The cardiovascular system [B1]
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is taken from class notes and the applied science textbook
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
What is the cardiovascular system?
it is a body system that allows the blood to circulate around the body to transport and supply nutrients to organisms so that they can survive.
What is the cardiovascular system known as?
the circulatory system
Why is the human circulatory system known as “double”
because blood passes through the heart twice in one complete circulation of the body
What is the meaning of systemic circulation?
parts of the circulatory system that relates to the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide from the heart to body cells
What is the meaning of pulmonary circulation?
a part of the circulatory system that relates to with the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide from the heart to the lungs.
What is the function of arteries?
carry blood away from the heart. has very high pressure
What is the structure of an artery?
small lumen
thick walls with collagen
elastic tissue in the wall, so it can expand and recoil
has smooth endothelium that reduces friction through the lumen
What is an arteriole?
smaller arteries which contain smooth muscle cells wrapped around the endothelium.
What is the function of capillaries?
they allow the exchange of materials between the blood and the cells by tissue fluid. They link arterioles to venules.
What is the structure of capillaries?
thin walls, one cell thick
narrow lumen to help the red blood cell release oxygen
site of diffusion
What are venules?
A group of larger capillaries that can join to form veins.
What is the function of veins?
carry blood to the heart
What is the structure of veins?
large lumen
thinner walls, because of low pressure
have valves to prevent the backflow of blood
How many chambers are there in the heart?
4
How many atria’s in the heart?
2
How many ventricles are there in the heart?
2
Where are the atria placed in the heart?
In the upper chambers
What does the right atrium receive?
deoxygenated blood coming from the superior and inferior vena cava.
Where does the right atrium take the blood received from the vena cava?
To the lungs
What does the left atrium receive blood from?
receives oxygenated blood from the lungs
What does the left atrium do with the blood?
pumps it to the left ventricle
What is the structure of the left atrium?
thicker muscular walls compared to the right atrium
Where does the right ventricle get the blood from?
deoxygenated blood from right atrium
What does the right ventricle do with the blood?
pump through the pulmonary artery to the lungs
Where does the left ventricle get blood from?
oxygenated blood from the left atrium
What does the left ventricle do with the blood now?
pumps the blood to the aorta
What is the structure of the left ventricle?
It is the thickest chamber as it is designed to pump blood against high pressure
What is the function of the septum?
separates the left and right side of the heart
What is the function of the vena cava?
to carry deoxygenated blood into the heart
What is the function of the pulmonary vein?
delivers oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
What is the function of the aorta?
transport oxygenated blood away from the left ventricle to the rest of the body
What is the function of the pulmonary artery?
transport deoxygenated blood away from the the right ventricle to the lungs
What is the location of the atrioventricular valve?
found between the atrial and ventricular chambers of the heart
What is the function of the atrioventricular valve?
Prevent the backflow of blood between the atria and the ventricle chambers of the heart
What is the atrioventricular valve known as?
bicuspid, mitral or tricuspid valve
What is the location of the sinoatrial node?
in the right atrium
What is the sinoatrial node known as?
SAN
What is the semi-lunar valve?
prevents the backflow of blood between from the aorta and the pulmonary artery
What are other names of the semi-lunar valve?
-pulmonary valve
-aortic valve
What is the function of the sinoatrial node?
generates electrical activity and initiates a wave of excitation at regular intervals
Why is the SAN commonly referred to as a pacemaker?
it continuously generates electrical impulses, and sets a healthy rhythm and pace.
Where is the atrioventricular node found?
found at the top of the septum
What is the atrioventricular node known as?
AVN
What is the function of the atrioventricular node?
picks up the wave of excitation from the atria and delays it so the atria has time to complete the contraction. Also stimulates the bundle of his
What is the bundle of his?
collection of heart muscle cells specialised for electrical conduction
What is the function of Purkinje fibres?
conduct electrical impulses to the ventricles, so it can coordinate the contraction to pump blood efficiently
Where are the Purkinje fibres located?
located in the walls of the ventricle
What is the function of the coronary arteries?
To supply the cardiac muscle with its own oxygen supply
What does myogenic muscle mean?
it can contract and relax without nervous or hormonal stimulation
What is the meaning of atrial systole?
when a wave of excitation spreads along the muscle tissue and causes muscles cells in both the left and right atrium to contract simultaneously.
