Bio II Exam 1 - Learning Catalytics
1/50
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
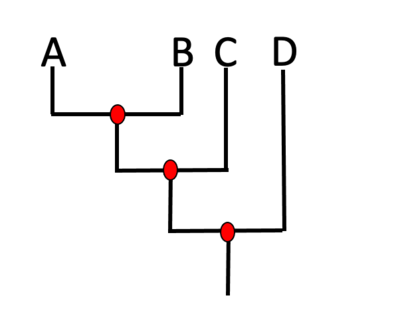
Which lineage is sister to C?
The lineage that includes A and B

The sea slug Elysia chlorotica is a photosynthetic animal that has chloroplasts! Its chloroplasts originated as free-living green algae. Which level/kind of endosymbiosis does this represent? Use one word to answer.
Secondary
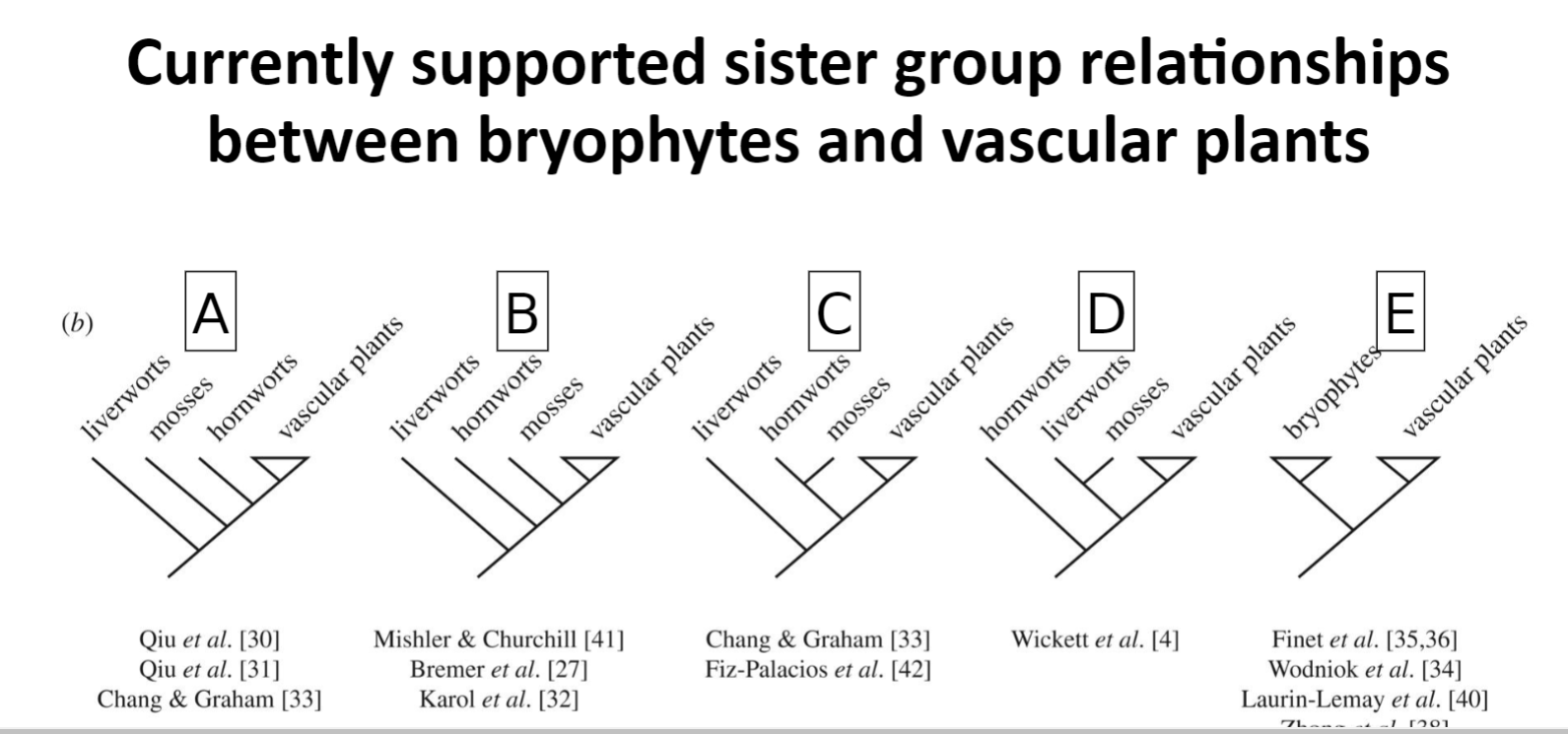
The phylogenetic trees on the slide represent the differing hypotheses that scientists have given for the relationship between the three groups of bryophytes and vascular plants. Among the bryophyte lineages, both mosses and hornworts have stomata, but liverworts do not. Which of the trees would most likely lead us to interpret a single origin of stomata? Select all that apply.
