ANFS 251 Exam 3 rabbits
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Lagomorphs
rabbits, hares, pikas. Based on GI physiology and circadian rhythm. Cecum bacteria make cecotropes.
Rabbit nutritional and GI classification
monogastric herbivore
Rabbit teeth
Big and sharp incisors. Flat molars to grind forage. Need forage to grind teeth down or else they will overgrow.
Rabbit jaw structure
large gap between molars and incisors to accommodate long forages.
GIT of rabbits
same as horse, large cecum with anaerobic bacteria that ferments cellulose
Cecotropes require
Low fiber high protein. pellets excreted from cecum. Must feed adequate forage for cecotropes to function properly.
Circadian rhythm of rabbit
GI motility slows down at night to allow time in the cecum. Cecotropes excreted at night
Cecotrophy
the behavioral process by which mucus-covered soft fecal pellets are expelled from the intestine and consumed by the animal. Takes advantage of microbial protein, and are digested separately from forages.
Suckling stage of nutrition
Only allowed to suckle a few times a day. Mother ignores litter to not be caught by predators.
Weaning
gradual so GI can adapt. Small amount of high quality forage and small amout of grower pellet. Once weaned, supply high quality forage and hay mixed with exercise
Growth stage
Optimal not maximal nutrients best for teeth and GIT. Forage with 12-16% crude fiber and 16-18% crude protein. like horses.
Maintenance
basic body functions, temp and activity
Can you feed rabbits cat or dog food?
No. Too much energy and not enough fiber.
Gestation
32 day period, 4-10 kits. Nutrient requirements jump at 15-20 days.
Gestation nutrition
Nutrition jumps at 15-20 days. By day 21 introduce supplement, increase energy by 10-25%. start with forage then add high quality supplement
Lactation nutrition
allow free forage and complete supplement. Feed intake decreases 24-48 hours before kindling. Energy increases rapidly during lactation.
Senior nutrition concerns
tooth loss, quality, reduced ability to forage and chew, obesity
Senior nutrition solutions
wet pellets
Obesity causes
reduced drive to forage, decrease in exercise, heart weakness, skin, and kidney problems
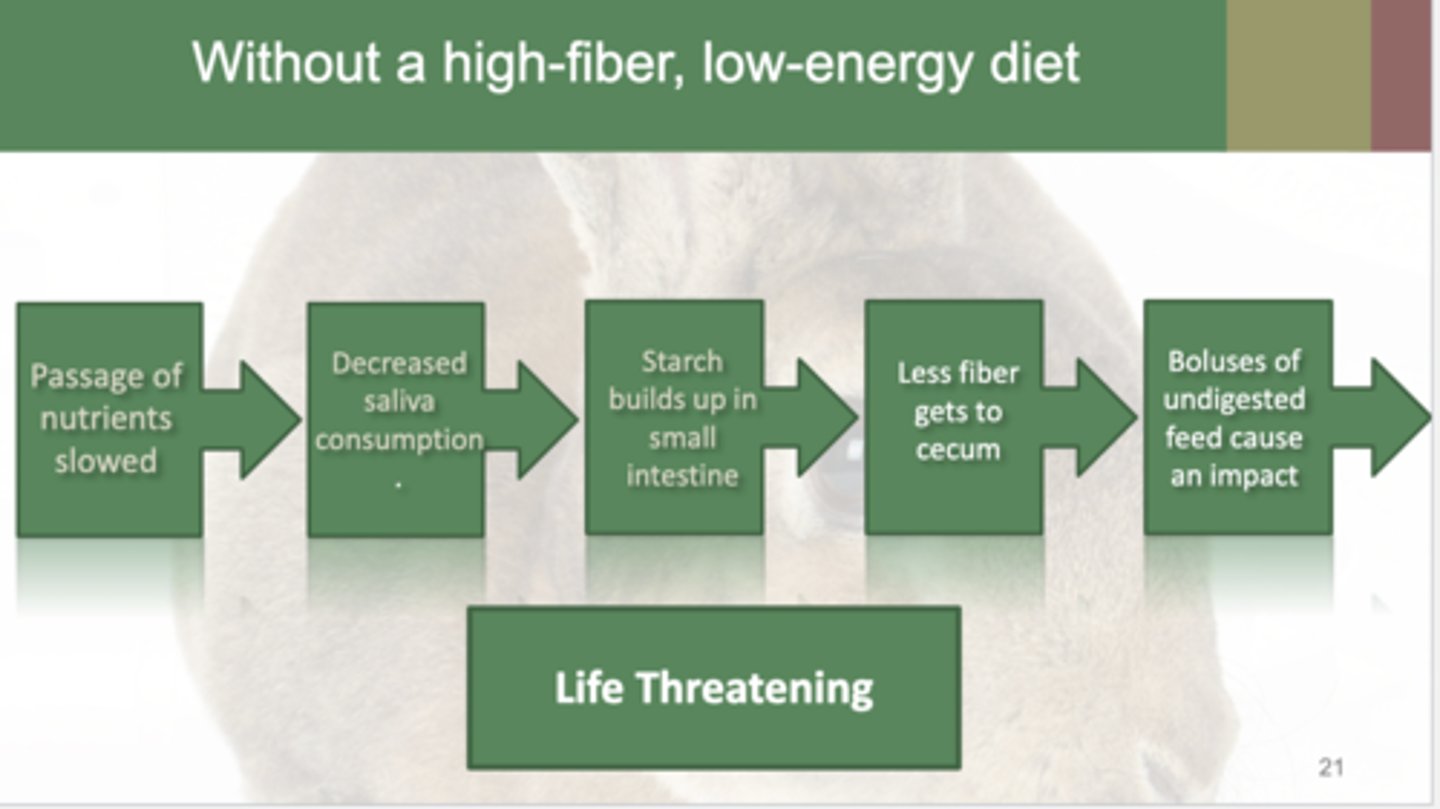
Diets without high fiber and low energy cascade
passage of nutrients slowed to decreased saliva production to starch buildup in small intestine to less fiber in the cecum to boluses of undigested feed causing an impaction
Grooming challenges
lots of hair in GI tract because of grooming. Need lots of saliva made from fiber consumption to keep GI moving.
GI stasis caused by
diets too high in grain
GI stasis causes
hair and other material to build in the gut, trichobezoar
Trichobezoars
hairballs in the stomach. rabbits cant throw up, so ball stays in stomach and causes life threatening impaction.
Symptoms of trichobezoars
feed and water intake decreases, waste droppings decrease, lethargy and depression
trichobezoar treatment
rehydrate, mineral oil, increase gastric motility, feed fiber. usually too late.
Where does hairball come from
Hair plus stomach contents, dehydration leaves largest particles behind. Turns into solid, tightly adhered mass. Long hair breeds may need brushing.
High energy low fiber second problem
chronic soft stool and lack of cecotropes = cannot meet protein requirement
Regular exercise importance
ability to graze increases motility