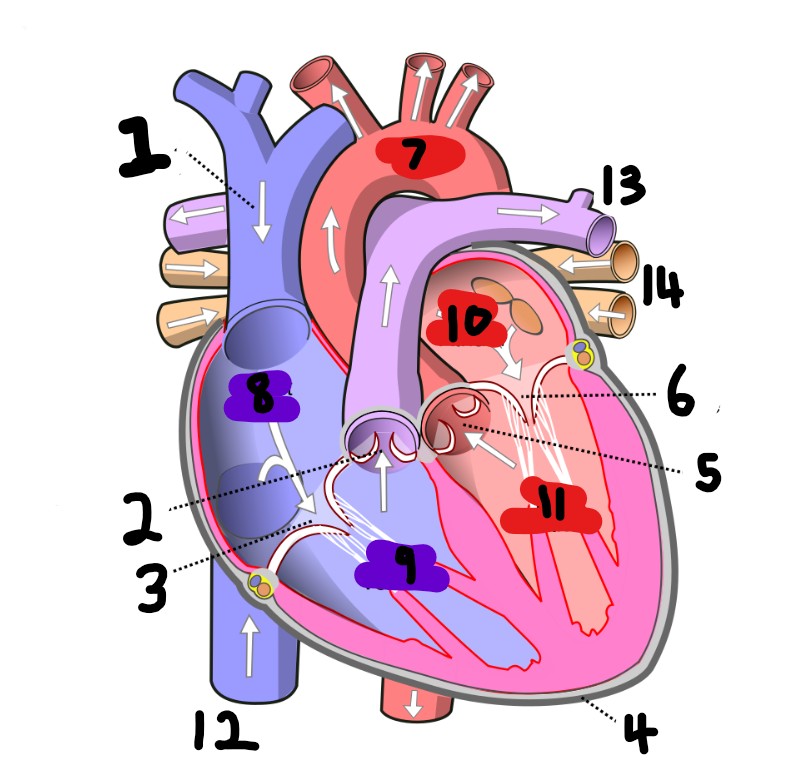
What is number 2?
pulmonary valve
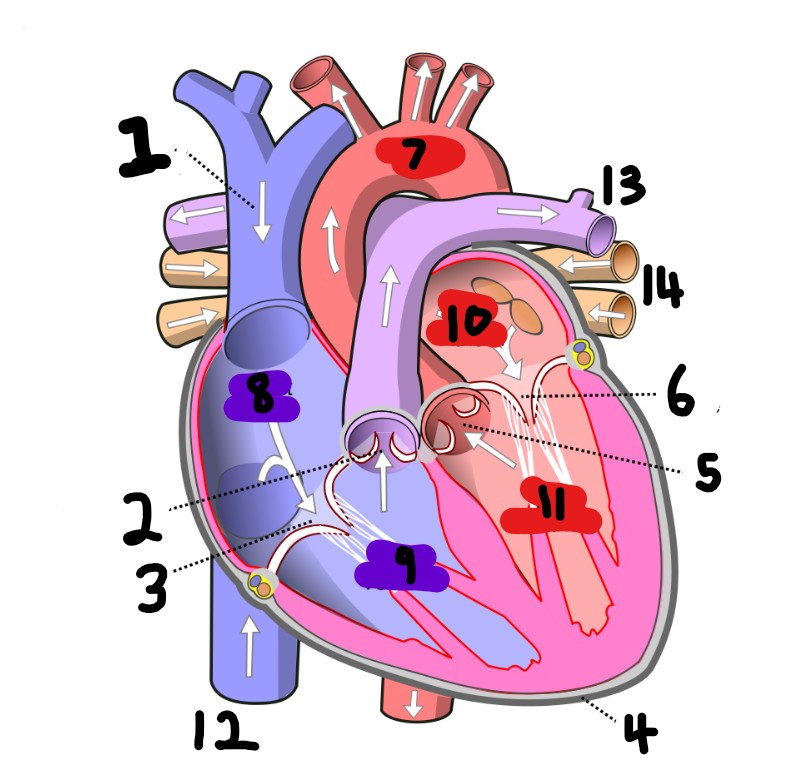
What is number 1?
superior vena cava
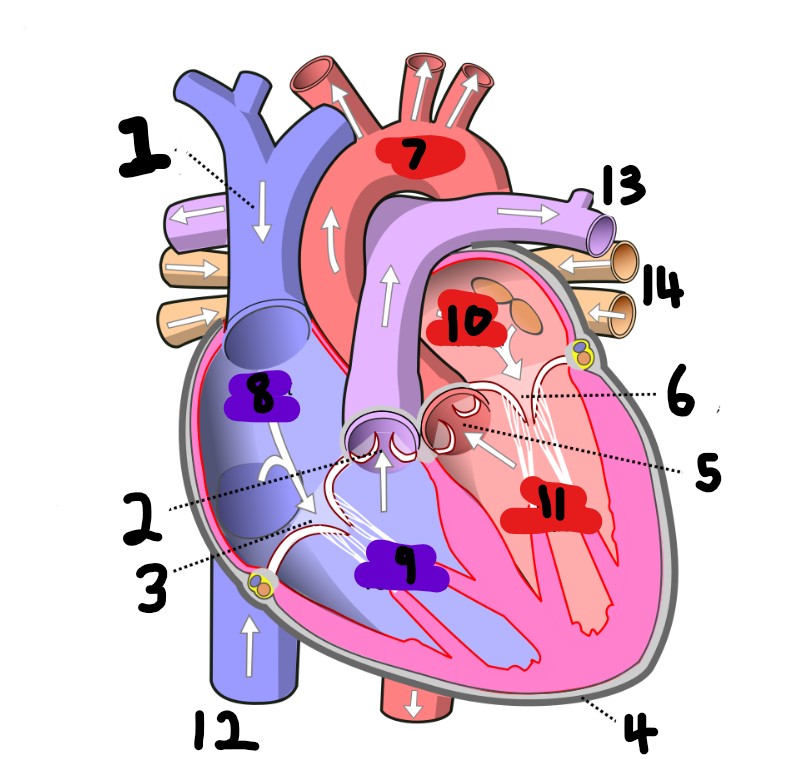
What is number 3?
