TEST 1 psyc ch 5, 10, motivation
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
developmental psychologists
types of psych that studies physical, cognitive and social development throughout your lifespan
cross sectional studies
research that compares people of different ages at the same point in time
longitudinal studies
research that retests the same people repeatedly over time
what three main issues are being explored in research?
Nature vs nurture
continuity and stages
stability and changes
explain the idea of continuity and stages:
scientists may see development as a biological (stages) process predisposed by genes (like going from childhood to puberty, which everyone goes trough at some point) or as a slow continous process if they emphasize learning (continuity)
what are the 3 stages theories we will consider and from whom they are?
Cognitive development (Jean Piaget)
Moral development (Lawrence Kohlberg)
Psychosocial development (Erik Erikson)
stability and changes
stability: temperament is stable and may be the same throughout your entire life
change: only because we grew up in a certain way means we will be like that for the rest of our lives

Stage theory is supported by the cognitive, moral and psychosocial development
Temperament
how does a sperm attach to a egg
the sperms (way smaller than the egg) attach to it and release digestive enzyme, which will eat the protective coat of the egg and the winning sperm will become one with the egg.
fertilized eggs are also called =
zygotes
explain the prenatal development:
impacted by genes and environment (aclcohol, drugs)
fetus is responsive to sounds
what is habituation?
when we get used to something and with time we react less to it
what is maturation?
its the orderly seguence of biological growth
what is infantile amnesia?
earliest memories ar when they r 3 years old
its because babies have inmature brain regions, lack of retrieval cues and unclear of self concept
what are schemas and its two types?
schemas: organized patterns of thoughts and action, its like a guide for interaction and a mold where we pour our experiences
types: assimilation and accomodation
assimilation: incorporating new experiences into our current understanding, its like saying doggy instead of cat
accomodation: adjusting/modifying existing schem or creating a new one
Piagets 4 stages? Only list them
Sensorimoto stage
Preoperational stage
Concrete operational stage
Formal operational stage
Define the sensorimotor stage of piaget: (1 key word)
babies acquire info by sensing and moving around
its from birth to nearly 2 years
object permanence: awareness that objects exist even when not perceived
define the preoperational stage of piaget:
use words to represent schema
engage in pretend play
replace egocentrism with theory of mind
theory of mind: when they can understand others mental states and that they have their own thoughts and perspectives
define the concrete operational stage of piaget
understand how actions can affect or transform concrete objects
7-12 years
conservation: notion that properties remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects
define the formal operational stage of piaget:
reasoning ability expands to abstract thinking
algebra, systematic reasoning
nowdays researchers believe development is a continous process
culture influences cognitive

difference between piaget and vygotsky research
piaget: how the childs mind grows through interaction with the physical environment
vygitsky: how the childs mind grows through interaction with the social environment
according to vygotsky, whats a scaffold
by mentoring children we give them so kind of support in their learning
by age 7, kids speak to themselves while doing things
its the mentoring or support a kid needs
explain stranger anxiety and attachment between kids and caregivers
kids dont like strangers
they are attached to their caregivers is a survival impulse, thought to be due to a need of nourishment, but not really.
explain attachment of kids and caregivers:
two reasons for attachment: body contact and familiarity.
Body contact gives comfort and a secure base, which will change from parents to peers.
Familiarity happens during the critical period (imprinting)
define avoidant and anxious attachment:
avoidant: people get discomfort in getting close to another and maintain distance
anxious: people crave acceptance but remain alert for rejection
list the 4 types of parenting styles:
Authoritarian (no exceptions)
Permissive
Neglectful
Authoritative (exceptions)
Adolscence starts with ______ ______
Myelin and glial cells ______
imaginary audience and _____ ______, which means ___________________________
sexual maturity (puberty)
increase
personal fable, which is when we think we r unique and what happens to others wont happen to us.
list the 3 types of morality:
moral reasoning
moral intuition
moral action
define moral reasoning:
the thinking that occurs when perceiving right from wrong
three stages: preconventional, conventional and postconventional. They used the example of stealing medicine
preconventional: if you steal medicine, you go to jail (absolute morality)
conventional: if you steal medicine, everyone will think you are a criminal (what others think)
postconventional: saving someone is worth more than whether stealing is wrong or not (morality depends on situation)
define moral intuition:
desire to punish somepne is more of an emotinal reaction, making judgements relying in our fears.
define moral action:
moral people corrupted by a poerwful evil situation, delay gratification
erickson thought that each age/stage had an ____ to solve
issue
attachment styles reflect …..
