S+F II Lab Midterm
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
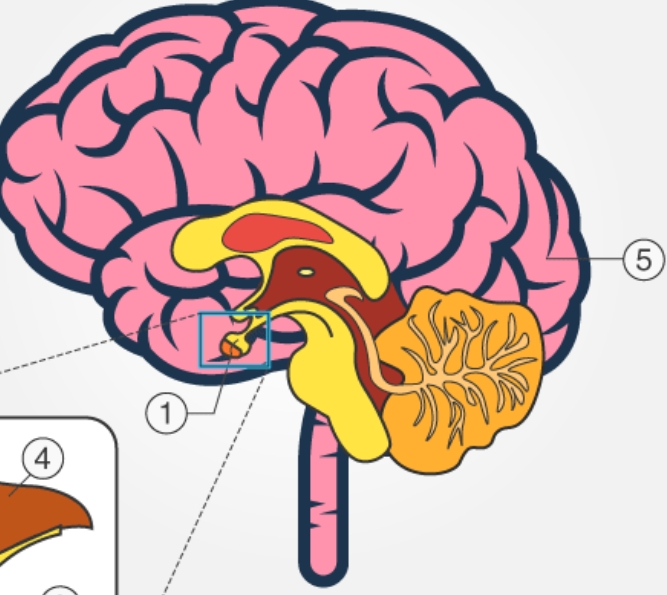
NAME
Pituitary gland
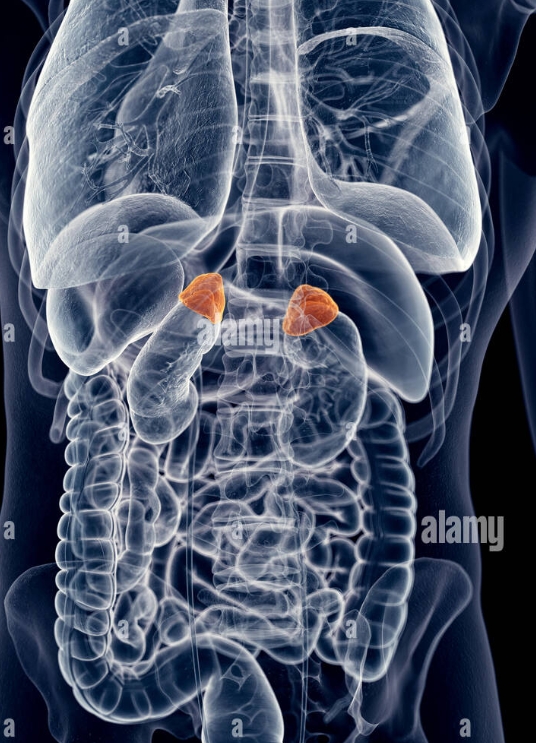
NAME
Adrenal Glands
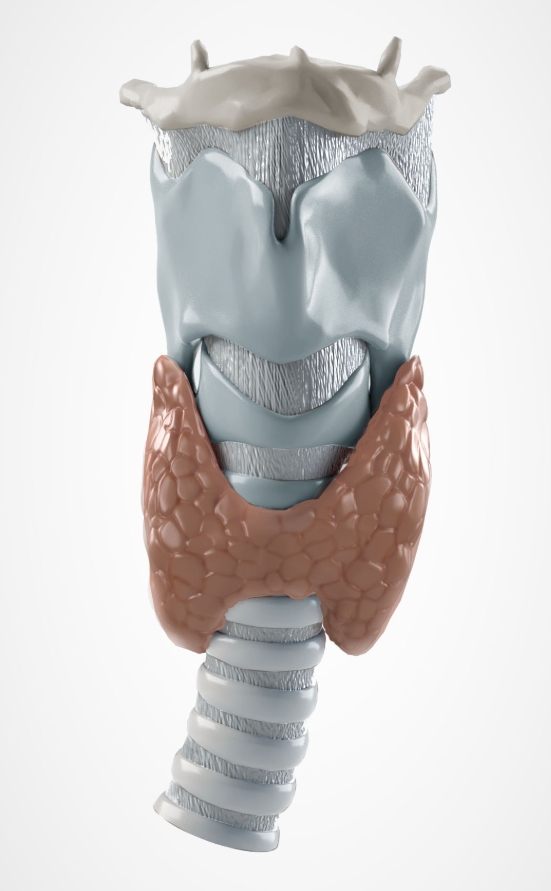
NAME
Thyroid
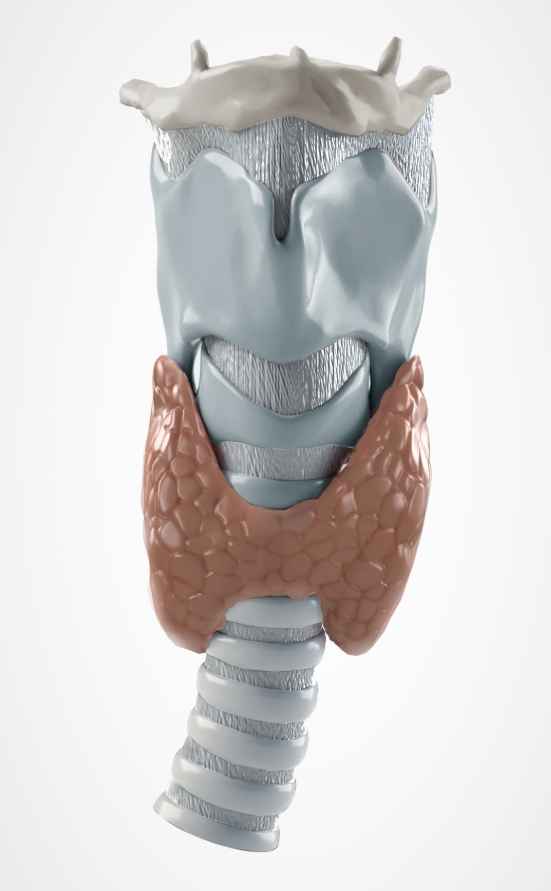
NAME (POSTERIOR)
Parathyroid
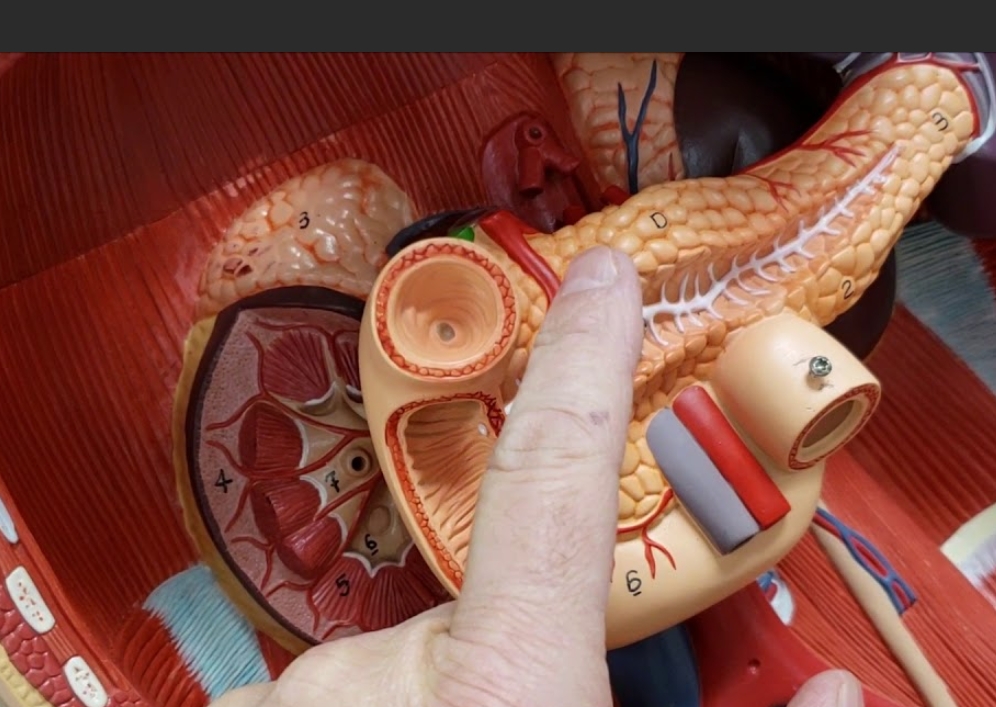
NAME
Pancreas
NAME
Thymus
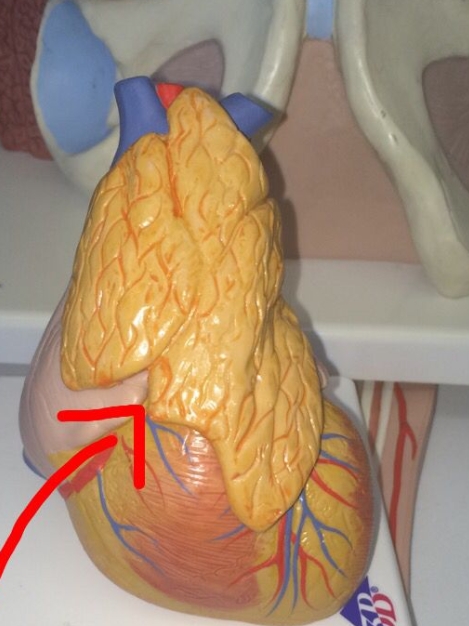
NAME - Tissue
Pituitary gland
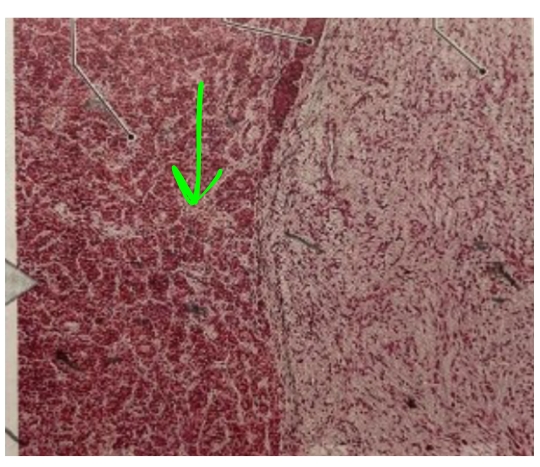
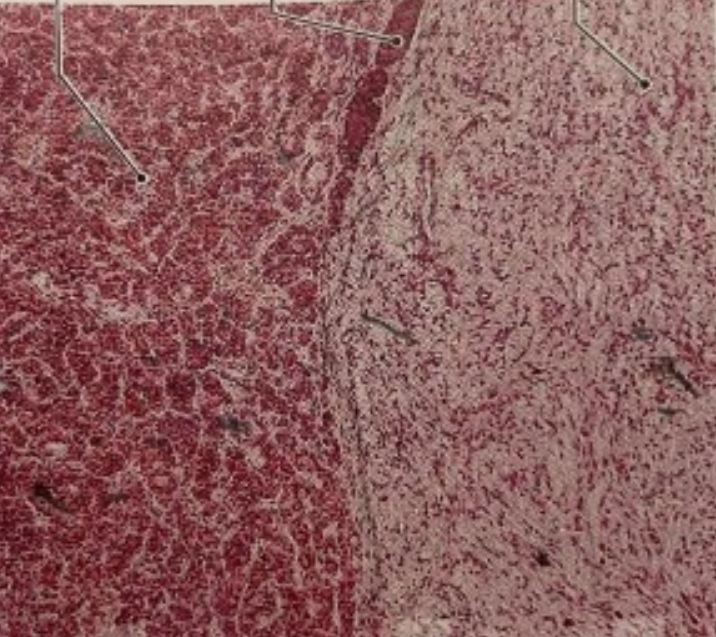
NAME
Pars Distalis
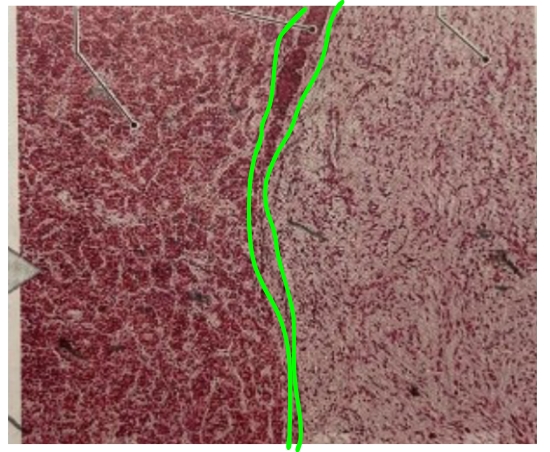
NAME
Pars Intermedia
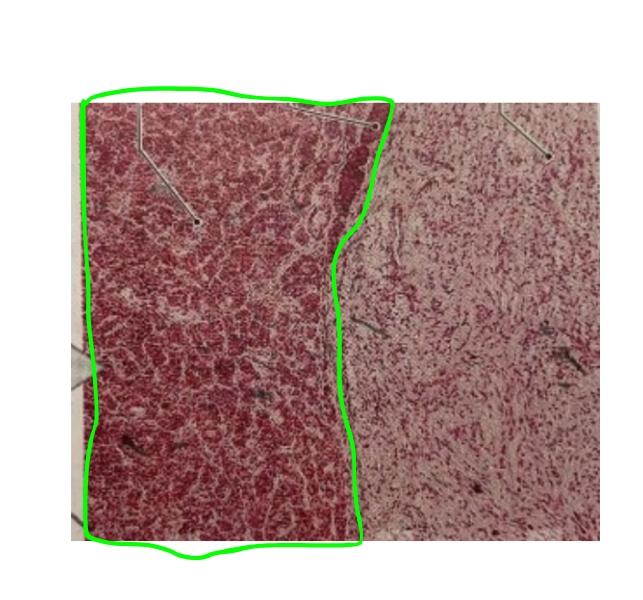
NAME
Adenohypophysis (Anterior Piturary Gland)
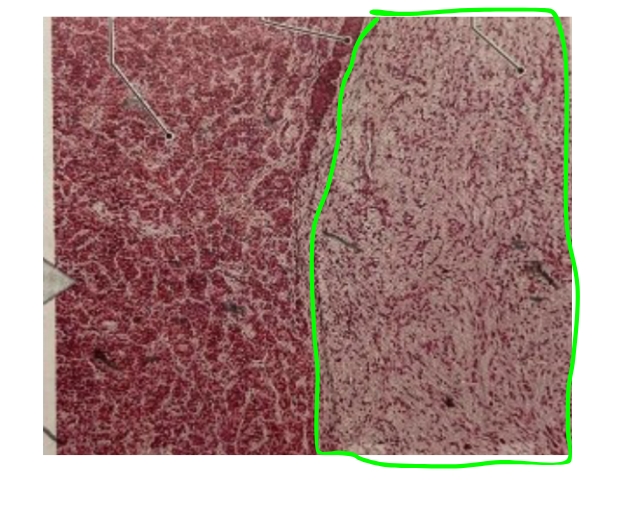
Name
Neurohypophysis (Posterior Pituitary Gland)
What does the anterior pituitary gland originate from?
