Brain and neurons
1/47
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Brain plasticity
the brains ability to modify itself after some injuries
Cerebellum
Voluntary movements, fine motor skills. Impaired by alcohol.
Pons
Facial expressions, sleeping and waking.
Medulla Oblongata
heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, vommiting
RAS (Reticular Formation)
Alertness and focus
Thalamus
directs messages from senses to the cerebral cortex
Limbic system
system that controls fear, aggression, food and sex drive
Hippocampus
processing explicate memory for long term storage
Amygdala
danger, fight or flight.
Hypothalamus
homeostasis and maintenance activities, like eating and drinking.
Corpus callosum
connects the two hemispheres, sends signals back and forth
Pituitary gland
produces growth hormones, controls other parts of the brain
Pineal gland
regulate sleep cycles, melatonin, circadian rhythm
Prefrontal cortex
executive functions - cognition, judgement, personality, mirror neurons
Broca’s area
muscles responsible for speech
Motor cortex
sends signals to our body, controlling muscles.
Parietal Lobe
behind frontal lobe, sensory information
Somatosensory cortex
coordinates incoming touch sensations
Occipital lobe
back of the brain, holds visual cortex
Primary visual cortex
organization and processing of visual information
Temporal lobe
sides of the brain, auditory and language, etc.
Primary auditory cortex
processing sound
Wernicke’s area
interpereting language
