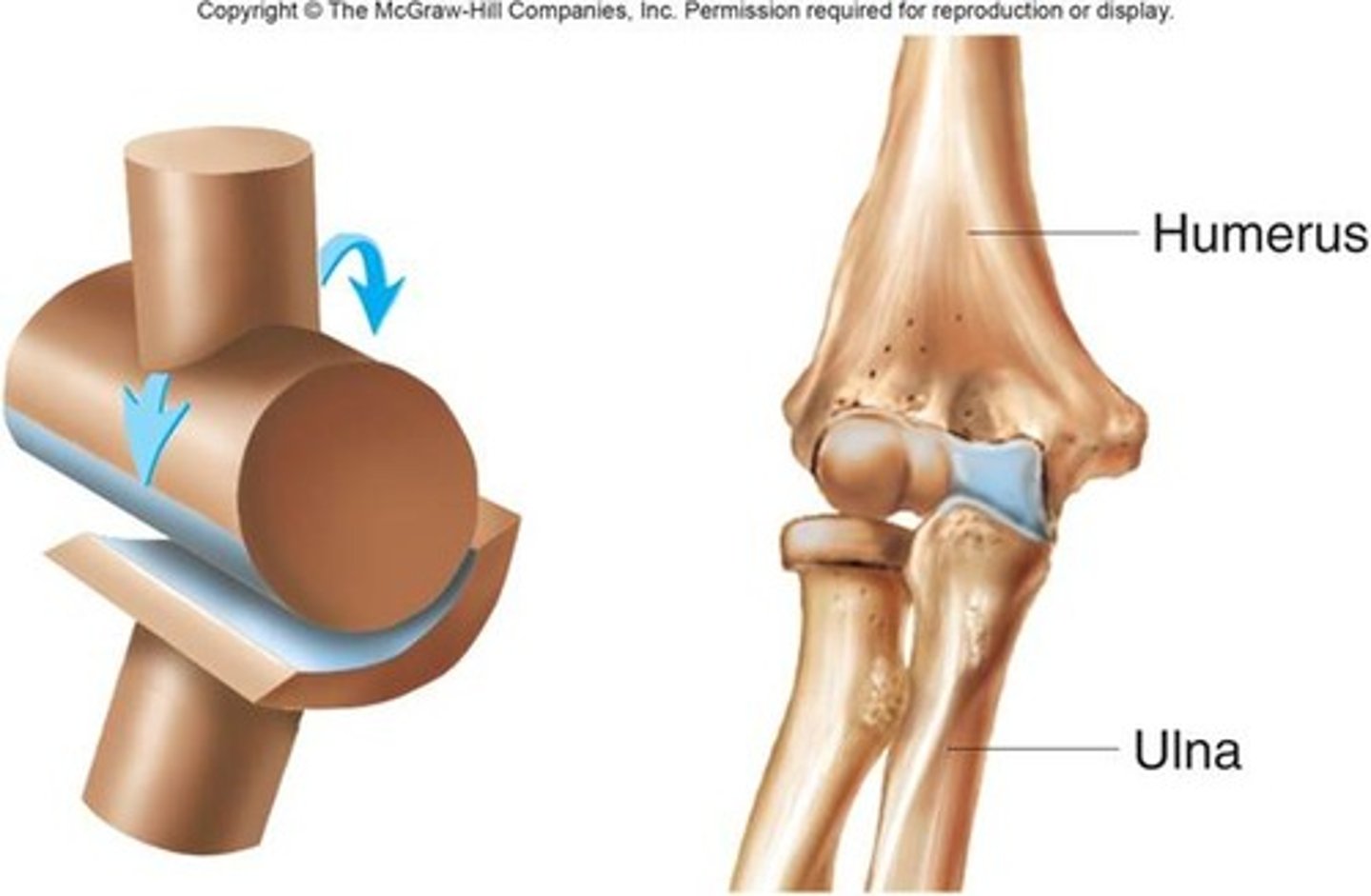
hinge joints
- uniaxial
- operate like a door hinge
- found in the elbows, knees, ankles, fingers, and toes
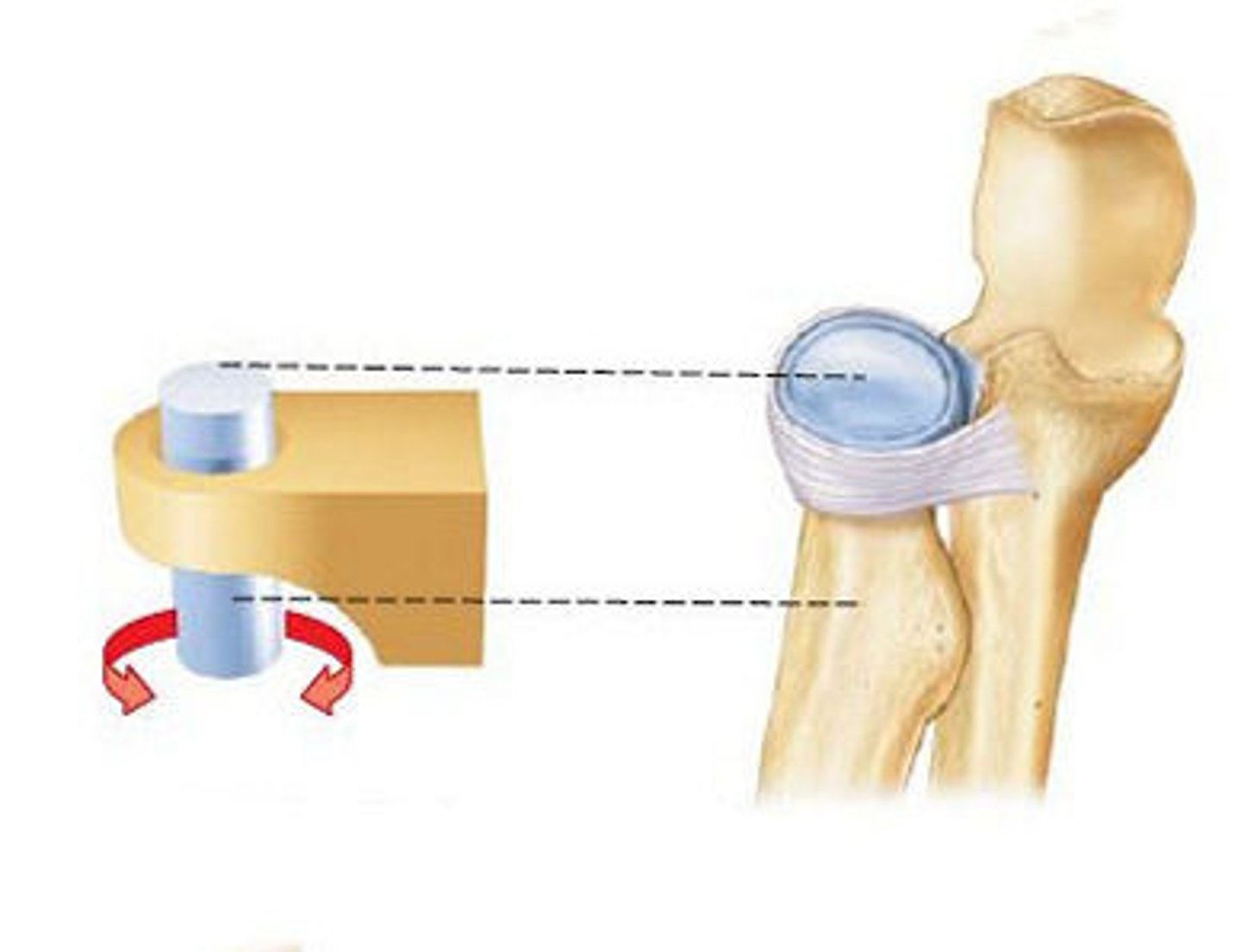
pivot joints
- uniaxial
- permit one bone to rotate around another
- ex: proximal radioulnar joints and atlantoaxial joints
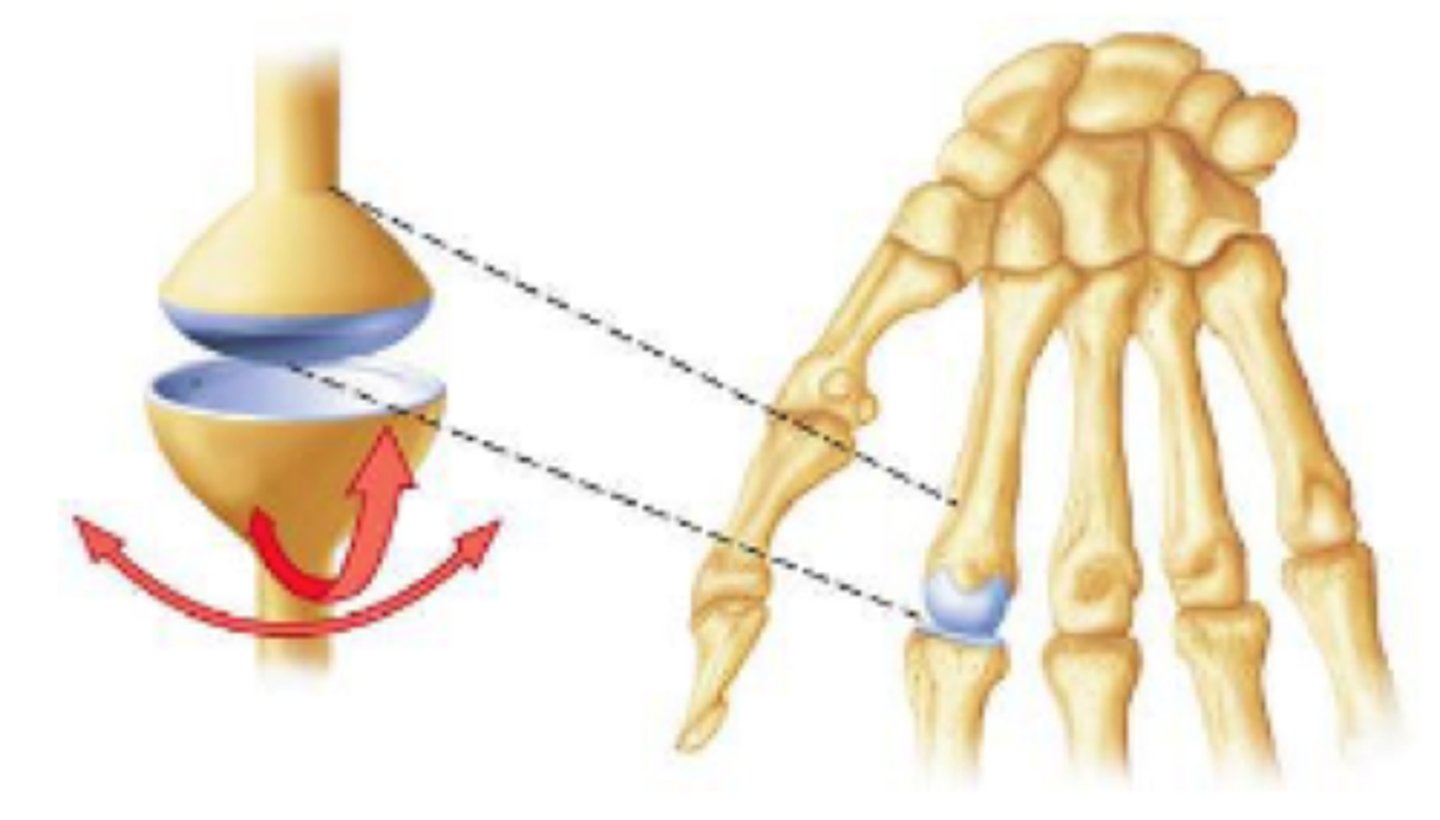
condylar joints
- biaxial
- characterized by the convex surface of one bone articulating in the concave surface of another bone
- found in the knuckles
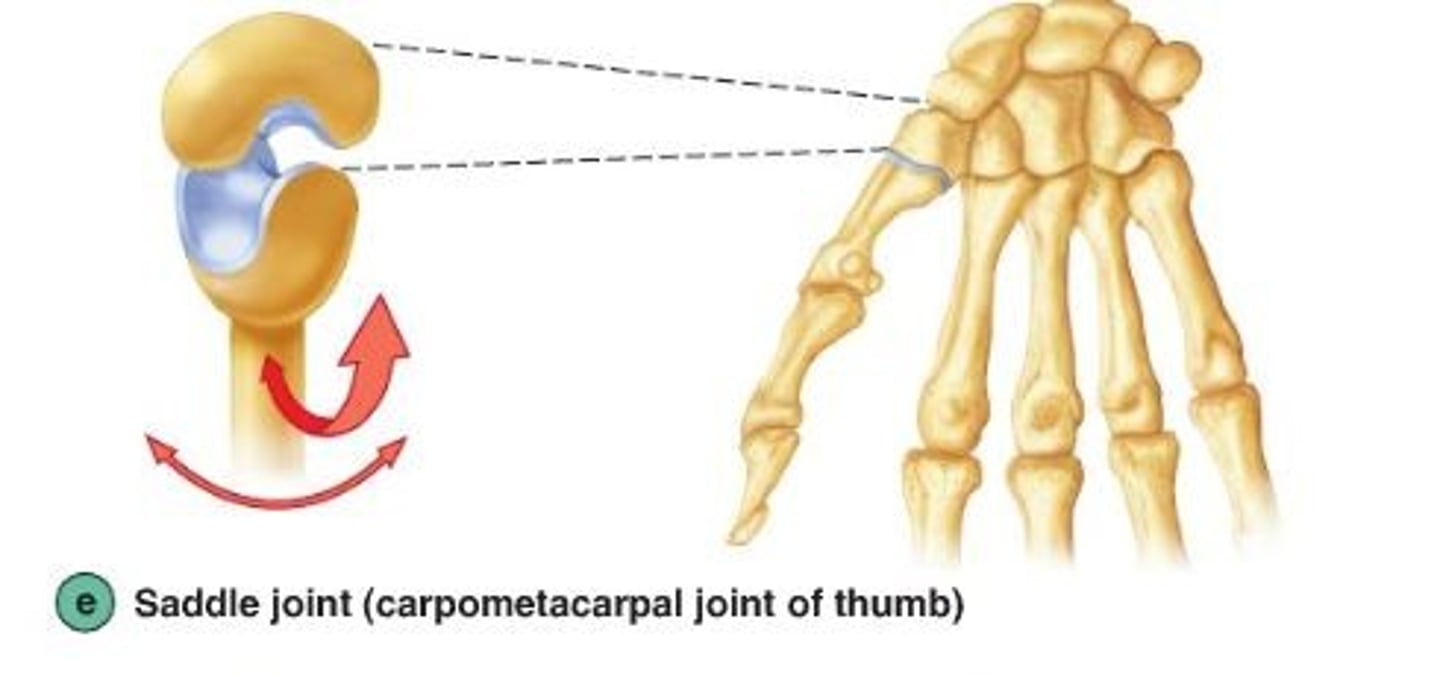
saddle joints
- biaxial
- found at the junction between the thumb metacarpus and the trapezium bone of the wrist
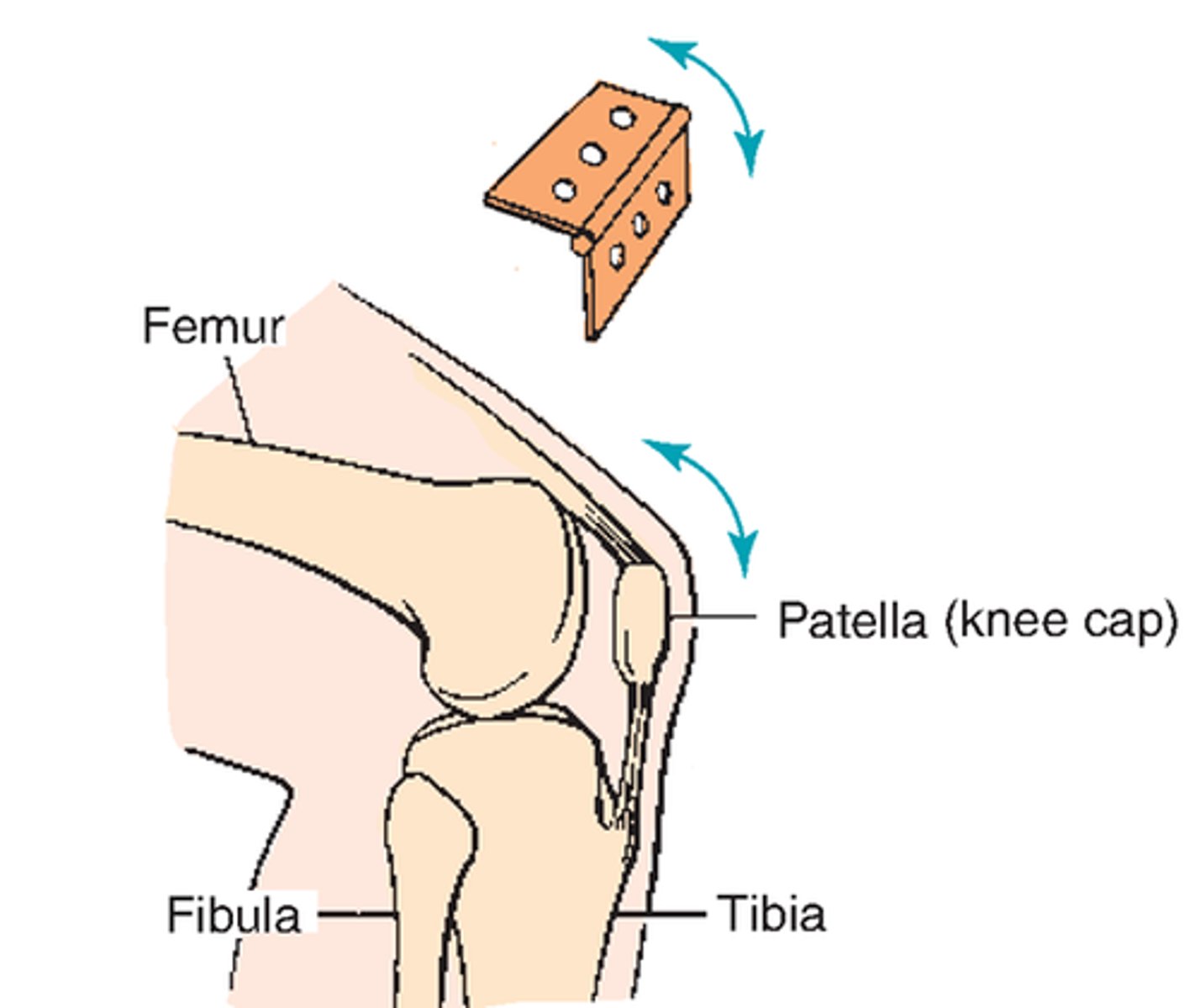
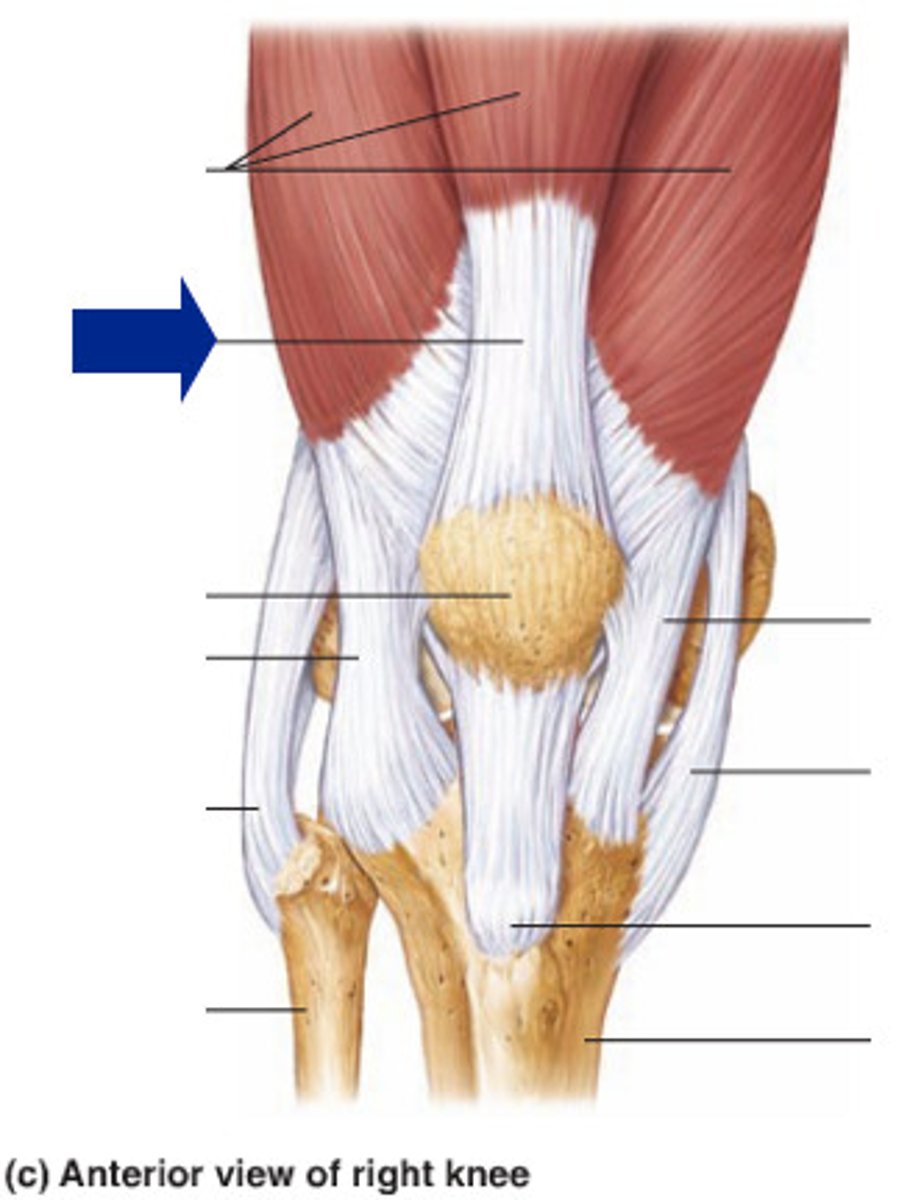