Glandular epithelial
What does the posterior pituitary gland originate from?
Neural tissue
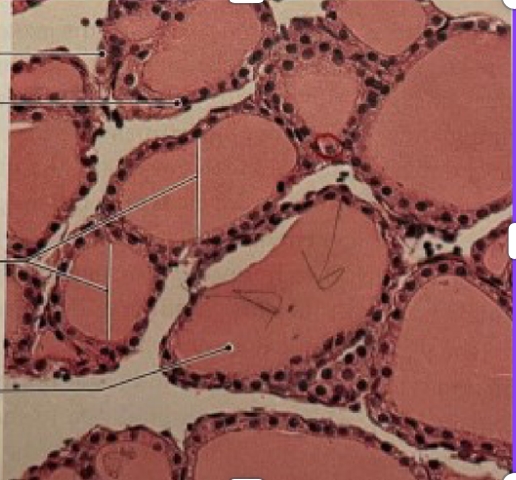
NAME (Tissue)
Thyroid
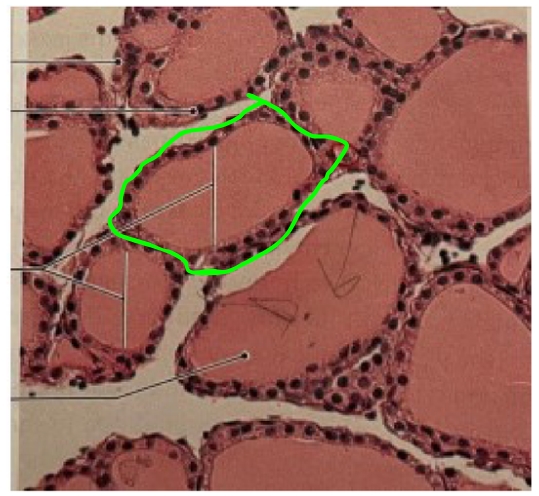
NAME
Follicle
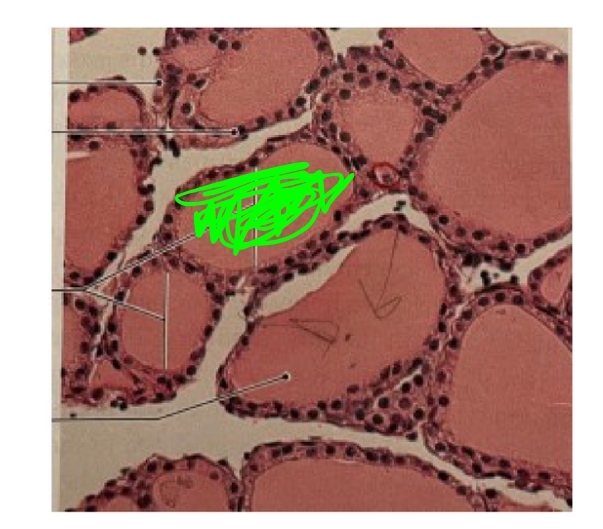
NAME
Colloid
What is colloid?
A fluid substance that fills thyroid follicles and is full of thyroglobulin
What is thyroglobulin?
A protein precursor for T3 and T4 hormones
What parts of the thyroid make certain hormones?
Follicle - T3 and T4
Parafollicular Cells - Calcitonin
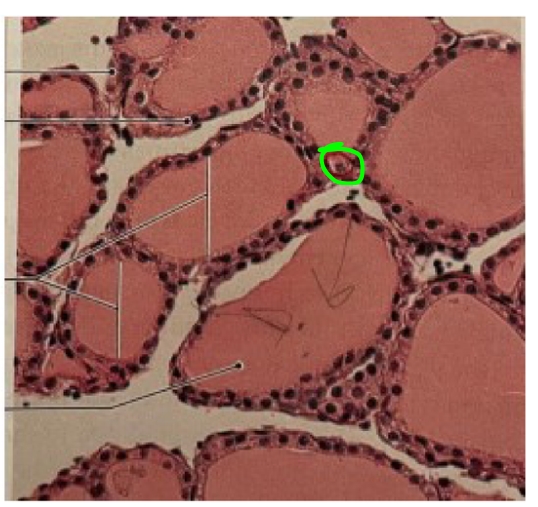
NAME
Parafollicular Cells
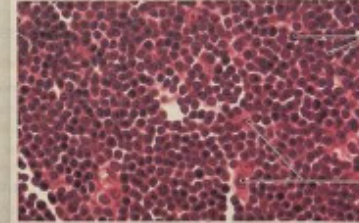
NAME (tissue)
Parathyroid
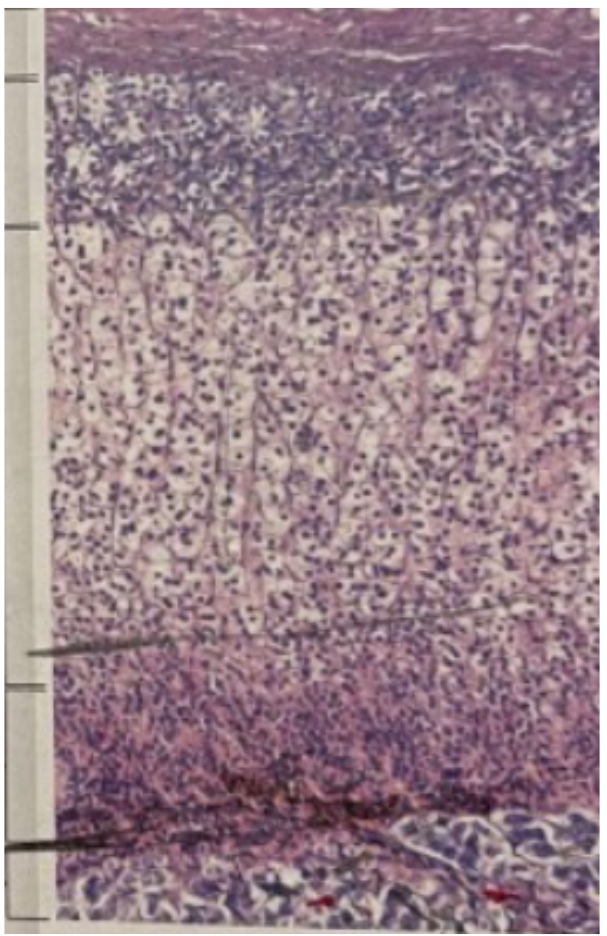
NAME (tissue)
Adrenal Glands
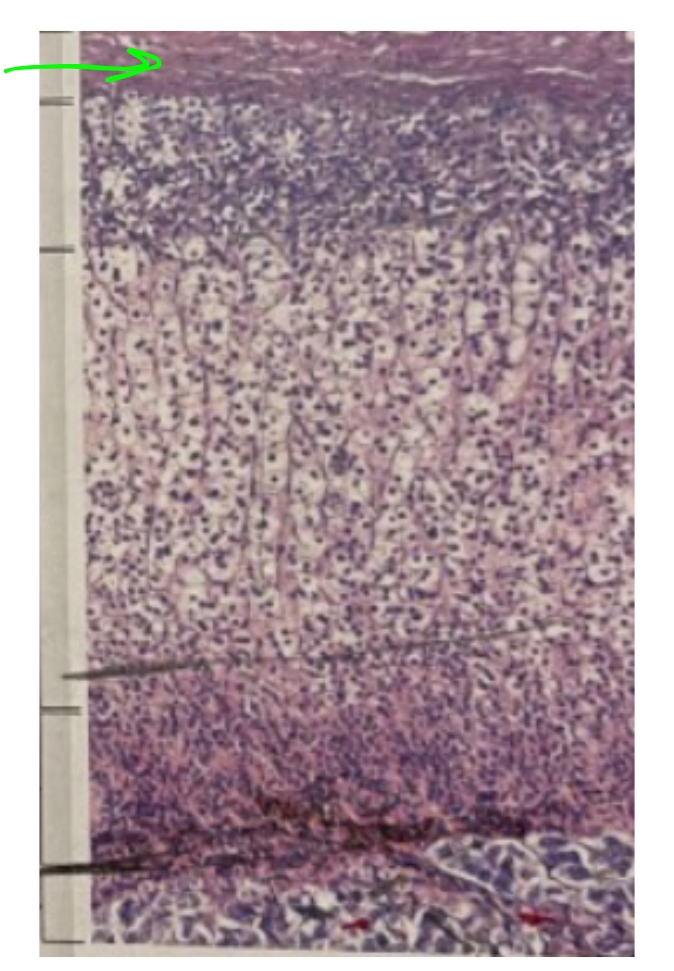
NAME
Capsule
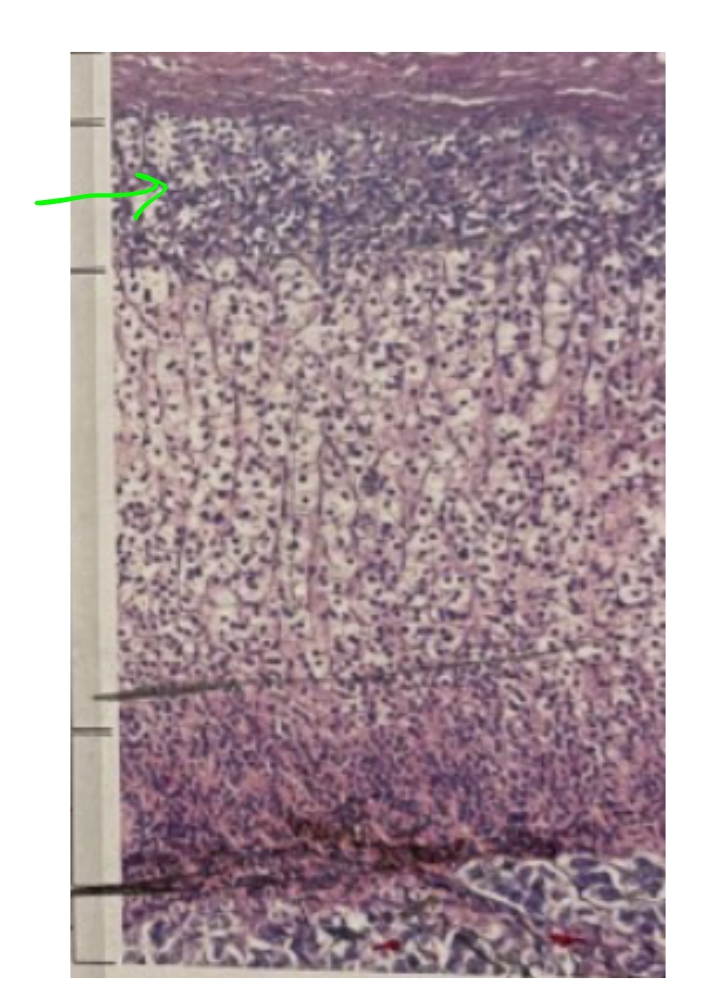
NAME
Zona Glomerulosa
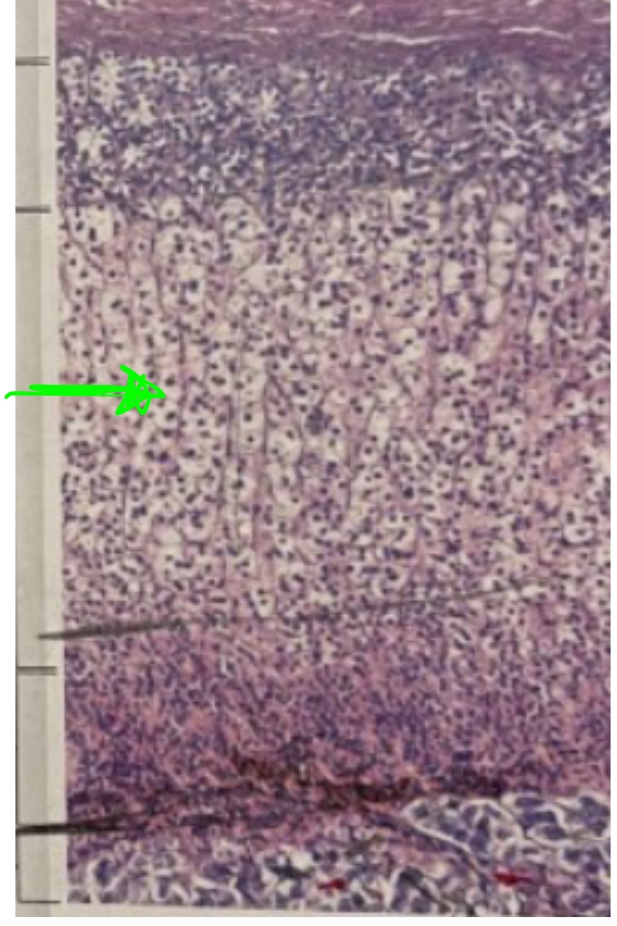
NAME
Zona Fasciculata
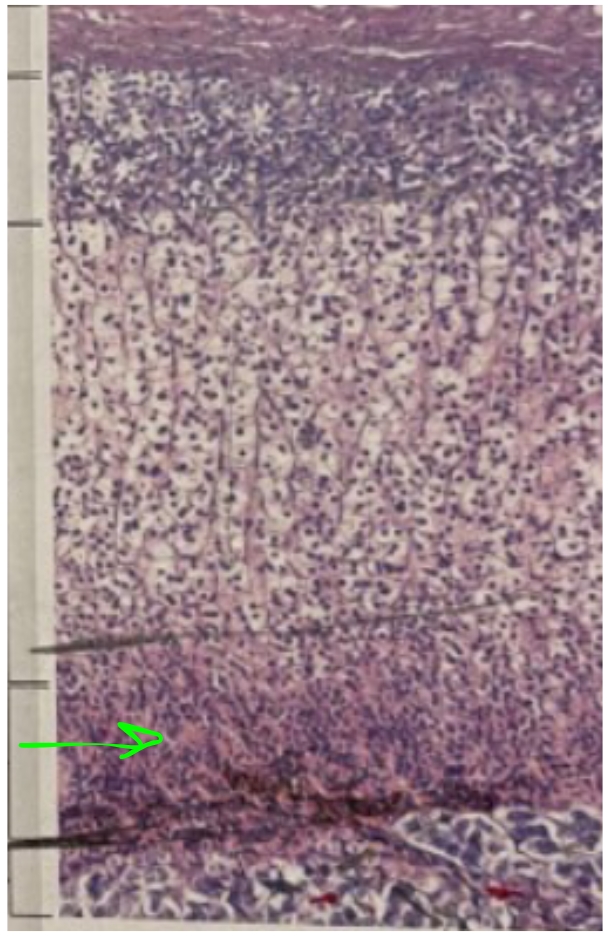
NAME
Zona reticularis
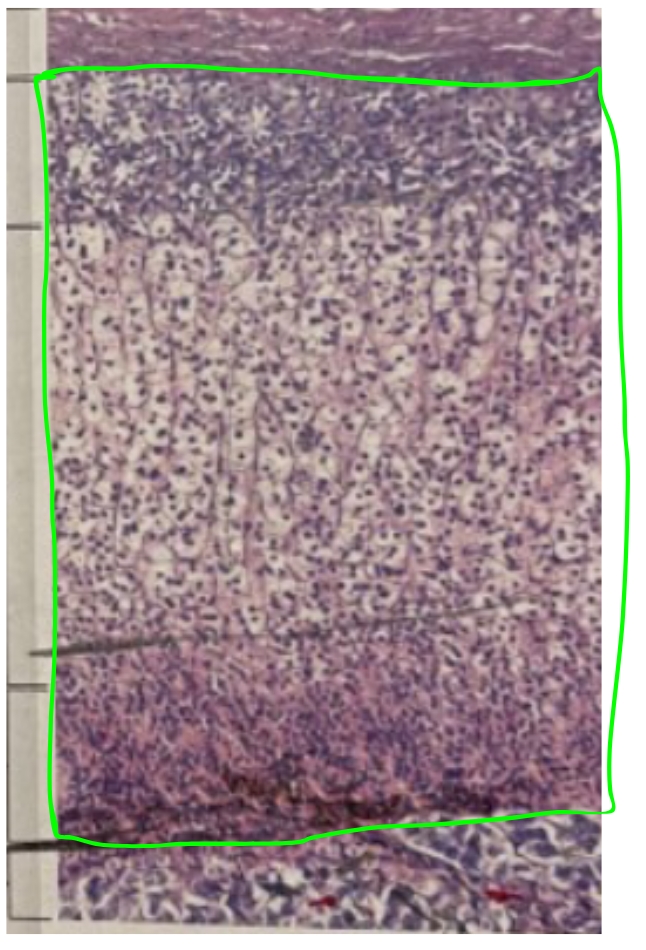
NAME
Adrenal Cortex
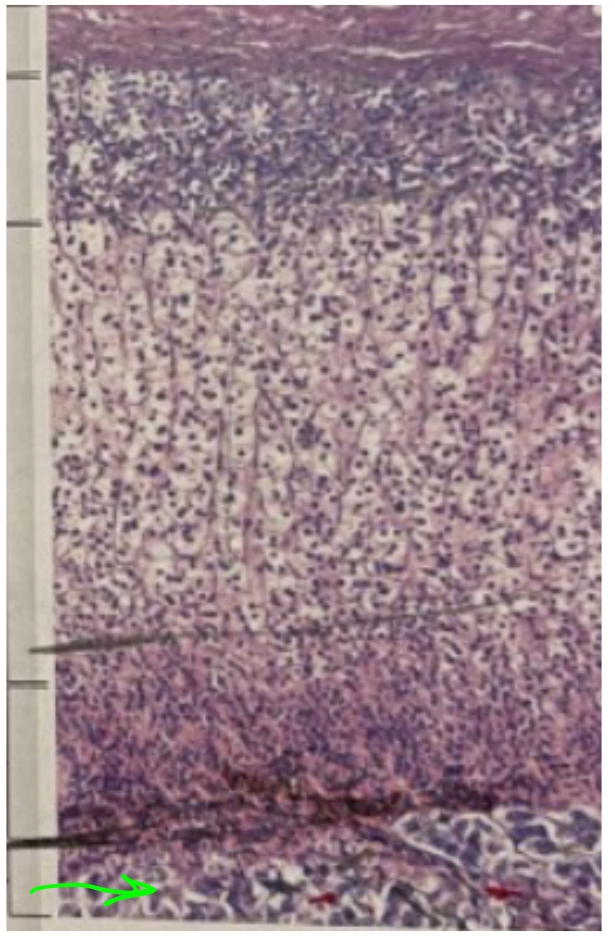
NAME
Adrenal Medulla
What is produced by medullary cells?
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
What is made by zona glomerulosa?
Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone)
What is made in zona fasciculata
Glucocorticoids (Coritsol)
What is made in zona reticularis?
Androgens (DHEA/Estrogen Precursor)
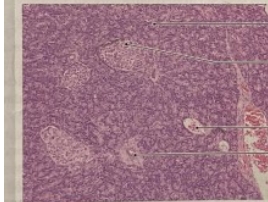
NAME
Pancreas
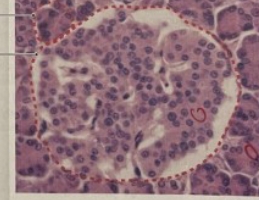
NAME
Islet of Langerhans or Pancreatic Islet
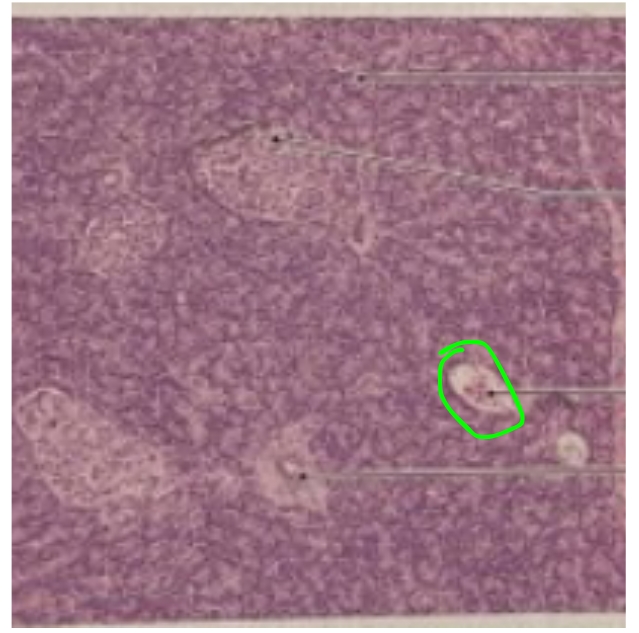
NAME
Blood Vessel
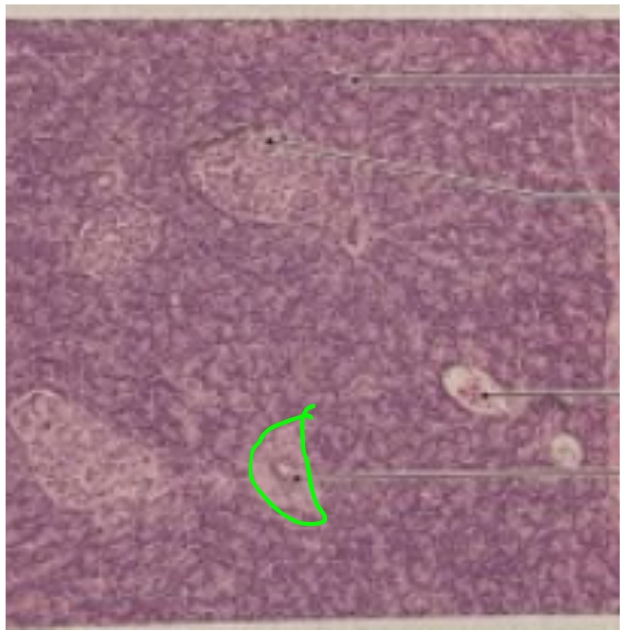
NAME
Pancreatic Duct
What hormone initiates ovulation?
