Ethical issues with Vaccines and Monoclonal Antibodies
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Why do some people find animal testing for vaccines ethically problematic?
Some individuals consider animal testing unethical due to concerns about the well-being of animals and the morality of using them for experimentation purposes.
What ethical concerns arise regarding the use of animal-based substances in vaccine production?
Some individuals disagree with the use of animal-based substances in vaccine production, raising ethical questions about the treatment of animals and the moral implications of using such materials
What are the ethical dilemmas associated with human testing during vaccine trials?
Human testing involves potential risks, including the chance of trial participants experiencing symptoms of the disease or unforeseen side effects. There's also concern about volunteers assuming full protection from the trial vaccine, leading to risky behavior.
Question: How can financial pressure impact the ethics of vaccine trials involving human volunteers?
Ethical issues arise when financial struggles may push individuals to volunteer for vaccine trials, potentially exposing themselves to harm due to the financial incentives offered.
Why do some people refuse a vaccine based on the small possibility of side effects?
Some individuals reject vaccines due to concerns about the minimal risk of side effects, even though these risks are generally very low. This refusal may lead to ethical considerations, especially in the context of herd immunity.
What ethical concerns surround parents who refuse to vaccinate their children?
Refusing vaccination for children raises ethical questions as it puts the child at a greater risk of contracting the disease. The balance between parental autonomy and the well-being of the child becomes a significant ethical dilemma.
What ethical dilemmas emerge during epidemics regarding vaccine distribution?
Issues arise during epidemics about prioritising certain groups for vaccination, such as the elderly. Additionally, there are ethical debates about fair global access, as richer countries may have better access to vaccines compared to poorer nations.
Should all countries have equal access to vaccines during a pandemic?
The question of equal access to vaccines during a pandemic raises ethical concerns, especially when considering disparities between wealthier and poorer countries. Ensuring fair distribution becomes a challenging ethical dilemma.
Why do some people find animal testing for monoclonal antibody therapies ethically objectionable?
Similar to vaccines, ethical objections to animal testing arise concerning the use of animals in the development of monoclonal antibody therapies, reflecting concerns about animal rights.
What is the ethical dilemma regarding the use of animals to produce cells for monoclonal antibodies?
The ethical concern centers on the utilization of animals to produce cells for monoclonal antibodies, prompting debates on the ethical treatment of animals and the appropriateness of such practices.
Why is it crucial to validate claims about vaccines and monoclonal antibodies with scientific evidence?
It is essential to validate claims with scientific evidence to ensure accuracy and reliability. This involves using rigorous methodologies and having other scientists repeat the same study to reproduce results, establishing a foundation of credibility.
What is the significance of scientists conducting studies to prove or replicate findings about vaccines and monoclonal antibodies?
The replication of studies by different scientists is critical for establishing the robustness of findings.
When multiple studies confirm the same theory or results, it enhances the reliability and trustworthiness of the information.
How does the evaluation of data contribute to the assessment of claims and new scientific findings related to vaccines?
The evaluation of data involves scrutinizing the methodology and results of studies supporting claims about vaccines. It ensures that the evidence presented is valid and trustworthy, helping to distinguish between credible and unreliable information.
Why is it important for scientists to use the same methodology when repeating studies on vaccines or monoclonal antibodies?
Consistent methodology in repeated studies is crucial for obtaining reliable results. Using the same approach allows for a direct comparison, ensuring that any variations in findings are due to the nature of the study rather than differences in methodology.
How does the process of evaluating data apply to monoclonal antibody therapies and treatments?
Similar to vaccines, the evaluation of data is equally important in the context of monoclonal antibody therapies. It ensures that scientific claims and findings related to these treatments are based on sound evidence and robust research methodologies.
What is the MMR vaccine, and what diseases does it protect against?
Answer: The MMR vaccine is a vaccine designed to protect against measles, mumps, and rubella, commonly administered to young children.
Question: Describe the findings of the 1998 study that suggested a link between the MMR vaccine and autism.
The 1998 study, based on only 12 children with autism, claimed a potential link between the MMR vaccine and autism. However, it was later revealed that one of the doctors involved had a conflict of interest, acting as a consultant to parents suing vaccine-producing pharmaceutical companies.
Why is the 1998 study considered less convincing in terms of its findings?
The 1998 study is deemed less convincing due to its small sample size of only 12 children, increasing the likelihood that the results were influenced by chance. Additionally, the doctor's potential bias towards supporting a lawsuit against the vaccine raises concerns about the study's objectivity.