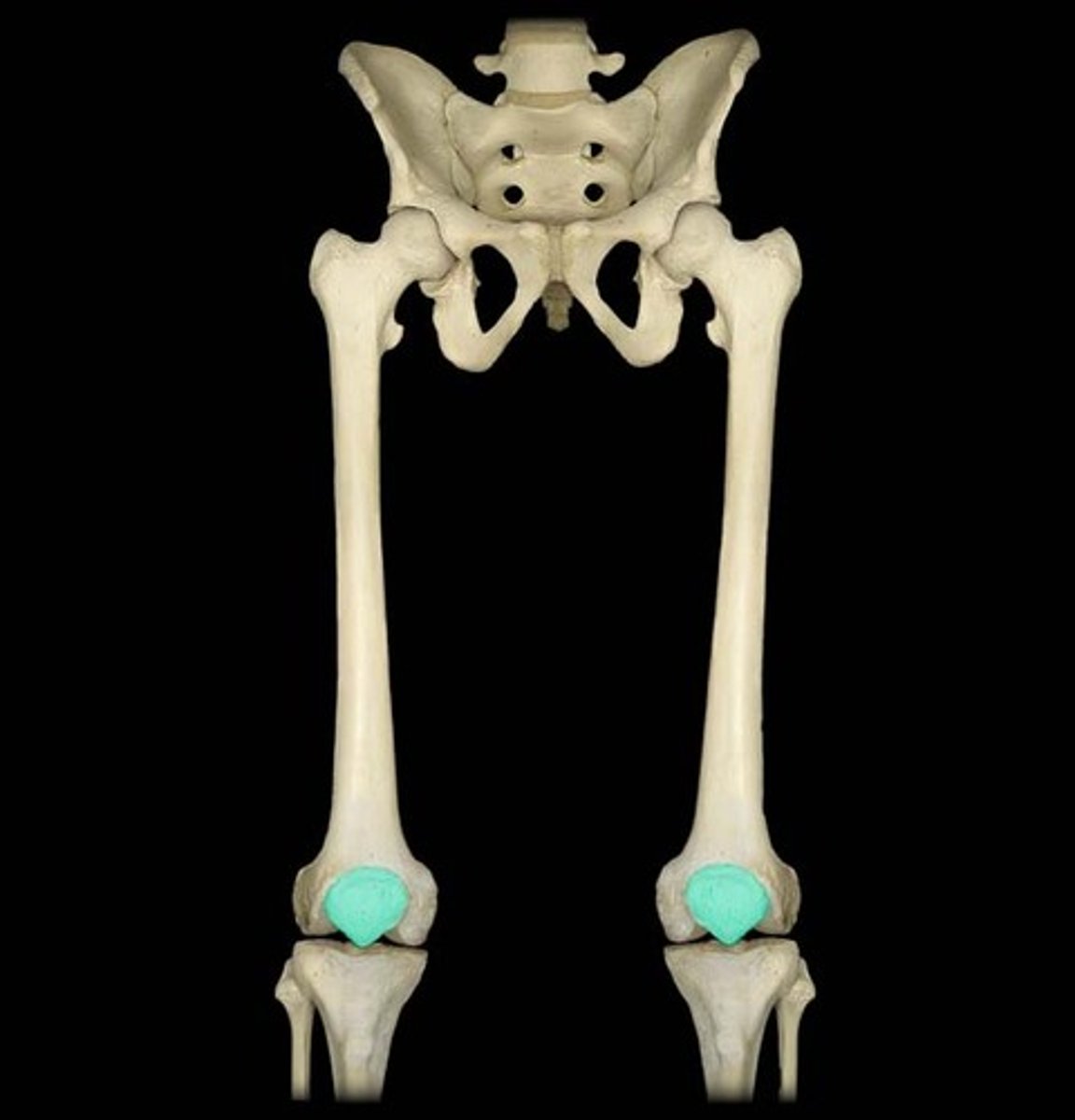
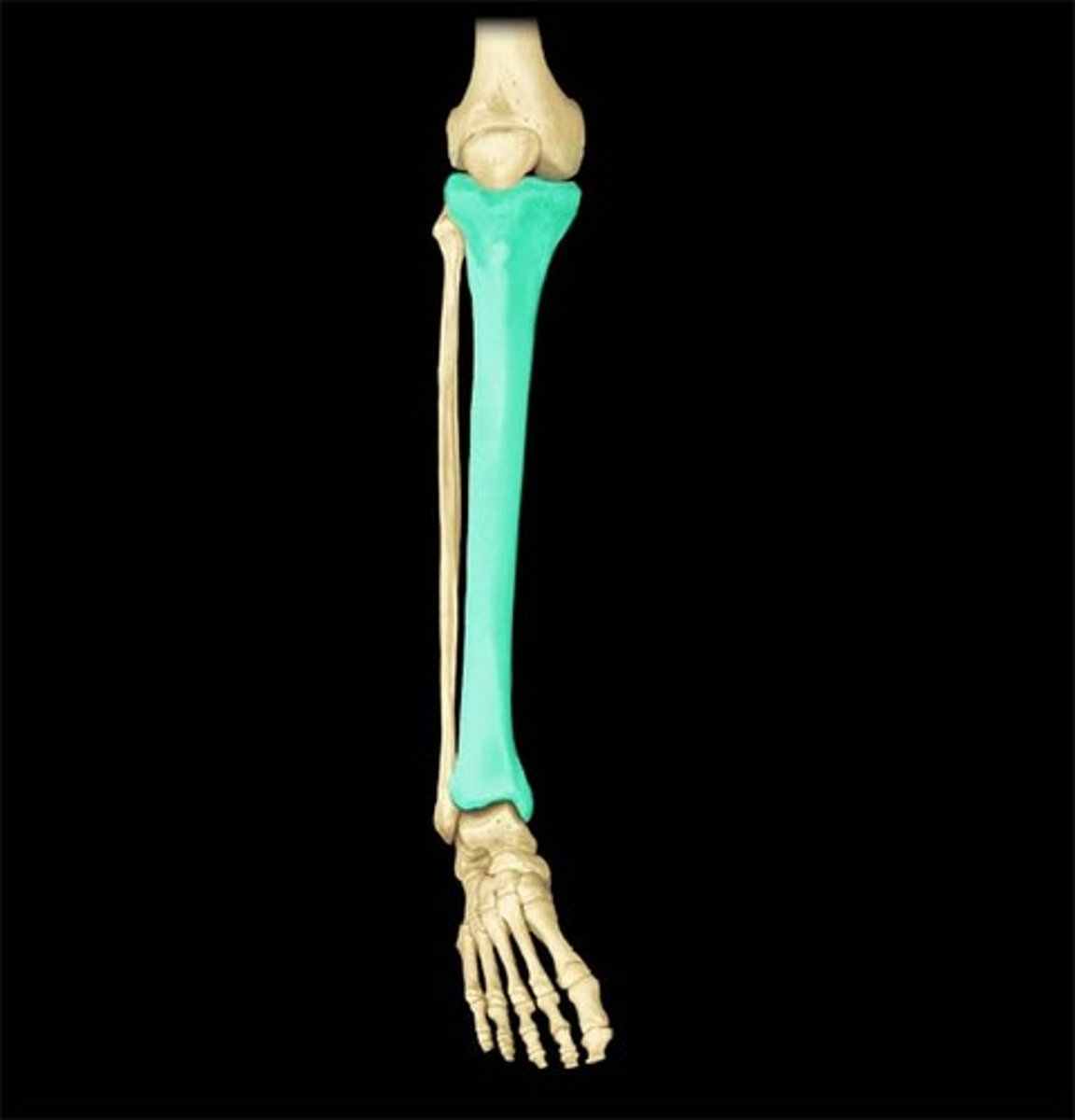
knee joint
- uniaxial synovial joint and hinge joint
- allows for flexion and extension of the lower leg
- includes the distal end of the femur, the proximal ends of the tibia, and the patella
- many small ligamentous connections work together to stabilize the joints while having some give and typically have 2 connections, one to each bone
knee injuries
- tears to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), meniscus, and medial collateral ligament (MCL)
- happen when the ligaments are stretched beyond their capacity to hold the bones
- hyperextension/hyperflexion or outward force to the knee
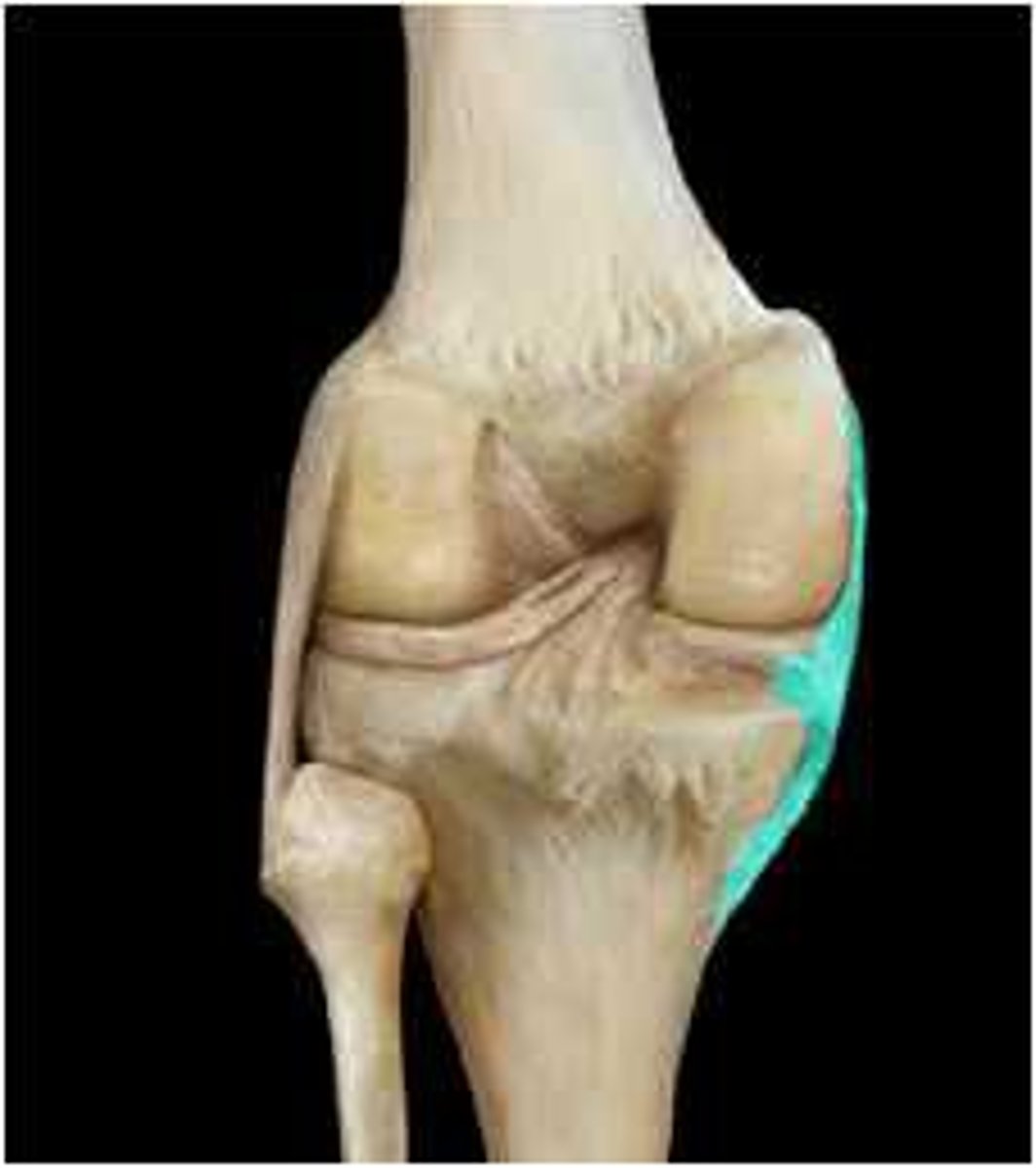