A, B, and C
What is the genetic relationship between a gametophyte and the gametes it produces?
The gametophyte and its gametes are genetically identical
What is the genetic relationship between a sporophyte and the spores it produces?
The sporophyte and every spore are each unique
Are each of the spores from a single individual plant genetically identical?
No, because spores are produced by meiosis and thus each is genetically unique.
Are each of the sperm cells from a single individual plant genetically identical?
Yes, because the sperm cells all come from the same individual and are produced by mitosis
Think about the genetic relationship between a sporophyte and that individual’s spores. How and why is a spore cell genetically different than a cell from the adult sporophyte? Please choose all of the true statements below:
Spores are haploid while sporophyte cells are diploid.
Spores are genetically distinct from sporophyte cells because they are produced by meiosis.
Are each of the sperm cells from a single individual human genetically identical?
No, because sperm cells are produced by mieosis and thus each is genetically unique.
Think about the genetic relationship between an adult human and thier gametes. How and why is an egg cell genetically different than, say, a skin cell from the same adult? Please choose all of the true statements below:
Gametes are haploid while skin cells are diploid.
Gametes are genetically distinct from skin cells because they are produced by meiosis.
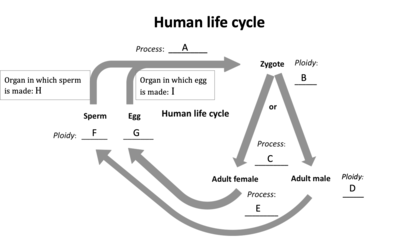
Which of the following stages are diploid (2n)?
B
D
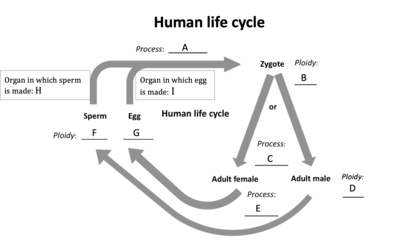
Which of the following stages are haploid (n)?
F
G
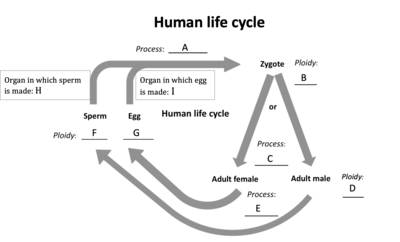
Match the letters in the diagram with the correct process.
A - Fertilization
C - Mitosis
E - Meiosis
H - Testes
I - Ovaries
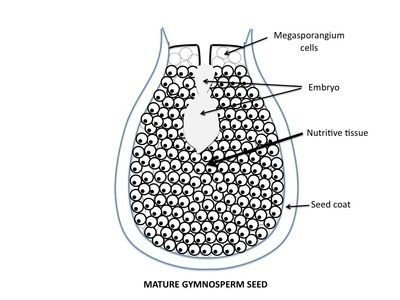
Point to a region of the mature gymnosperm seed that is composed of haploid cells.
