Chapter 13: Measuring and Evaluating Financial Performance
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/49
Last updated 11:54 PM on 12/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
1
New cards
financial statement
A(n) ________ user should be able to understand relationships, activities, and results from business operations when viewing a statement.
2
New cards
debt and stockholders’ equity
Financing for assets come from ________.
3
New cards
Horizontal (trend) analyses
_________ help financial statement users recognize important financial changes that unfold over time.
4
New cards
horizontal, vertical, and ratio
The three different types of analyses:
5
New cards
trends
They compare individual financial statement line items to ______.
6
New cards
Vertical analyses
________ show relationships between items on a financial statement. They compare the balance of one account to another.
7
New cards
Ratio analyses
________ are used to understand relationships between items on one or more financial statements. It shows a company’s performance from using their resources.
8
New cards
analysis
A(n) _________ is considered “complete” once it is successfully able to create a better understanding for those who review financial statement and its results.
9
New cards
time-series analyses
Horizontal analyses is also called __________ because of the comparison of results over time.
10
New cards
dollars or percentages
Horizontal analyses results are presented as year to year _________.
11
New cards

\
Equation for calculating change (%)
12
New cards
Vertical (common size) analysis
__________ focuses on relationships regarding financial statements.
13
New cards
percentages
Vertical (common size) analysis relies on __________ to translate results and relationships.
14
New cards
common size balance sheet
A(n) _________ shows the percent of total assets and each liability or stockholders’ equity as a percent of their total.
15
New cards
common size income statement
A(n) _________ gives the percentage of sales for items on the income statement.
16
New cards
common size
Ratio analyses is similar to _________ in the manner of how they both consider size in comparisons.
17
New cards
profitability, liquidity, solvency
The three categories of ratios:
18
New cards
Profitability
_________ ratios focus on a company’s net income within a current period.
19
New cards
Liquidity
_______ ratios indicate how well a company can use or sell current assets to pay the liabilities they have.
20
New cards
Solvency
________ ratios assure that a company can repay lenders and interest payments.
21
New cards
Net profit margins
_________ help when evaluating a company and shows the percentage of revenue a company generates.
22
New cards

\
Equation to calculate Net Profit Margin:
23
New cards
gross profit percentage
A(n) __________ shows the overall profit made on sales.
24
New cards

\
Equation to calculate gross profit percentage:
25
New cards
fixed asset turnover
The _______ ratio tells us the revenue earned for the amount of money a company puts into fixed assets.
26
New cards