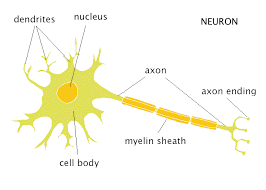
Neuron
nerve cell, the “building blocks” of the nervous system
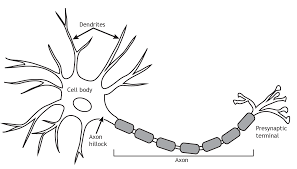
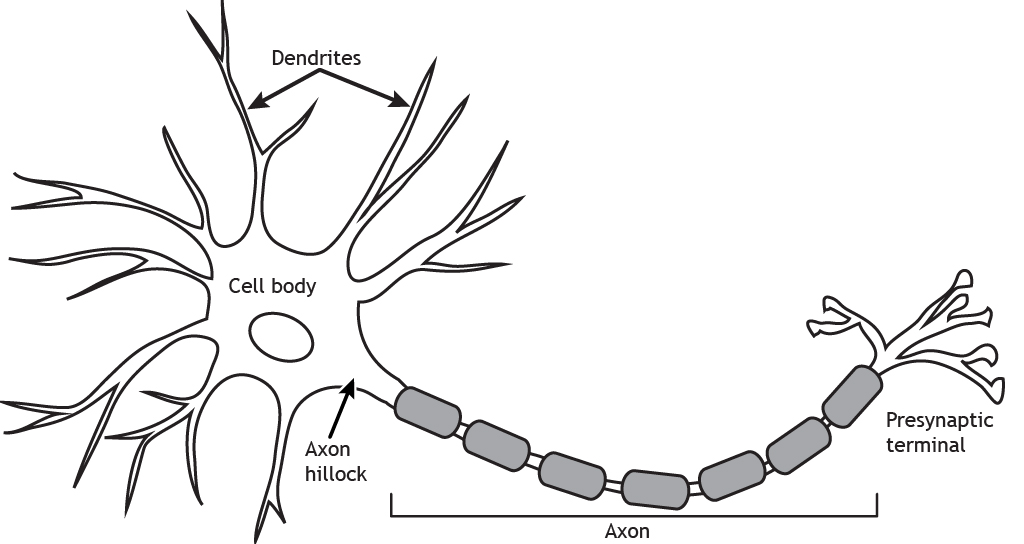
Dendrites
big end of the neuron, receive messages from other cells
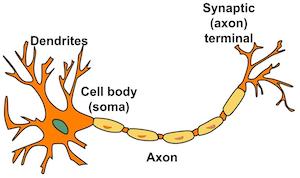
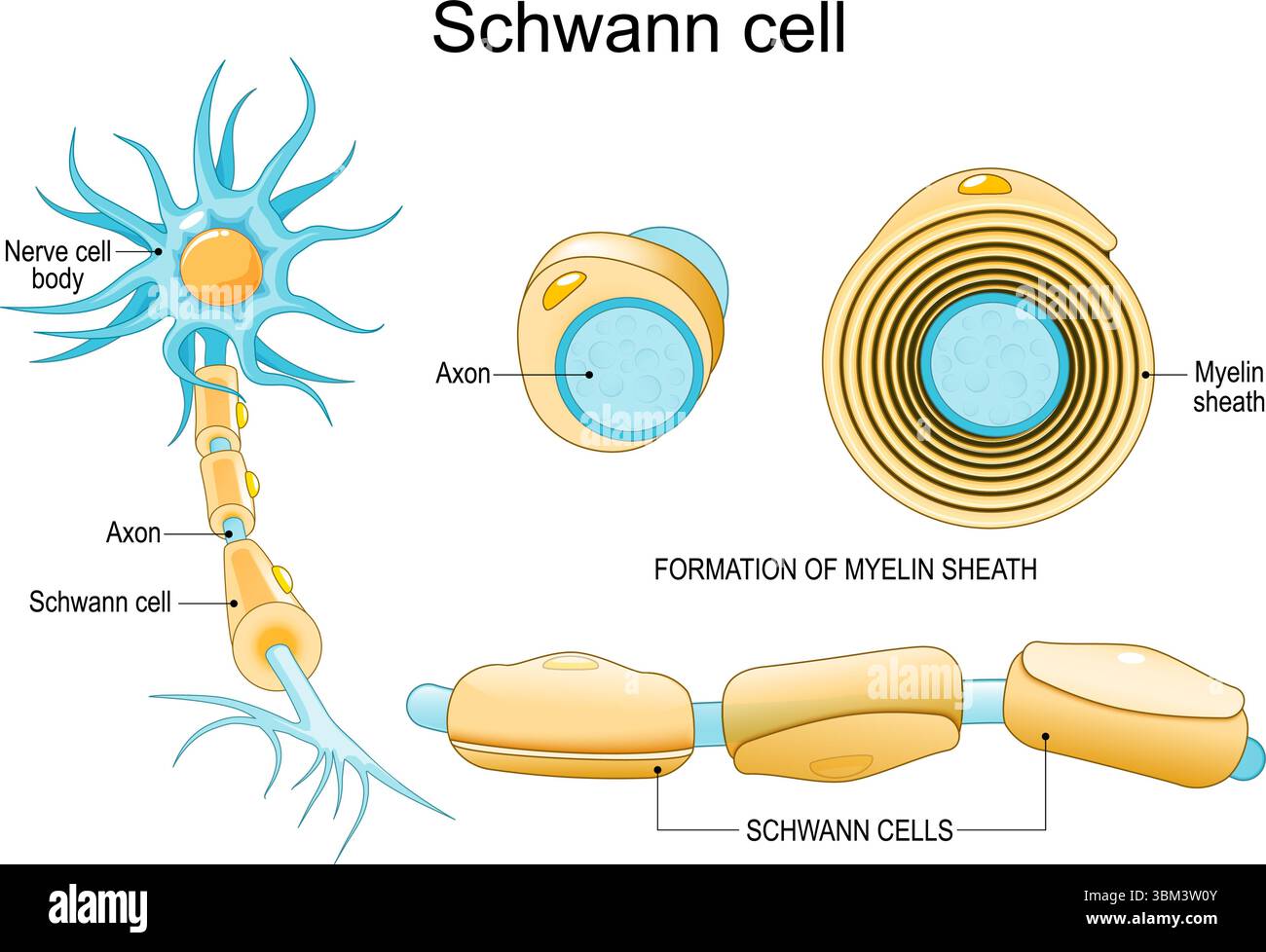
Axon
long cable-like part of a neuron, passes messages to other neurons, muscles, or glands
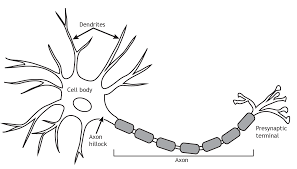
Axon terminal
small end of the neuron, connects with another cell’s dendrites
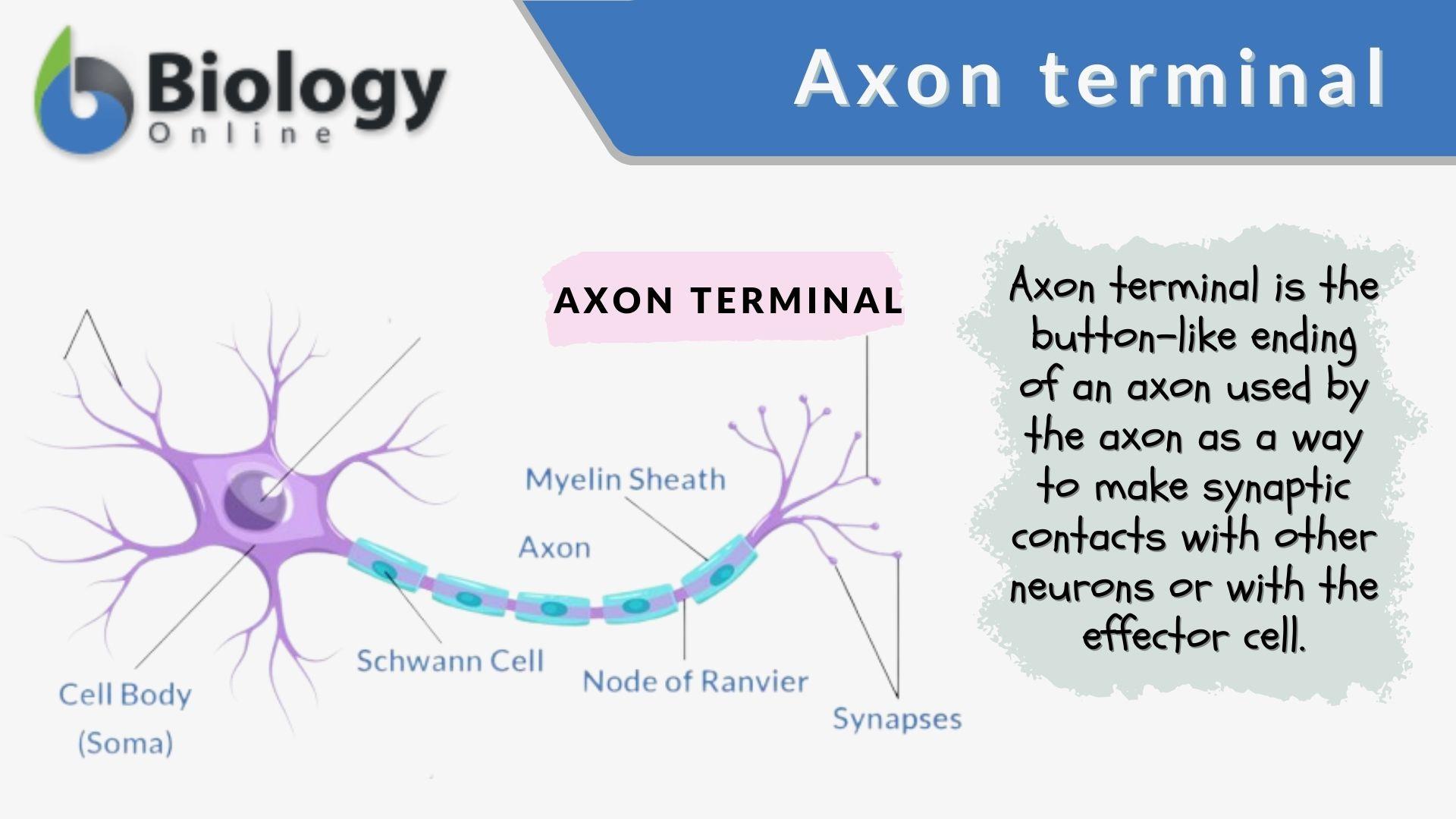
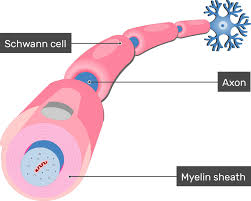
Myelin sheath
insulating fatty layer, speeds transmission
glial cells
type of cells, help remove waste, insulate neurons, provide nourishment.