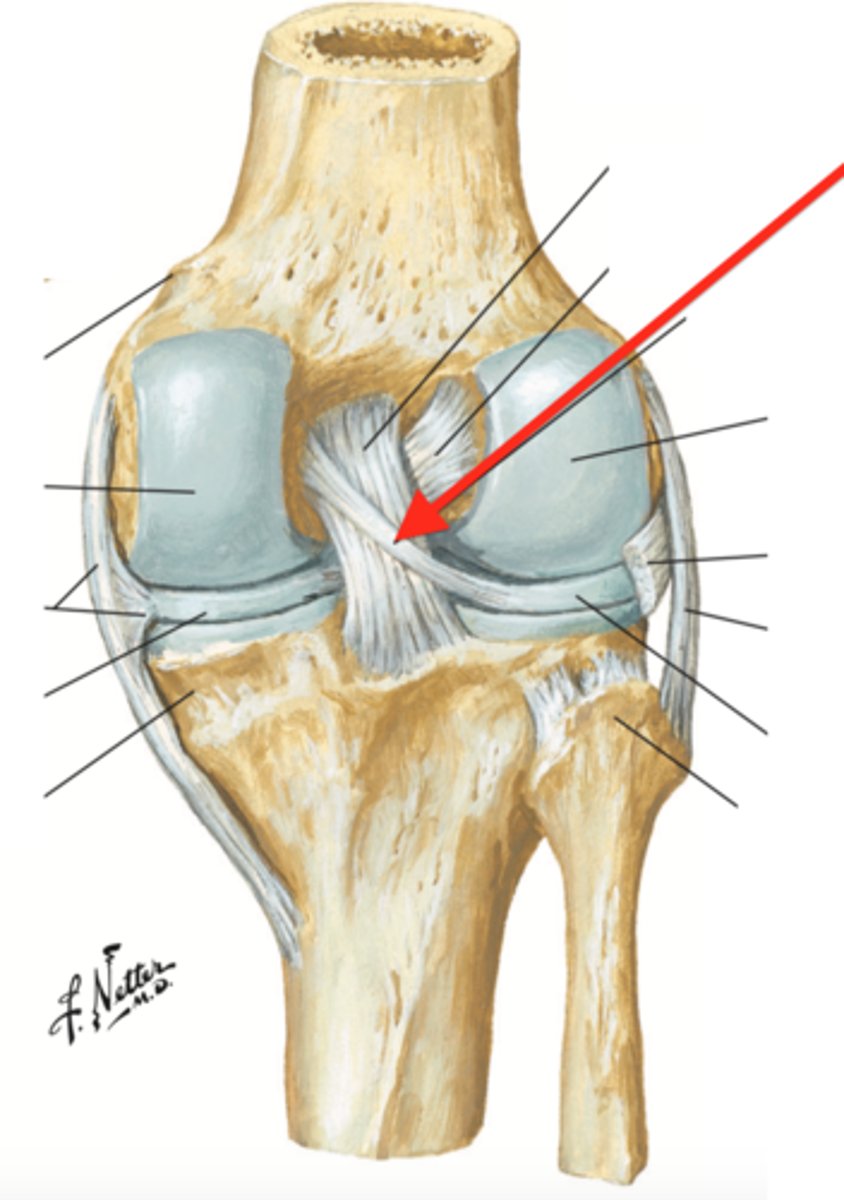
lateral collateral ligament (posterior knee joint)
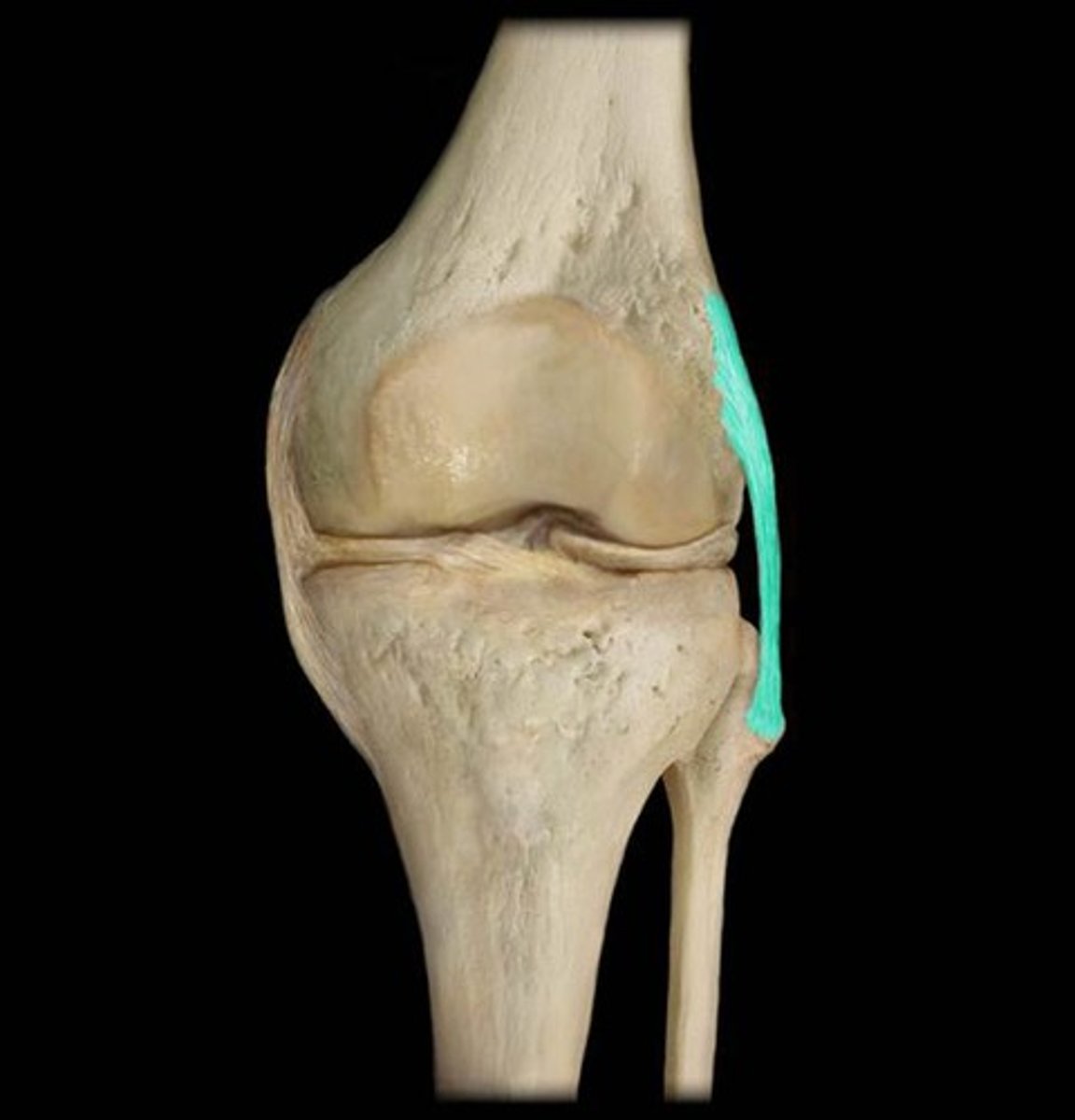
lateral meniscus (posterior knee joint)
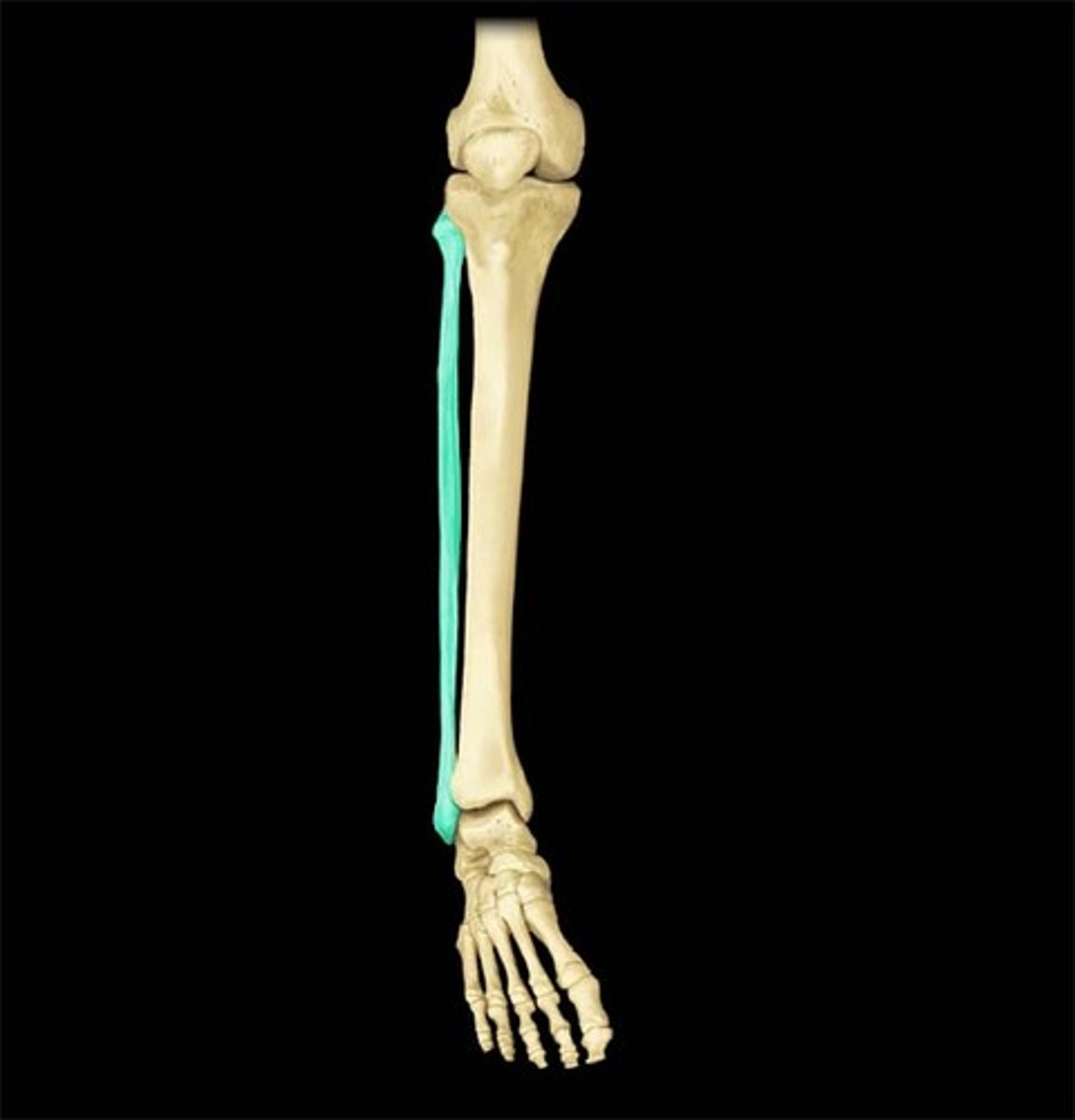
fibula
quadriceps tendon (anterior knee joint)
patella
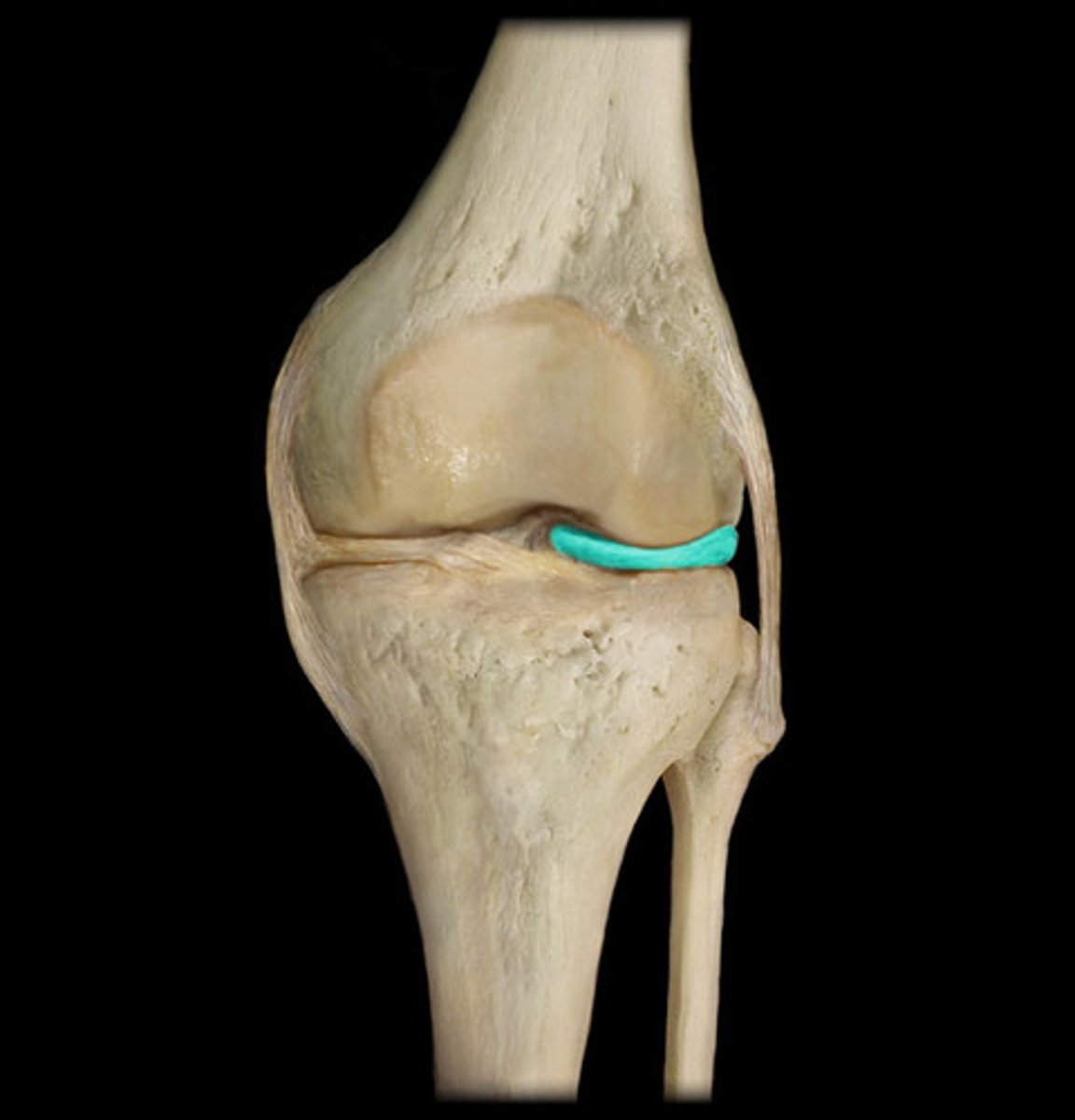
medial meniscus (posterior knee joint)
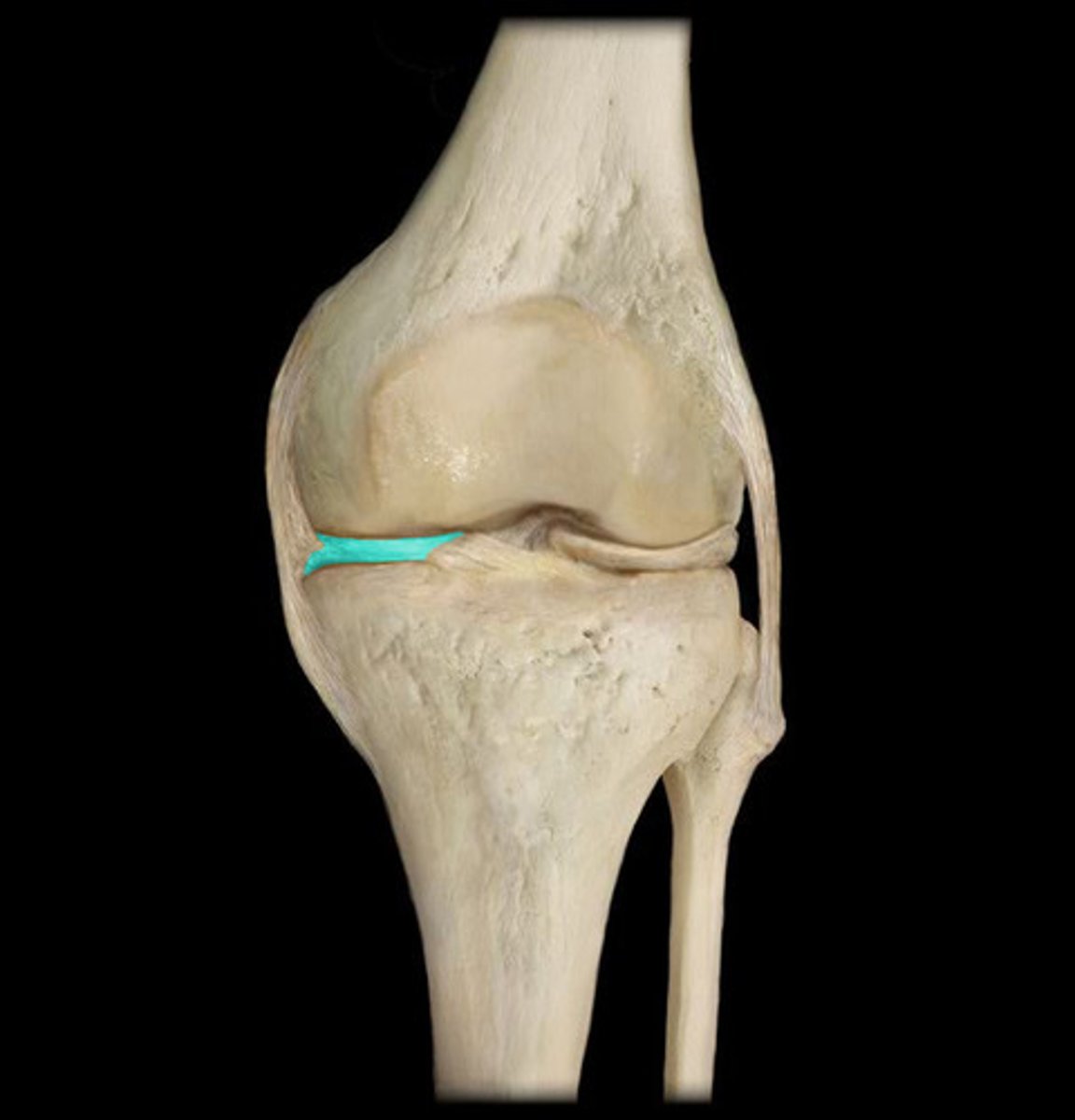
patellar ligament (anterior knee joint)
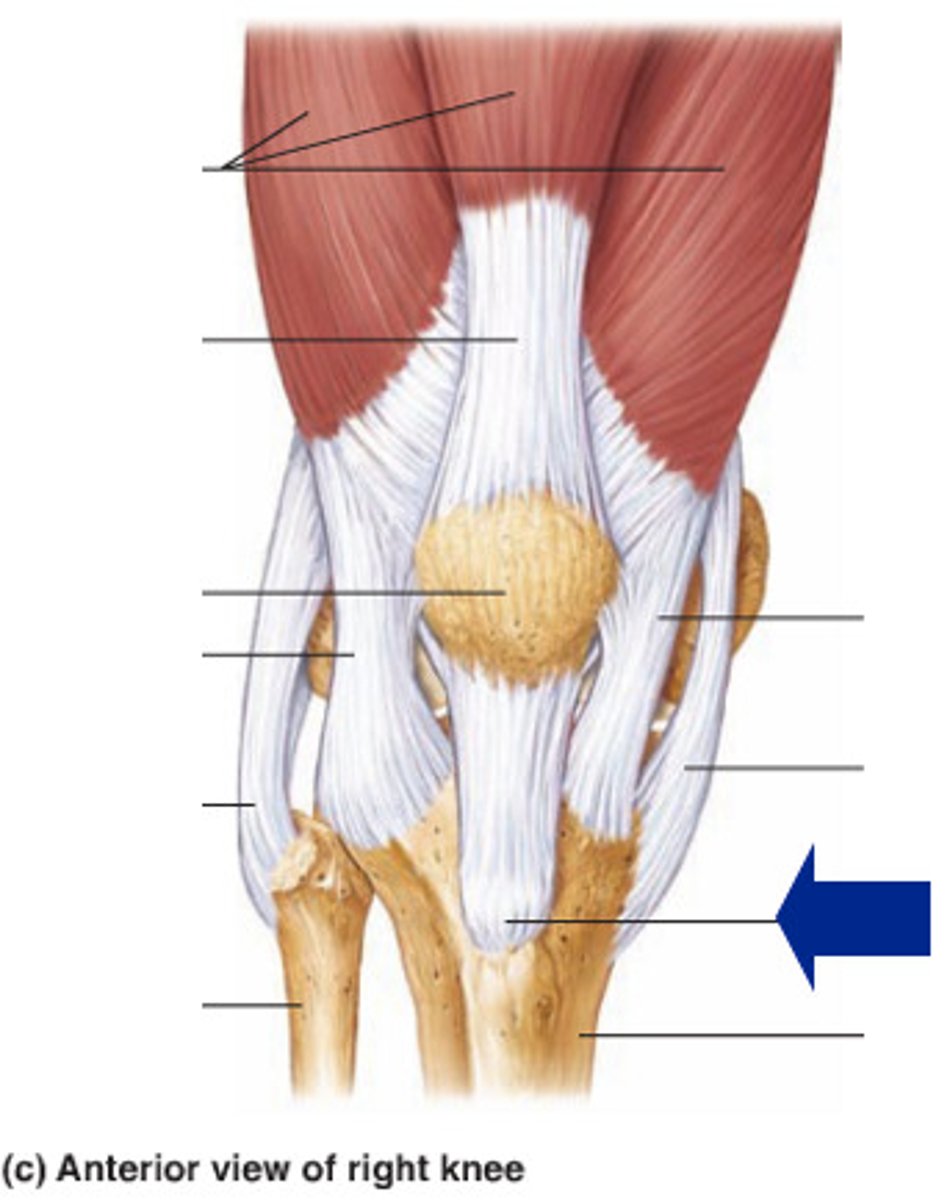
medial collateral ligament (anterior knee joint)
tibia
posterior cruciate ligament (anterior knee joint)
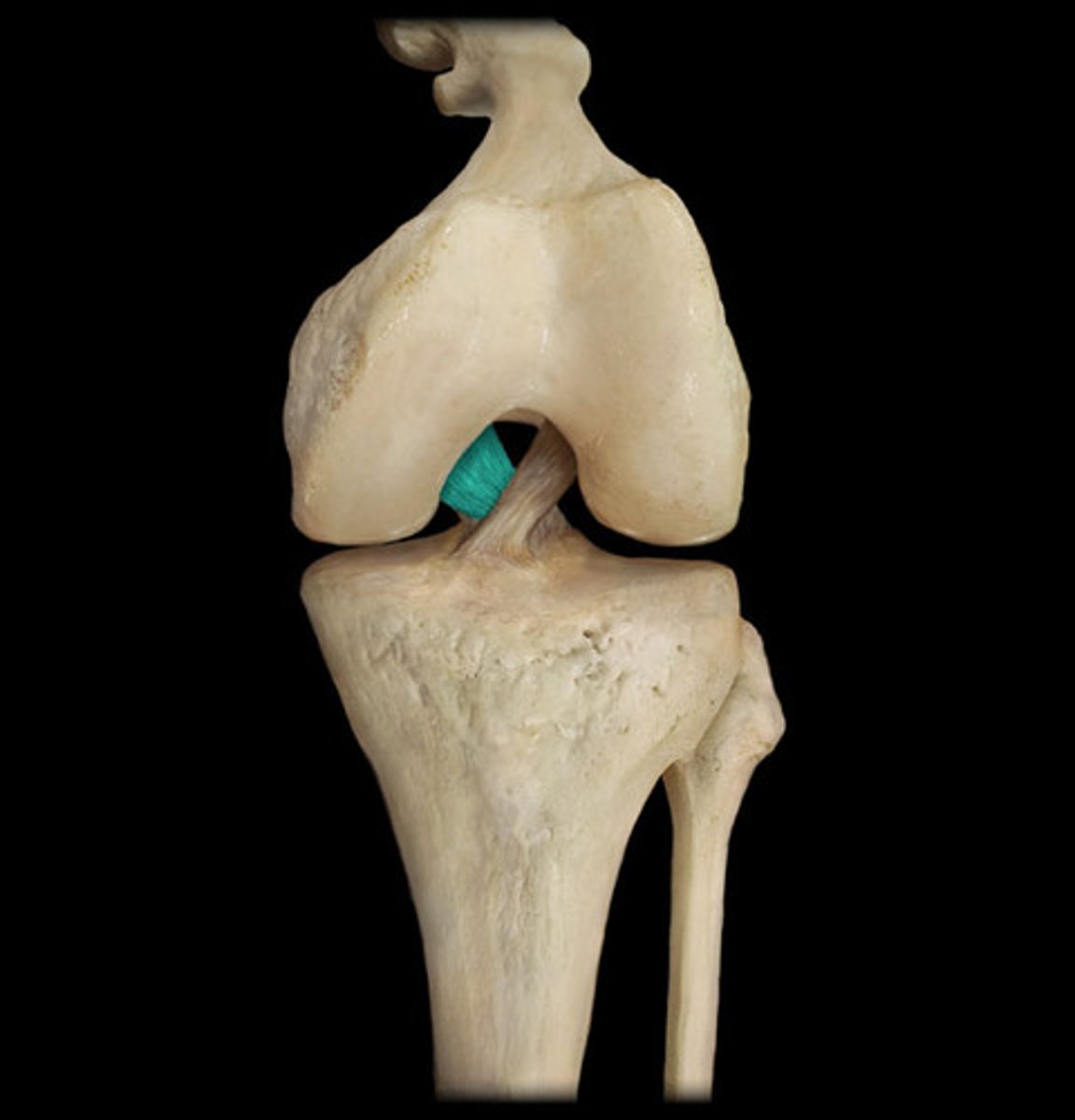
anterior cruciate ligament (anterior knee joint)
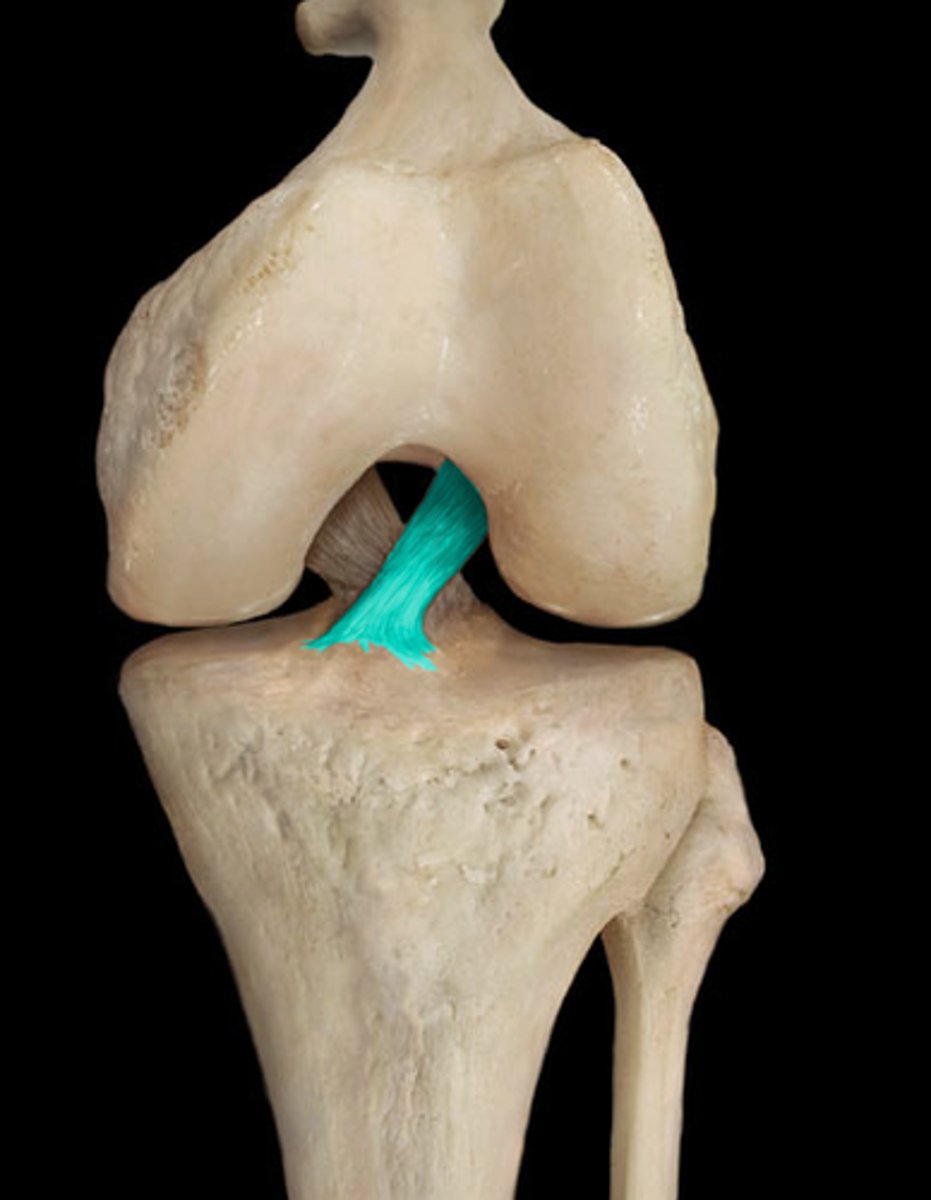