\
Equation to calculate fixed asset turnover:
27
New cards
return on equity
The ________ ratio compares earned income for stockholders to the average amount of equity. It is reported as a percentage.
28
New cards
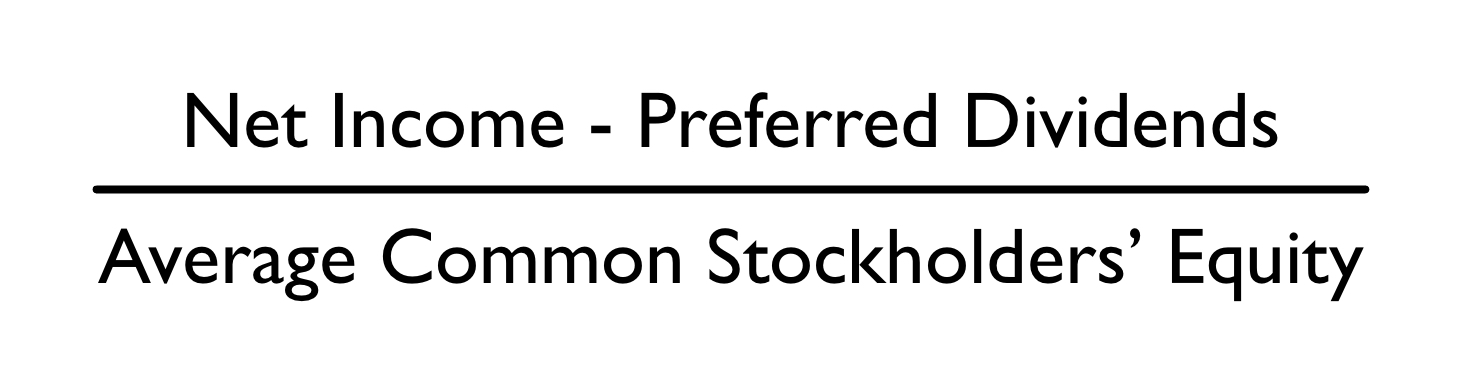
\
Equation to calculate return on equity:
29
New cards
Earnings per share
________ gives the amount of earnings from outstanding shares.
30
New cards
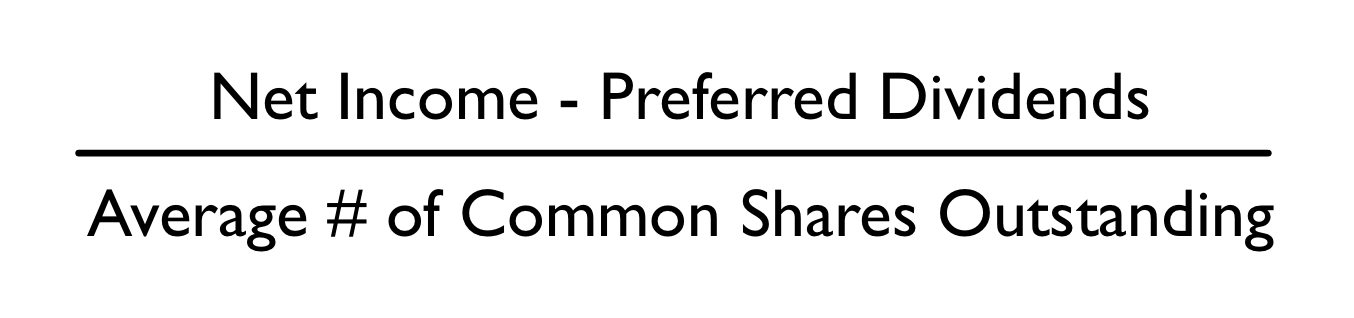
\
Equation to calculate earnings per share:
31
New cards
price/earning
The ________ ratio correlates the stock price to the stock’s earnings per share.
32
New cards
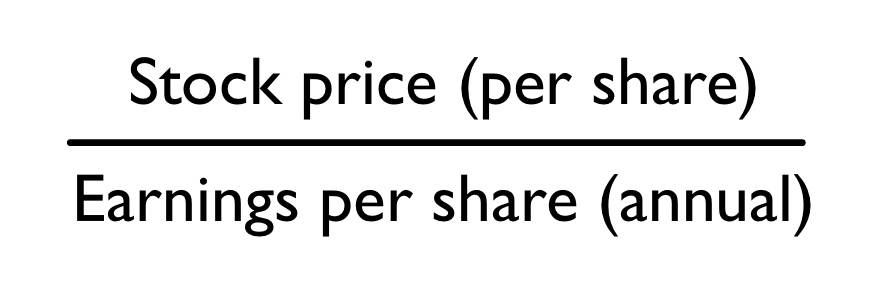
\
Equation to calculate price/earnings ratio:
33
New cards
receivables turnover
The ________ ratio indicates how well a company can collect on its’ receivables.
34
New cards
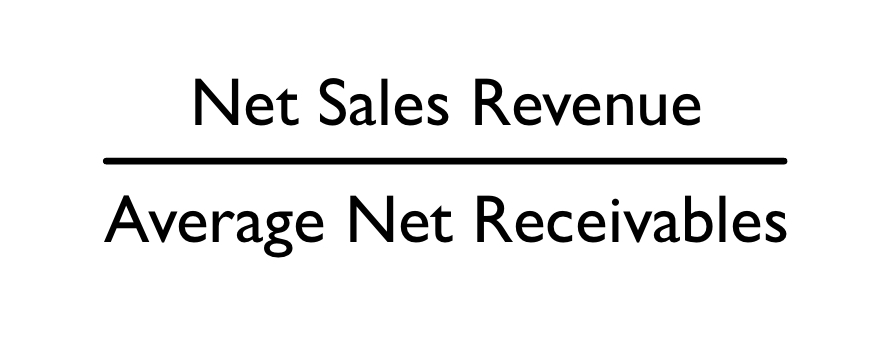
\
Equation to calculate receivables turnover:
35
New cards
inventory turnover
The _________ ratio is the frequency of inventory being bought during the process of buying and selling items.
36
New cards

