Organic chemistry Test 2 Vocab
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Markovnikov’s rule
The nucleophile adds to the more substituted carbocation (the most stable carbocation)
regioselective
1 structural isomer product is favored more than the other (but the other is still formed)
regiospecific
only 1 structural isomer is made in the reaction (even though multiple should be possible)
1,2 methyl shift
a methyl group shifts to a neighboring carbon to form a more stable carbocation
1,2 hydride shift
a hydrogen shifts to a neighboring carbon to form a more stable carbocation
deprotonation
removing a hydrogen from a molecule or ion
anti addition
when a reaction causes atoms to always form bonds on opposite sides of the molecule
syn addition
when a reaction causes atoms to always form bonds on the same side of the molecule
stereospecific
only 1 stereoisomer is made in the reaction (even though multiple should be possible)
stereoselective
1 stereoisomer product is favored more than the other (but the other is still formed)
concerted
All bond making/breaking happens in one step
vinylic cation
cation where the positive charge is on an atom that also has a double bond
tautomers
2 isomers of a compound that interconvert easily
ΔG
ΔH-TΔS=?
ΔG
-RTlnKeq=?
[products]/[reactants]=?
Keq
ΔG++
activation energy
exothermic
release of thermal energy, negative ΔH
exergonic
release of energy, negative ΔG
kinetic product
product with the lowest energy transition state for the rate-determining step (lowest ΔG++)
thermodynamic product
the product with the lowest energy product
heat of hydrogenation
change in ΔH of the reaction
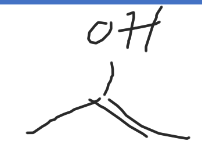
vinyl alcohol
molecule where the alcohol is on an atom with a double bond (also called an enol)