tricuspid valve
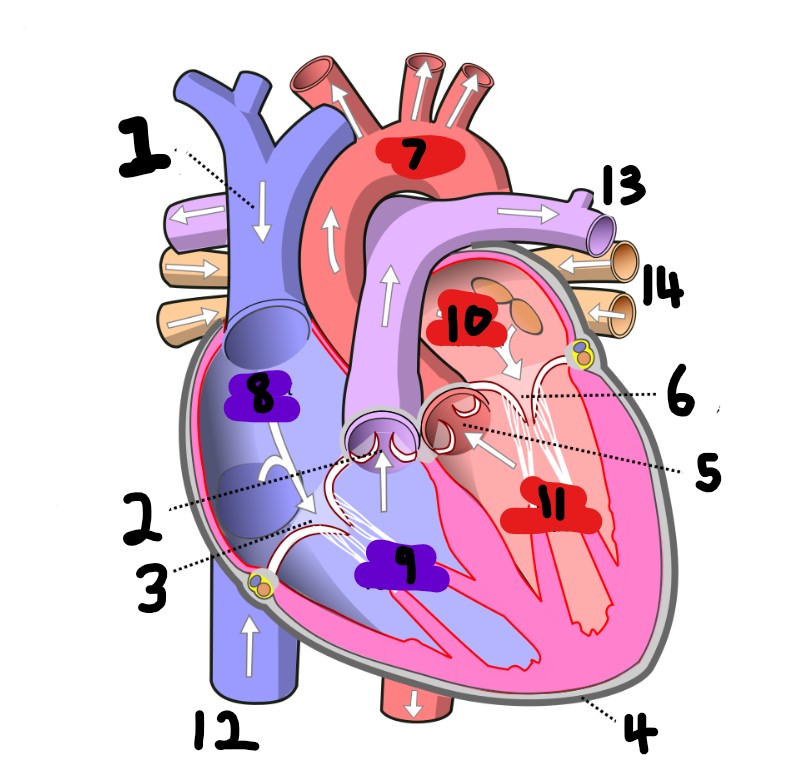
What is number 4?
pericardium
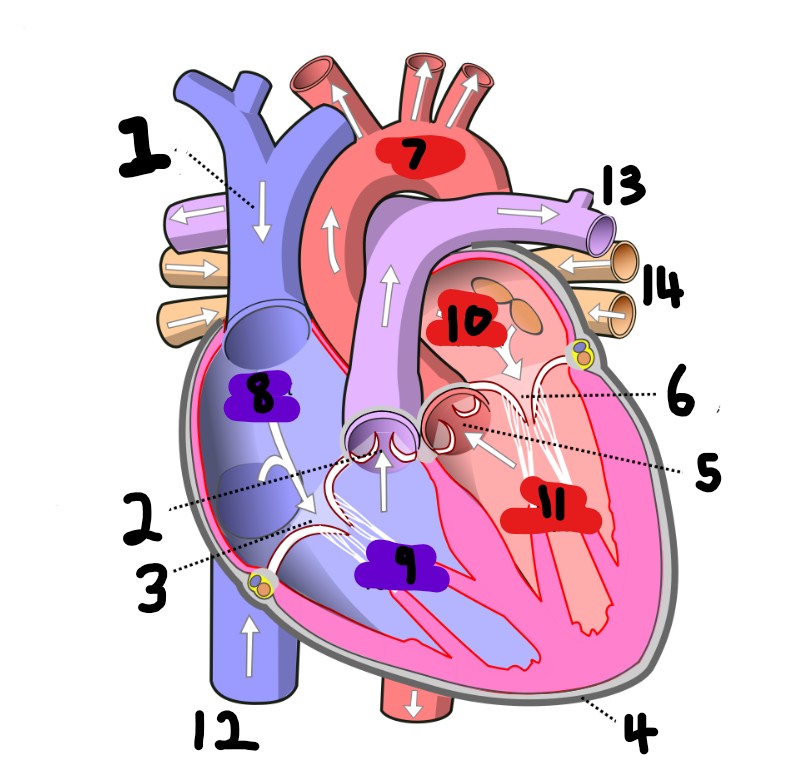
What is number 5?