\
Equation to calculate inventory turnover:
37
New cards
current
The ________ ratio compares current assets to current liabilities to see if those assets can pay the liabilities.
38
New cards
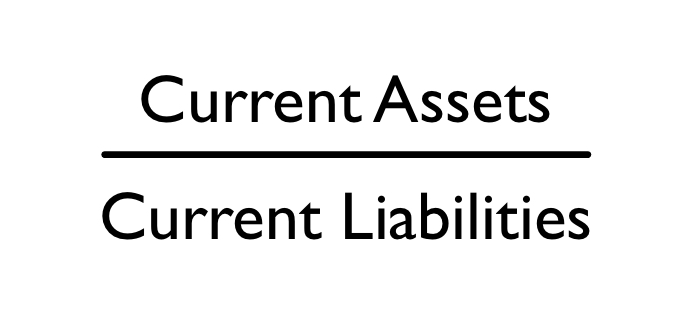
\
Equation to calculate current ratio:
39
New cards
debt-to-assets
The ________ ratio is able to show how much of a company is funded by debt and financed by creditors.
40
New cards

\
Equation to calculate debt-to-asset ratio:
41
New cards
times interest earned
The ________ ratio indicates if a company’s current income can cover its debts.
42
New cards
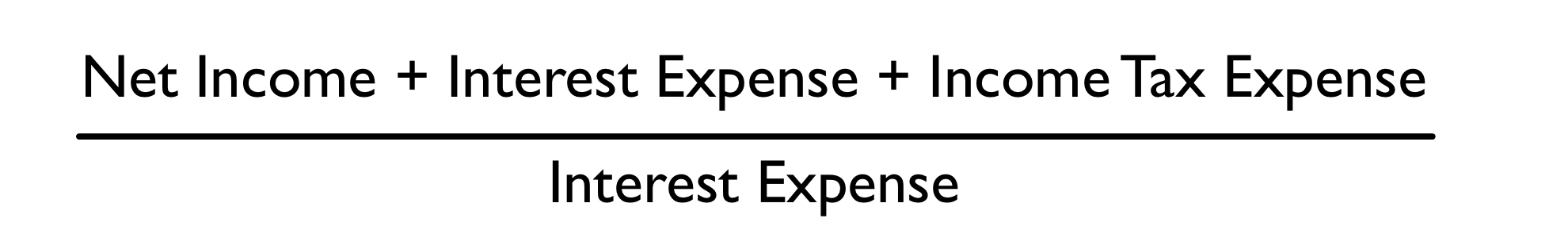
\
Equation to calculate times interest earned:
43
New cards
how and why a company makes the decisions they do
Ratios can give us insight into ________.
44
New cards
Choice of method
_________ for certain aspects of business are different from business to business.
45
New cards
full disclosure principle
The _________ demands that all appropriate information regarding a business’s operations must be included on their financial statements.
46
New cards
going-concern assumption
The ________ lays out accounting rules.
47
New cards
continuity
The going-concern assumption is also called _________.
48
New cards
significant changes
________ are the focus of horizontal computations.
49
New cards
horizontal (trend) computations
Horizontal (trend) analyses is also called _________.
50
New cards
dollar amount and percentage
Examine and compare the ________ to ensure your final results and conclusion.