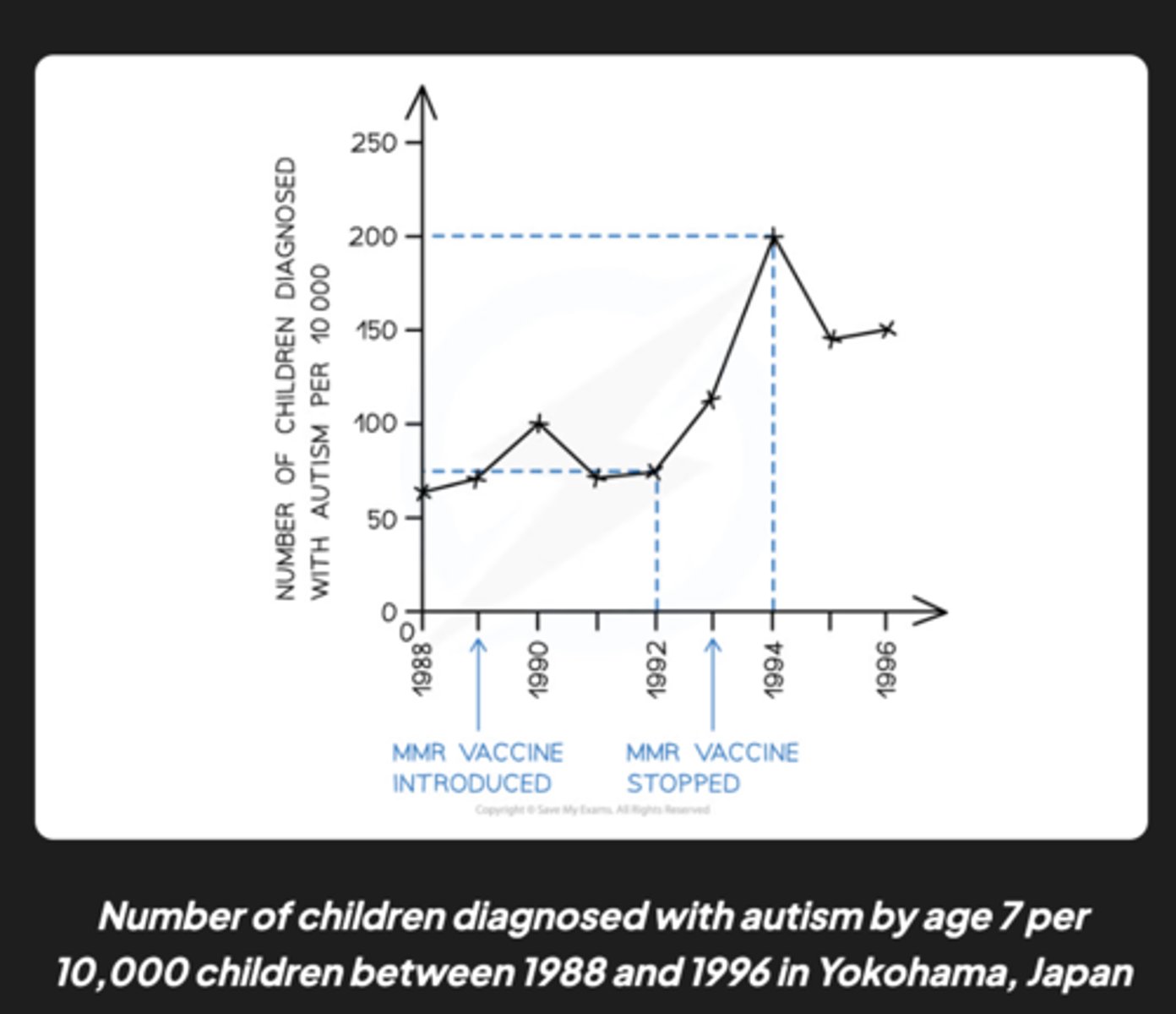
How did the 2005 study in Japan contribute to the evaluation of the MMR vaccine and autism link?
The 2005 study examined the incidence of autism in 30,000 children in Japan and found that even after the MMR vaccine ceased administration in 1993, the number of autism diagnoses continued to increase. This data suggests no link between the MMR vaccine and autism.