Luteinizing Hormone
What hormones are made by the pituitary gland
LH - Luteinizing
GH - Growth
ACTH - Adrenocorticotrophic
TSH - Thyroid Stimulation
FSH - Follicle Stimulation
PRL - Prolactin
OT -Oxytocin
ADH - Antidiuretic
What does hyperinsulinism present as a neurologic condition
The brain is deprived of glucose
How does Epinephrine affect the Heart?
Harder contractions (MAIN EFFECT)
Faster bpm
How does Acetylcholine affect the heart?
Decrease BPM (MAIN)
Weaker contraction
What is hyperinsulinemia?
Excessive blood insulin
What is hypoinsulinemia?
Low blood insulin
What is hyperglycemia?
High blood sugar
What is hypoglycemia?
Low blood sugar
What is a ketone?
A byproduct of breaking down fat
What is ketoacidosis
The rising of blood pH due to an excess of ketone bodies
What is diabetic shock?
A state of severe hypoglycemia, usually due hyperinsulinemia
What is diabetic coma?
A loss of consciousness due to a lack of glucose in the brain
What is diabetes mellitus?
A disorder where a person loses functionality of insulin due to lack of production or insensitvity
What tests are done with diabetes?
Fasting Blood Glucose
Blood Ketones
Blood pH
Hematocrit
Urine Glucose
Urine Volume
Urine pH
How does diabetes affect fasting blood glucose
Higer (Insulin doesn’t pull into cells)
How does diabetes affect blood ketones?
Raises (Fats are broken down for enegry)
How does diabetes affect Serum pH
Lowers (Ketoacidosis)
How does diabetes affect Hematocrit
Raises (Removed water in urination)
How does diabetes affect urine glucose?
Raises (Sugars aren’t metabolized)
How does diabetes affect urine volume?
Raises (Need to expel excess glucose and ketones)
How does diabetes affect urine pH?