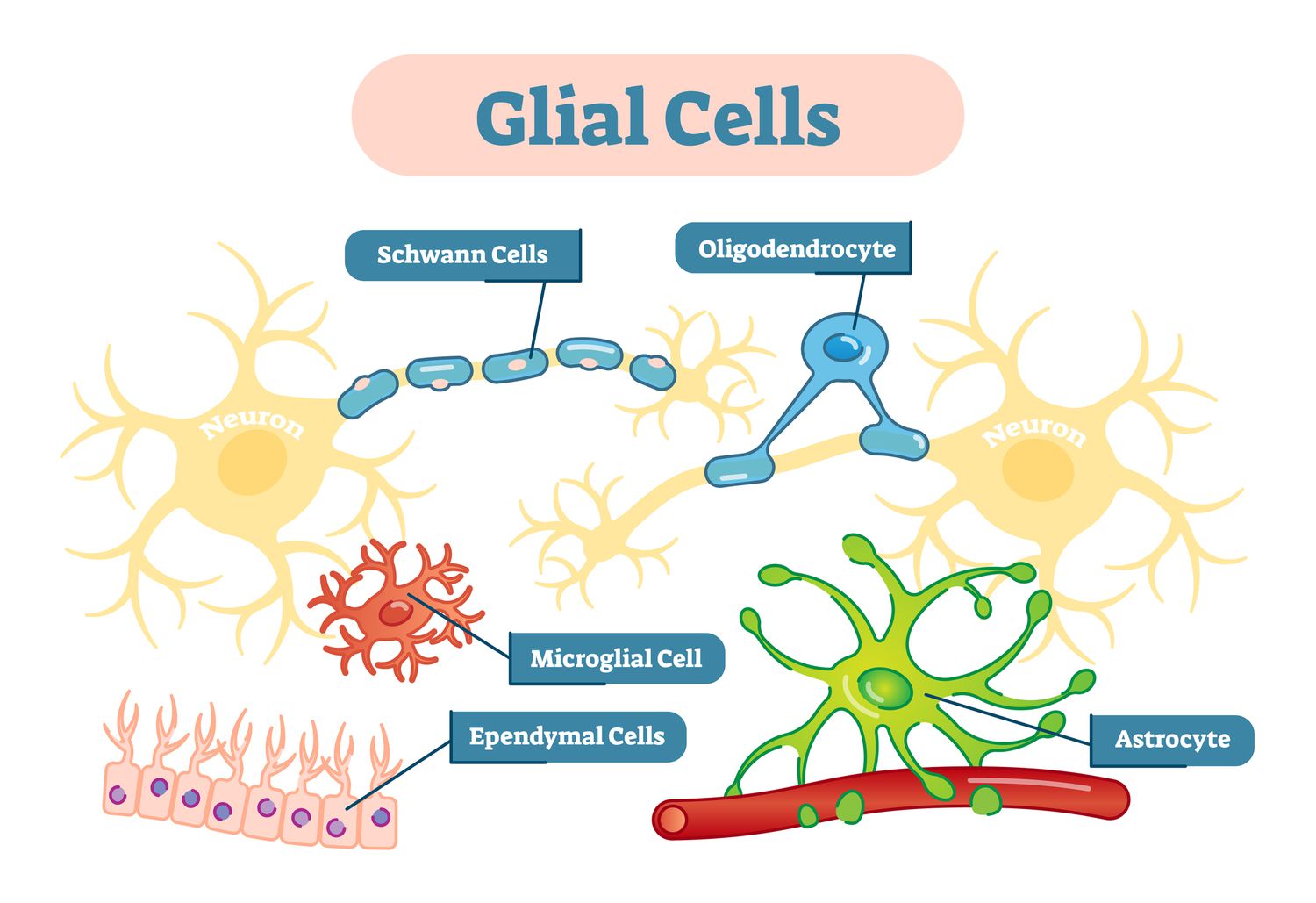
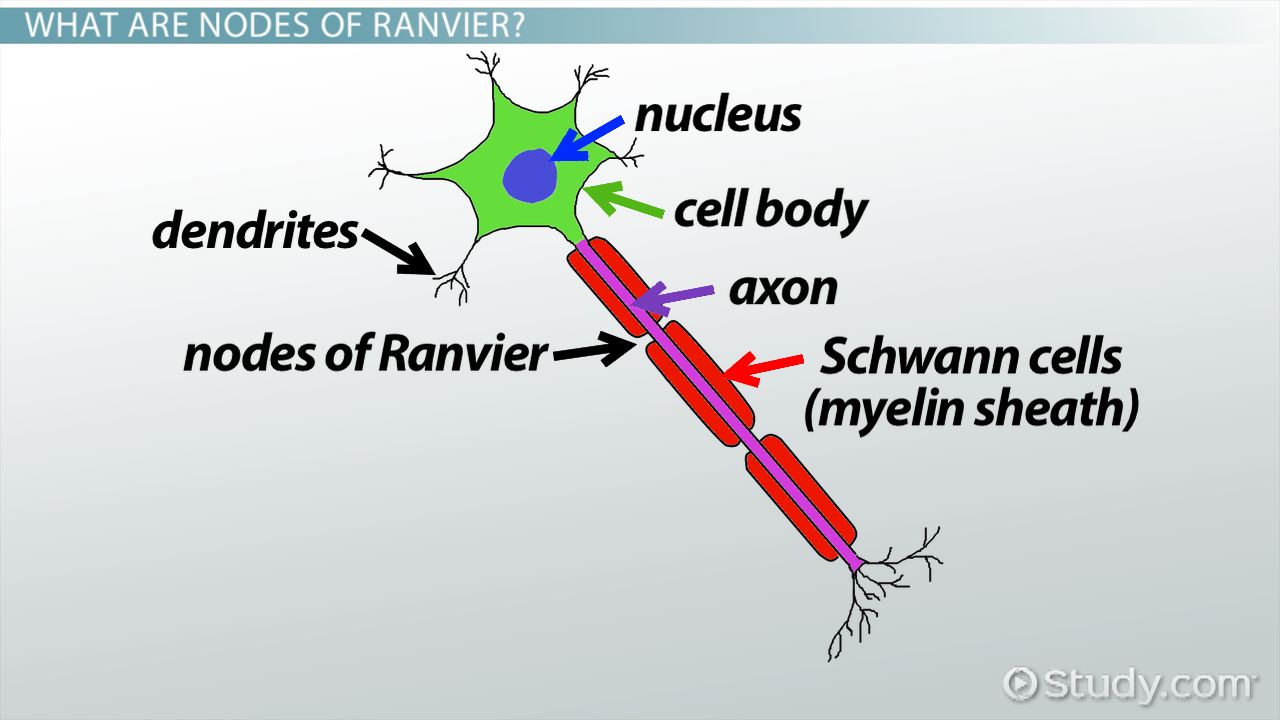
Schwann cell
type of glial cell, makes myelin
node of ranvier
natural gaps in myelin sheath
neuron cell body
contains the nucleus and organelles, necessities for function.
neuron’s nucleus
center of the neuron cell body, controls the cell