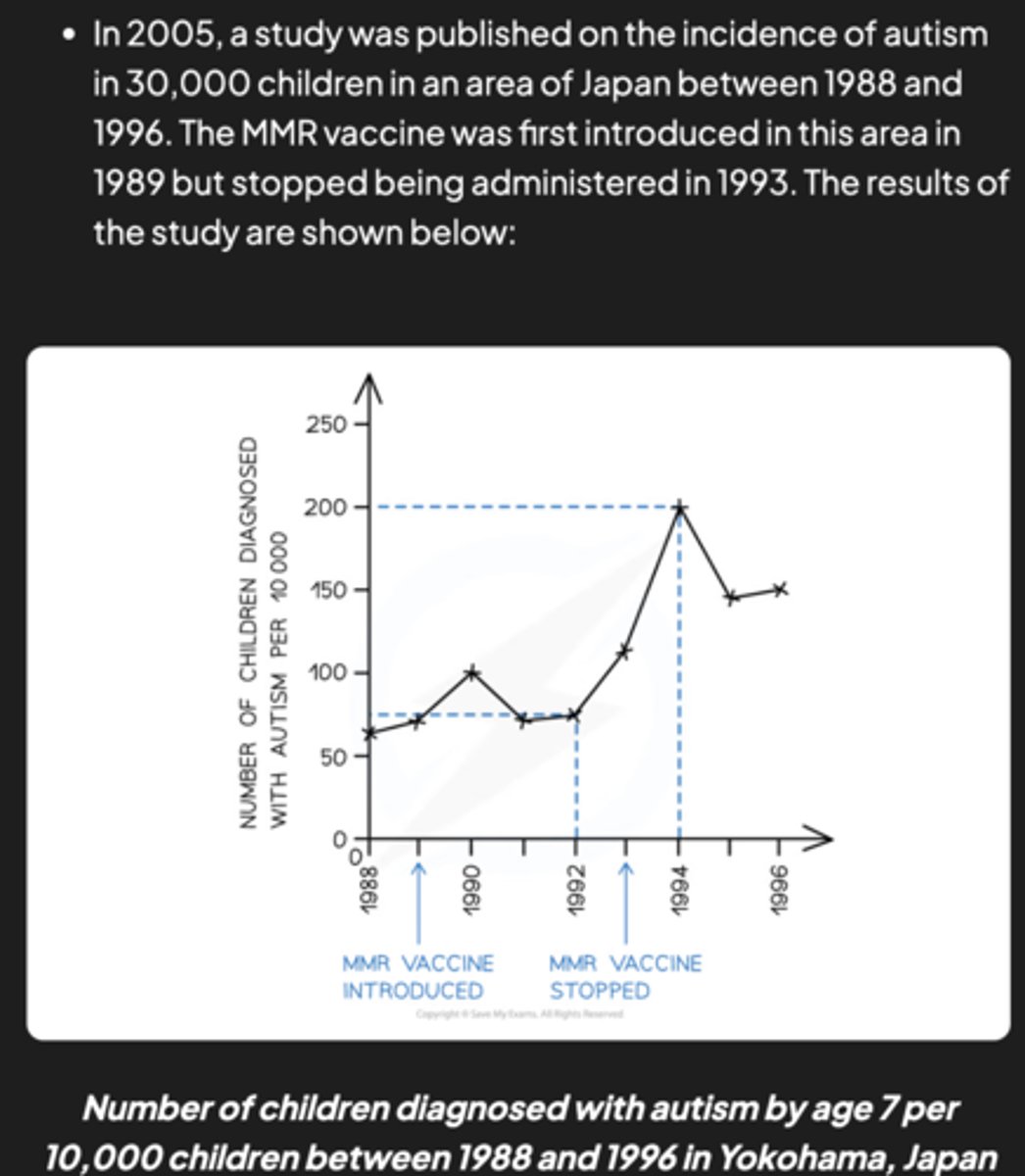
What does the data from the Japan study indicate about the relationship between the MMR vaccine and autism?
The data from the Japan study indicates that the cessation of the MMR vaccine did not correlate with a decrease in autism diagnoses. In fact, the number of diagnoses continued to rise, suggesting no direct link between the MMR vaccine and autism.
Why does the 2005 study provide more confidence in its results compared to the 1998 study?
The 2005 study is considered more reliable due to its significantly larger sample size of 30,000 children. This improved methodology reduces the likelihood that the results were influenced by chance, increasing confidence in the study's conclusions
What role does methodology play in evaluating the reliability of a scientific study?
Methodology is crucial in determining the reliability of a scientific study. A well-designed study with a large sample size, like the 2005 Japan study, enhances confidence in the results, making them less likely to be influenced by bias or chance.
How does the potential bias of researchers impact the credibility of a study's findings?
Potential bias, as seen in the 1998 study where a researcher had a financial interest in a lawsuit against the vaccine, can compromise a study's objectivity and credibility. It raises questions about the motives behind the research and the reliability of the findings.