lecture quiz
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
BMI
A measure of body fat based on height and weight.
Phenotype
The observable traits expressed by an organism.
Chlorophyll a
The primary pigment involved in photosynthesis.
Chemoautotrophs
Organisms that do not use light energy from the sun to produce food.
Pigments in plants
Absorb light from a wider range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that are separated during meiosis I.
Light-dependent reactions
Use light energy to produce ATP and NADPH.
Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment
Disrupted by crossing over.
Discontinuous variation
A type of variation represented by traits such as attached/detached earlobes.
Sexual reproduction
Advantageous because it increases genetic diversity.
Independent assortment
The random alignment of non-homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Meiosis I
Results in two genetically unique, haploid cells.
Photosystem II
Uses water to replace lost electrons during photosynthesis.
Calvin cycle
Processes that produce glucose from CO2.
Genotype of the parents
Identified as both being heterozygous.
Mesophyll cells
Cell type with the highest density of chloroplasts in plants.
Probability of type O blood
Inherits type O at a rate of 1/2 with a type A and type O parent.
Oogenesis
Meiosis is completed after ovulation.
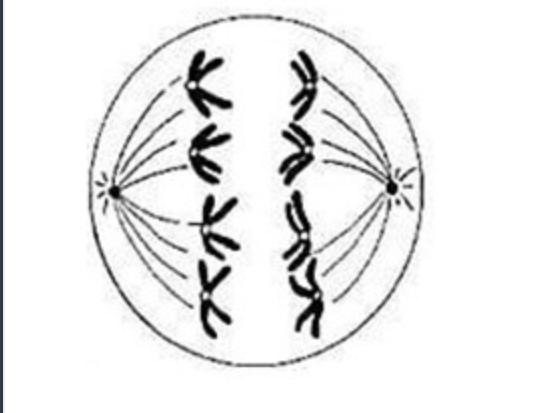
2n=8
Which of the following best describes the ploidy of the cell at this stage of the cell cycle?
Inheritance pattern
Characterized as incomplete dominance in the hypothetical bear cubs.
Thylakoids
Disc-shaped structures in chloroplasts for light-dependent reactions.
Differential gene expression
Explains the differences in proteins between nerve and pancreatic cells.
Recombination frequency
Percentage derived from crossing over events.
Operon
A cluster of genes with related functions regulated by a single promoter.
Gene expression regulation
Affects cellular needs and adaptation.
Meiosis stage
Indicated as telophase II.
Chromosome distribution issue
Resulting from non-disjunction during cell division.
Repressible operon
The trp operon conserves energy by reducing production when tryptophan is abundant.
Mendel's law of segregation
Exhibited during anaphase I of meiosis.
Calvin cycle purpose
To fix inorganic carbon.
Test cross example
Crossing dominant phenotype with homozygous recessive individual.
Independent assortment conclusion
Supported by observed phenotypic ratio in F2 generation.
Color vision inheritance
Describes potential outcomes for children of colorblind parents.
Albinism genetics
Result of epistasis when one gene blocks pigment production.
Lac operon expression
Highest when there's no glucose and high lactose concentration.
Probability in offspring
Calculated for heterozygous conditions across three loci.
F2 generation outcomes
Expected phenotype ratio of 3:1 for black to brown mice.
Recombination map
Shows how X, Y, and Z are linked based on given frequencies.