In the nutritive tissue
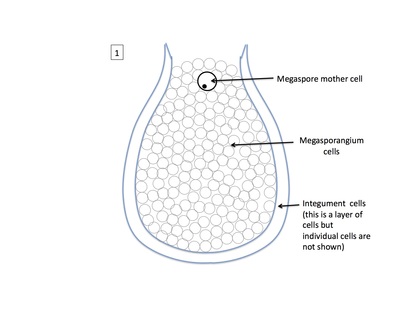
Rank stages of gymnosperm seed development
1st stage of gymnosperm ovule and seed development
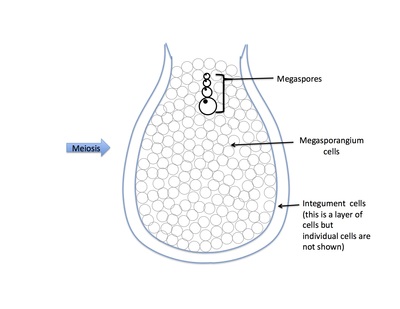
Rank stages of gymnosperm seed development
2nd stage of gymnosperm ovule and seed development
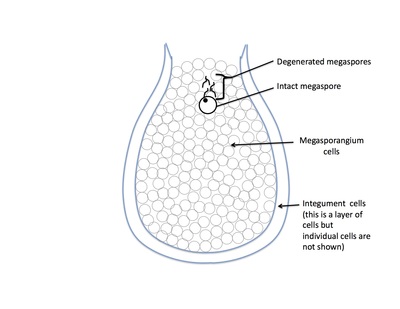
Rank stages of gymnosperm seed development
3rd stage of gymnosperm ovule and seed development
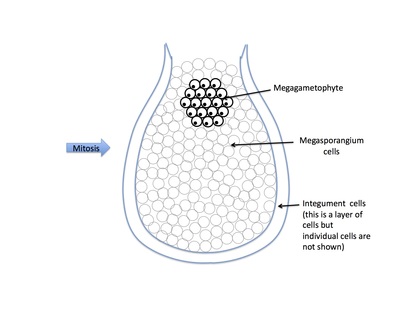
Rank stages of gymnosperm seed development
4th stage of gymnosperm ovule and seed development
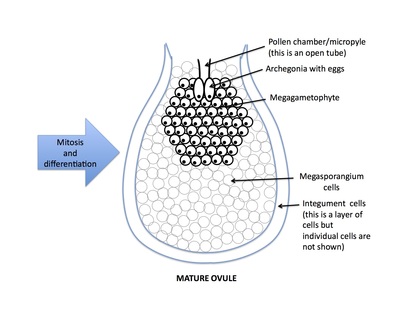
Rank stages of gymnosperm seed development
5th stage of gymnosperm ovule and seed development
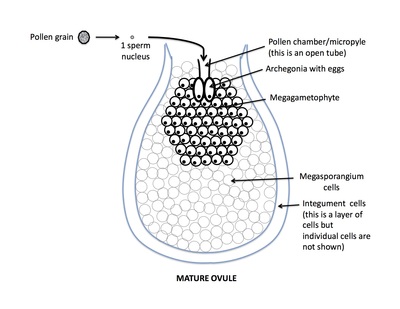
Rank stages of gymnosperm seed development
6th stage of gymnosperm ovule and seed development
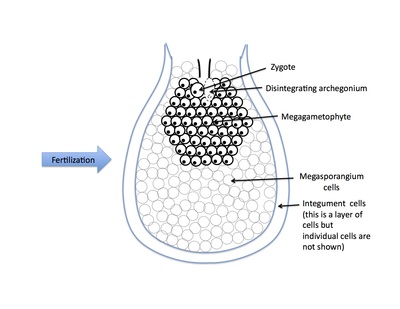
Rank stages of gymnosperm seed development
7th stage of gymnosperm ovule and seed development
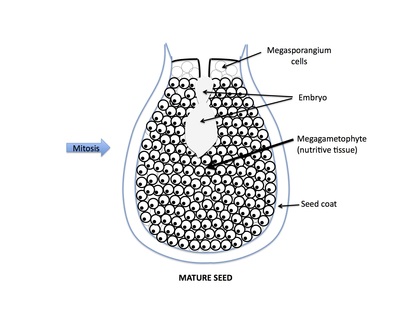
Rank stages of gymnosperm seed development
8th stage of gymnosperm ovule and seed development
Which of the following statements about gymnosperm seeds is FALSE:
The nutritive tissue contains genes from the father of the embryo.