aortic valve
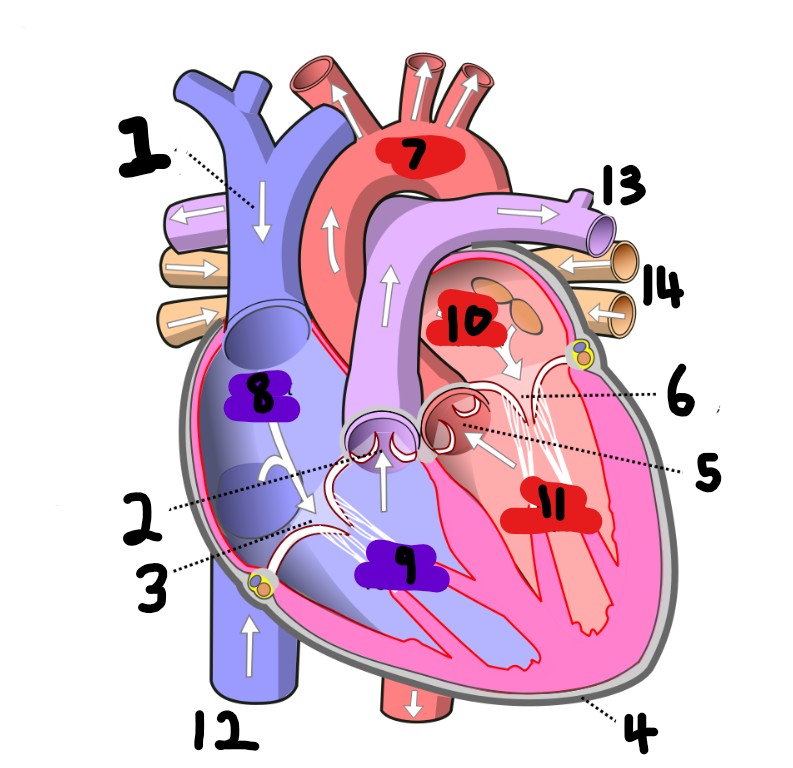
What is number 6?
mitral valve
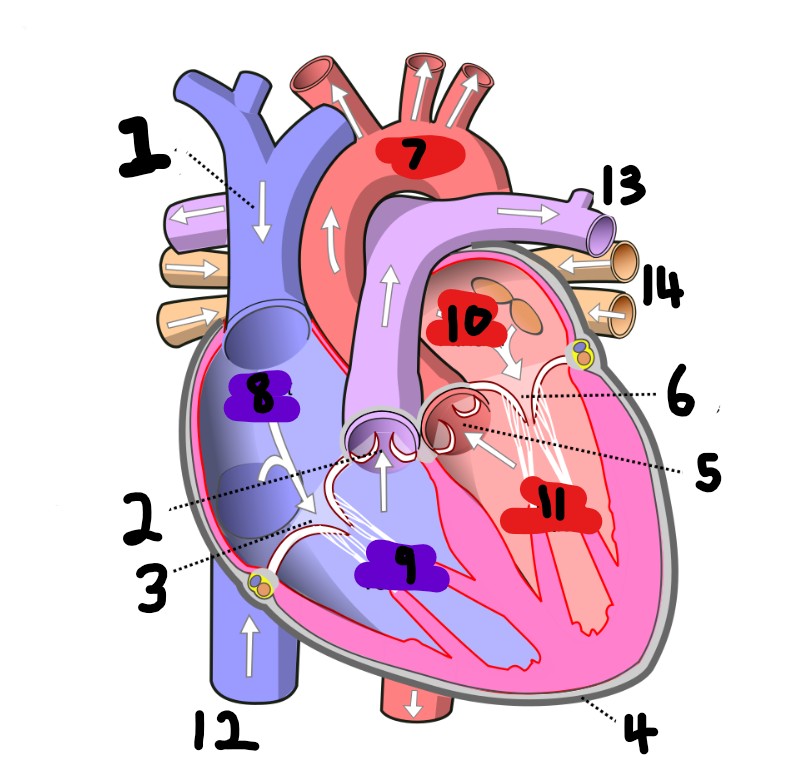
What is number 7?