patterns of emotions/behaviours
define anxious ambivalent and anxious avoidant
they are both insecure attachments styles
ambivalent characterized by a strong need for intimacy, high anxiety about abandonment, and inconsistent caregiving, leading to clinginess,
avoidant involves discomfort with closeness, prioritizing independence, and emotional distance due to insensitive caregiving, creating a conflict between wanting connection and fearing vulnerability.
define intelligence:
ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
who are the 5 psychologists who came up with theories:
Charles Spearman
Thurstone
Cattell-Horn-Carroll
Gardner
Robert Sternberg
What was Charless spearman ideology/theory:
he believed in the g factor (general intelligence), heart of all intelligent behaviour
factor analysis: statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related variables
What was Thurstones ideology/theory:
he thought there were 7 clusters of primary mental abilities and used multiple scales. the people who scored well in all factors showed that there is some kind of g factor acting as an umbrella.
What was Cattell-Horn-Carroll ideology/theory:
used thornstone ideology and brought it down to 2 factors: Fluid and Crystallized intelligence
Fluid: Abstract thinking, solving problems
Crystallized: accumulated knowledge
they recognized that intelligence comprises many abilities and they all live under a broader umbrella of intelligence.
What was Gardner ideology/theory:
8 relatively independent intelligence
9th intelligence: existential intelligence
what is savant syndrome:
when you have an island of brilliance but low score on intelligence score
this supports theories of multiple intelligences
What was Robert sternberg ideology/theory:
triarchic theory proposes 3 intelligences
analytical: academic, problem solving, solve problems with one single right answer
creative intelligence: ability to adapt to new situations and generate novel ideas
practical intelligence: for everyday tasks and poorly defined and have multiple solutions
talk about emotional intelligence:
it gives us 4 abilities:
perceiving emotions
understanding emotions
managing emotions
using emotions
what does an intelligence test do? what are the achievement and aptitude tests?
asseses peoples mental aptitudes and compares them using numerical scores
achievement: reflects what you have learned
aptitude: predict what you will be able to learn
What was Alfred Benoit ideology/theory:
he believed in the mental age: the level of performance topically associated with children of a certain chronological age
his idea for the test was to find children who need help at school and help them
What was lewis ternman ideology/theory:
intelligence quotient (IQ): fomrula for score tests
supported eugenics
What was david wechsler ideology/theory:
Wechsler adult intelligence scale
it finds similarities, vocab, block design, letter and number sequencing
What are the 3 principles an IQ test should follow:
Standarization: defining uniform testing procedures and then comparing the test score
Reliability: it needs to give consistent scores and have to be tested many times
Validity: the extent to which the test actually measures or predicts what it promises
predictive validity: it is how well a test predicts the behaviour its supposed to preditc
What are the 2 extremes of intelligences?
Low: intellectual development disorder, apparent before 18 and due to physical causes
High: academically succesfull
in the aging and intelligence topic…
Ci (accumulated intelligence) increases with old age
Fi (solving logic problems) may decline
what is heritability:
portion of variation among individuals in a group that we can contribute to genes
it only applies to why people in a group differ from one another
fraternal twins score are more alike than ————
non twin siblings
What was carol dweck ideology/theory:
growth mindset which focuses on learning and growing
there is a _____ _____ when it comes to testing
stereotype threat
define motivation:
describes the wants and needs that direct bahviour towards a goal
define extrinsic and intrinsic motivation
intrinsic: internal factors, cuz of personal satisfaction
extrinsic: external factors, in order to receive something from others
what is the overjustification effect:
intrinsic motivation is diminished when extrinsic motivation is given
makes us being dependent on extrinsic rewards for continued performance
verbal reinforcements may increase intrinsic motivation
William james theory: (define instincts and homoestasis)
behaviours was driven by a number of instincts which aid survival
instincts: species specific pattern of behaviour that is not learned
seeks for homoestasis: tendency to maintain balance within biological system
define the Drive Reduction Theory of Motivation:
deviations from homoestasis create physiological needs
makes our behaviour do something to bring body back to homoestasis (like hunger)
what is a habit:
its a pattern of behaviour in which we regularly engage.