Central nervous system (CNS)
Includes brain and spinal cord. Body’s main processing and control centers
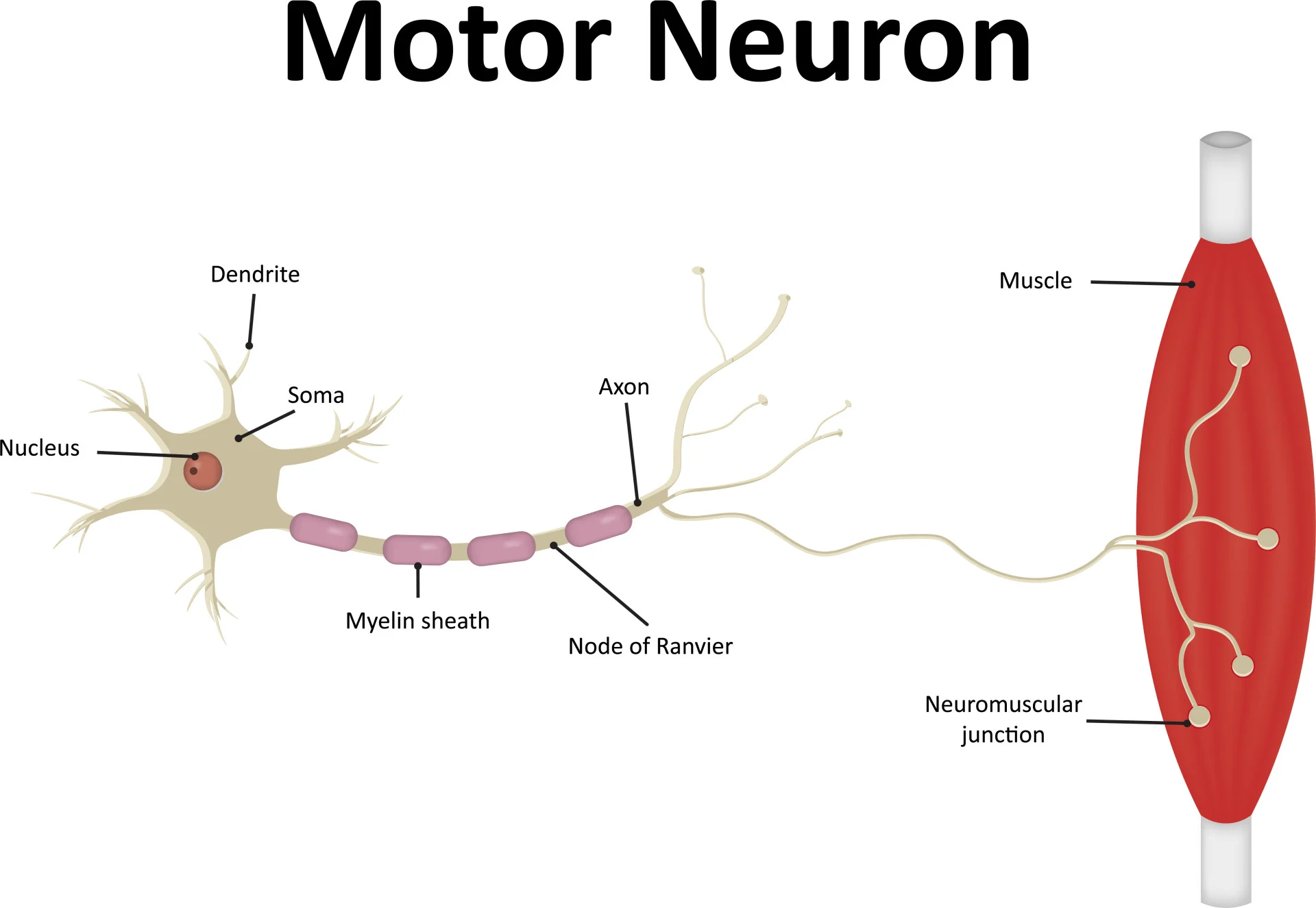
Motor neurons
carry info from the brain to muscles.
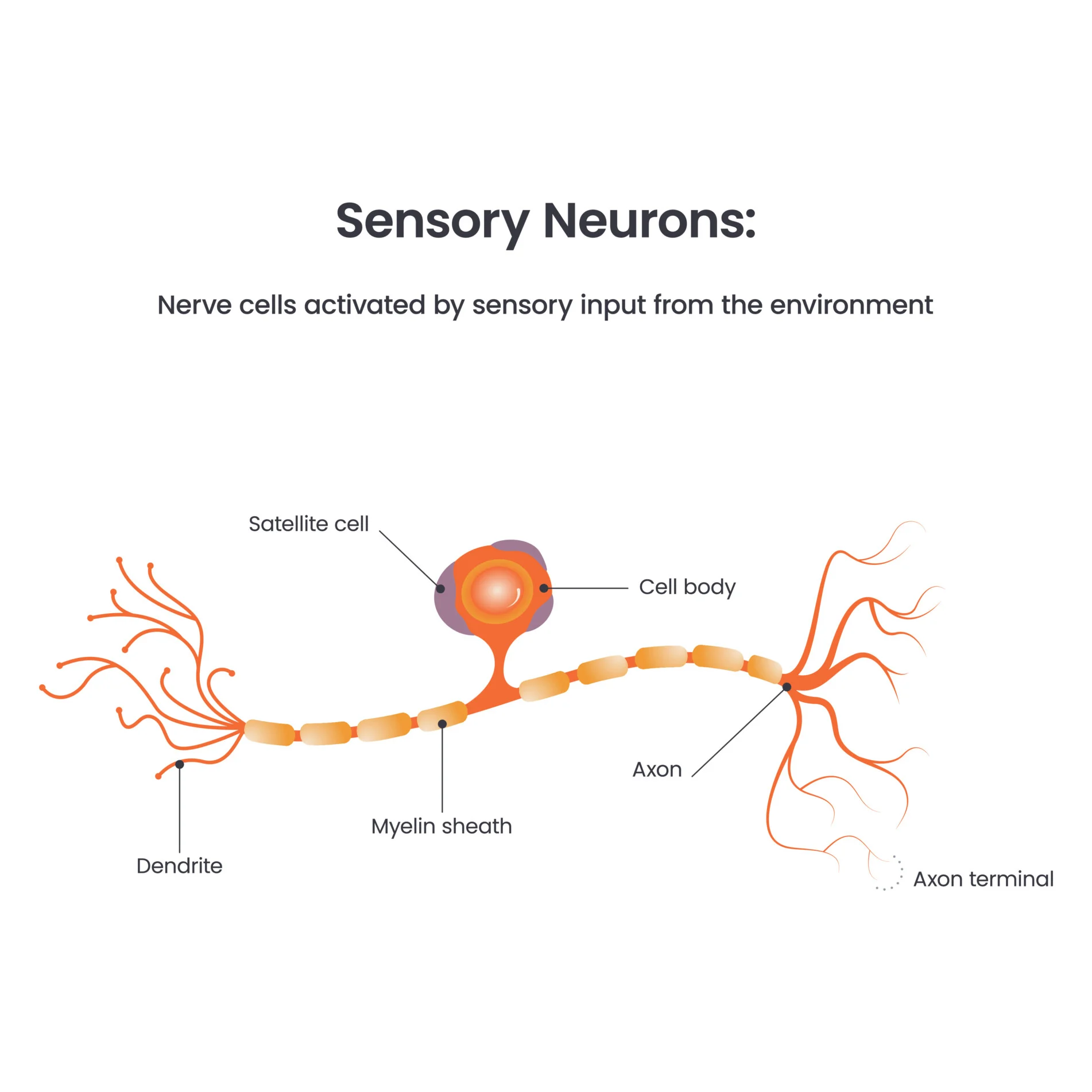
sensory neurons
carry incoming sense information to the brain
Interneurons