aorta
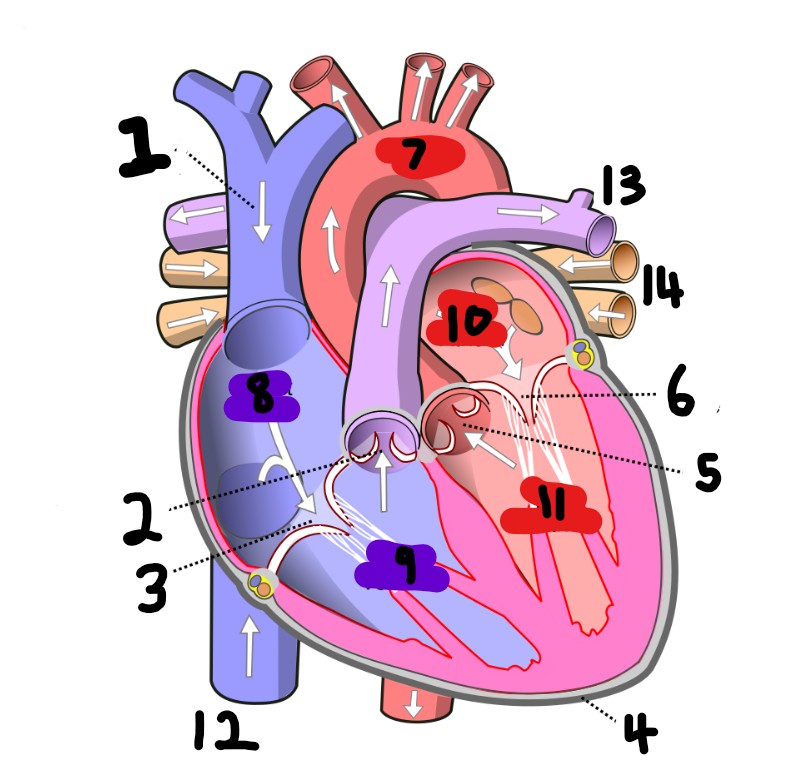
What is number 8?
right atrium
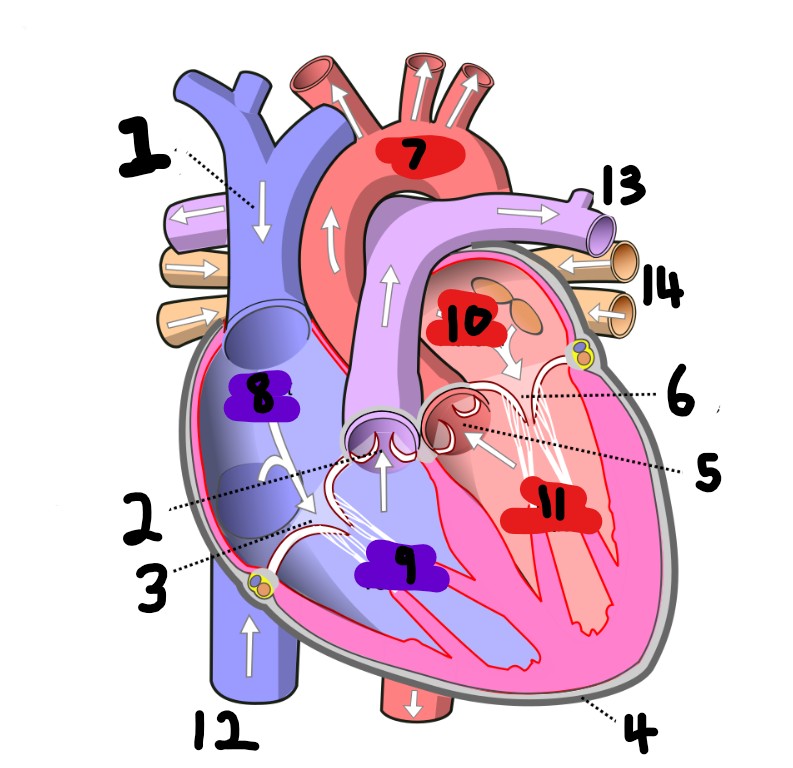
What is number 9?
right ventricle
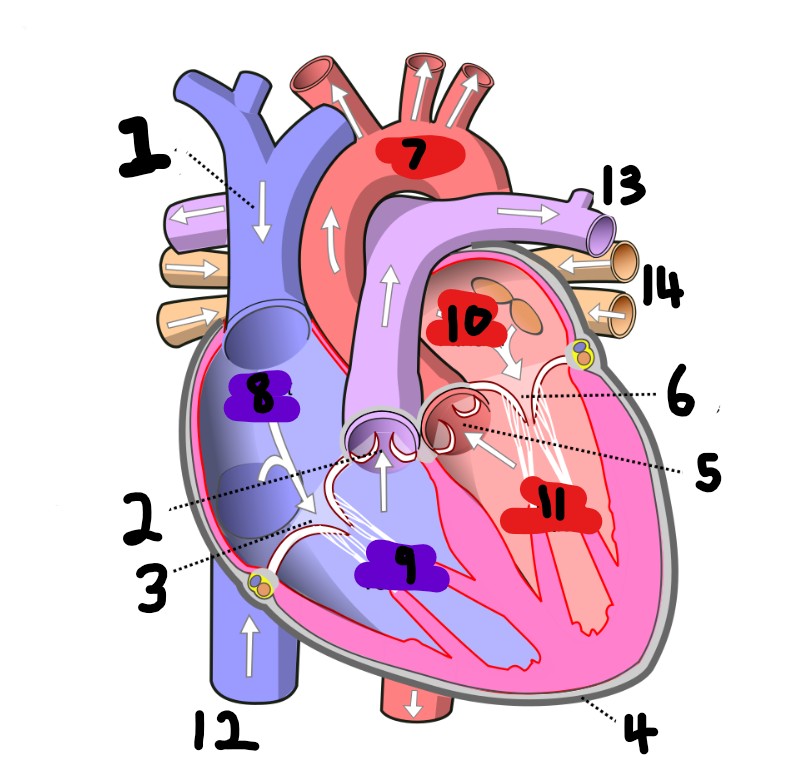
What is number 10?