posterior meniscofemoral ligament (posterior knee joint)
injury to a joint
may cause inflammation of the membrane and lead to excessive fluid production (swelling)
hip joint
- multiaxial synovial joint and a ball-and-socket joint
- articulation between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the coxal bone (ilium, ischium, and pubis)
hip dysplasia
- acetabulum develops too shallow and the head of the femur cannot fit properly into coxal bone
- causes femur to dislocate from the hip
- childhood: hip clicks
- adulthood: excessive friction causes arthitis
acetabulum (anterior hip joint)
head of femur

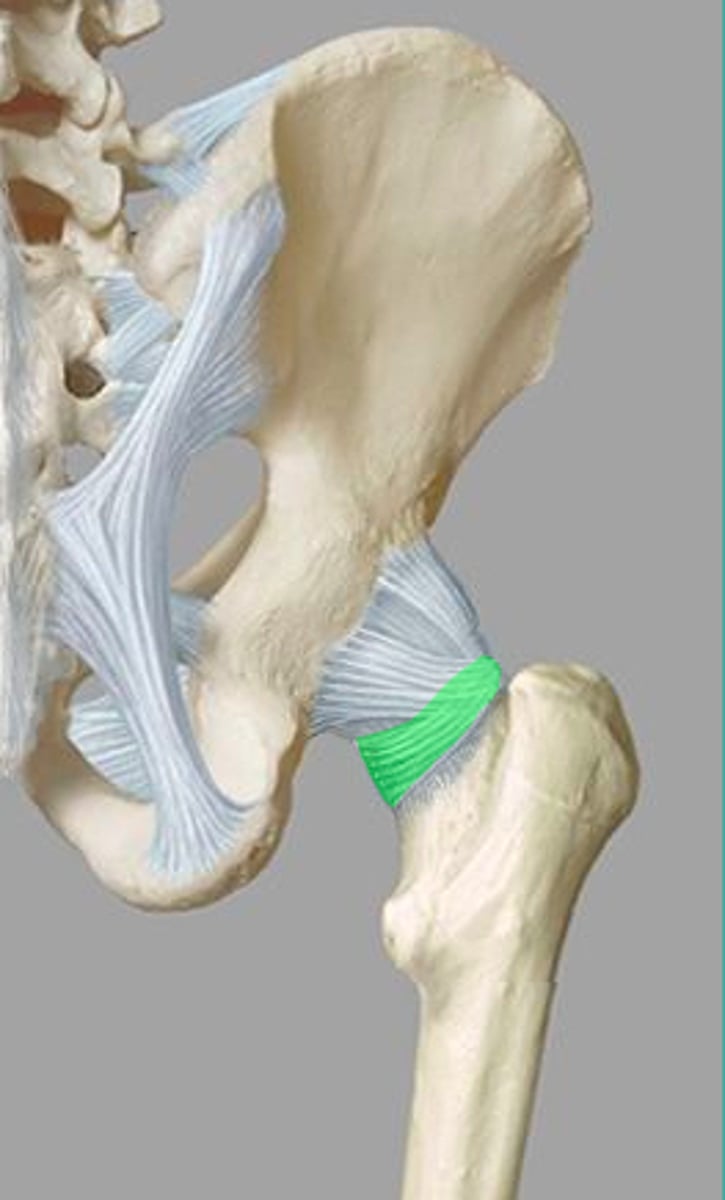
iliofemoral ligament (hip joint)
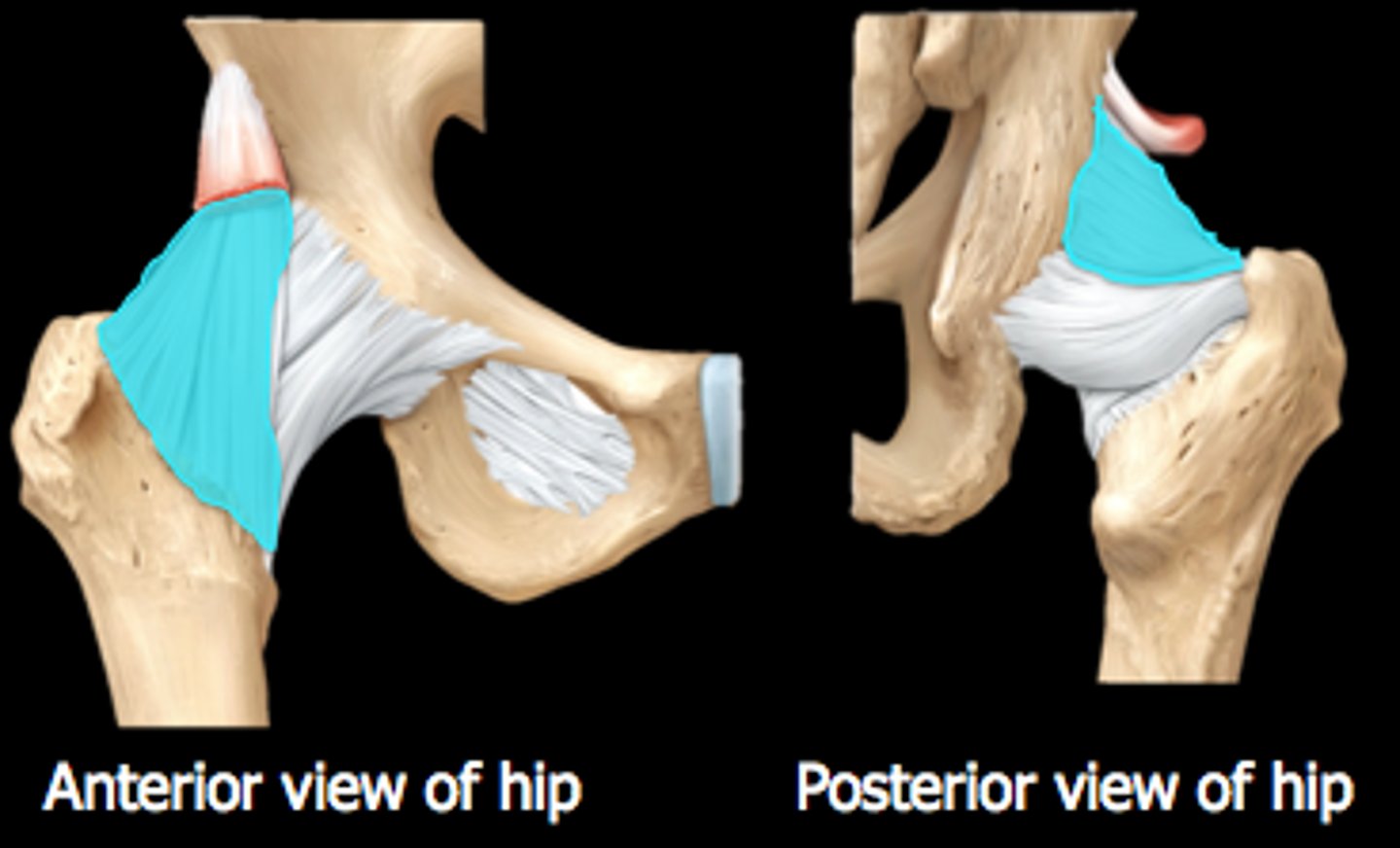