Carry signals between neurons, from one neuron to another
mirror neurons
fire when seeing others doing something, help us learn through observation.
Action potential
brief electric charge that travels down the axon
Polarized neuron
at rest, ready to fire. + ions outside, - ions inside
depolarized neuron
ions mixed, neuron fired. takes some time to re-polarize, become ready again
refractory period
time it takes to recharge the neuron, to polarize it.
neuron threshold
when the “fire” signals outweigh the “don’t fire” signals, firing the neuron
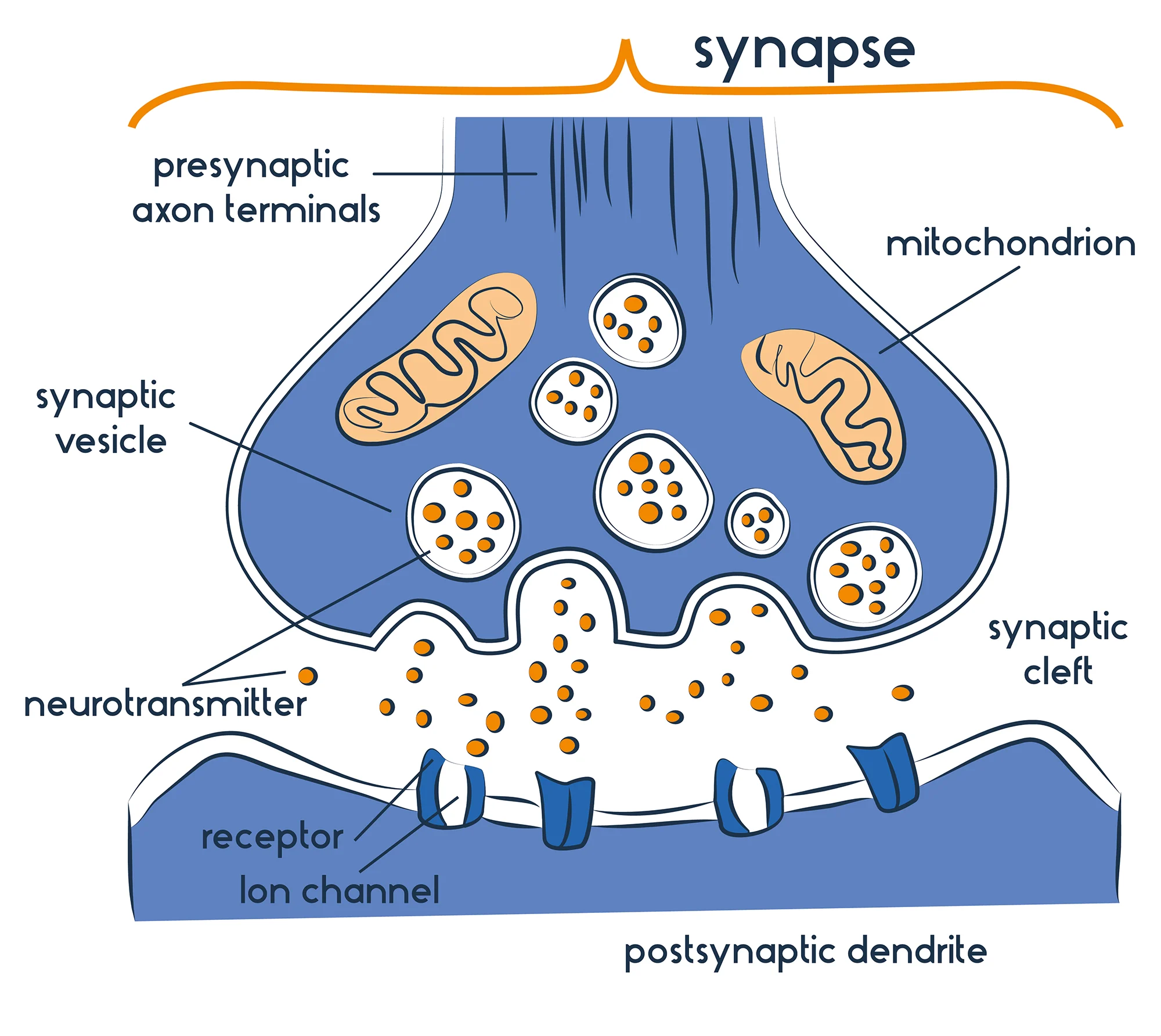
Synapse
small gap between the axon and dendrite