What percentage of genes are shared between the seed coat and the embryo?
50
What percentage of genes are shared between the megagametophyte and the embryo?
50
Describe the movement of water from the spongy mesophyll cells to the atmosphere.
Water evaporates from the surface of the spongy mesophyll cells. Transpiration is when the water vapor passes through the stomata to the atmosphere
In leaves, where do where evaporation and transpiration occur? Describe the movement of water from the inside of the leaf to the atmosphere.
Evaporation primarily occurs from the surface of the spongy mesophyll cells. Water evaporates from the surface of the spongy mesophyll cells. The water vapor passes through the stomata to the atmosphere via transpiration.
What is the effect of evaporation and subsequent transpiration on the surface tension of the water in the cell walls of the spongy mesophyll cells?
Surface tension on the water in the cell walls will increase
In vascular plants, the unbroken column of water from the roots to the highest leaves is kept intact by…?
Cohesion
It’s a cloudy, rainy day. What do you expect to happen to the rate of water movement through the plant?
It will slow down, because transpiration will decrease due to the lack of a humidity gradient
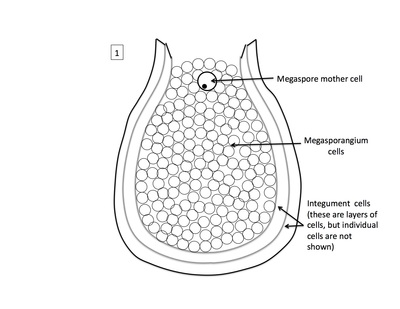
Rank stages of angiosperm seed development
1st stage of angiosperm ovule and seed development
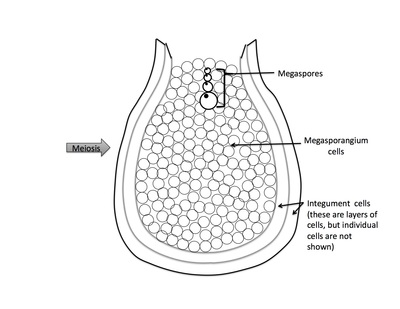
Rank stages of angiosperm seed development
2nd stage of angiosperm ovule and seed development
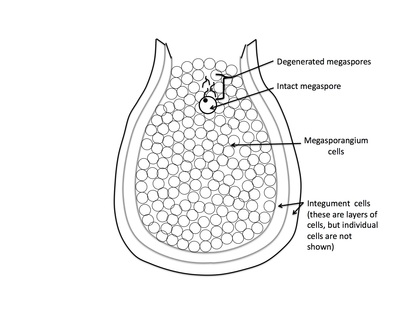
Rank stages of angiosperm seed development
3rd stage of angiosperm ovule and seed development
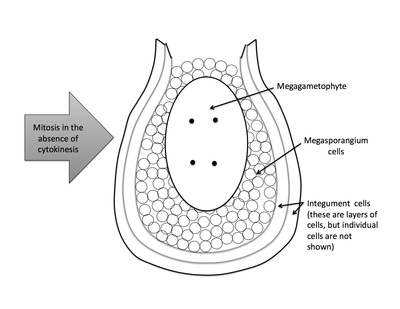
Rank stages of angiosperm seed development
4th stage of angiosperm ovule and seed development
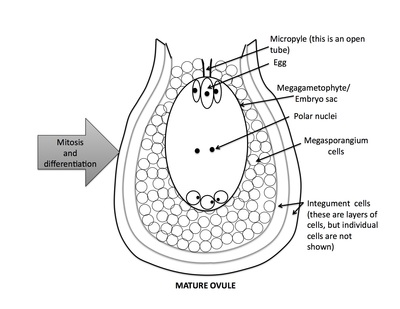
Rank stages of angiosperm seed development
5th stage of angiosperm ovule and seed development
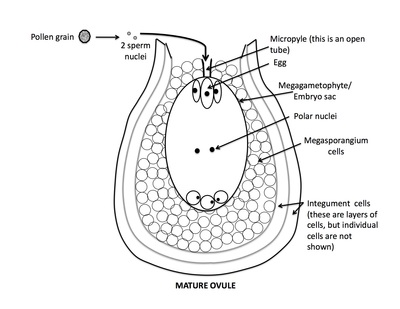
Rank stages of angiosperm seed development
6th stage of angiosperm ovule and seed development
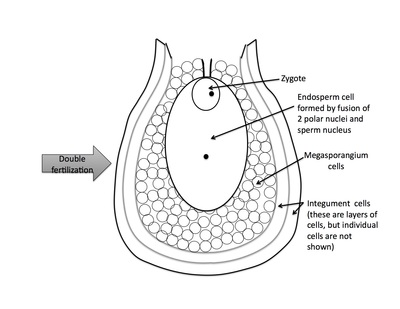
Rank stages of angiosperm seed development
7th stage of angiosperm ovule and seed development
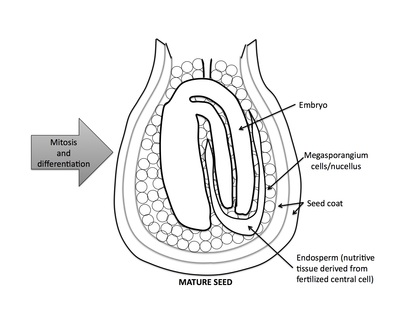
Rank stages of angiosperm seed development