left atrium
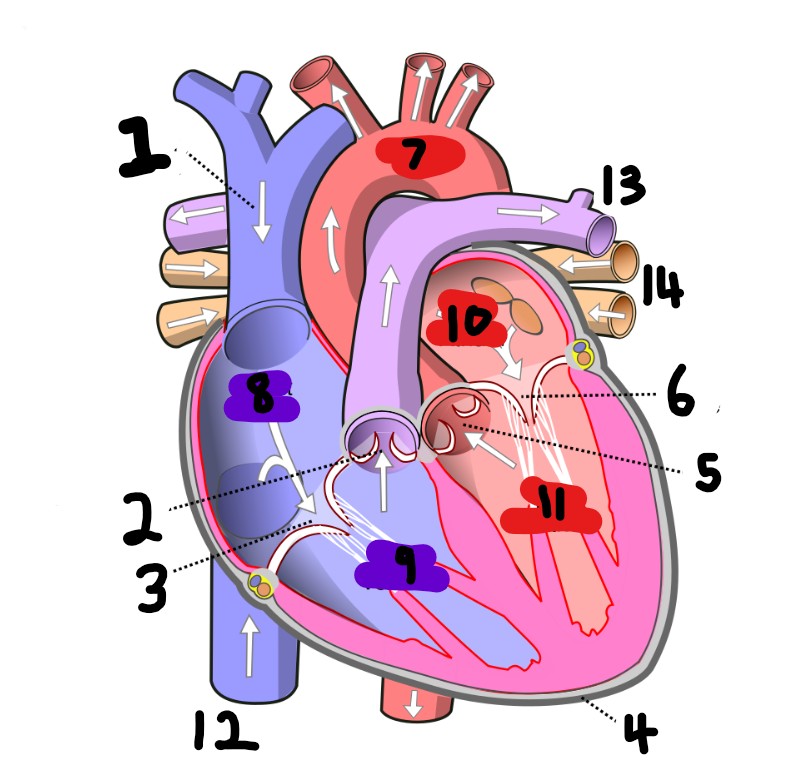
What is number 11?
left ventricle
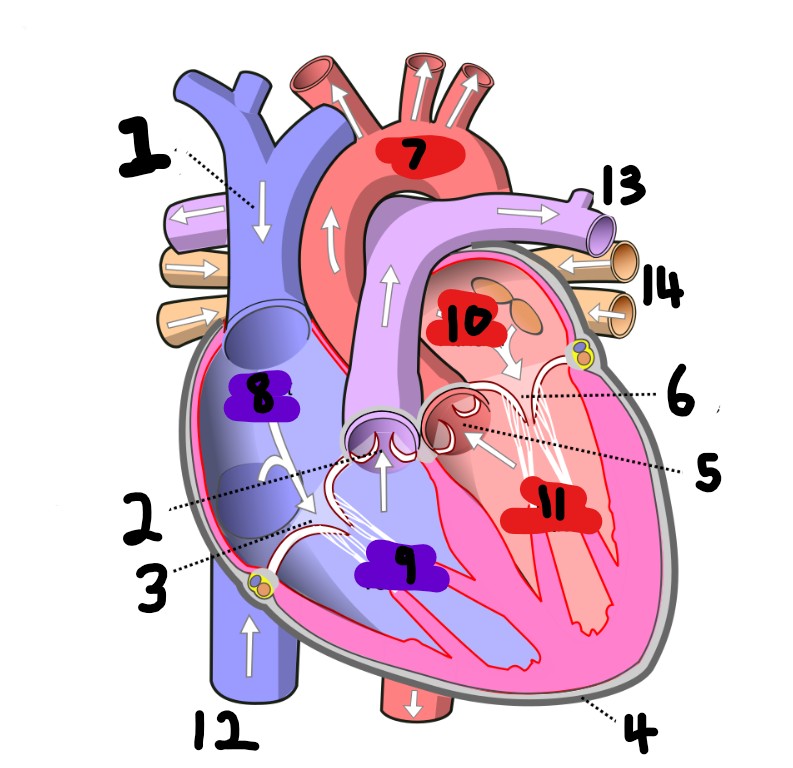
What is number 12?