Lowers (Ketones)
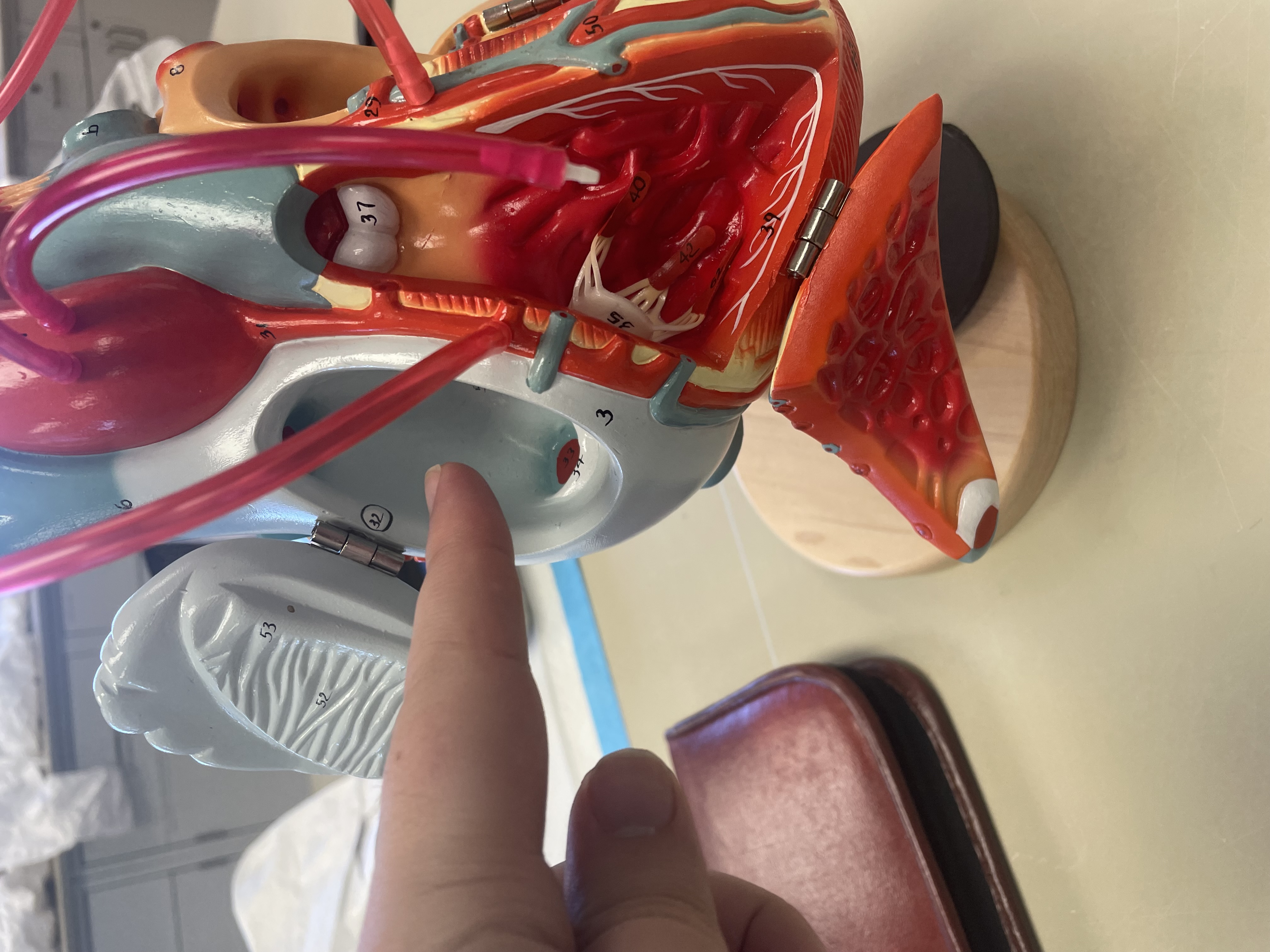

NAME
Right Atrium
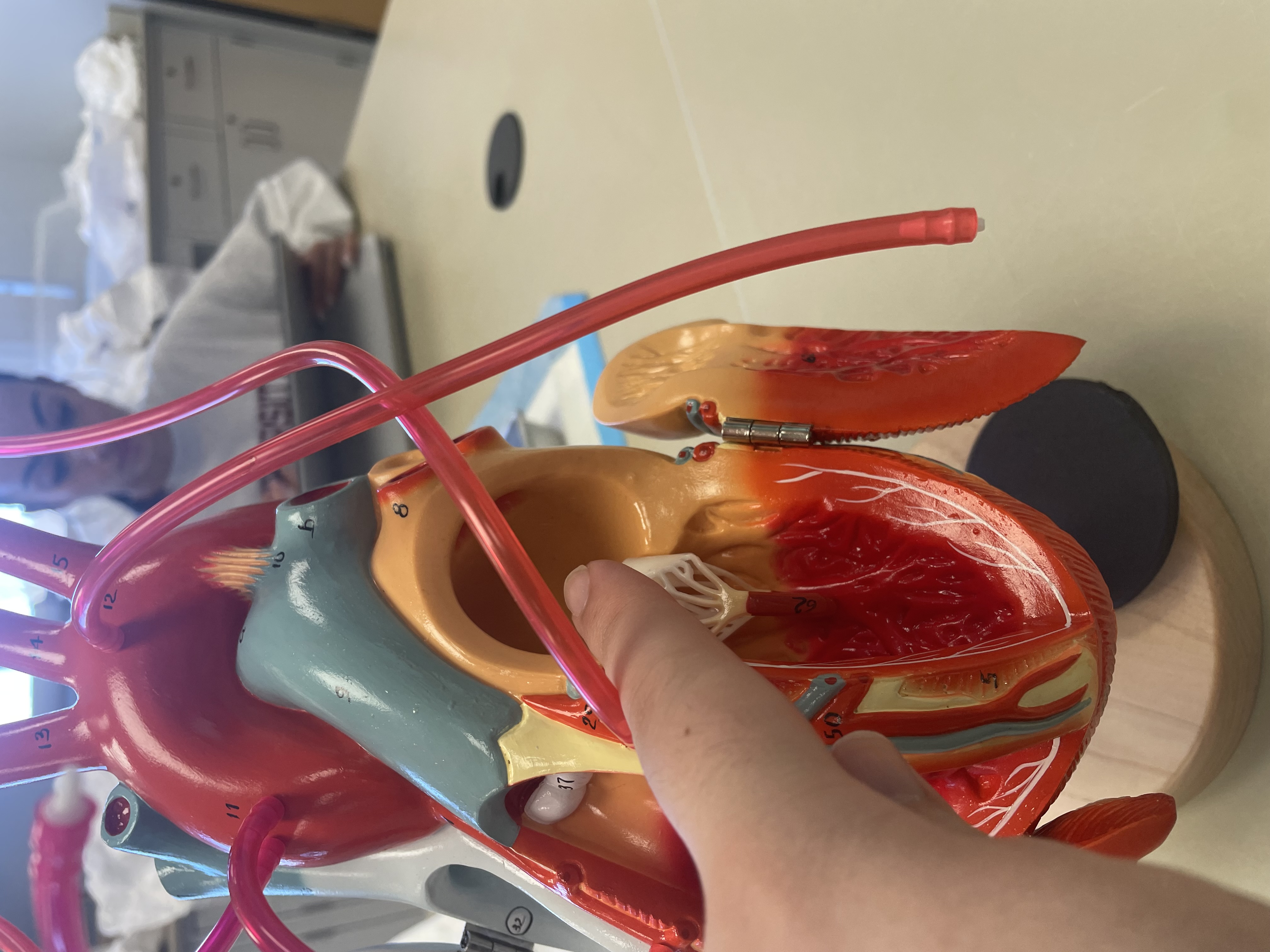
NAME
Left Atrium
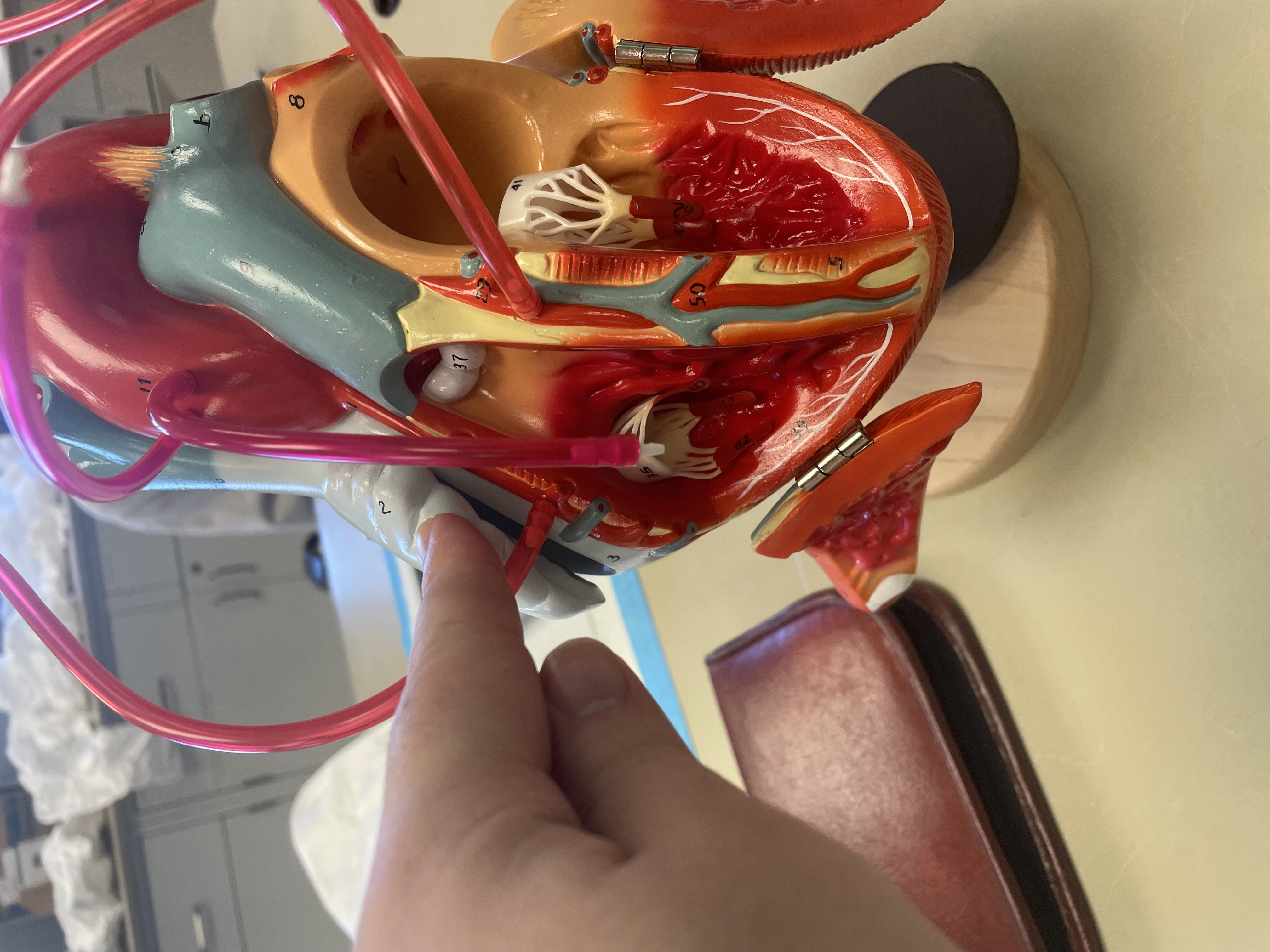
NAME
Right Auricle
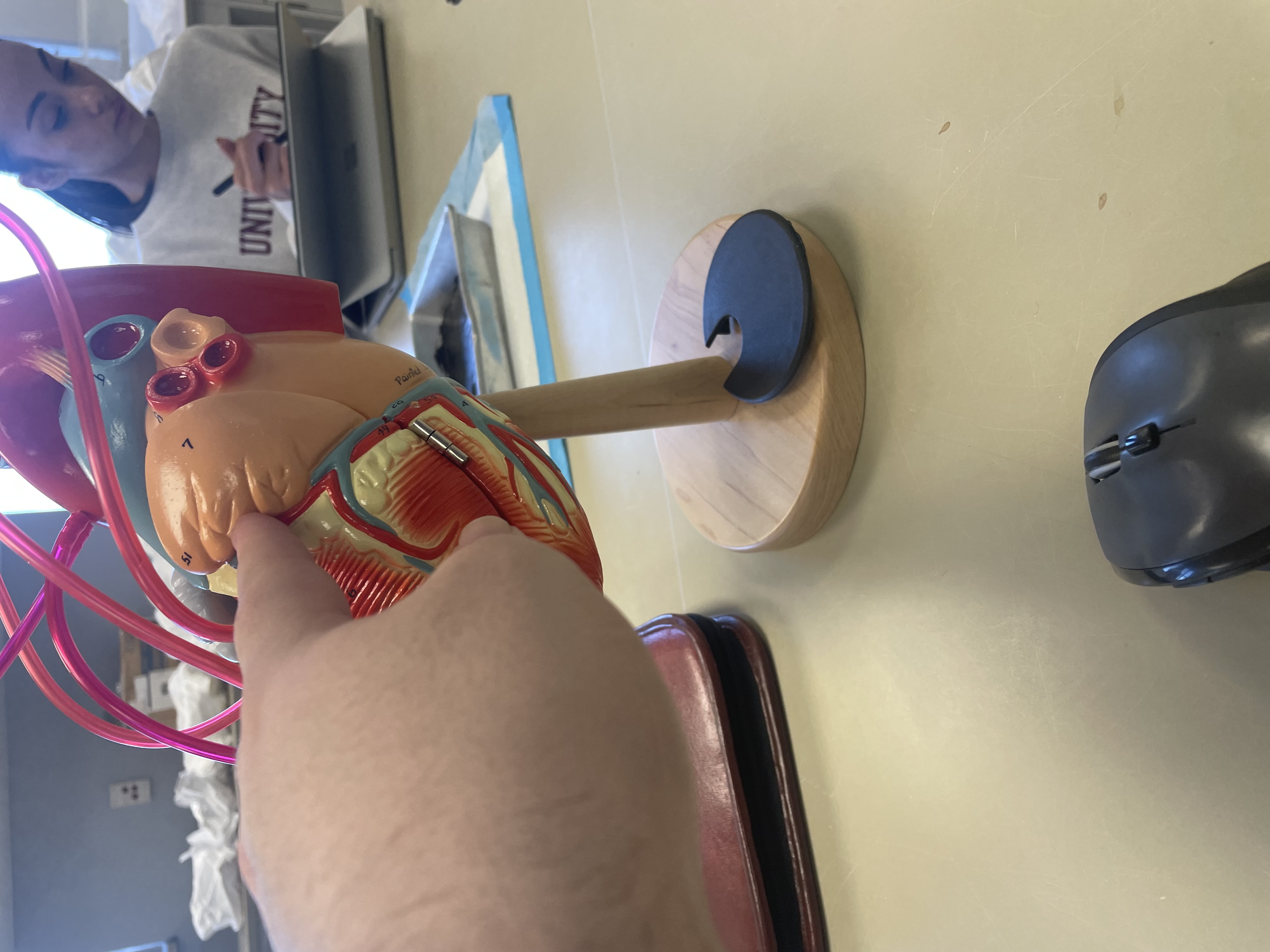

NAME