8th stage of angiosperm ovule and seed development
Which of the following best defines “tropism”?
A cellular response to external stimuli that results in a structural change
Auxin causes a plant to grow larger by:
Stimulating cells to stretch and become larger
Which are correct regarding expansins?
Expansin activity is stimulated by the decrease in pH of the cell wall.
Expansins loosen the cell wall to allow elongation.
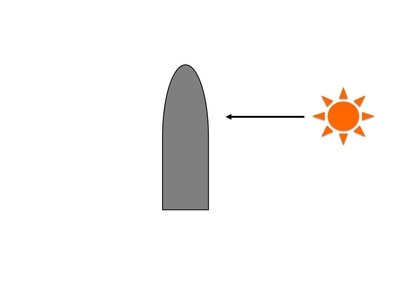
Refer to the diagram of the shoot tip below. The arrow in the diagram indicates the direction of the sun's rays falling upon the shoot tip. Draw an arrow indicating the direction in which you expect the shoot tip to grow.
arrow pointing to the right
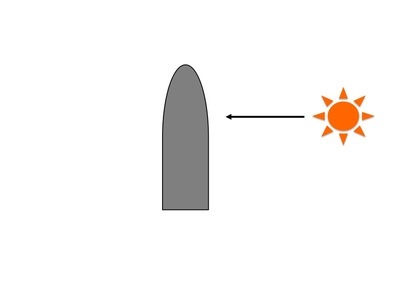
The bending of a plant towards sunlight is the result of:
Elongation caused by increased auxin concentration on the shaded side of the plant

What is the most likely pollinator of a large, bright blue flower, sweet smelling, with yellow spots leading to the center, that is held horizontally from the stem?
Bees
"Secondary metabolites" in plants are those chemical substances that:
Protect the plant from fungi and bacteria
Deter herbivory by insects and other animals
Attract human interest due to medicinal, recreational, and flavoring properties, among others

Place a dot where the oldest wood is found.
In the center
Two of the following characteristics are different between CAM and C4 photosynthesis, and two are shared. Which are shared between the two pathways?
The use of malate as a intermediate in which CO2 can be stored and/or moved.
An adaptation to xeric climates
Which phenomenon(a) best explains the fact that, in similar habitats, similar growth forms and similar physiological adaptations have evolved repeatedly in unrelated plant clades?
Convergent evolution
Adaptation
Natural selection
Which statement best describes systemic acquired resistance?
It is a general, non-localized increase in pathogen resistance
Some plants are able to trigger immune responses in neighboring plants before those plants have been attacked. To do this, they produce
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)

Which is illustrated in the image below?
Hypersensitive response indicated by the necrotic lesions