inferior vena cava
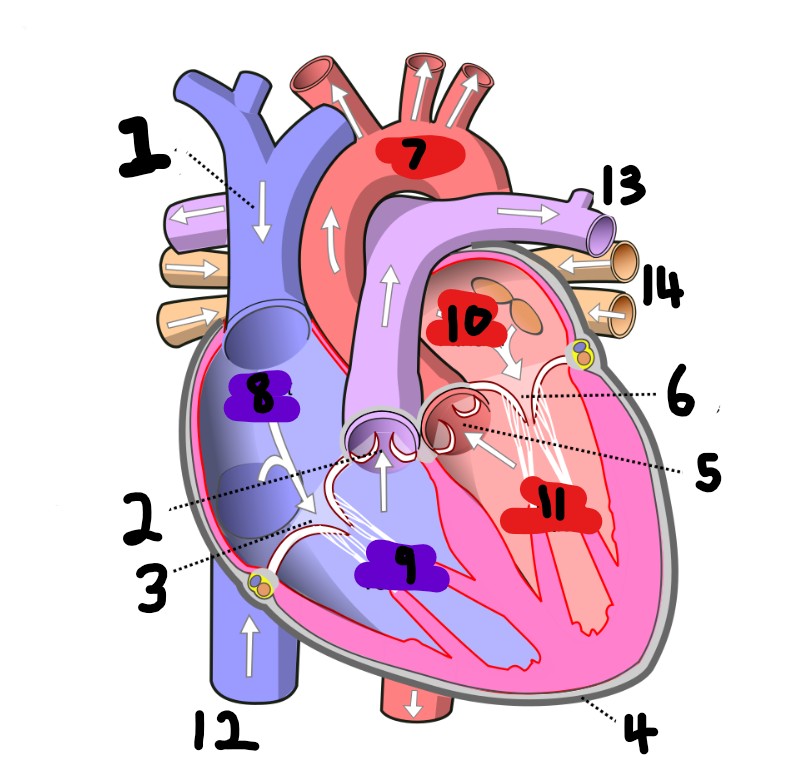
What is number 13?
Pulmonary artery
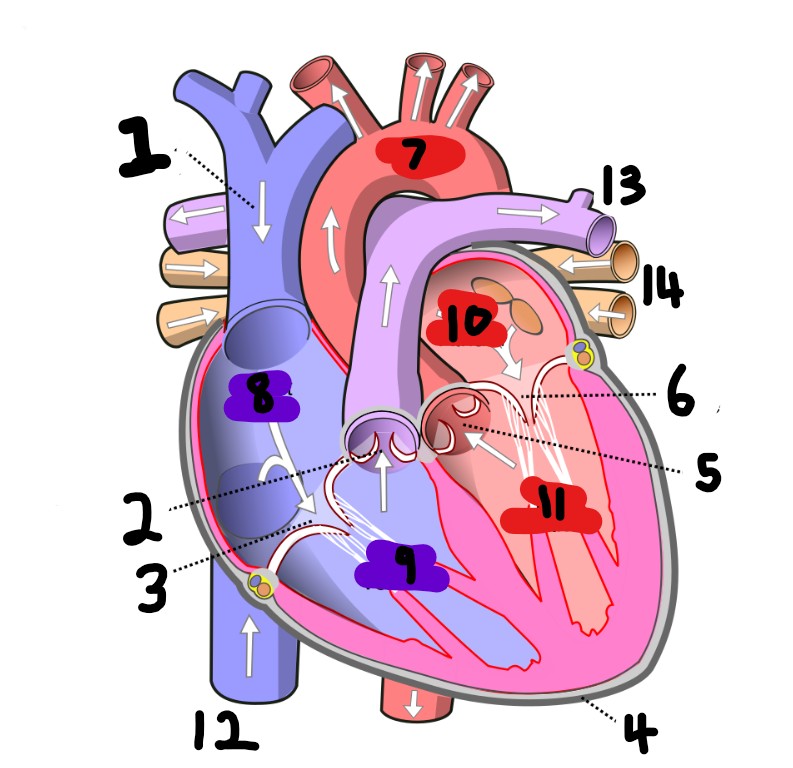
What is number 14?