it usually reduced the drive, so we will keep doing it
define the Yerkes-Dodson Law:
the optimal arousal level depends on the complexity and difficulty of the task to be performed
simple tasks are worked better when arousal levels are ______
difficult tasks are worked better when arousal level are _______
high
low
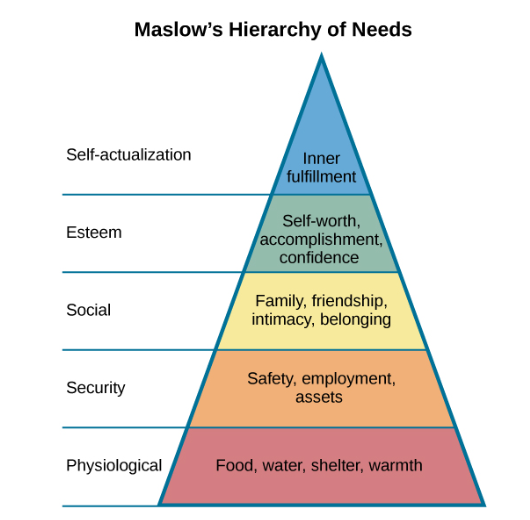
talk about the Maslow hierarchy of needs, mention the parts of the pyramid
define satiation and to what hormone is it associated:
when you are done with eating and stop eating
leptin
what parts of the brain determine whether or not to engage with behaviour:
hypothalamus and hindbrain
what does glucose do:
keeps tabs on its available resources
if insulin increases, _______, and this converts it into _____ ___.
If glucose decreases, brain will trigger _____,
blood glucose decreases and this converts this into stored fat
hunger
what happens if the neural arc called arcuate nucleus nucleus gets destroyed?
starving animals have no interest in food
what is grehlin?
hunger arousing hormone secreted by an empty stomach
when apetite increases:
grehlin: by stomach, sends hungry signals to brain
orexin: by hypothalamus
when apetite decreases:
insulin: by pancreas, controls blood glucose
leptin: protein hormone by fat cells, when abundant causes brain to increase metabolism and decrease hunger
PYY: digestive tract hormone, send the im not hungry signals to brain
what is metabollic rate:
amount of energy expended in a given period of time
what is the set-point theory:
each individual has an ideal body weight (or set point) which is resistant to change
this doesnt take into account environmental or social factors
what is the affiliation need:
need to belong is key to human motivation
what is the self determination theory:
its a theory that strives to satisfy 3 needs: competence, autonomy and relatedness
what is ostracism:
social exclusion, it hurts as much as physical pain, used to controls social behaviour
karl pribram 4 basic human drive states
feeding, fighting, fleeing and sex
define the following terms:
sex
gender
sexual orientation
sexual fluidity
sexual orientation concordance rate (SOCR)
2 intersex conditions
sex: biological gender
gender: psychological identity
sexual orientation: to what u r attracted
sexual fluidity: changing due to circumstances
sexual orientation concordance rate (SOCR): probability tat a pair of individuals have the same sexual orientation
2 intersex conditions: androgen sensitivity and turners syndrome
what are the two types of validity: content and predictive validity?
content: extent test measures a particular behaviour
predictive: can a test predict a particular behaviour
what are the 3 types of reliability? split half, test retest and interjudge?
split half: internal consistency, dividing the test in 2 parts
test retest: use same test on 2 ocassions
interjudge: different scorers of same test
what is retification:
viewing an abstract thing as if it was a concrete thing
Aptitude test are _____ and necessarily ______
Valid, biased
What are cultural intelligences 4 components:
Metacognitive
Cognitive
Motivational
Behavioural
Mindsets are _________
Believes we hold
Incremental theorists believe that
Traits are changeable
what are the 4 psychological perspectives theories??
Instinct theory/evolutionary theory
Drive reduction theory
Arousal theory
Maslows hierarchy of needs
Talk about the instinct theory
fixed pattern of behaviour not acquired by learning (genes)
Drive reduction theory:
motivated to reduce drives (restores homoestasis)
aroused state related to physical need
Optimal arousal theory
motivated to maintain a level of arousal thats optimal
less arousal - boredom - motivation for stimulation (procastinate)
more arousal - overstimulation - motivation for calm
the Yerkes dodson law: optimal level of arousal varies with easy and difficult tasks
Maslow Hierarchy of needs
holistic approach, always motivated by needs
levels from bottom to top: basic needs, psychological needs, self-fullfiling needs
affiliation need?
need to build relationships
Self determination theory
humans are driven by a need to grow
what are the 3 psychological needs:
autonomy
relatedness
competence
List the appetite hormones in the groups of increase and decrease appetite:
increase appetite:
ghrelin: by empty stomach, sends hungry signals to brain
orexin: hunger triggering hormones by hypothalamus
decrease appetite:
insulin: by pancreas, controls glucose
leptin: by fat cells, causes brain to increase metabolism and decrease hunger
PYY: digestive tract hormone, send im not hungry signals to brain
talk about glucose:
form of sugar circulating the blood
source of energy for body tissues
level low- hungry