Left Auricle
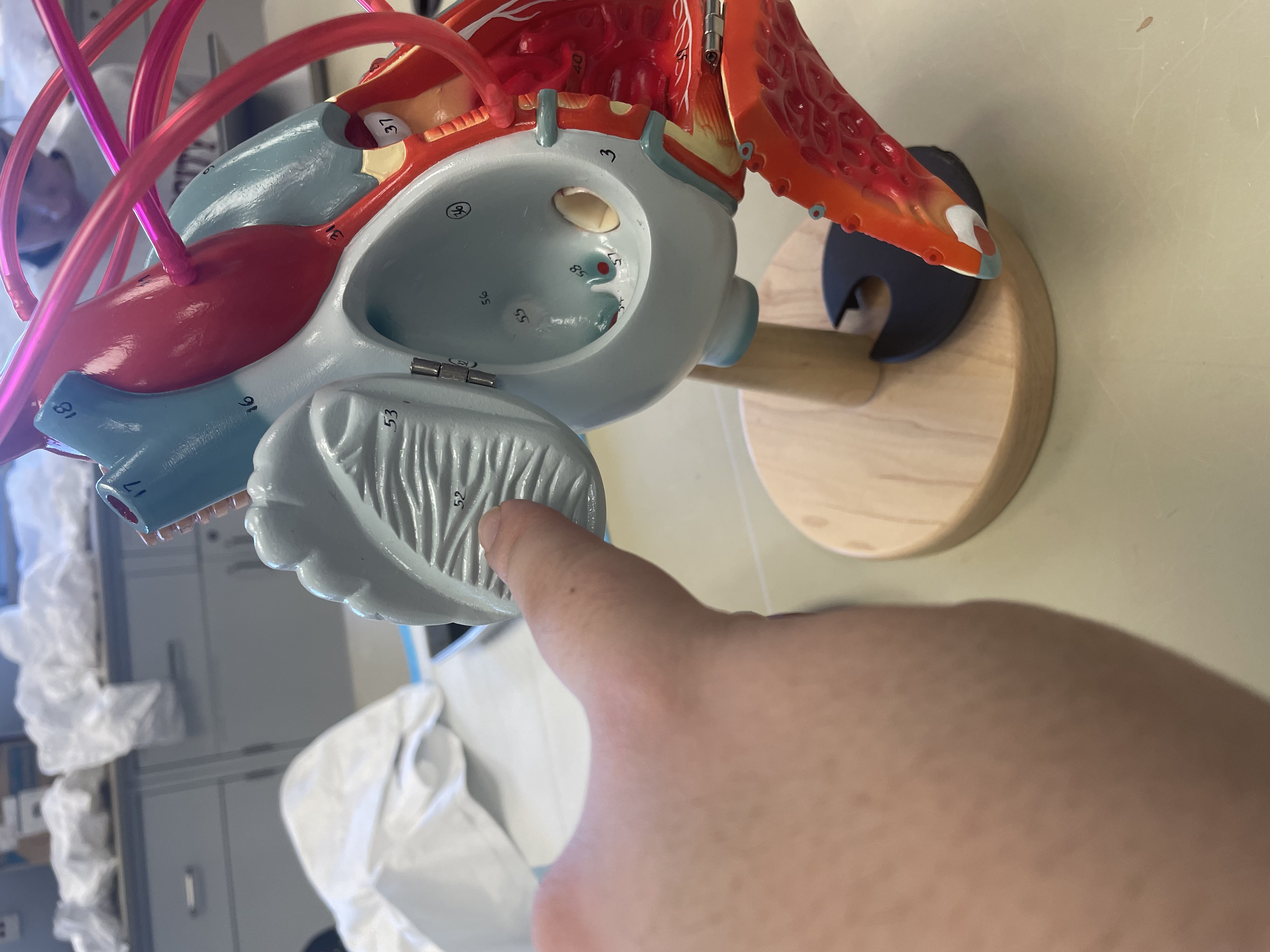
NAME
Pectinate Muscle
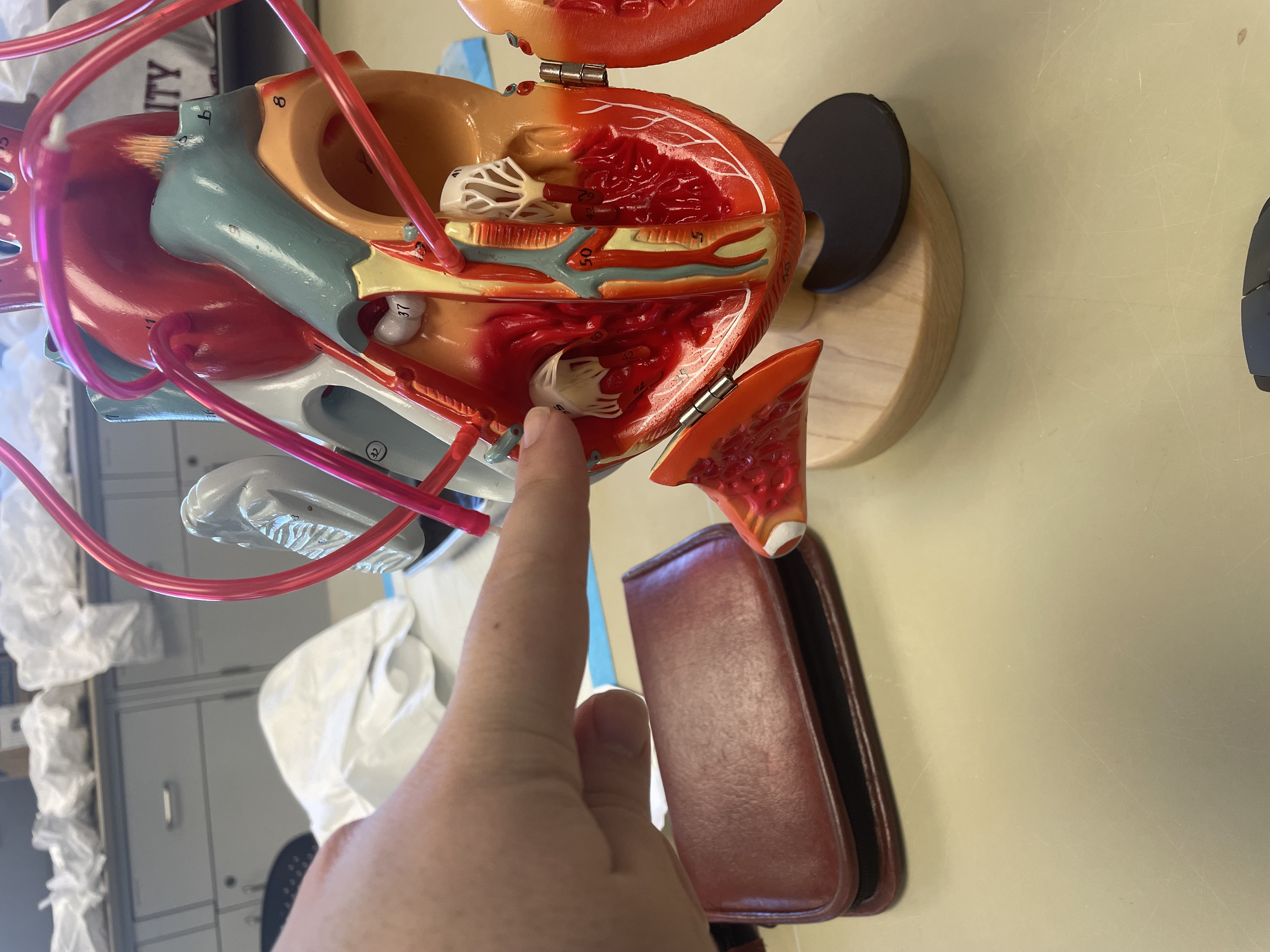
NAME
Left Ventricle
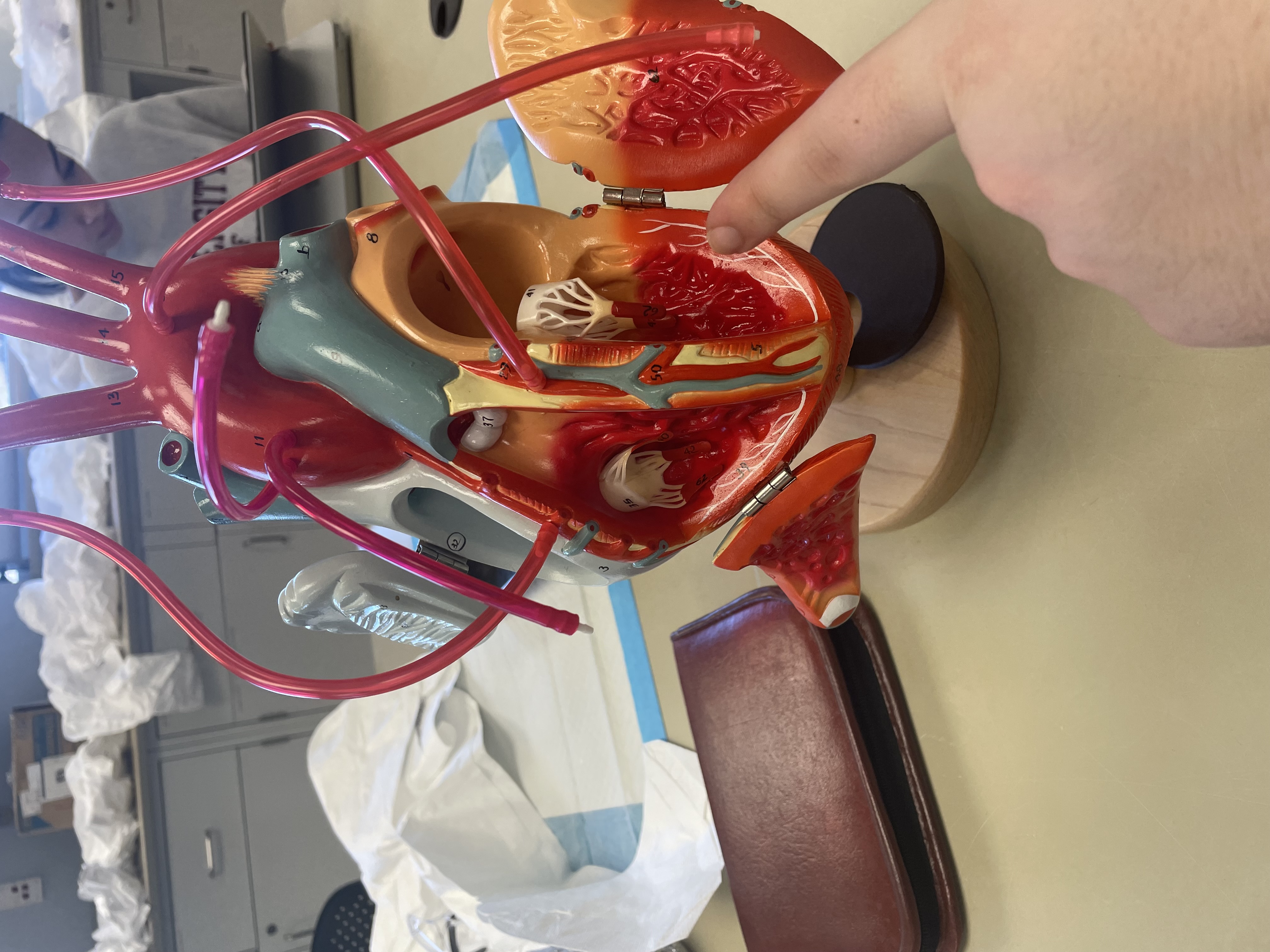
NAME
Right Ventricle
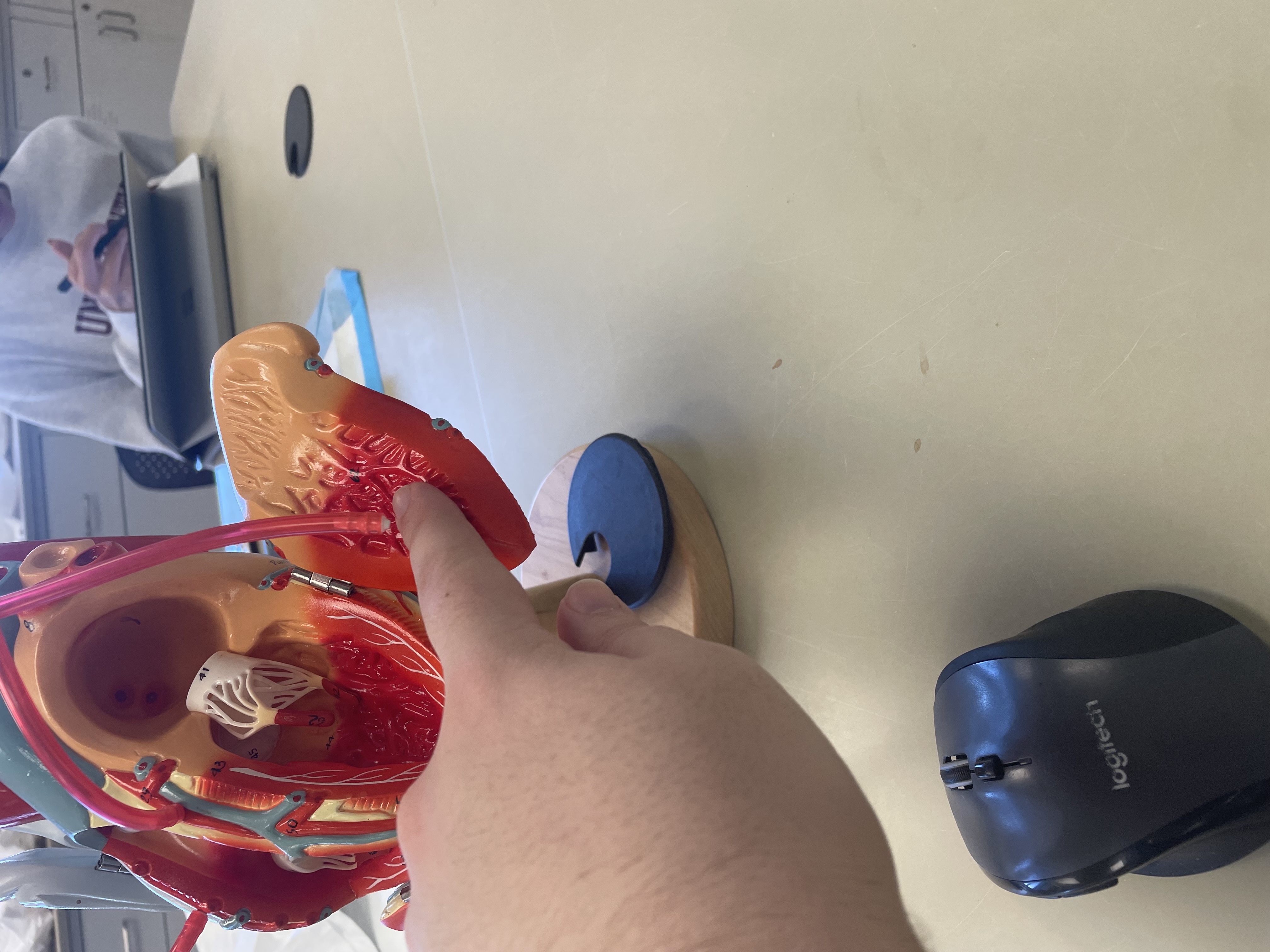