pubofemoral ligament (hip joint)
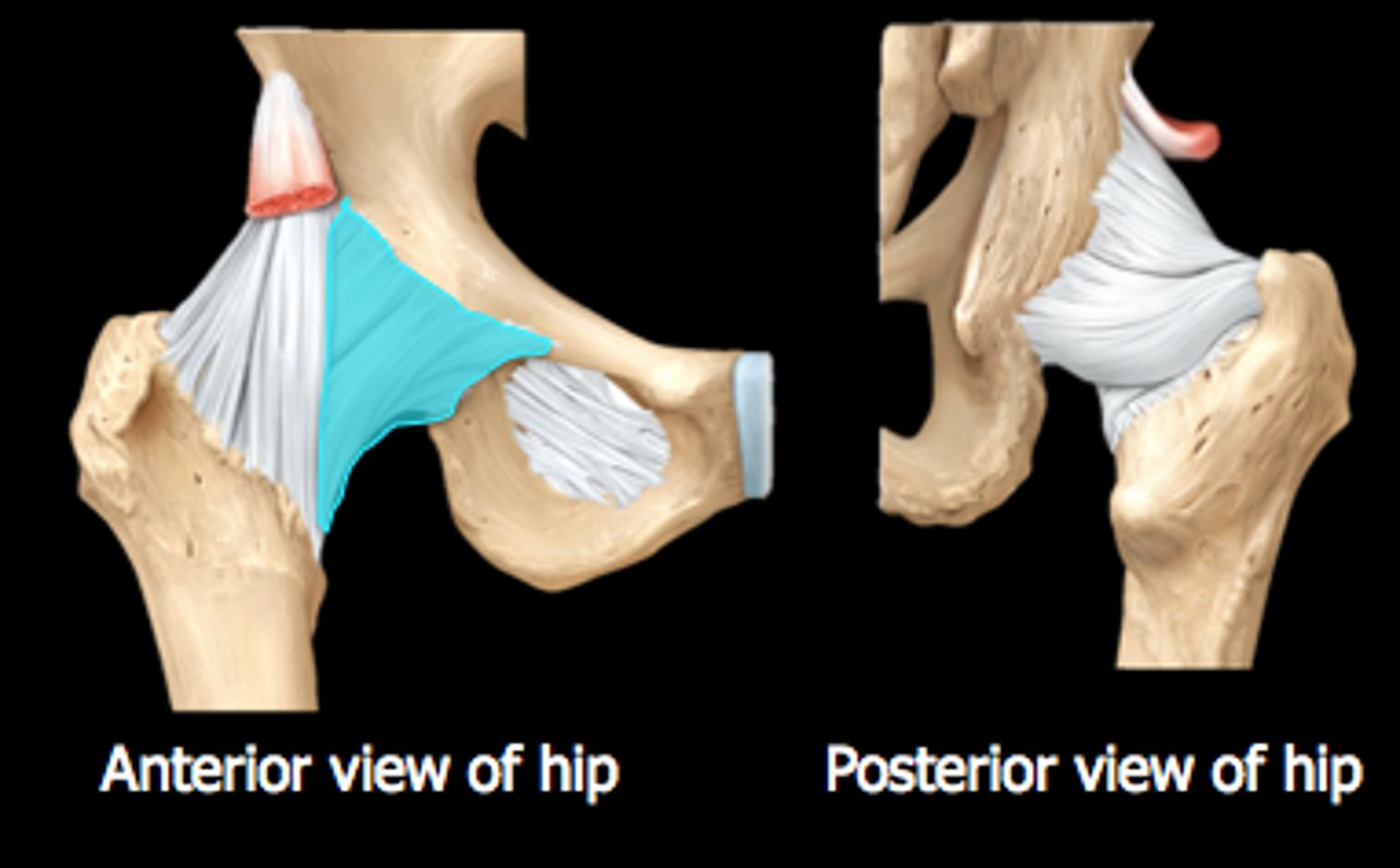
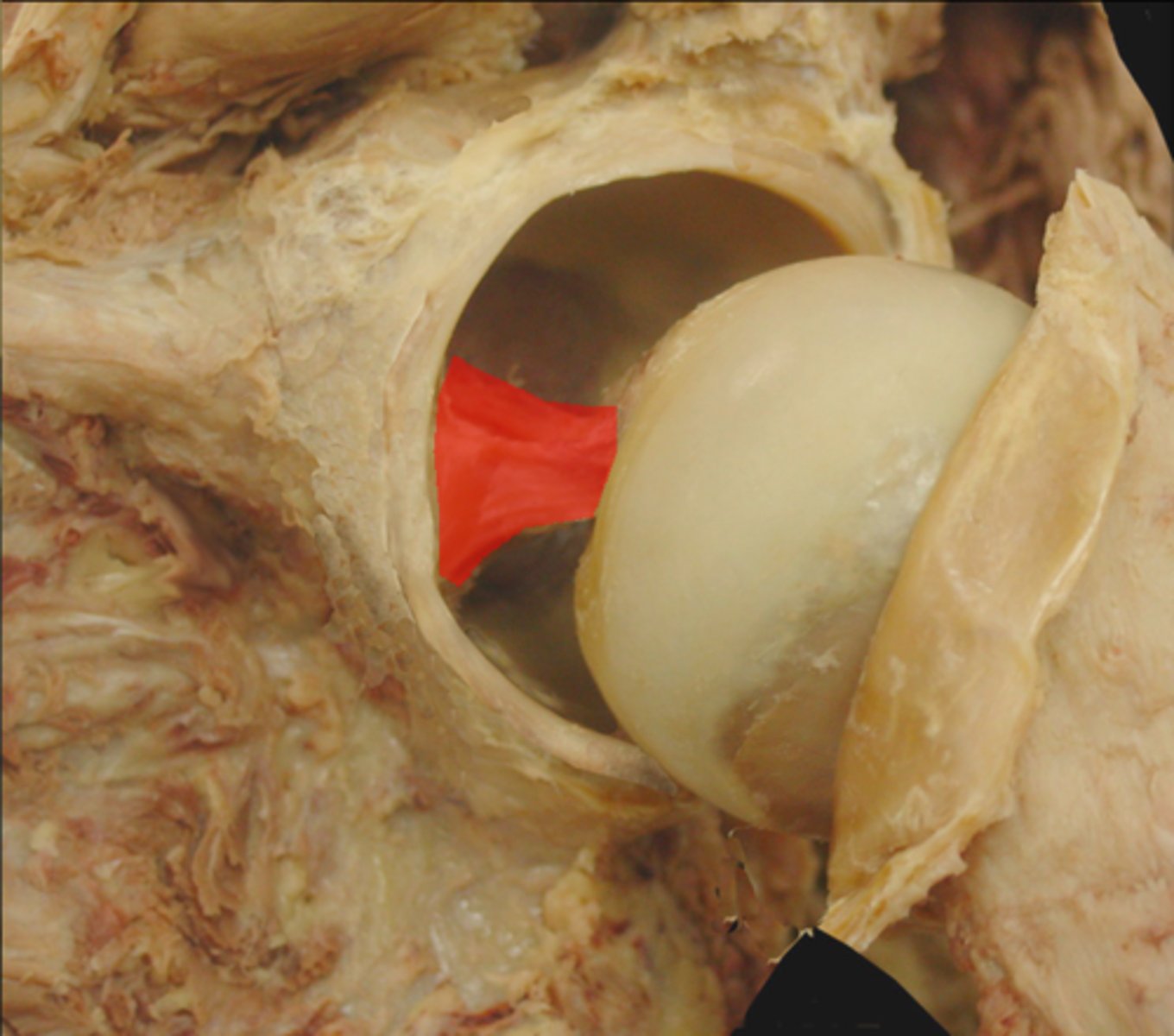
ligamentum teres/ligament of head of femur (hip joint)
inside joint
ischiofemoral ligament (hip joint)
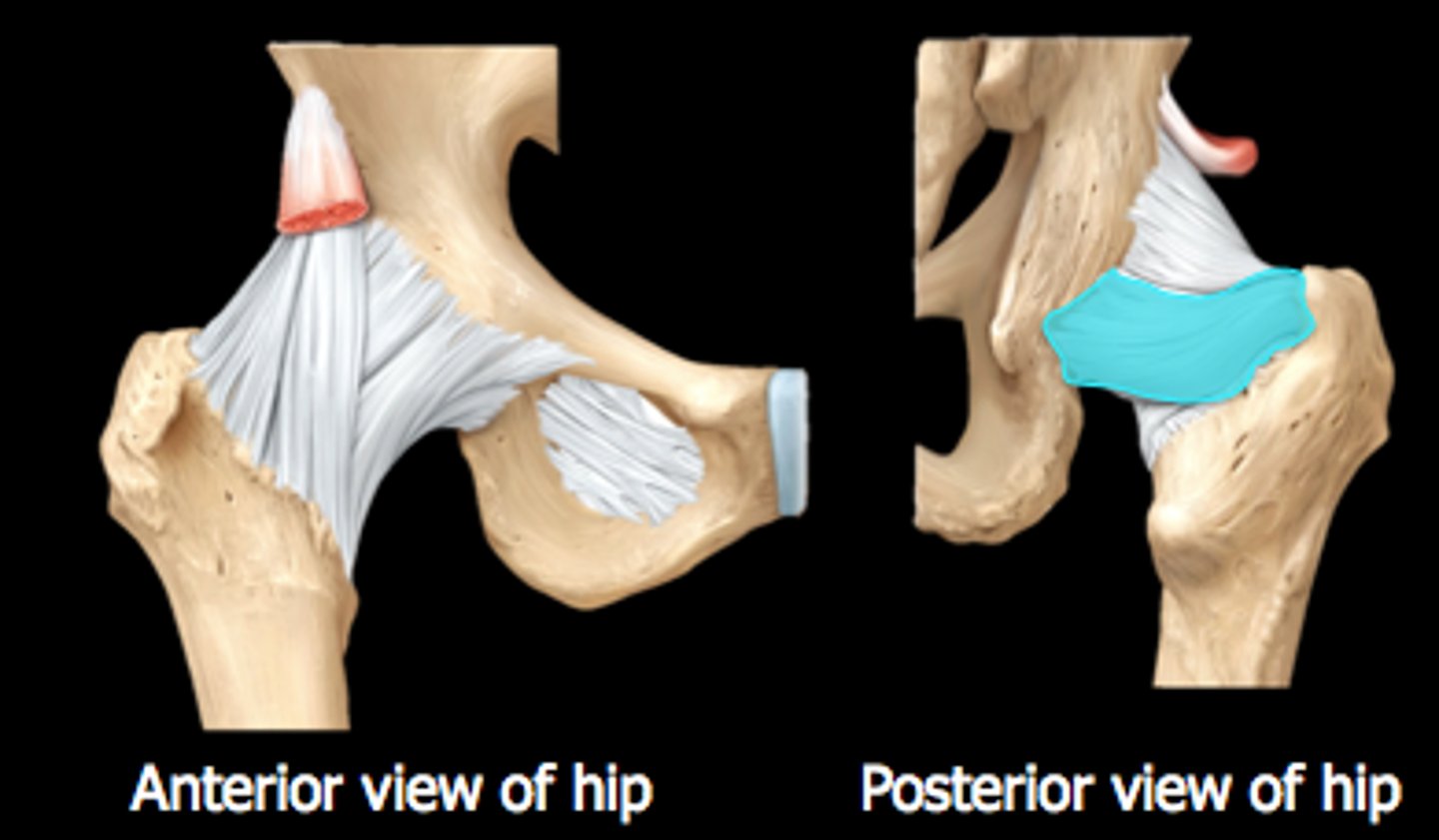
zona orbicularis (posterior hip joint)
periosteum of synovial joint
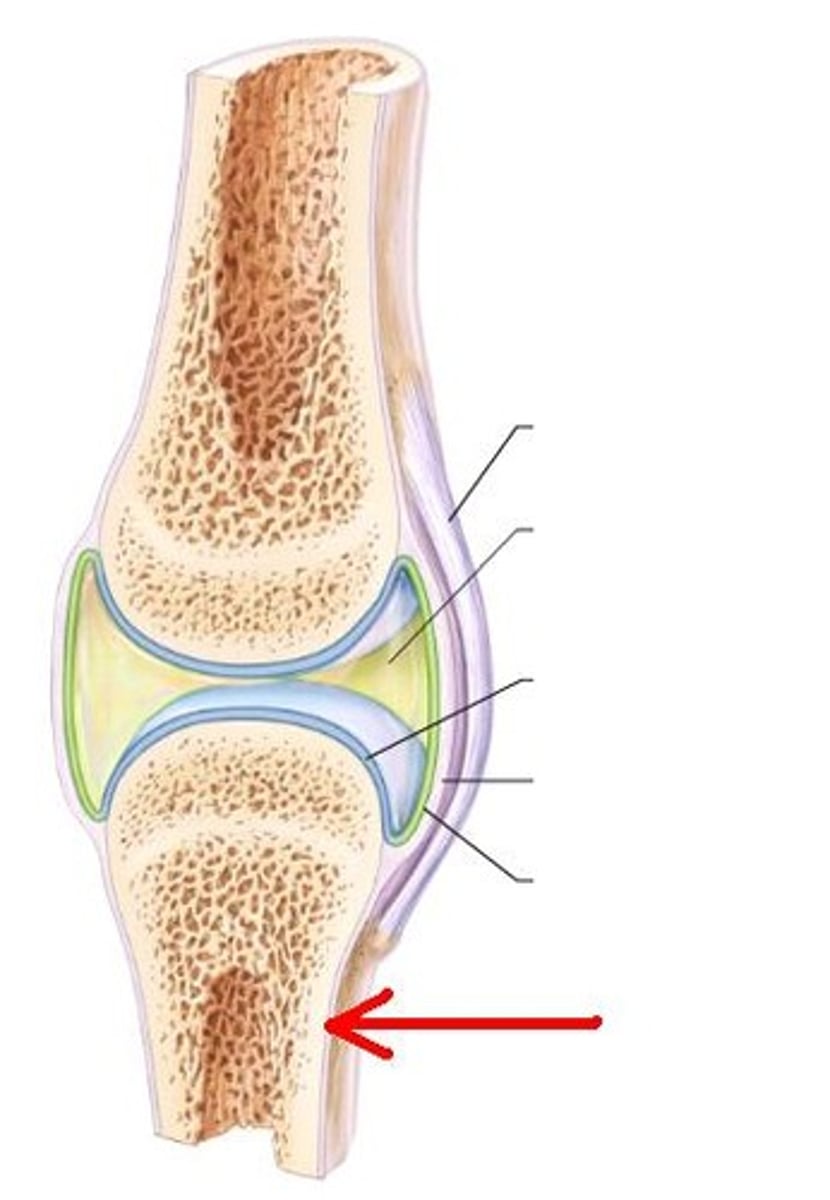
epiphysis of synovial joint
look at bottom box on the left
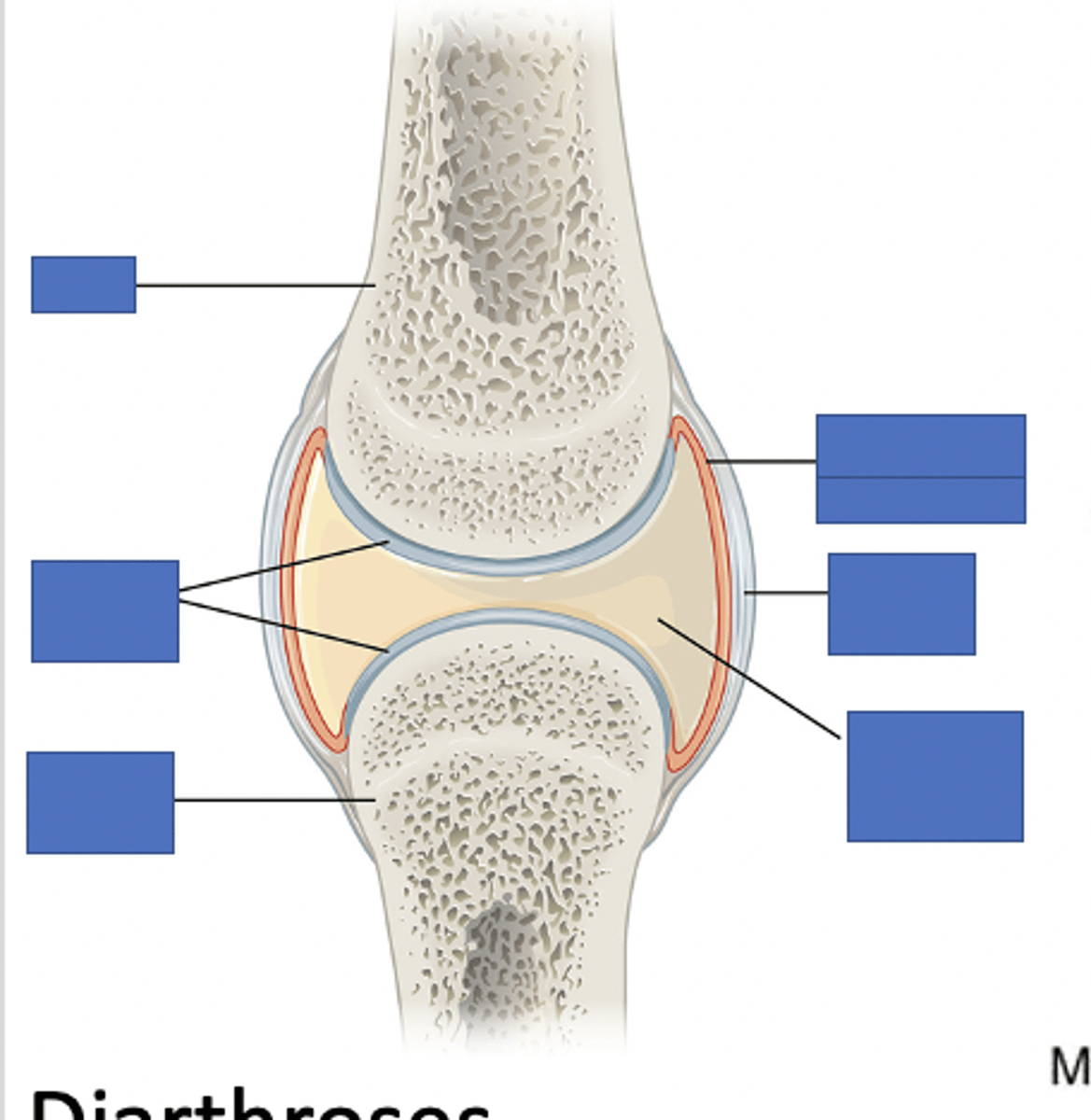
fibrous tissue of capsule of synovial joint
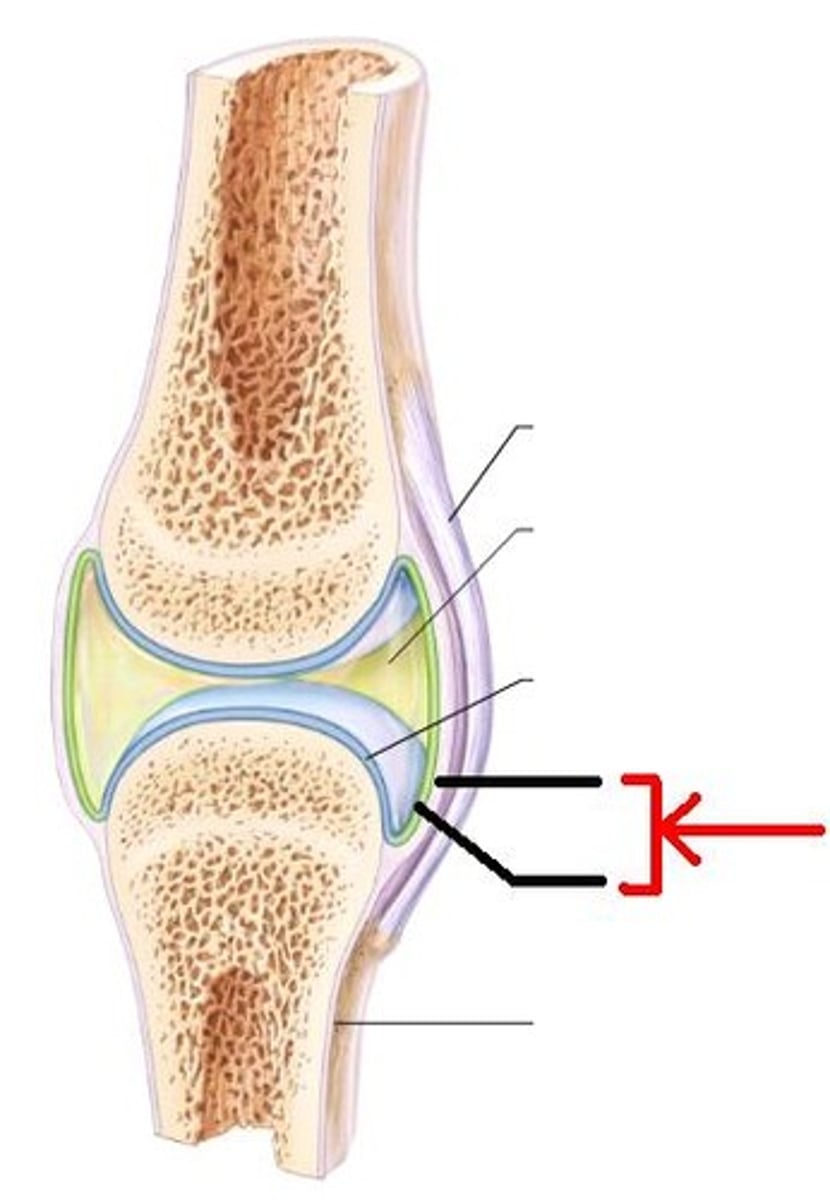
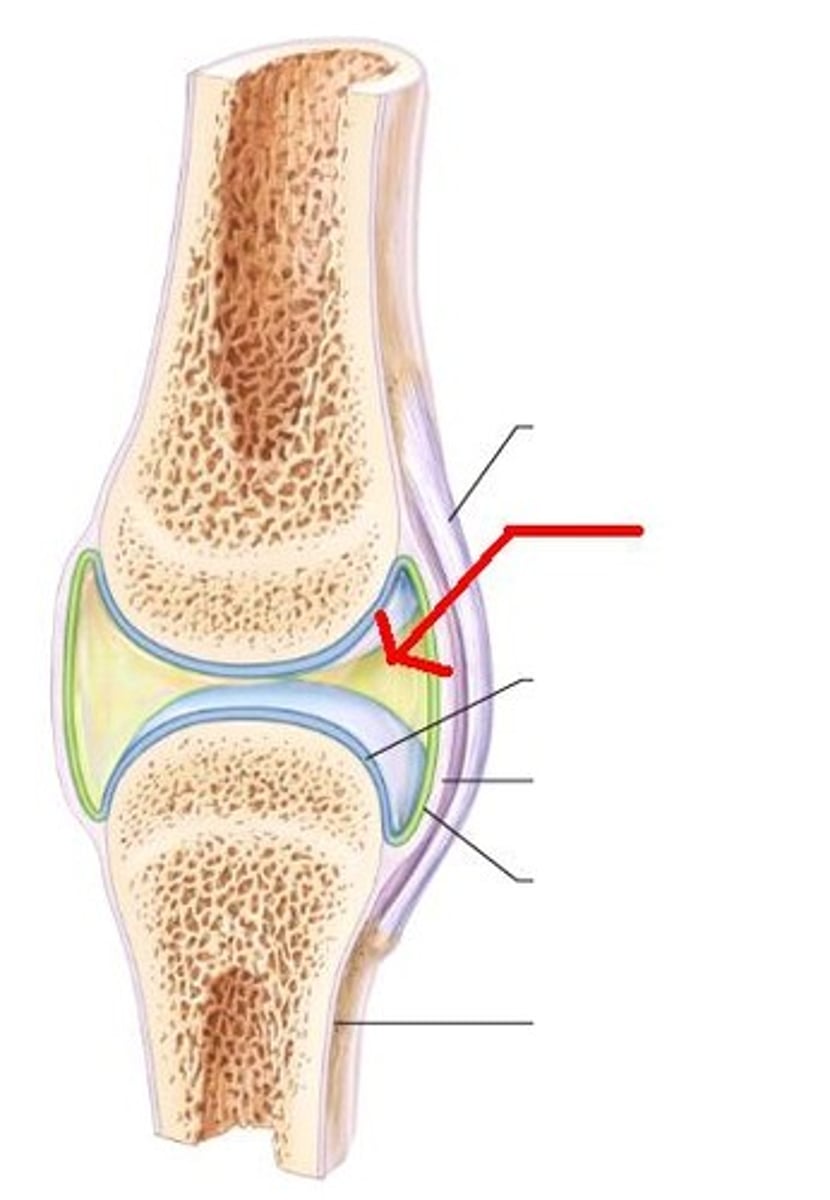
hyaline cartilage of synovial joint
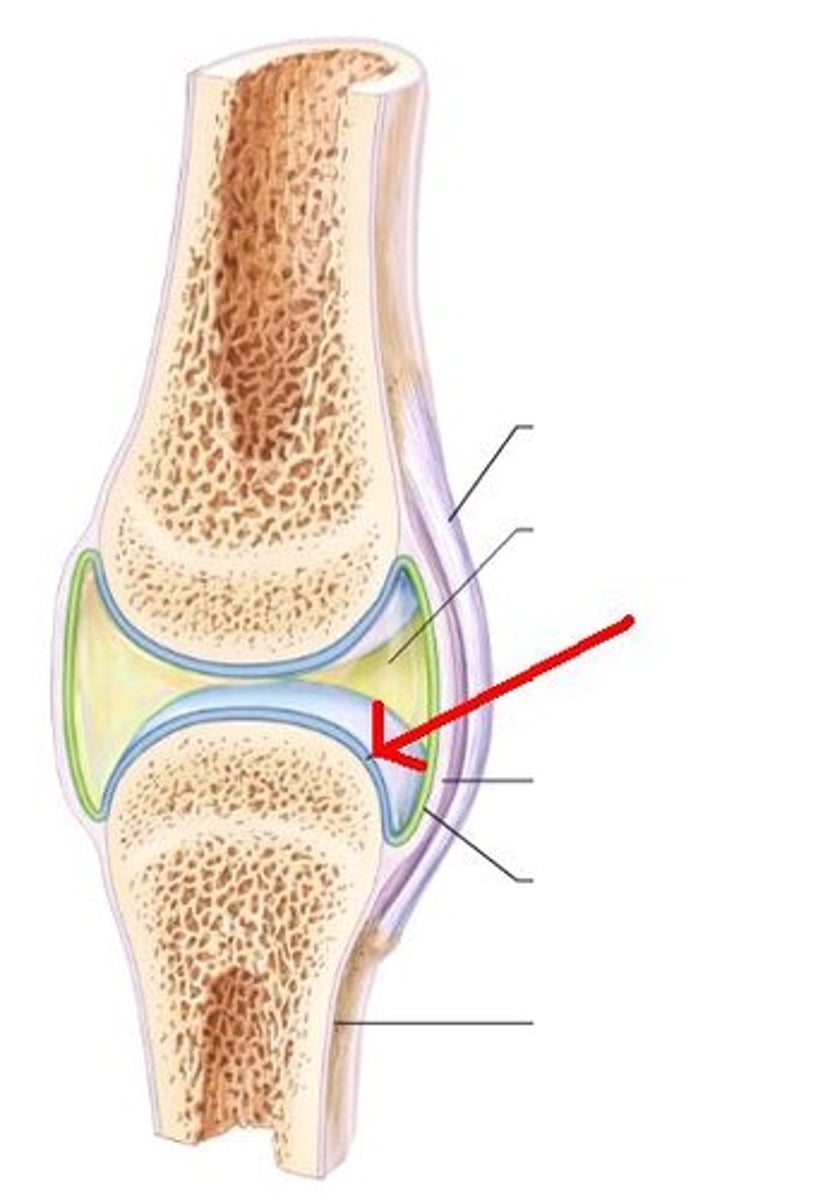
synovial membrane
lines the joint cavity and produces synovial fluid
