AP Macroeconomics Unit 1 Section 2 Vocabulary
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
black market
an economic activity that takes place outside government-sanctioned channels, usually to let participants avoid government price controls, taxes, or laws
2
New cards
change in demand
a shift in consumer desire to purchase a particular good or service, irrespective of a variation in its price
3
New cards
change in supply
a shift in production or output of a good/service
4
New cards
competitive market
a market wherein there are a large number of entities offering the same goods/services, and a large number of consumers to interact with said producers, creating a lack of a single dominant power
5
New cards
complement
goods/services/ that are frequently used together or add value to one another, therefore affecting each other’s supply and demand
6
New cards
demand curve
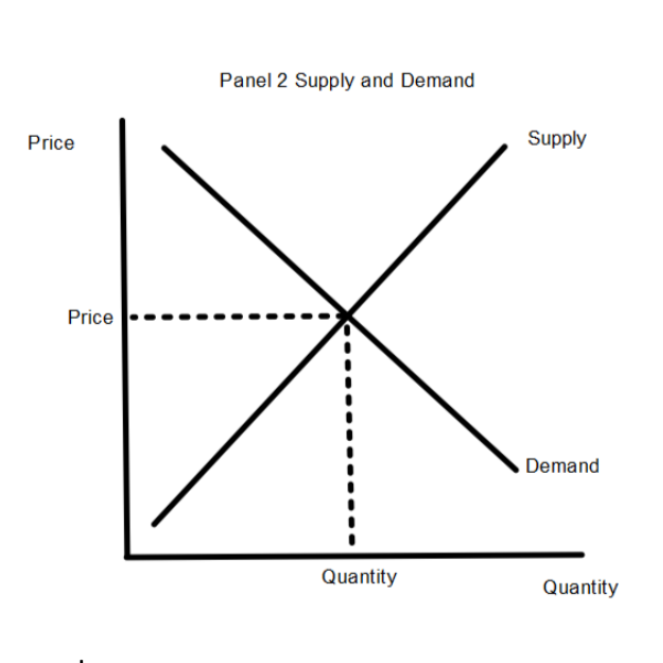
a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good/service and the quantity demanded for a given period of time
7
New cards
demand schedule
a table that shows the quantity demanded of a good or service at different price levels; can be graphed as a demand curve
8
New cards
equilibrium
condition or state in which economic forces are balanced; economic variables remain unchanged from their equilibrium values in the absence of external influences
9
New cards
equilibrium (market clearing) price
the price at which the number of goods for sale is exactly equal to the quantity that buyers wish to purchase
10
New cards
equilibrium quantity
no shortage or surplus of a product in the market; supply and demand intersect, the amount of an item desired by consumers is equal to the amount being supplied
11
New cards
inferior good
a good whose demand drops when people’s incomes rise; goods that fall out of favor when consumers can begin buying more costly substitutes
12
New cards
input
any resources used to create goods and services, both tangible and otherwise
13
New cards
law of demand
principle that states that at a higher price, consumers will demand a lower quantity of a good
14
New cards
law of supply
principle that states that as the price of a good/service increases, the quantity (supply) that producers offer will increase
15
New cards
market
any place where two or more parties can meet to engage in an economic transaction
16
New cards
minimum wage
the minimum amount of remuneration that an employer is required to pay wage earners for the work performed during a given period, which cannot be reduced by collective agreement or an individual contract
17
New cards
normal good
consumer products such as food and clothing that exhibit a direct relationship between demand and income; as a consumer’s income increases, the demand for these goods does as well
18
New cards
price ceiling
the mandated maximum amount a seller is allowed to charge for a product or service; typically applied to staples such as food and energy products when such goods become unaffordable to regular consumers
19
New cards
price controls
the legal minimum or maximum prices set for specified goods; implemented as a means of direct economic intervention to manage the affordability of certain goods/services
20
New cards
price floor
the lowest legal price that can be paid in a market for goods and services, labor, or financial capital
21
New cards
quantity demanded
the total amount of a good or service that consumers demand over a given interval of time
22
New cards
quantity supplied
the number of goods or services that suppliers will produce and sell at a given market price; differs from the actual amount of supply (the total supply) as price changes influence how much supply producers actually put on the market
23
New cards
shortage
a condition where the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied at the market price
24
New cards
substitute
a product or service that consumers see as essentially the same or similar-enough to another product, so it can be used in place of it
25
New cards
supply curve
a graphic representation of the correlation between the cost of a good or service and the quantity supplied for a given period
26
New cards
supply schedule
a table that shows the price of a good/service in relation to quantity supplied; can be graphed as a supply curve
27
New cards
surplus
the amount of an asset or resource that exceeds the portion that's actively utilized
28
New cards
supply and demand
a theory explaining the interaction between the sellers of a resource and the buyers of it