NAME
Trabeculae carnea
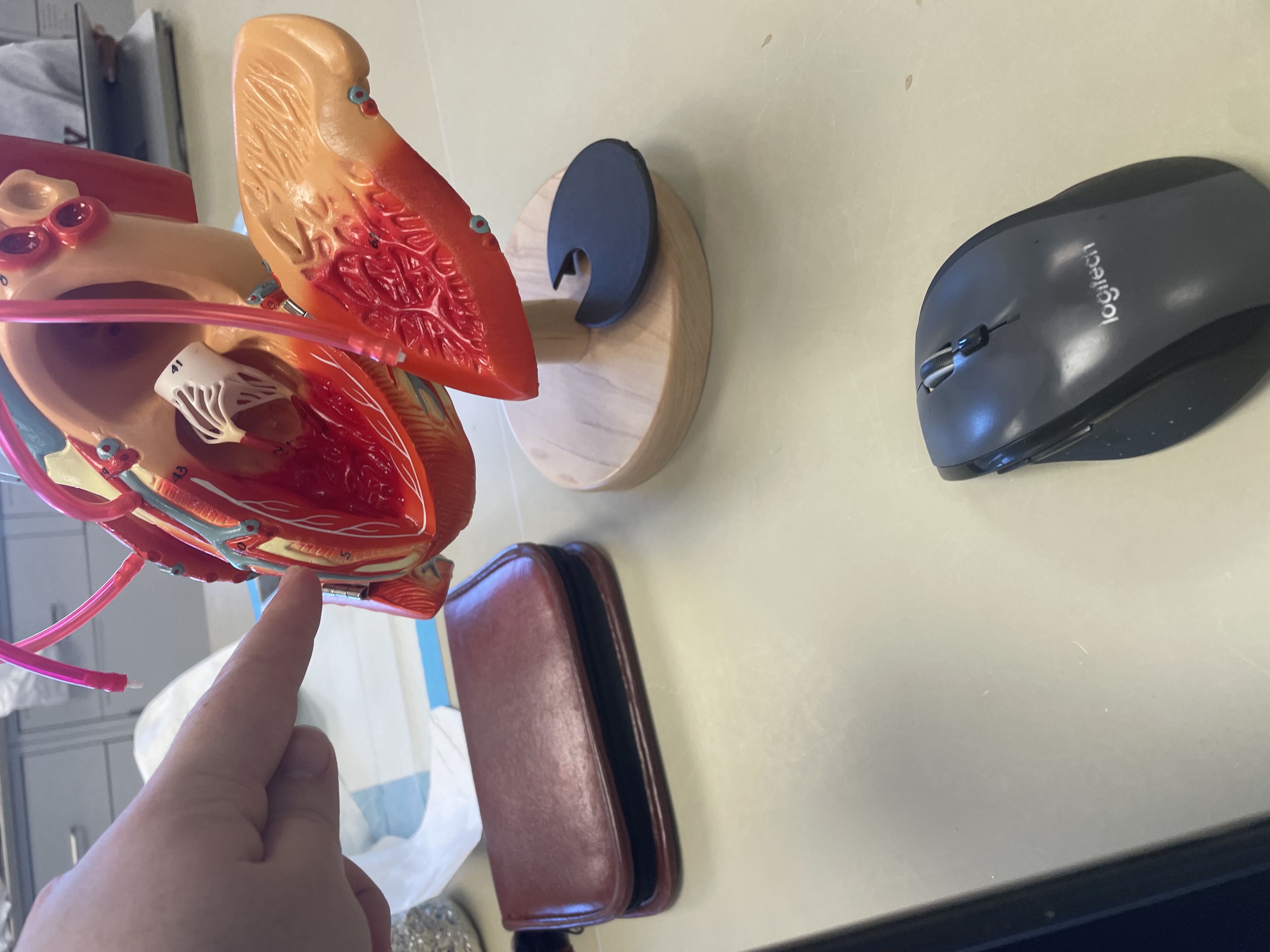

NAME
Interventricular septum

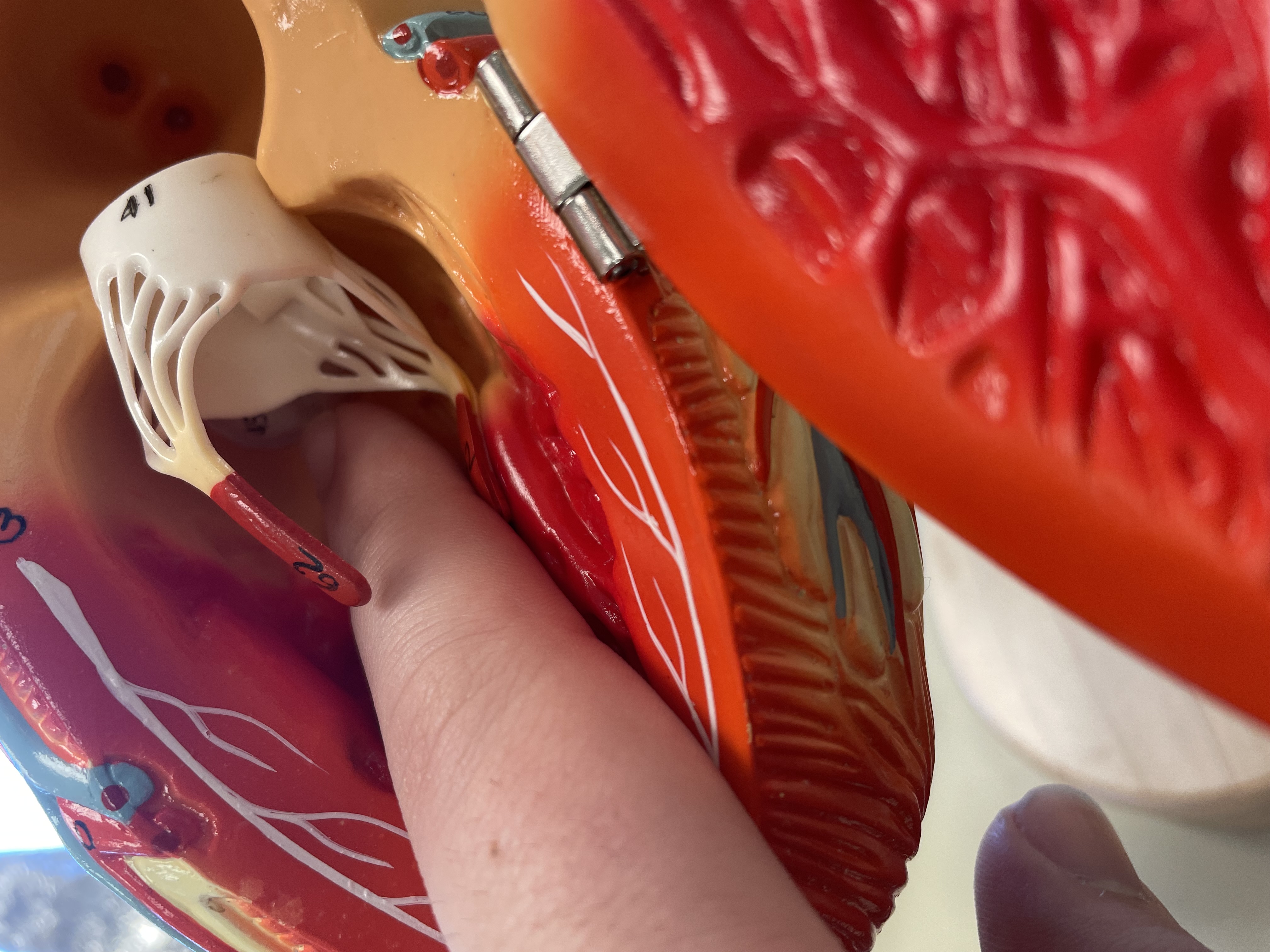
NAME
Chordae tendineae
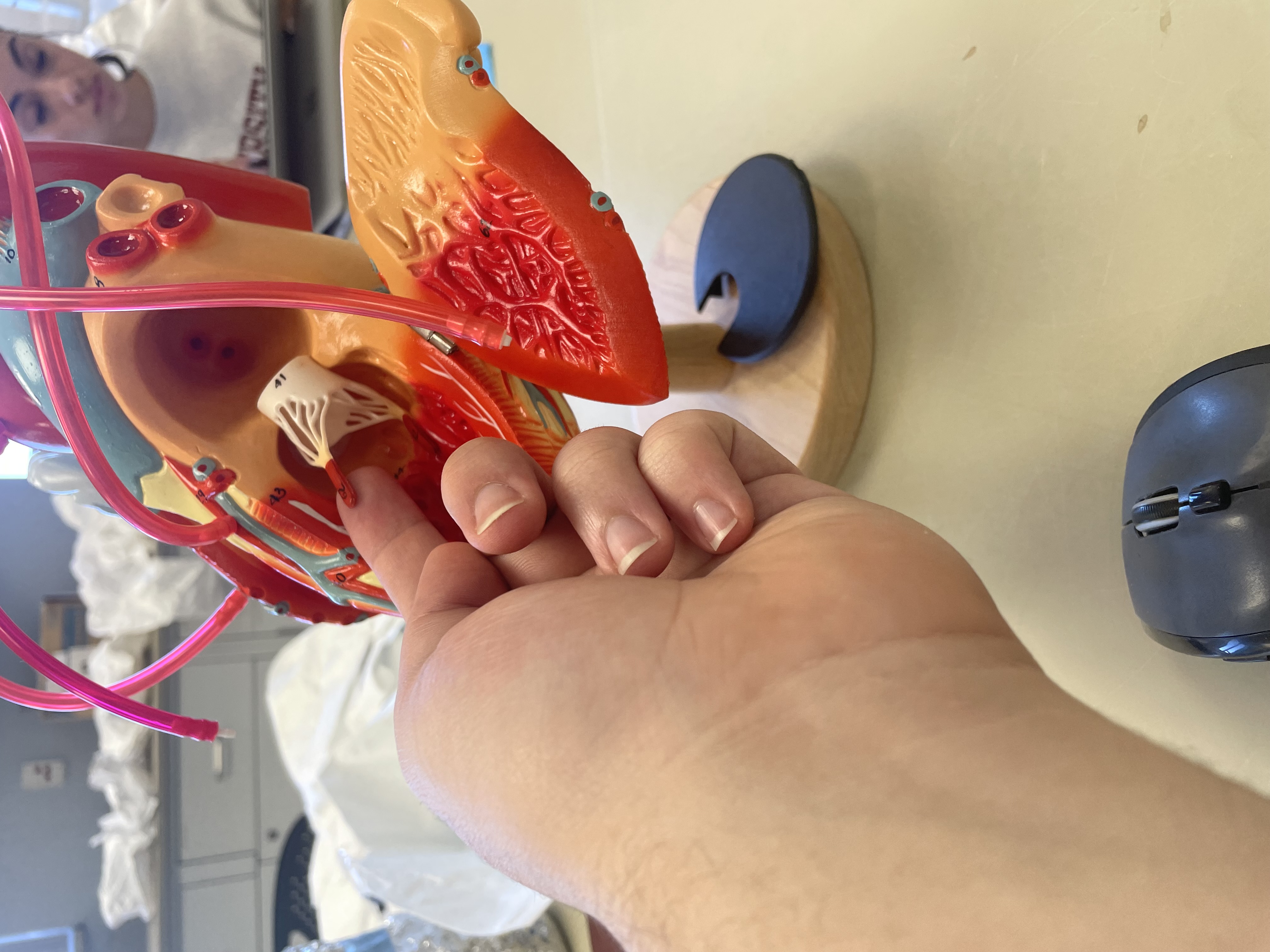
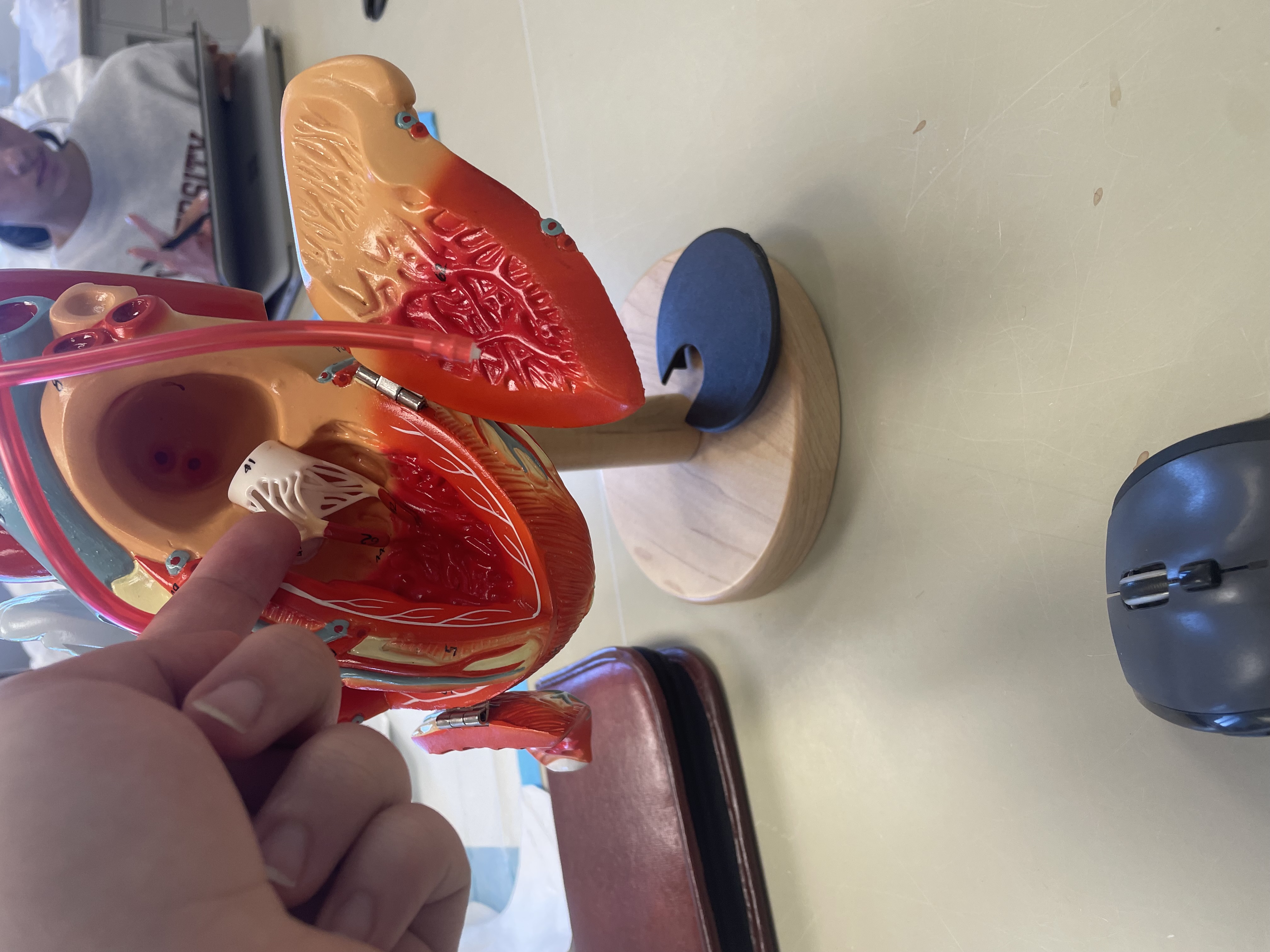
NAME