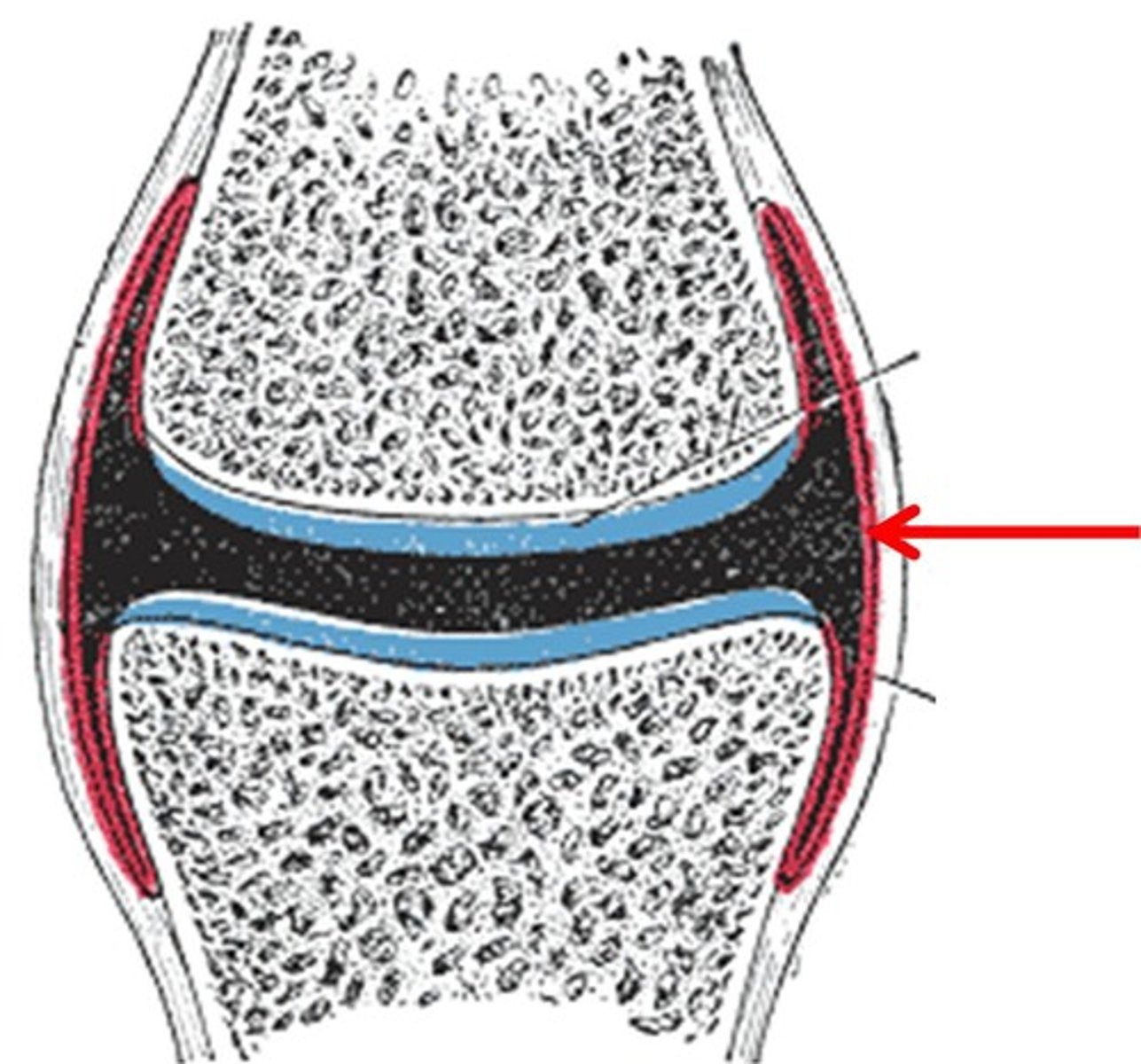
joint cavity of synovial joint
trabeculae of bone of synovial joint
focus on D
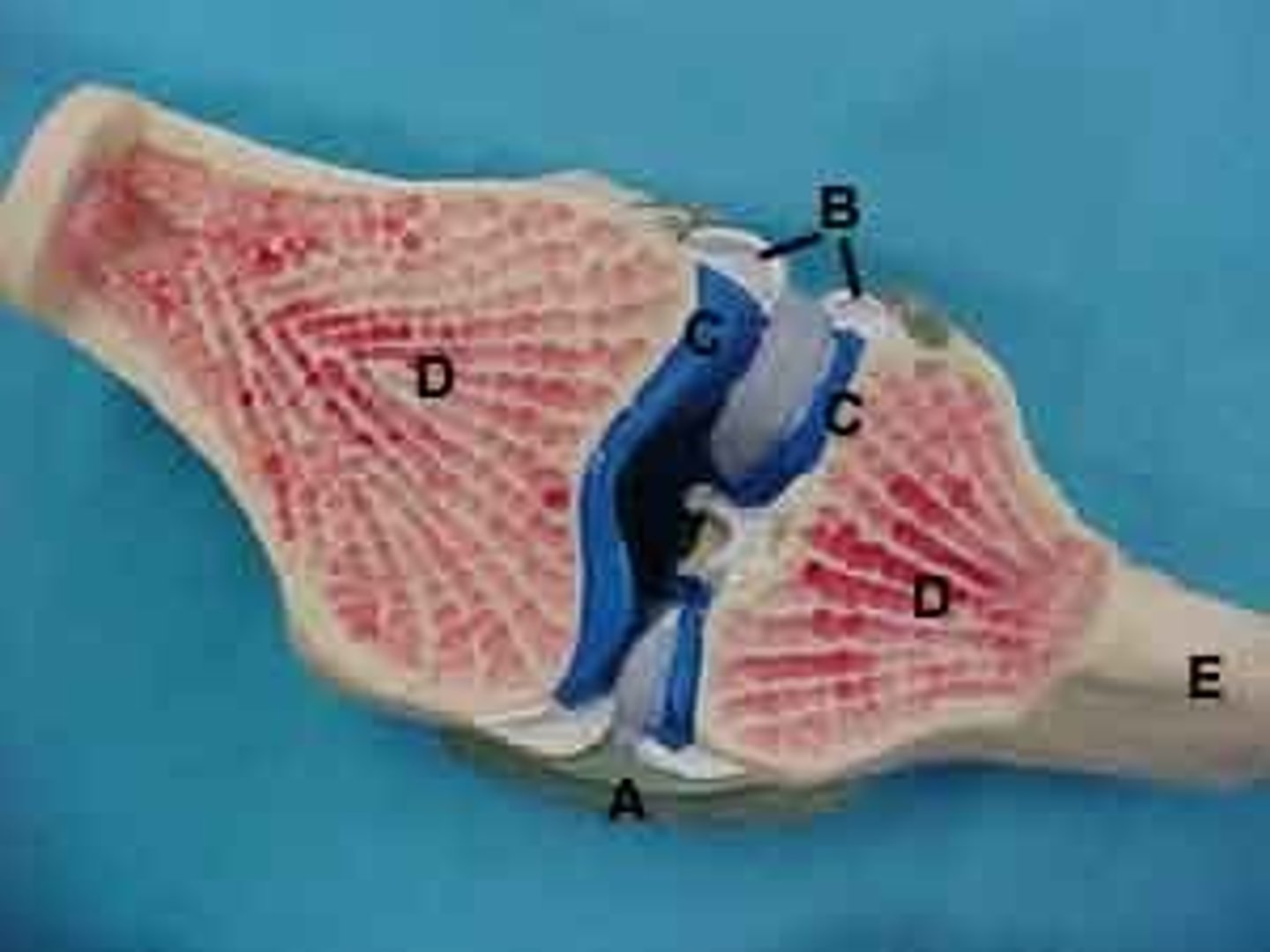
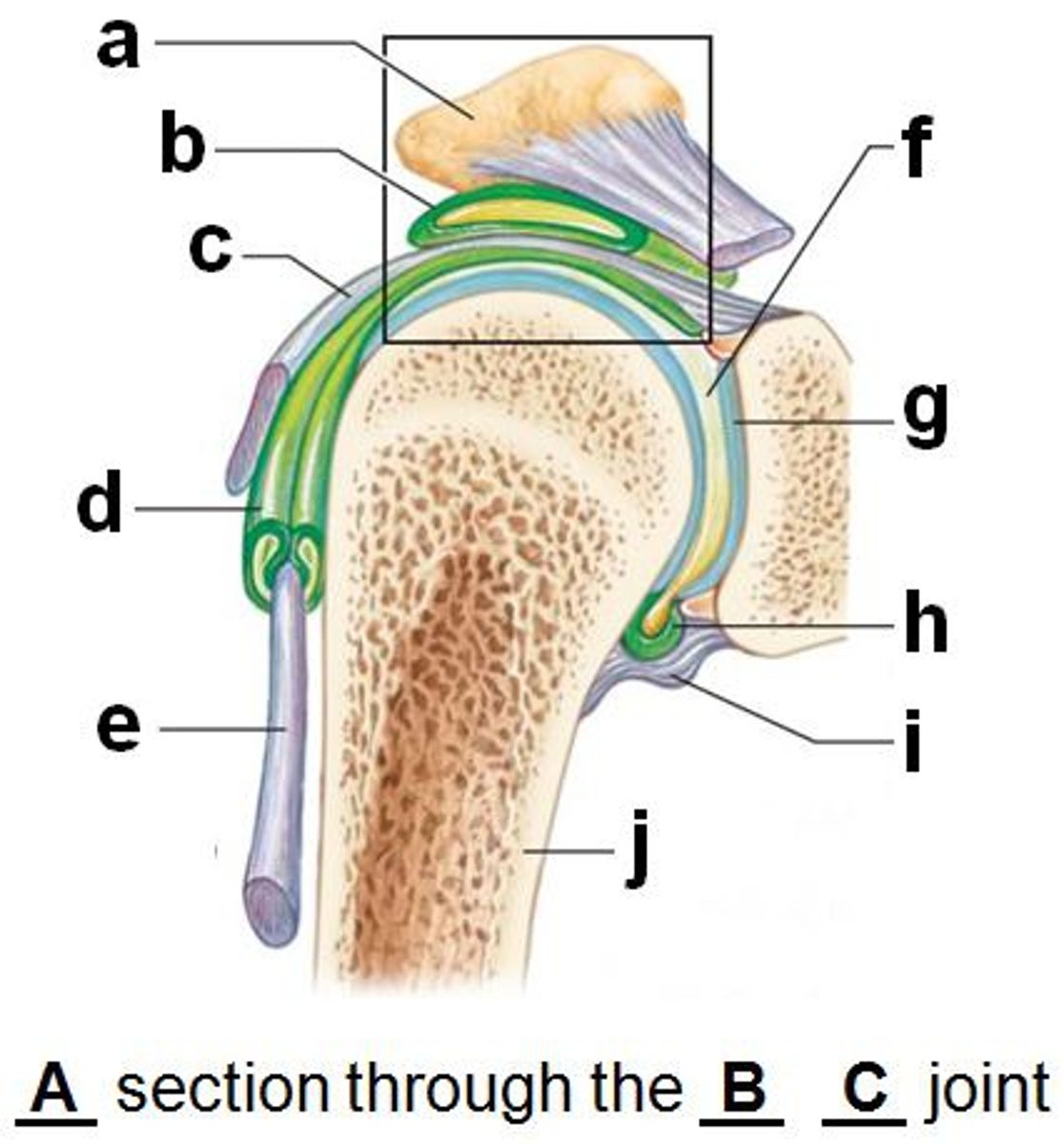
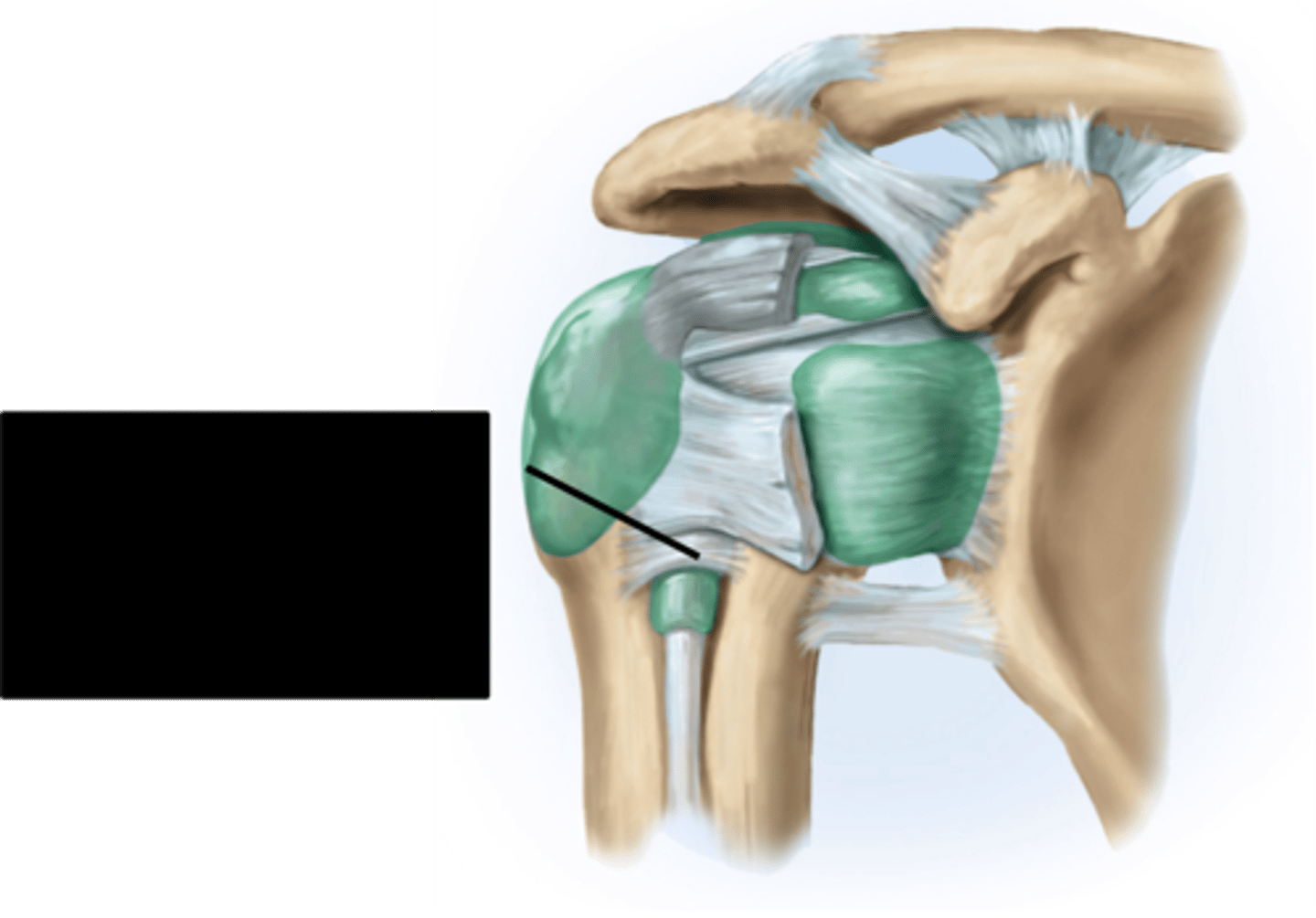
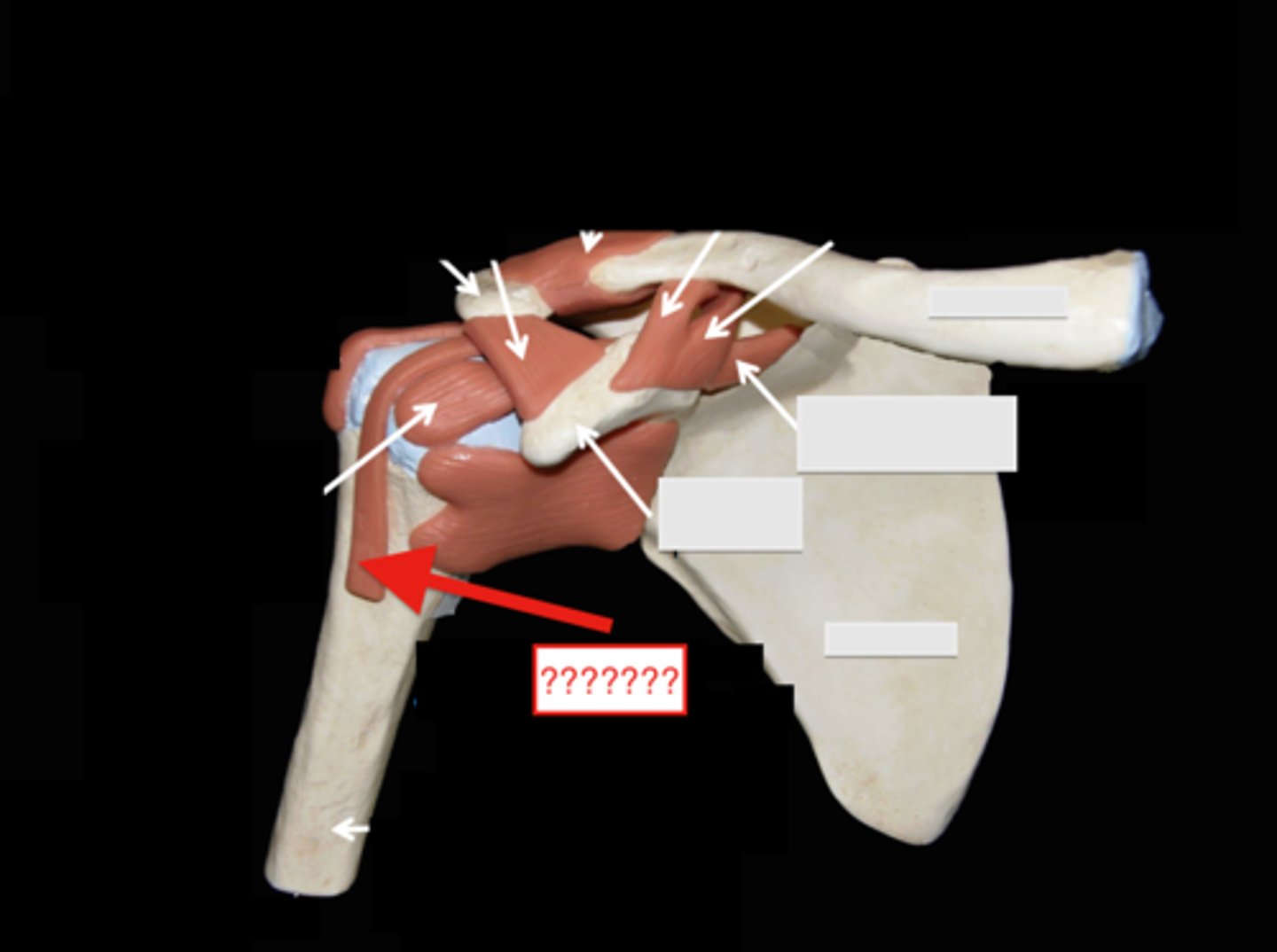
shoulder joint
- multiaxial synovial joint and ball-and-socket joint
- ligaments and tendons across the joint are designed to keep the arm connected to the scapula
- due to wide range of movements the connections of the ligaments go around the outside of the joint
- rotator cuff muscles are well known for stabilizing; their tension stabilizes the humerus head within the glenoid cavity
acromioclavicular ligament (anterior shoulder joint)