Pulmonary vein
How do you calculate cardiac output?
multiplying the heart rate (beats per minute) by the stroke volume (blood pumped per beat)
What is the cardiac output?
the total volume of blood the heart pumps to the body's circulatory system in one minute
Why are blood transfusion important?
relevant for treating medical conditions
How does the ABO system play a role?
it determines blood types based on the presence of the A or B antigen in the red blood cells
How does the Rh system help with blood transfusions?
identifies people with or without the Rh D antigen and Rh d positive blood has more immunity. Negative can be universal donor
Can a person with AB blood give blood to a person with type O blood?
NO
What antigen is for type A blood?
A
What is the antibodies needed for type A blood?
B
What is the antigen for type B blood?
B
What is the antibodies for type B blood?
Antibody A
What antigen is type AB blood?
has both antigen A and B
What antibodies are for type AB blood?
No antibodies
What antigens does type O blood have?
No A or B antigens
What antibodies does type O blood have?
Has both A and B antigens
What is the meaning of cardiac diastole?
a phase in the cardiac cycle where the heart muscle relaxes and the chambers of the heart fill with blood, this allows the ventricles to expand and blood to flow in.
What is the meaning of ventricular systole?
a phase in the cardiac cycle where the ventricles contract, which forces blood out and into the pulmonary artery and the aorta
What is the first stage of the cardiac cycle?
1) the atria relax and fill with blood from the pulmonary vein and the vena cava.
What is the name for the first stage of the cardiac cycle?
atrial diastole
What is the second stage of the cardiac cycle?
2) the atria contract and force the AV valve open. Blood flows into the ventricles and they fill up.
What is the name of the second stage of the cardiac cycle ?
ventricular diastole
What is the third stage of the cardiac cycle?
3) the AV valve close when the pressure in the ventricles rises above the pressure in the atria, to prevent any backflow of blood into the atria
What is the fourth stage in the cardiac cycle?
4) the walls in the ventricle contract and increase pressure in the ventricles. This forces the semi-lunar valves to open and the blood flows into the pulmonary artery and the aorta.
What is the fifth and final stage of the cardiac cycle?
5) when the pressure in the aorta and the pulmonary artery rises, the semi-lunar valves close to prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles.
What does ECG stand for?
electrocardiogram
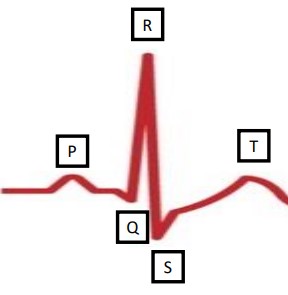
What does an ECG do?
detects electrical signals in the heart, this can show if the heart is working properly
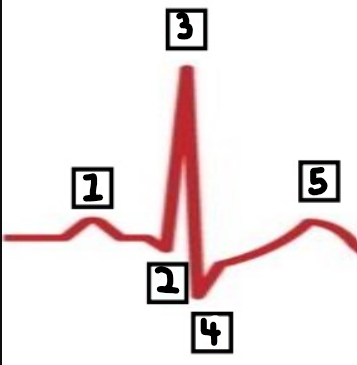
What is number 1?
P
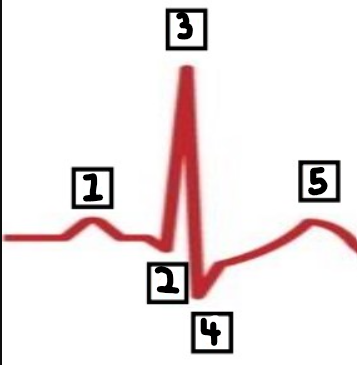
What is number 2?
Q
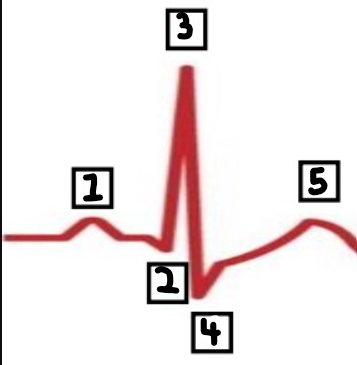
What is number 3?
R
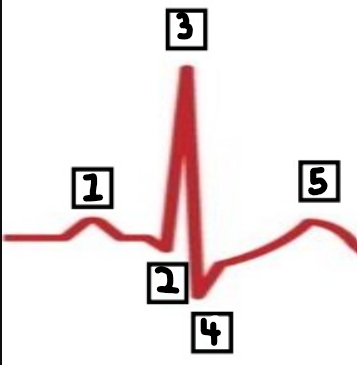
What is number 4?
S

What is number 5?
T
What is the meaning of the P wave?
depolarisation of the atria
What does depolarisation of the atria mean?
the electrical activation of the atria, triggers them to contract and pump blood into the ventricles
What is the QRS wave?
depolarisation of the ventricles
What does the depolarisation of the ventricles mean?
the electrical activation of the ventricle contract and pump blood throughout the body
What is the T wave?
repolarisation of the ventricles
What is the meaning of depolarisation?
an influx of calcium and sodium ions