Papillary muscles
NAME
Bicuspid Valve
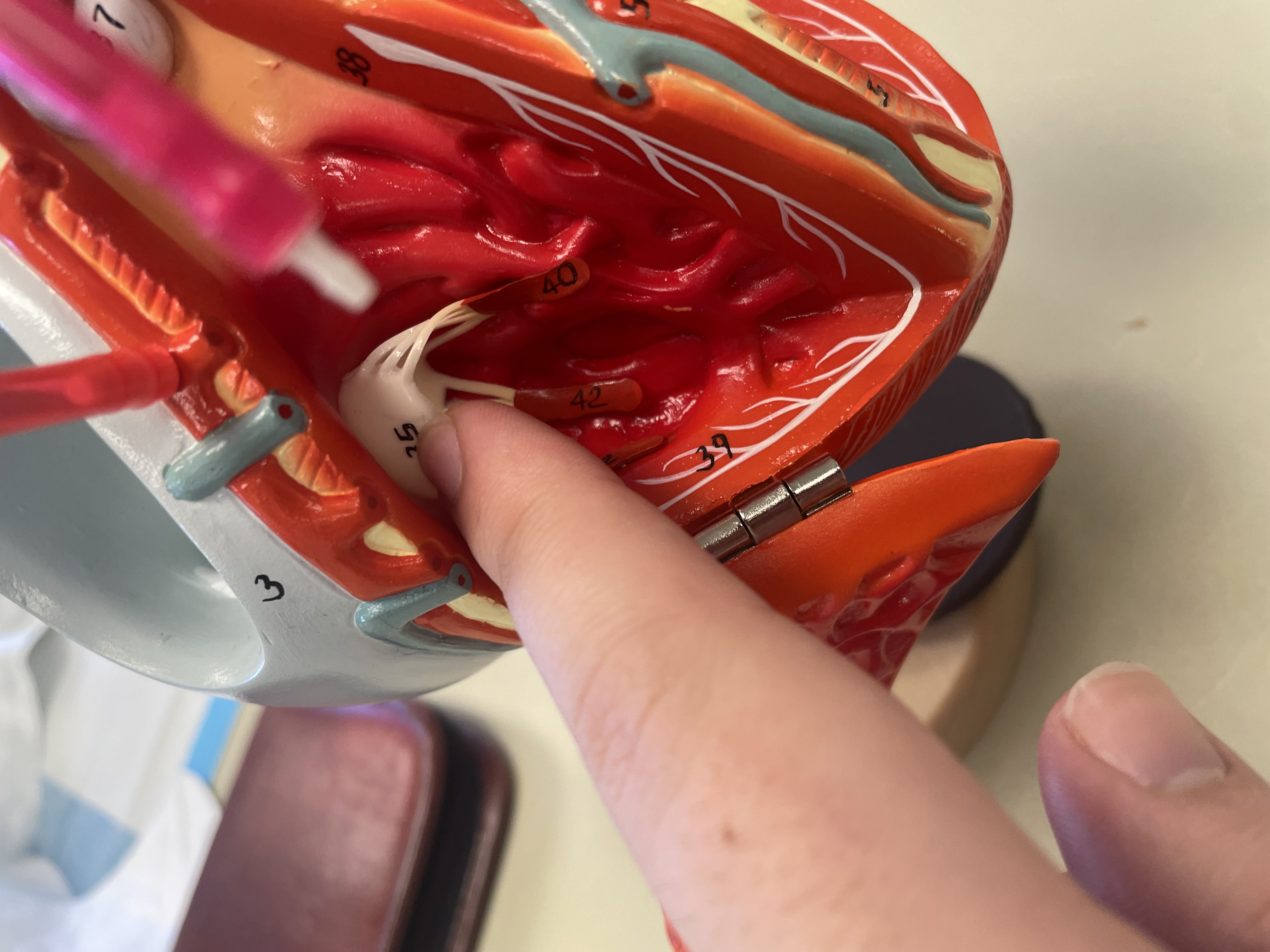
NAME
Tricuspid Valve
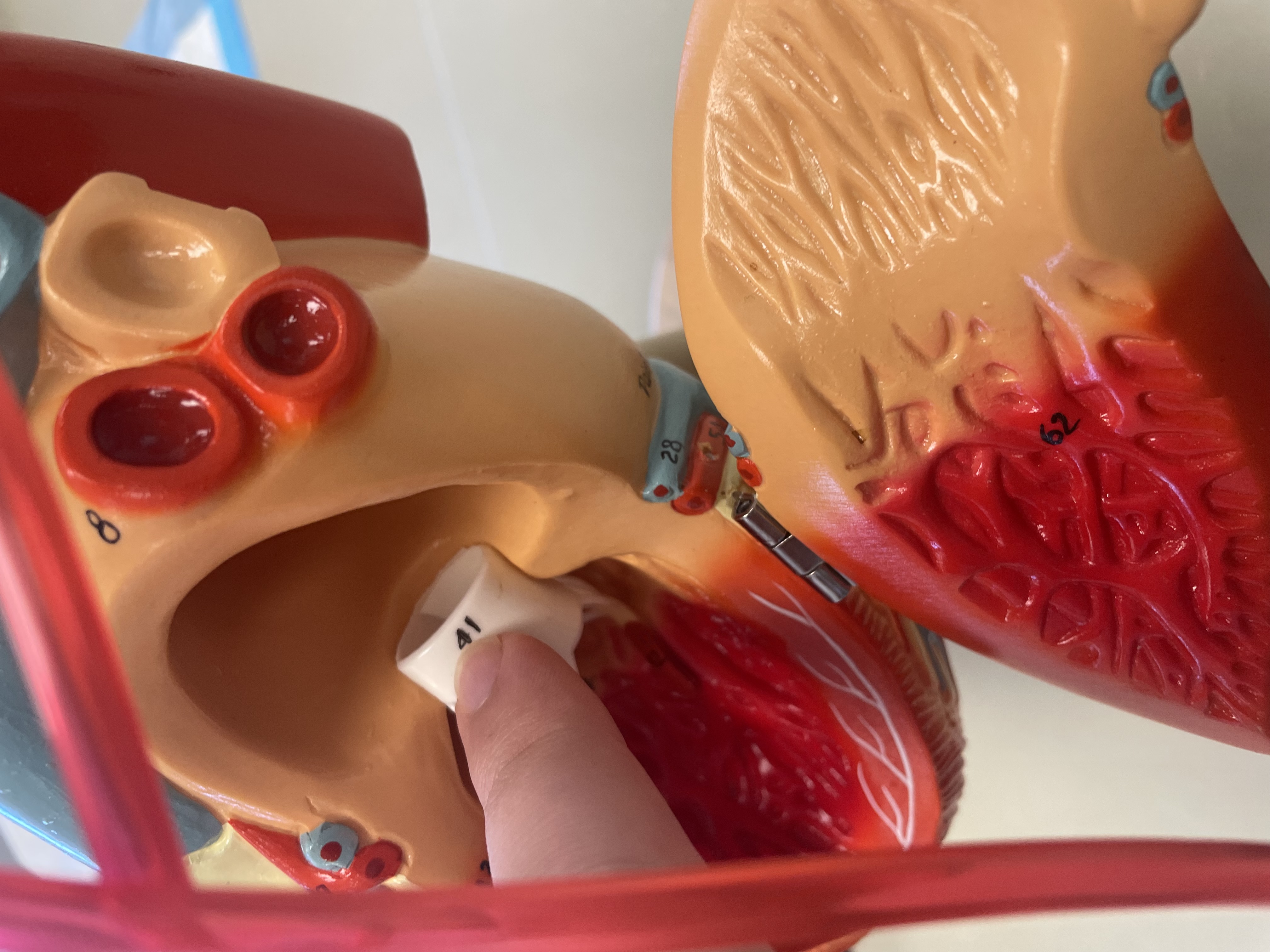
NAME
Aortic Valve
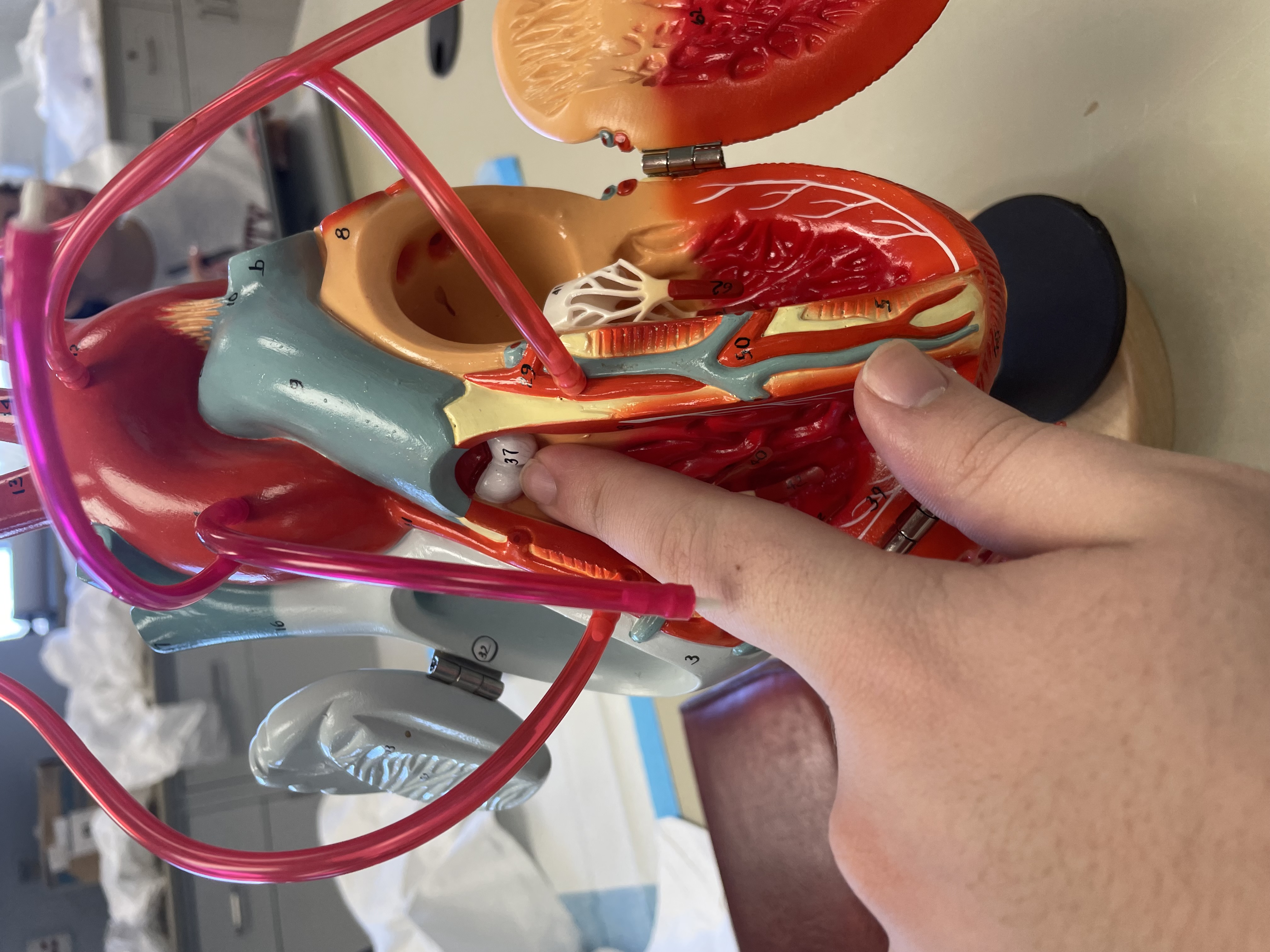
NAME
Pulmonary Valve
What is hematocrit?