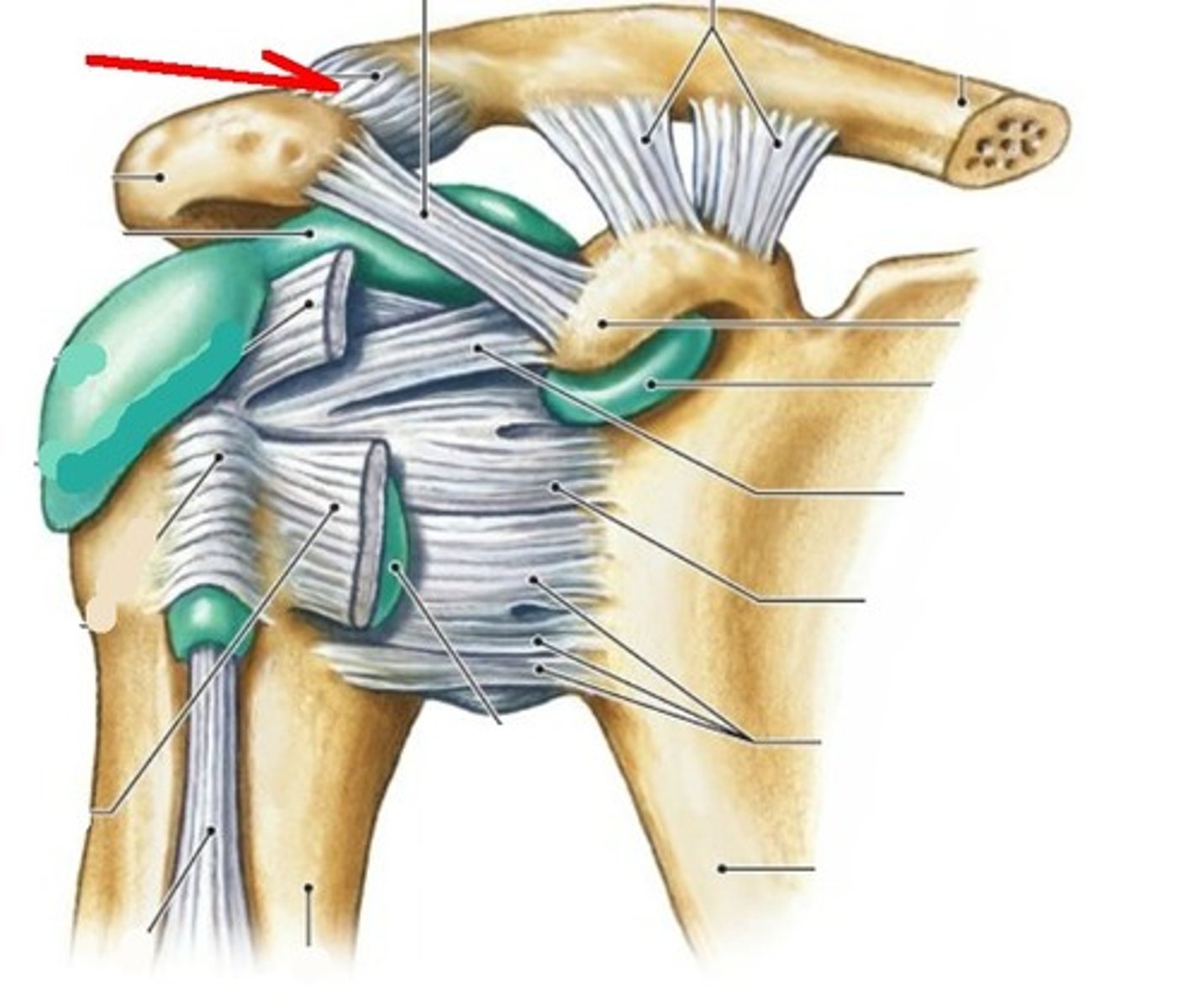
acromion
coracoacromial ligament (anterior shoulder joint)
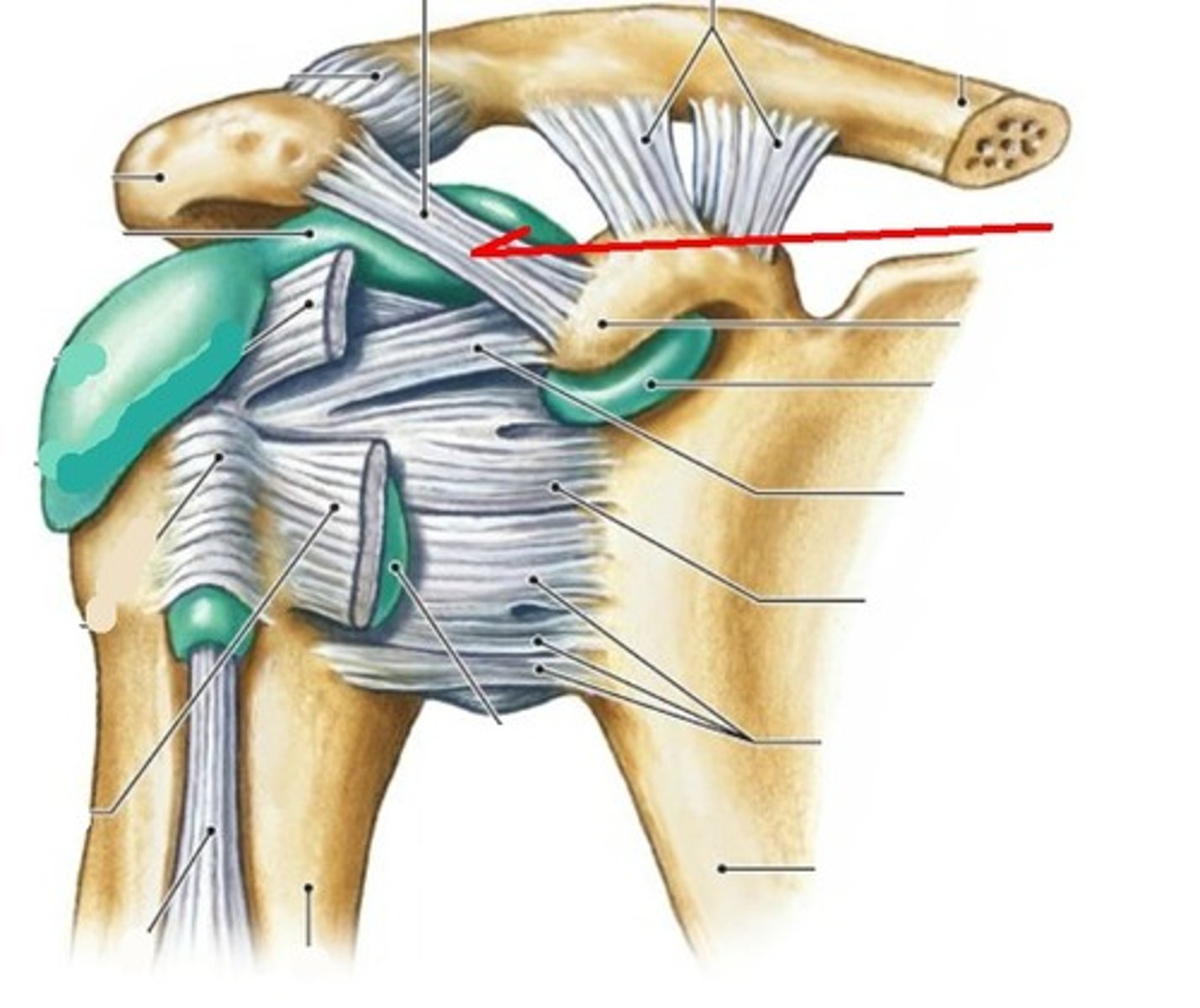
coracohumeral ligament (anterior shoulder joint)
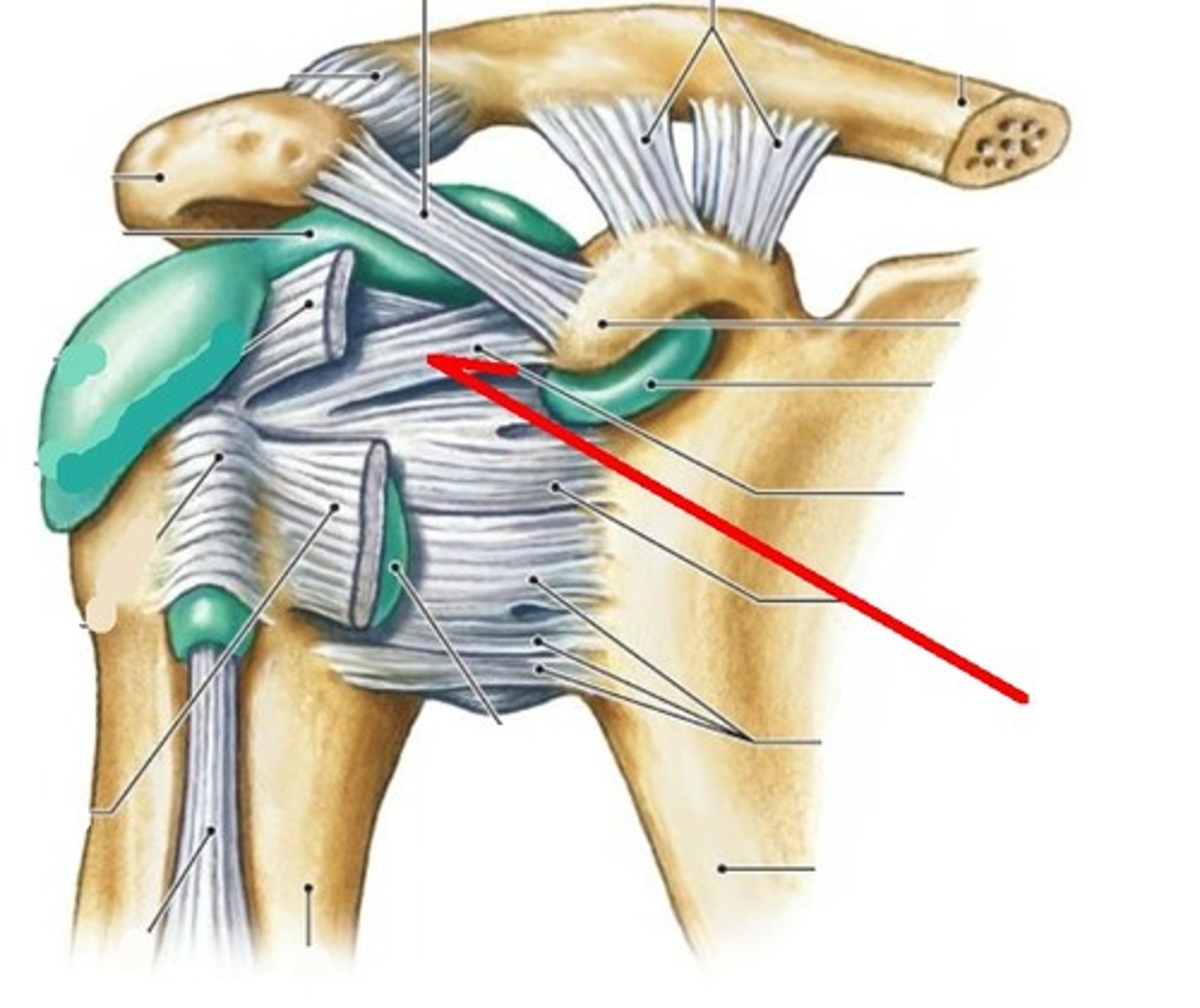
transverse humeral ligament (anterior shoulder joint)
subscapularis tendon - cut (anterior shoulder joint)
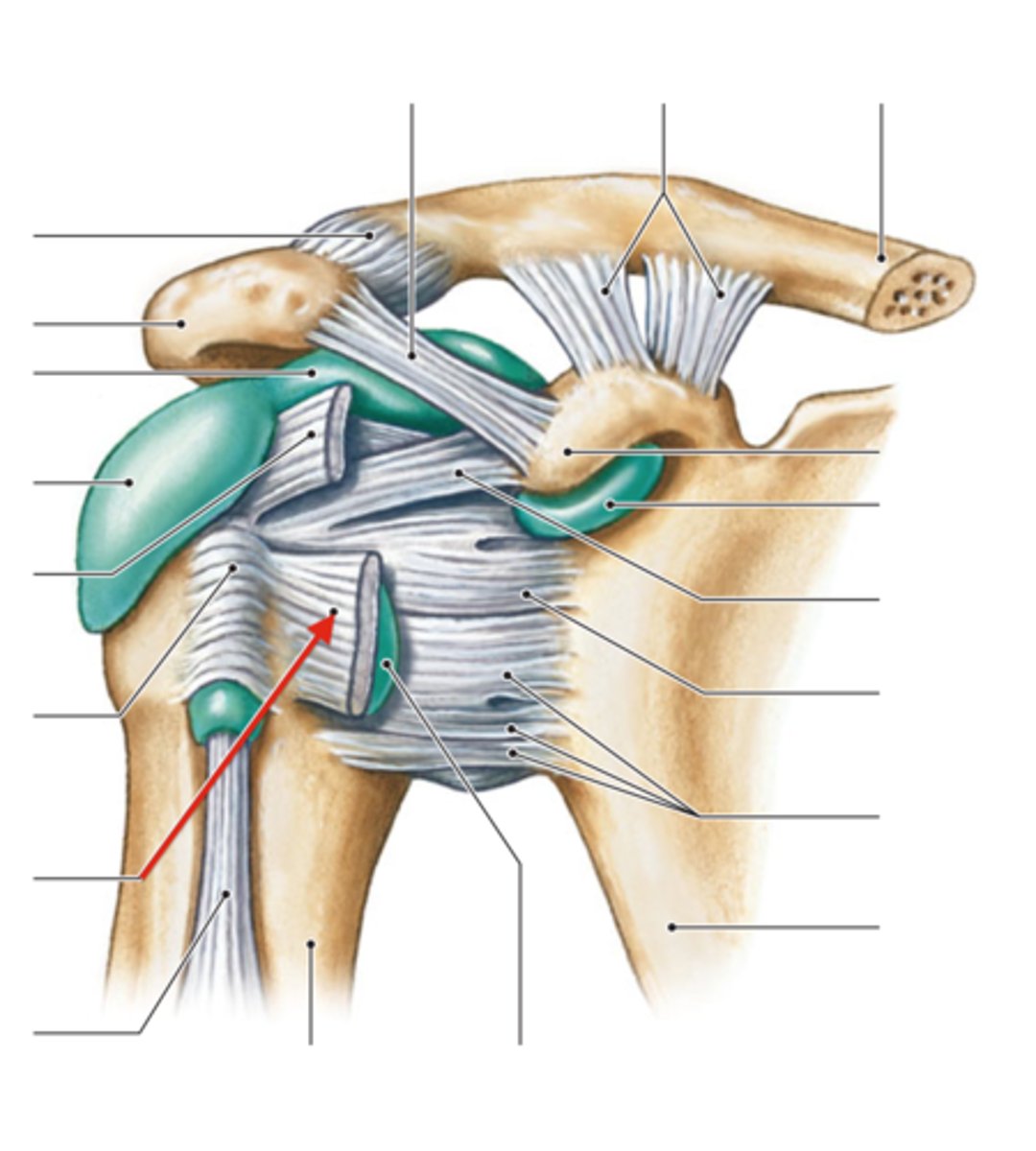
long head of biceps brachii tendon (anterior shoulder joint)
clavicle
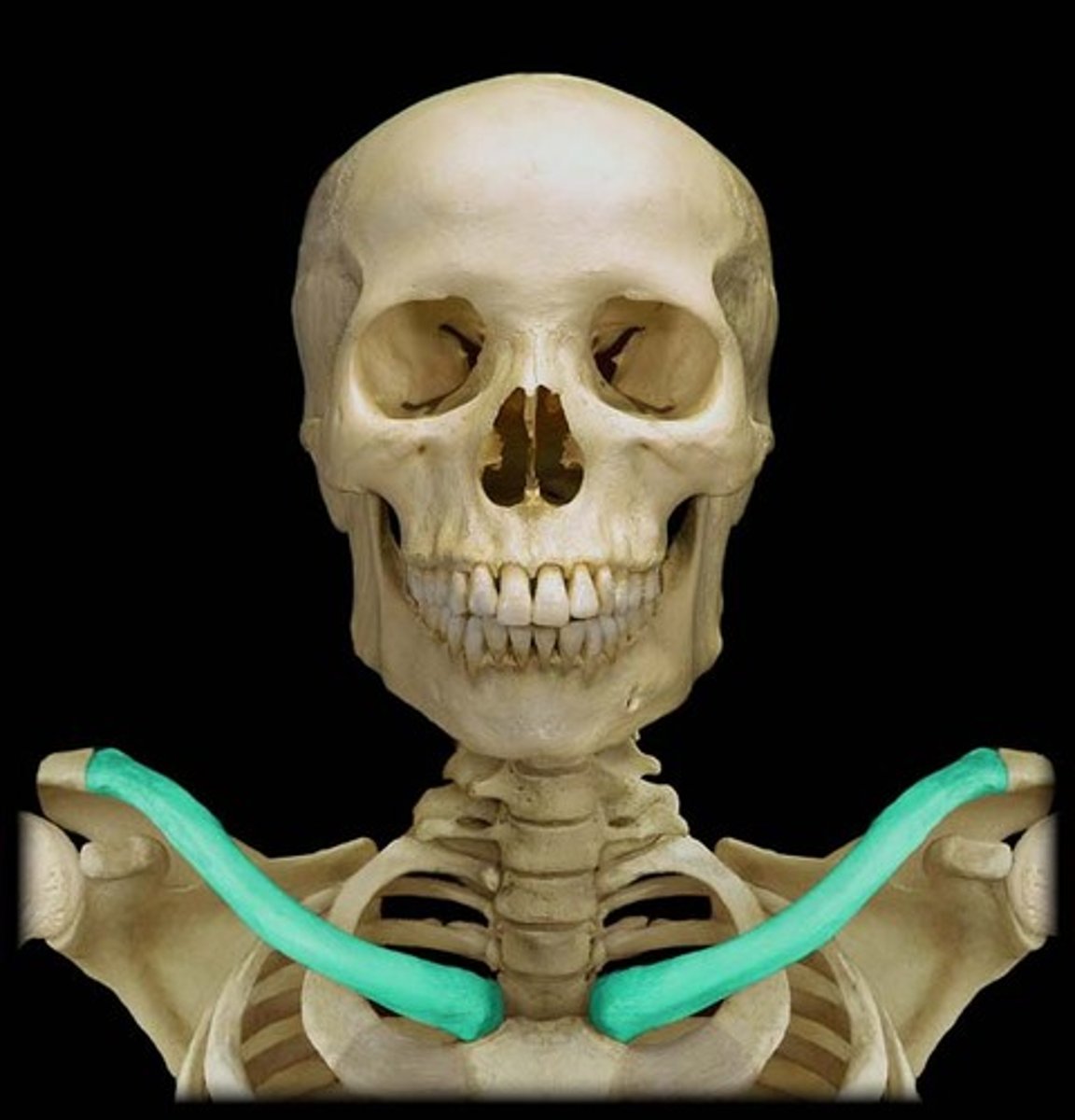
coracoclavicular ligament
look at 2
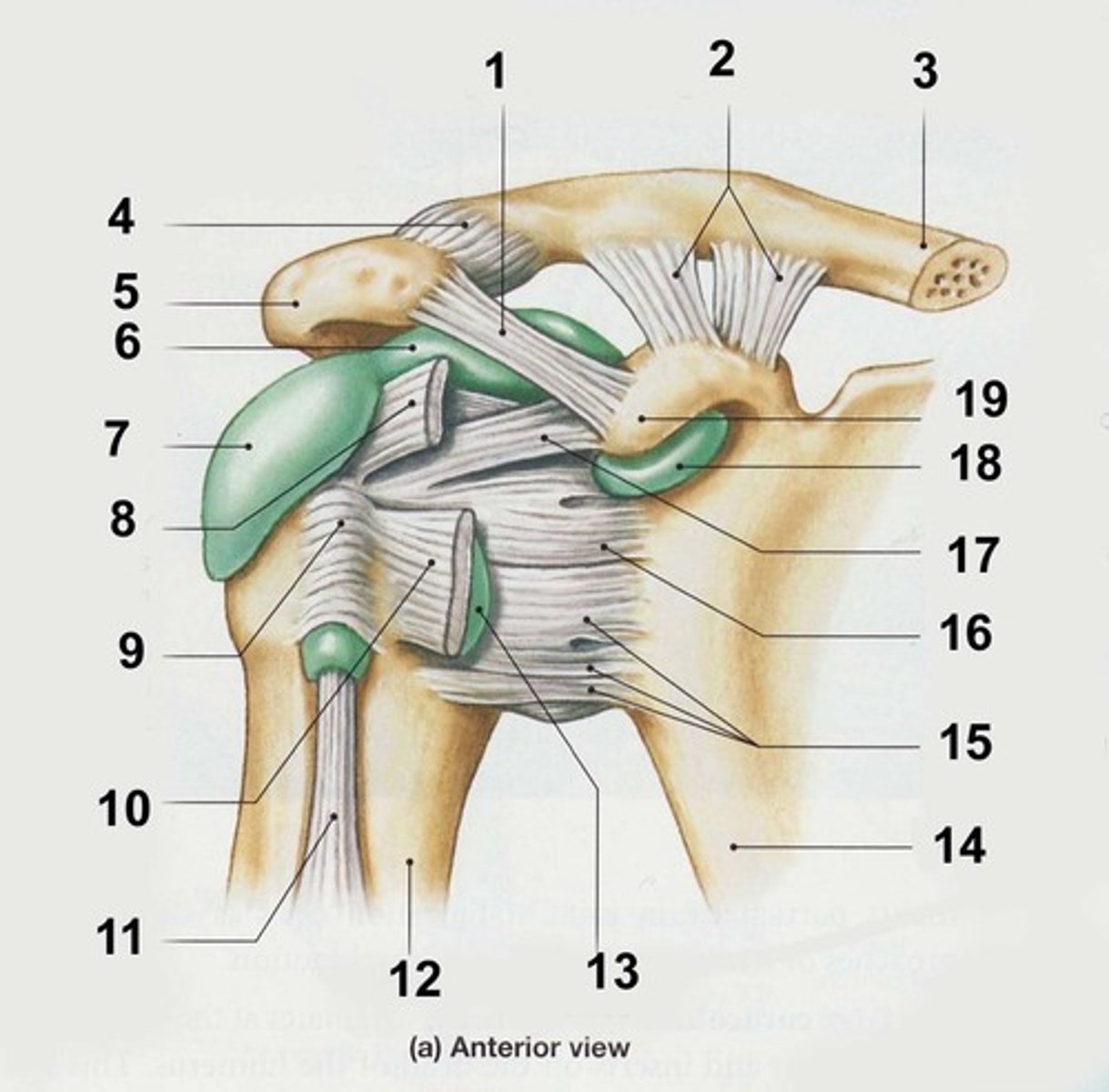
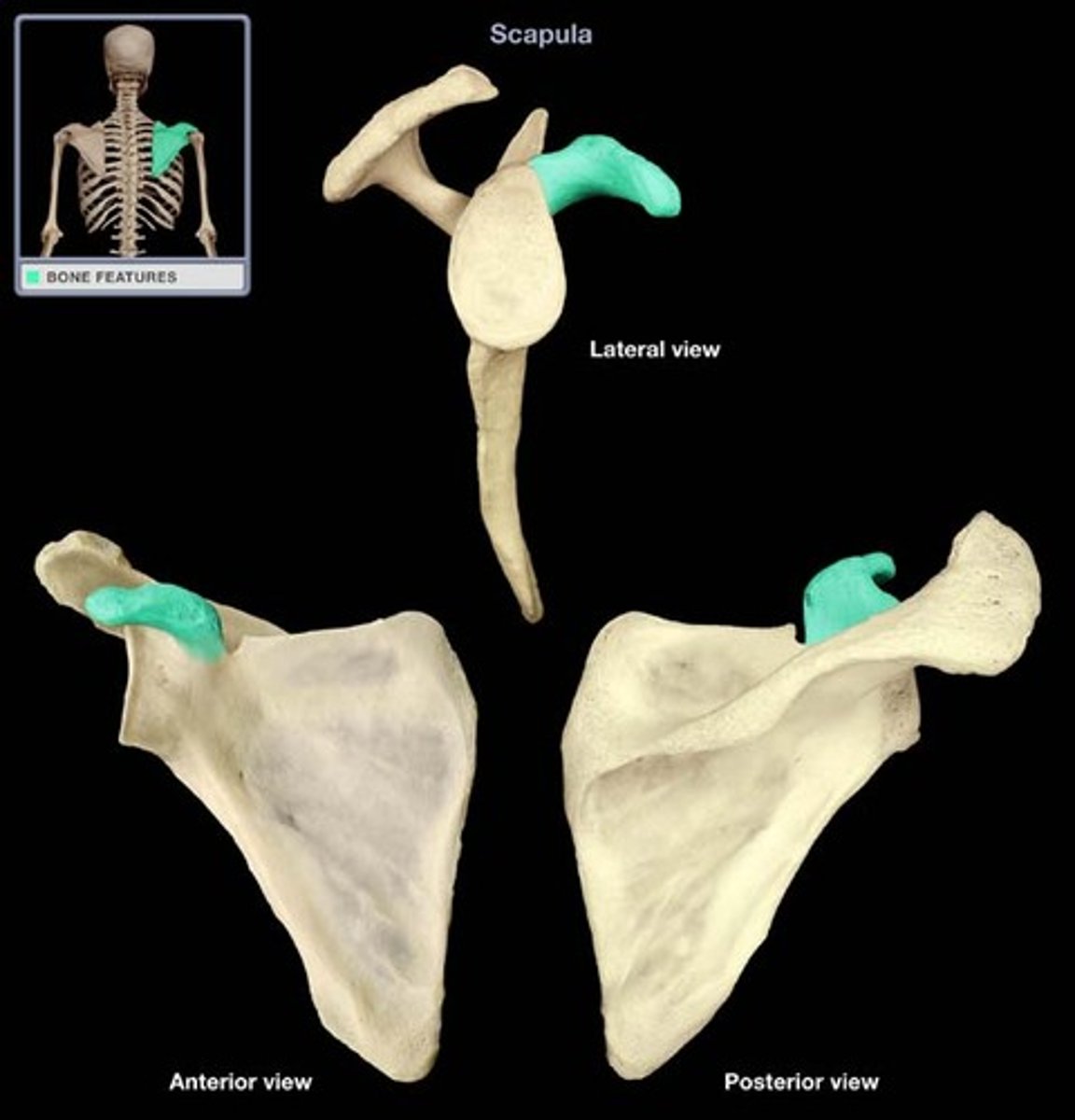
coracoid process of scapula
fibrous layer of articular capsule (anterior shoulder joint, coronal view)
look at j