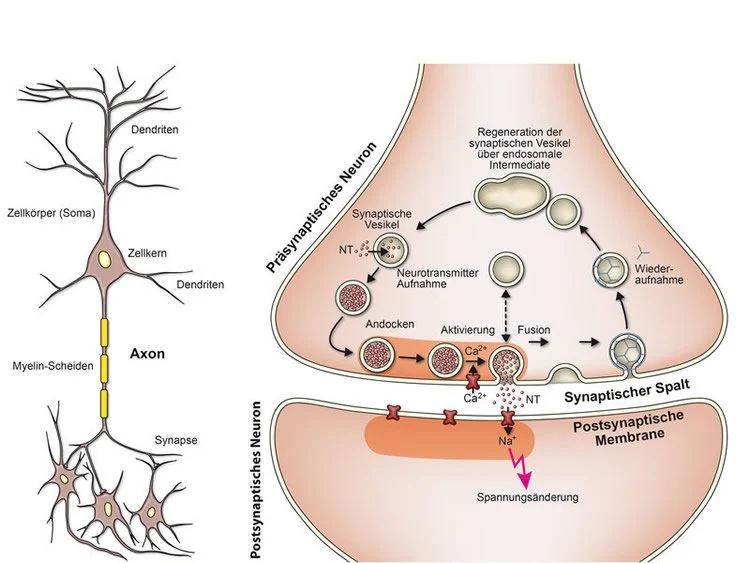
presynaptic neuron
before synapse, sending the signal
postsynaptic neuron
after synapse, receiving signal
Neurotransmitters (NT)
chemical messengers, used to send signals across the synapse
reuptake
recycling of excess NTs, absorbed back into the presynaptic neuron