The percentage of blood that is made of RBC
How is hematocrit calculated?
(Total Blood Volume/ Total RBC Volume) * 100 = RBC%
What are Eldoncards?
A tool used to do blood typing using anti-A, anti-B, and anti-Rh serum
What are the main blood antigens?
A
B
Rh
How is a positive result shown on a eldoncard?
The blood will agglutinate or clump
How is Rh expressed in blood type
As - or + types
What is O blood?
Blood that has neither A or B antigen
What is the universal donor type?
O-
What is the universal acceptor?
AB+
What is erythroblastosis foetalis
A development of anemia in a fetus due to the fetal blood being Rh+ and the mother’s blood being Rh-
What is thromboplastin?
An enzyme that catalyzes part of the clotting process
What is the purpose of Ca in clotting?
Promotes the formation of a clot
What is APTT?
A test done to see the clotting time for a patient
In the clotting lab, the thromboplastin mimics…
The Extrinsic Pathway
In the clotting lab, the APPT reagent mimics…
The Intrinsic Pathway
In the clotting lab, which pathway was the faster clotting? Why?
Extrinsic
This pathway is the response for trauma
What is iron deficiency anemia?
A condition where the body cannot make enough RBC due to a lack of iron needed to make hemoglobin
What is sickle cell disease?
A hereditary condition that causes hemoglobin to stiffen up with oxygen, forming crescent shaped RBC
What is sickle cell trait?
A condition where a person is a carrier for the sickle cell gene and can crescent the RBC with higher pressures
What is leukemia?
A cancer of the WBC
What is chronic myeloid leukemia?
A rare cancer of the bone marrow, increasing the amount of RBC and WBC
What is lymphoma?
A cancer of the lymph system, causing an out-of-control growth of lymphocytes
What is Deep Vein Thrombis
A condition where, due to inactivity, a clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the leg and pelvis
What is hemophilia
A condition in which the body cannot make clots due to a lack of clotting proteins
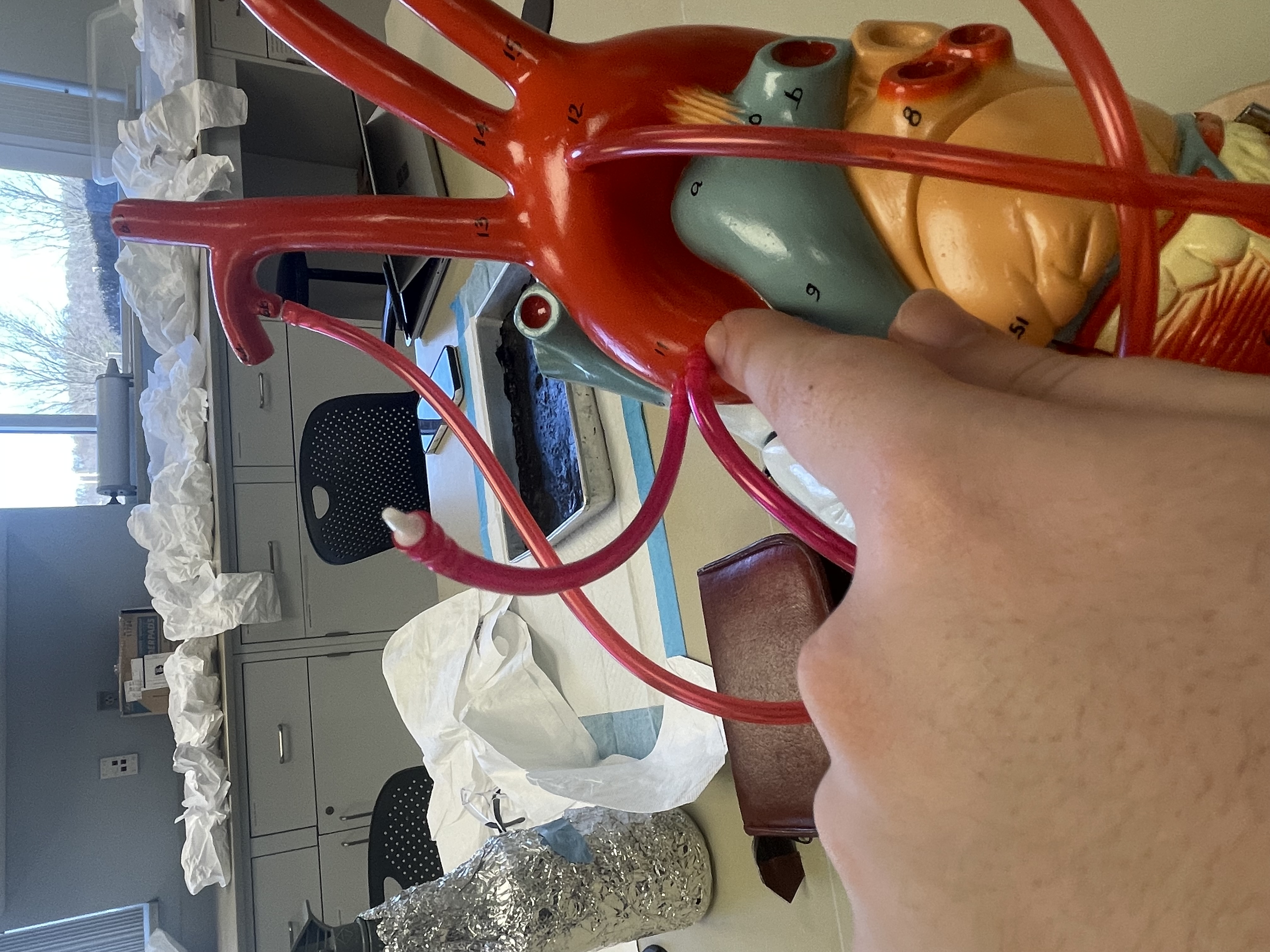
NAME
Ascending Aorta
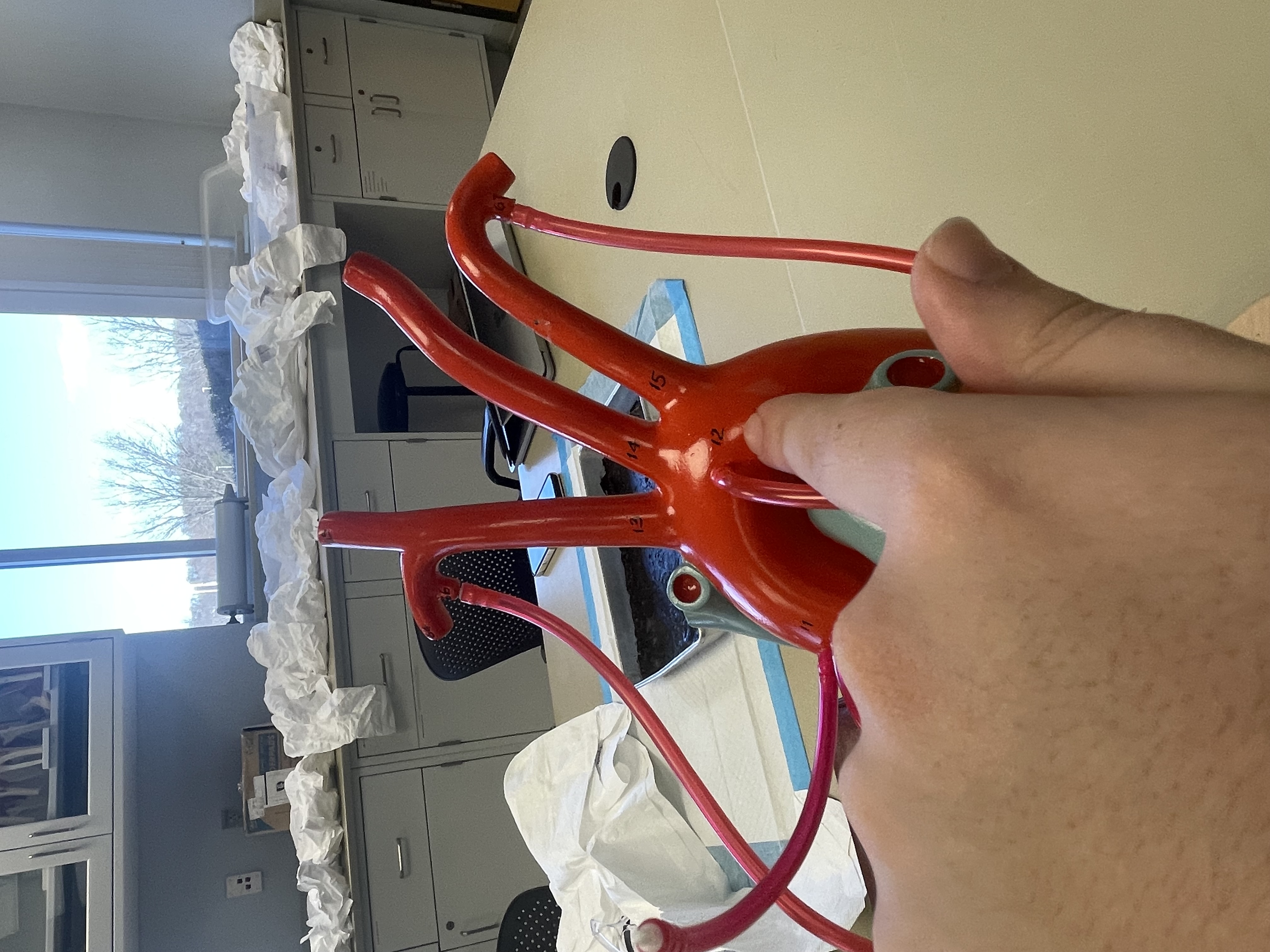

NAME
Aortic Arch
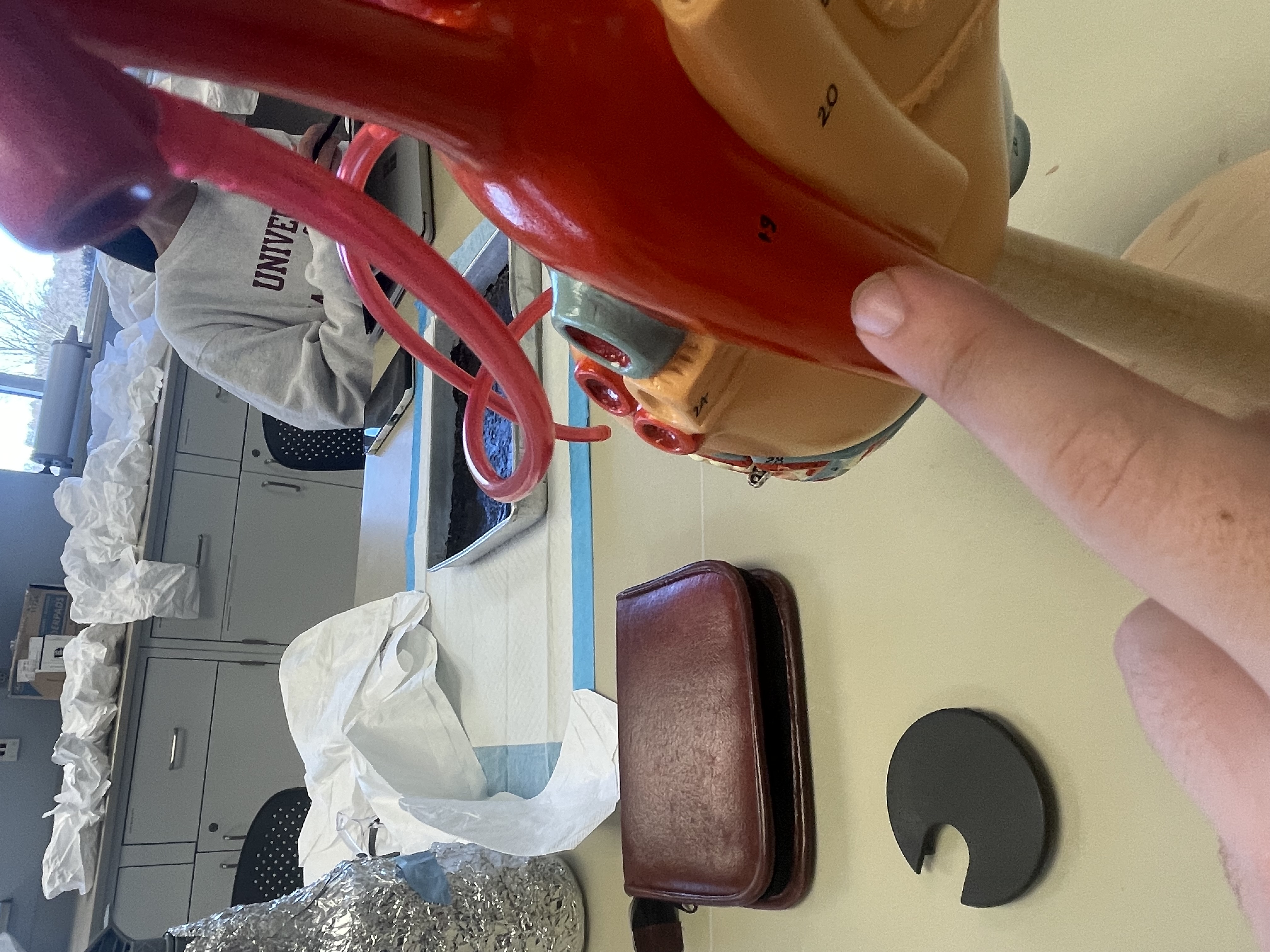

NAME
Descending Aorta