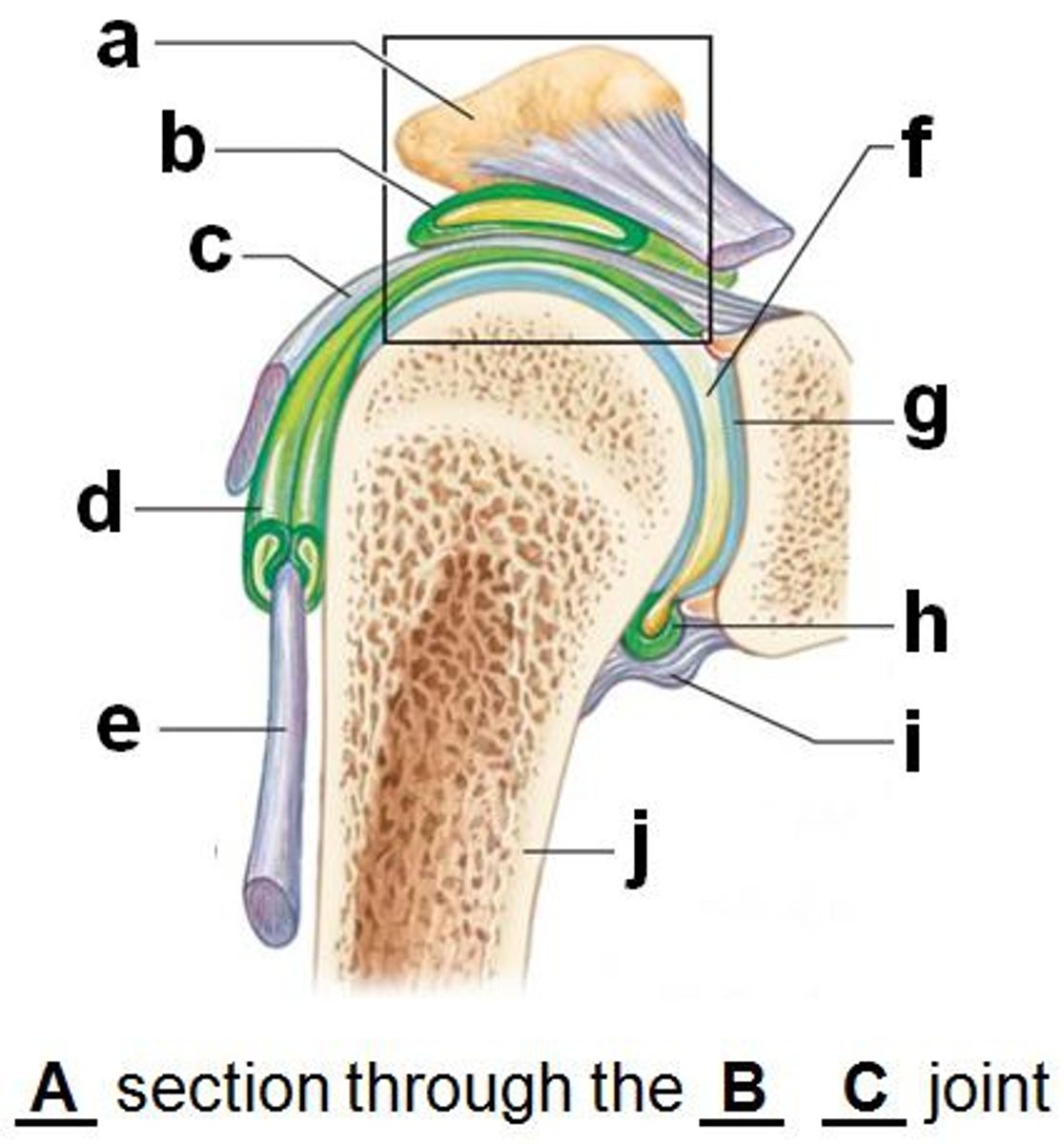
humerus
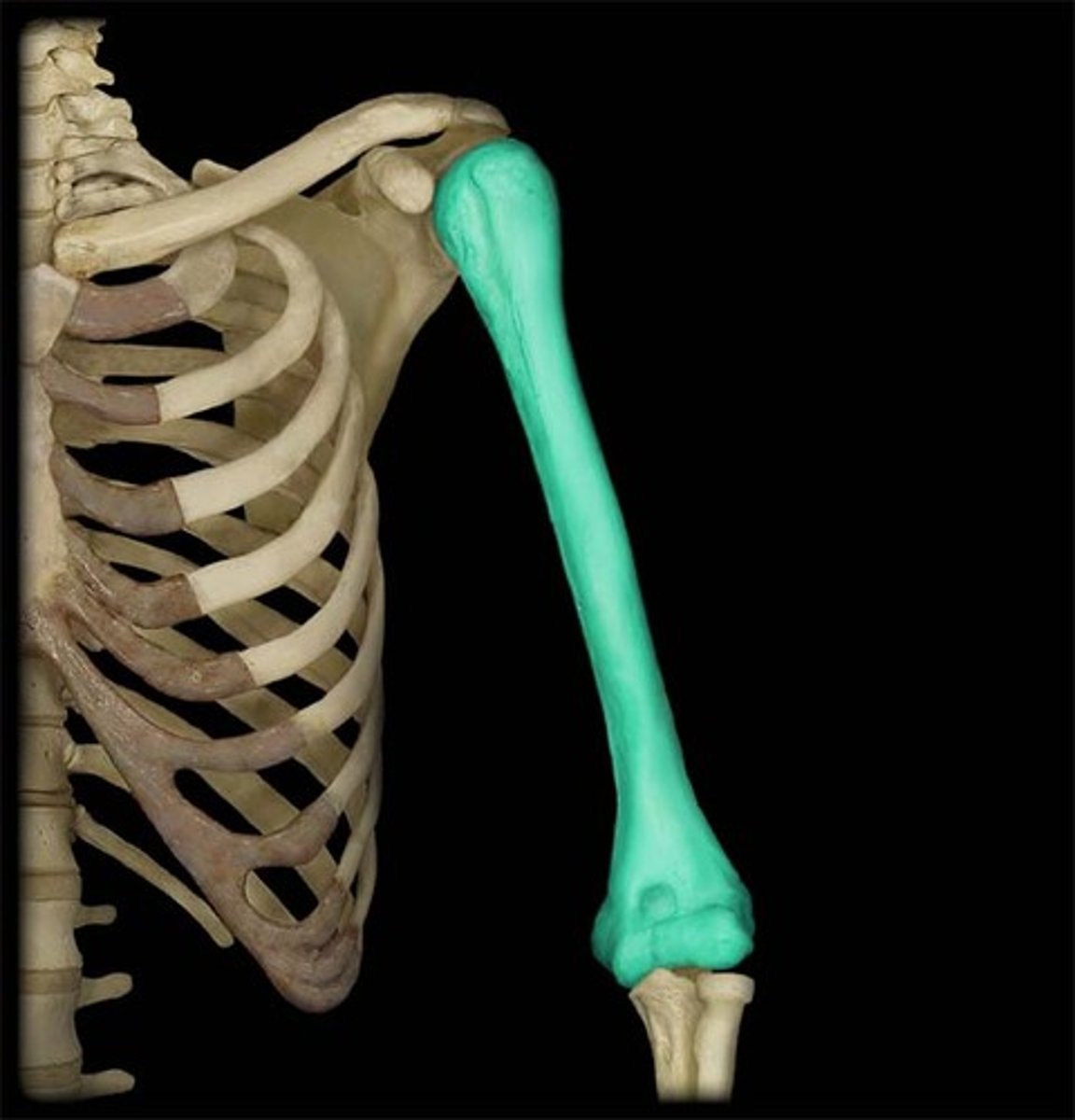
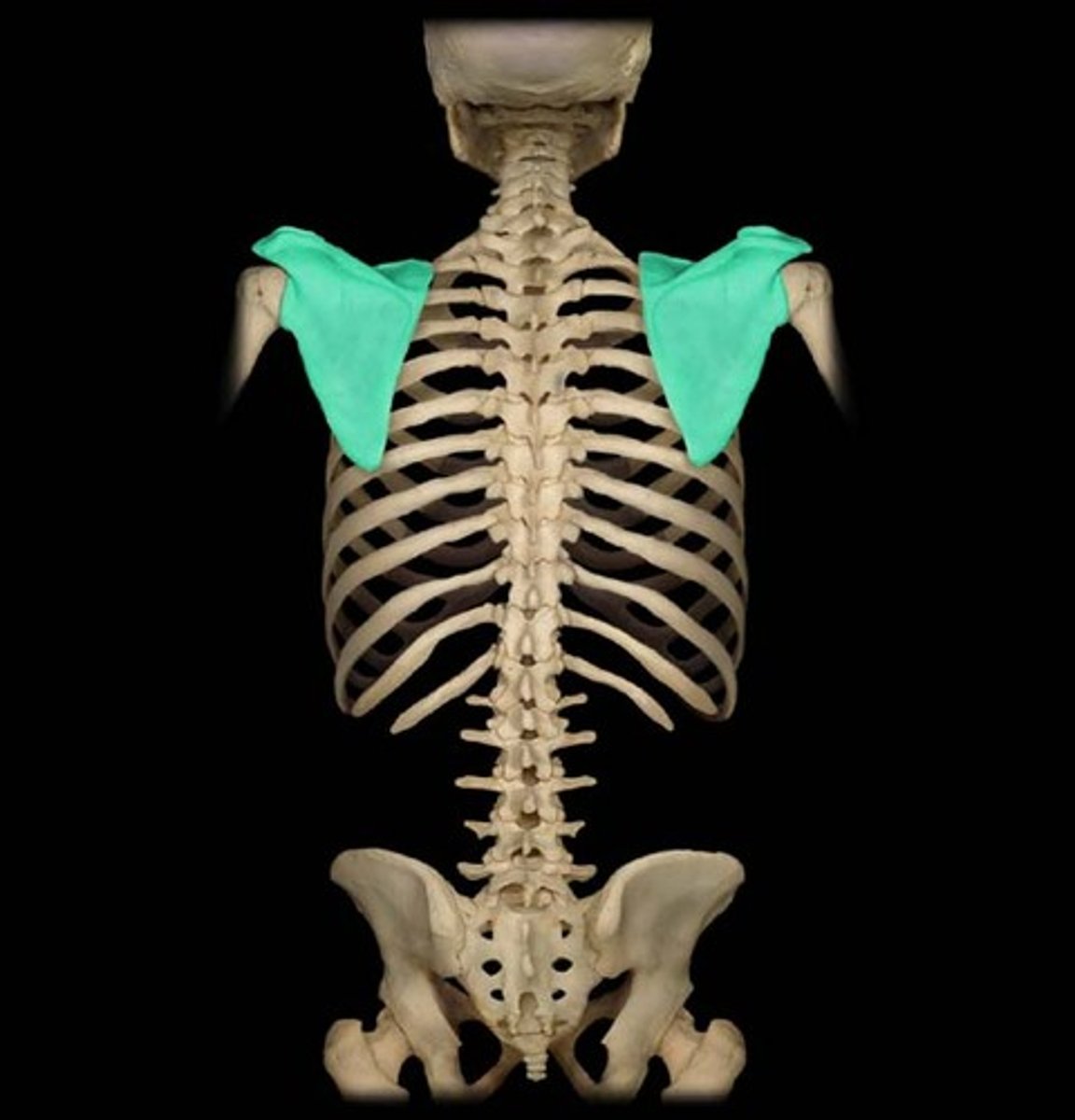
scapula
glenoid labrum (anterior coronal section of shoulder joint)
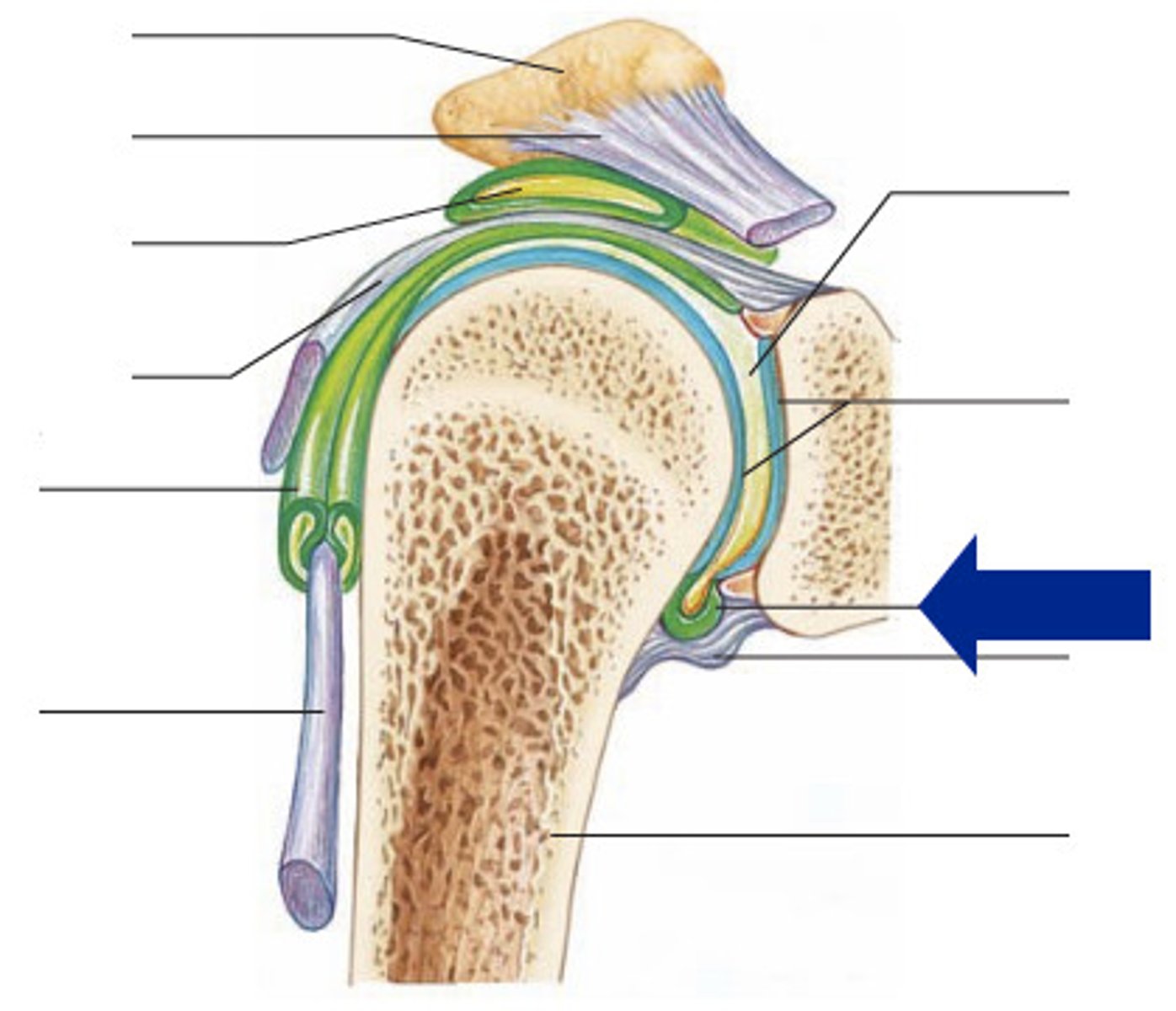
subacromial bursa (anterior coronal shoulder joint)
look at b
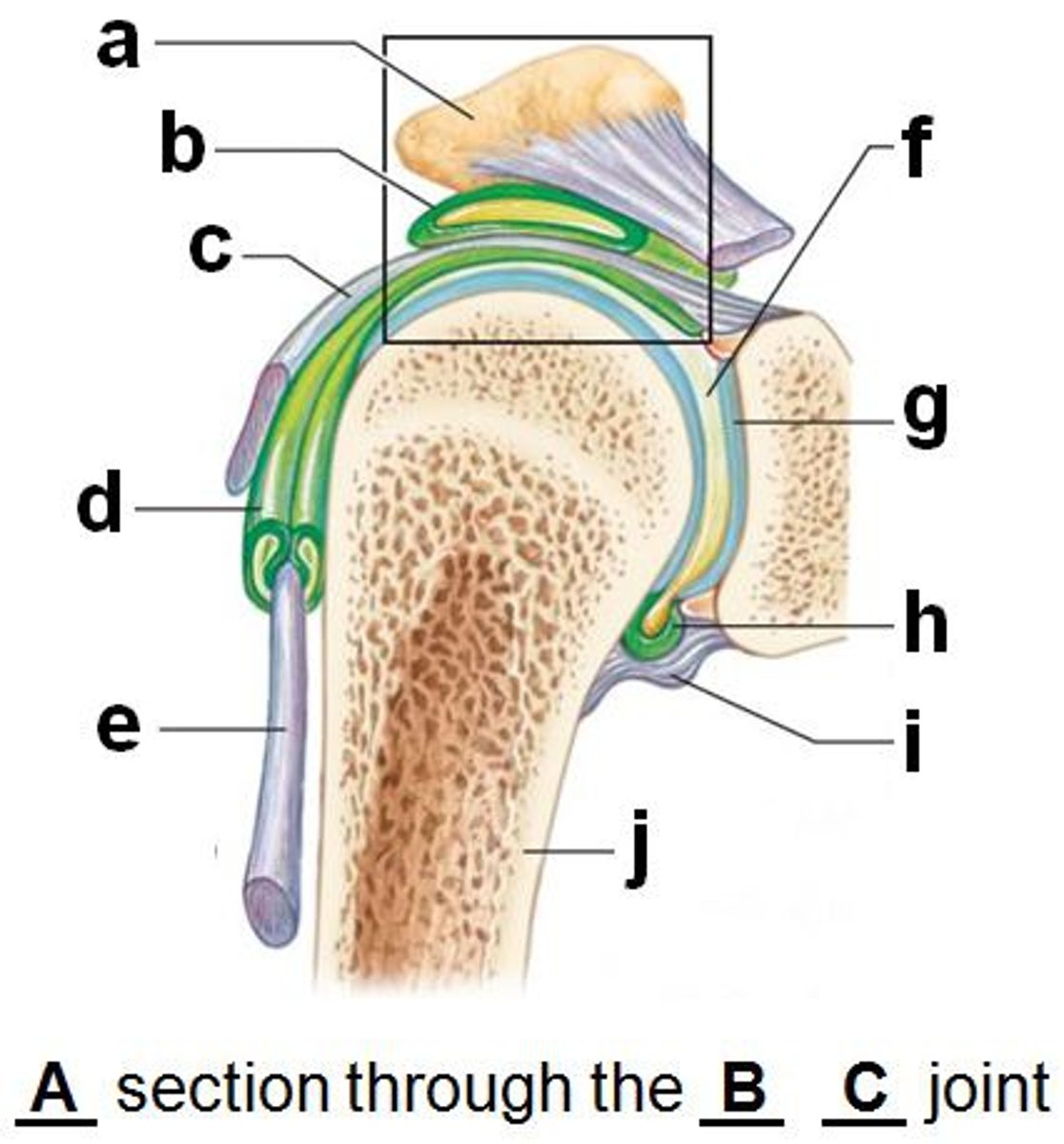
tendon sheath (anterior coronal shoulder joint)
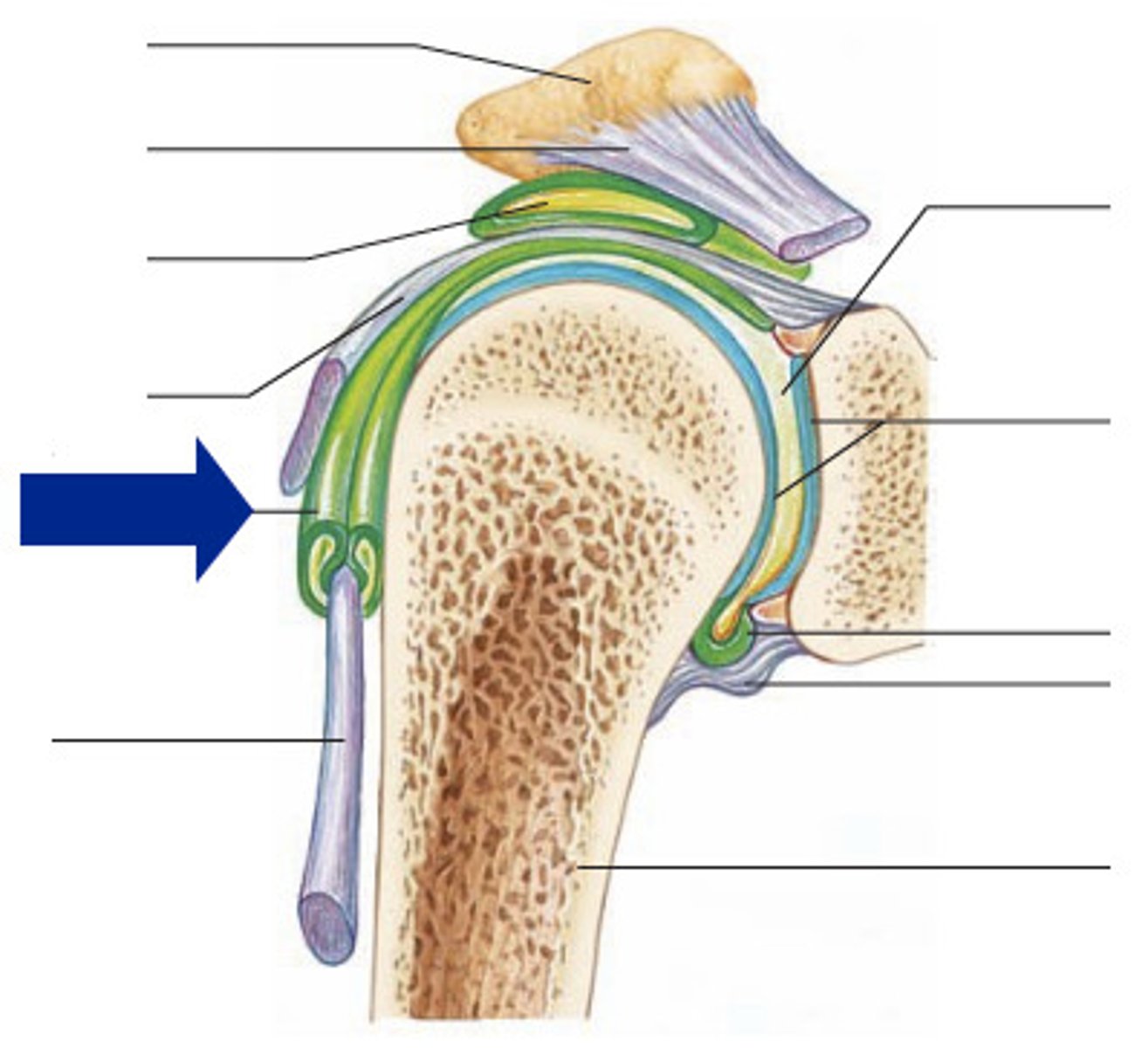
articular cartilage (anterior coronal shoulder joint)
look at g
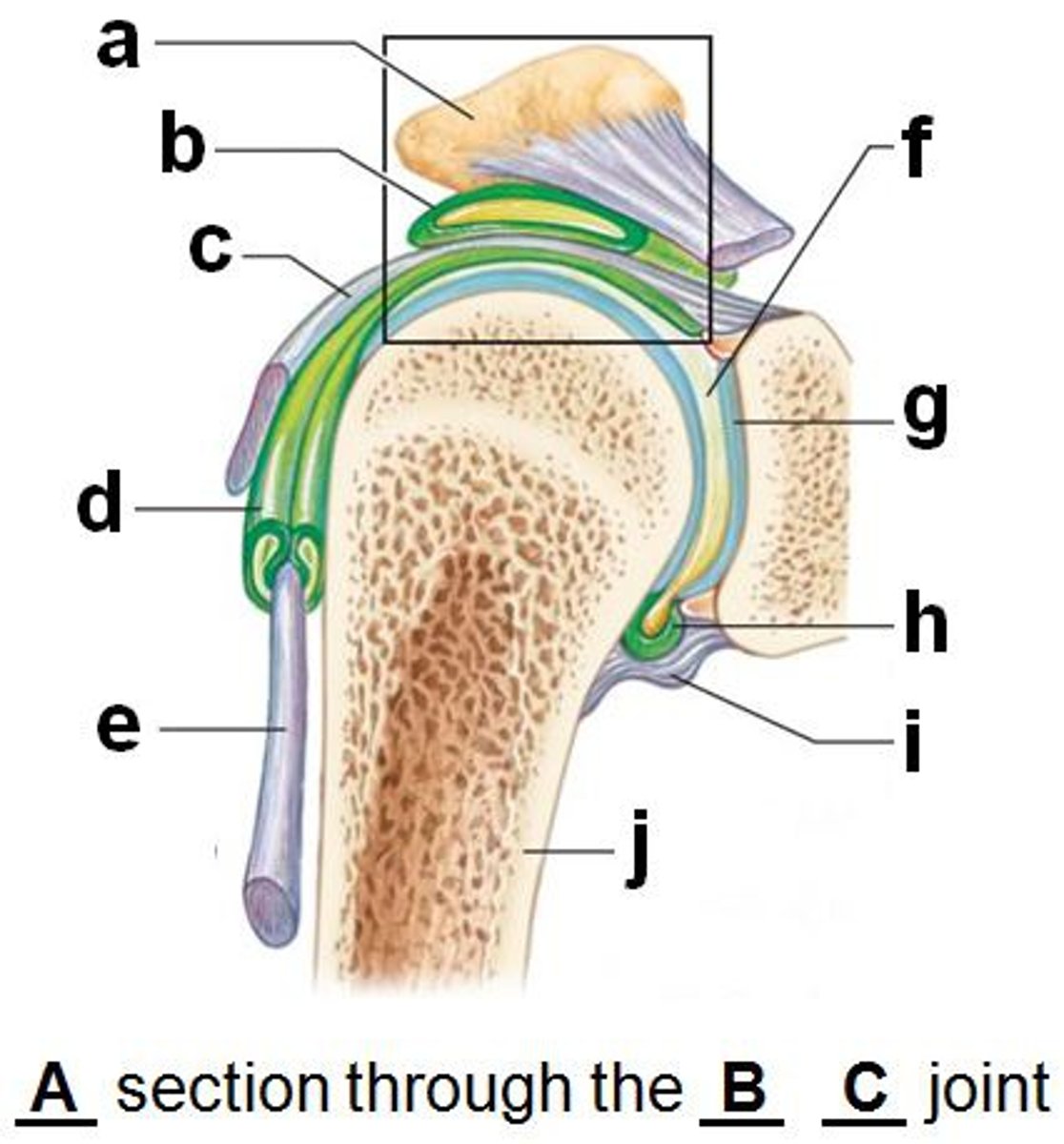
joint cavity containing synovial fluid (anterior coronal shoulder joint)
look at f
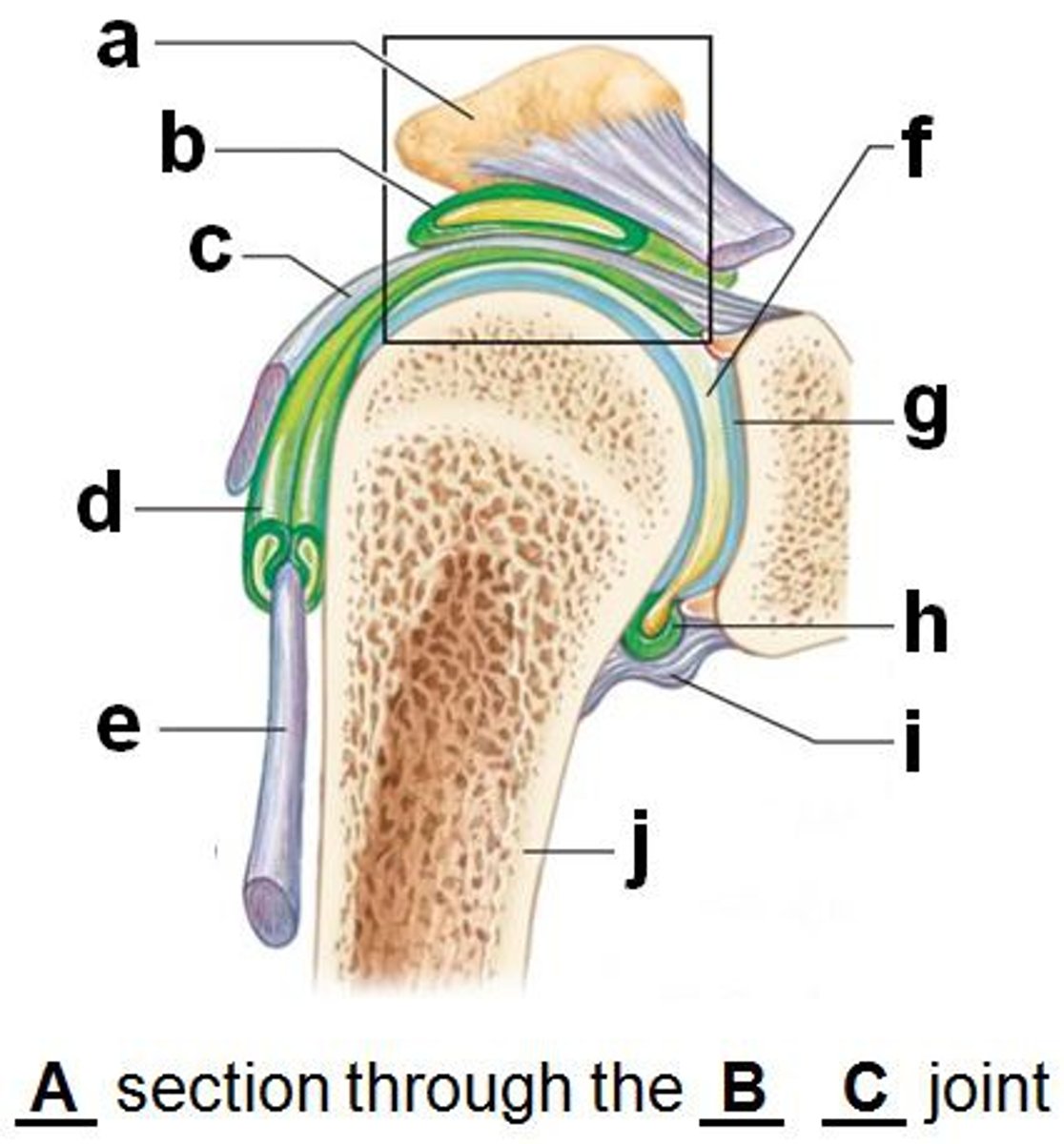
synovial membrane of articular capsule (anterior coronal shoulder joint)
look at h