Prevention, Identification, Recovery and Management of Substance Abuse and Mental Illness
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Talk. They Hear You. Campaign
Reduce underage drinking and substance use for youths (under the age of 21)
Provide resources for parents and caregivers to discuss topics with children
Interagency Coordinating Committee on the Prevention of Underage Drinking (ICCPUD)
Coordinate 15 federal agencies to develop A Comprehensive Plan for Preventing and Reducing Underage Drinking
STOP Underage Drinking
ICCPUD website with research, federal and state resources, and fundraising opportunities to reduce and prevent underage drinking
National Prevention Week (May)
Promote community involvement, resource distribution, and partnerships to increase public awareness of substance use and mental disorders
Communities Talk to Prevent Alcohol and Other Drug Misuse
National initiative providing resources and stipend for community-based organizations, institutions of higher education, and statewide or state-based organizations
Organize activities to raise awareness of the harmful consequences of alcohol and other drug misuse in youth and young adults aged 12 to 25 years old
National Children’s Mental Health Awareness Day (May)
Increase public awareness of the needs of children with serious mental illness and severe emotional disturbance
Share children’s mental health initiatives that promote positive youth development, recovery, and resilience
Federal Commission on School Safety
Recommend policy and best practices for school violence prevention
National Child Traumatic Stress Initiative (NCTSI)
Raise awareness about the impact of trauma on children and adolescents as a behavioural health concern
Develops and implements evidence-based interventions to reduce the mental health impact of traumatic experiences on children and adolescents
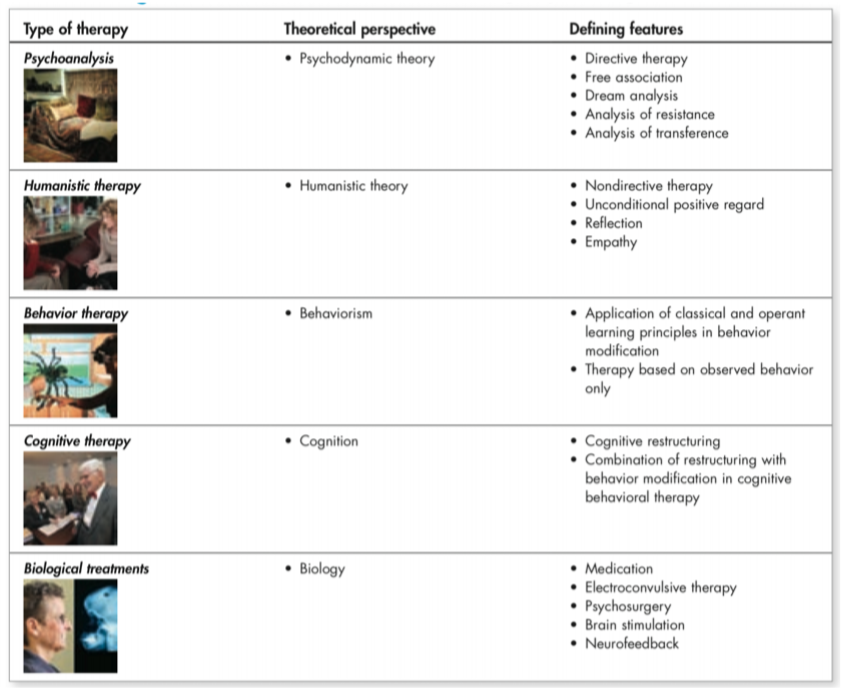
Medication
Medication is the most commonly used of the medical therapies
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
Is used in some severe cases of depression that do not respond to other treatments
The patient is anesthetized and given a muscle relaxant before the induction of general seizures, which are produced by electricity applied through electrodes on the head
Psychosurgery
The attempt to improve psychological disorders through the use of brain surgery
Brain Stimulation
Electrical stimulation applied through surgically implanted electrodes that is used to treat some anxiety and mood disorders
Neurofeedback
A type of biofeedback used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and seizures by teaching the client to keep measures of brain activity within a certain range
Approaches to treating psychological disorders
Treating autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
Although Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is accompanied by abnormalities in the neurotransmitters serotonin, GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid), and glutamate, no medication has been proved effective in alleviating symptoms
The most commonly used psychological treatment for ASD is ABA (applied behaviour analysis), which relies on the principles of operant conditioning
ABA focuses on observable, socially important behaviours such as language and should produce lasting improvements that generalize to settings outside the therapy setting
Treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Many children with a diagnosis of ADHD are treated with medication, either alone or in combination with behaviour therapy
The most commonly prescribed drugs for ADHD are closely related stimulations methylphenidate (Ritalin), dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine or Dextrostat), and a combination of amphetamine salts (Adderall)
These drums increase the activity of dopamine and norepinephrine
The rationale for stimulant treatment of ADHD suggests that impulsive hyperactivity occurs if the parts of the brain responsible for planned, thoughtful behaviour, such as the basal ganglia and frontal lobes, are not active enough
Treating schizophrenia
The medication, phenothiazines, reduce psychosis, which acts as dopamine antagonists, blocking dopamine at the receptor sites
Problem: nearly one quarter of patients with schizophrenia do not respond to these drugs
The drugs successfully reduce psychotic symptoms, such as hallucinations and delusions, but are often less effective in reducing negative symptoms, such as social withdrawal and emotional disturbance
Tardive dyskinesia: a syndrome that results from the use of phenothiazines by some patients; the syndrome produces tremors and involuntary movements, especially of the face and tongue
Most individuals with schizophrenia are treated with medication, but psychological treatments still have much to offer
Treating bipolar disorder
The primary method of treating bipolar disorder is medication
The most commonly prescribed medication is a simple salt, lithium carbonate
Lithium’s actions are specific to bipolar disorder - people who do not have bipolar symptoms show no changes in behaviour when given lithium
Has unpleasant and potentially dangerous side effects
Toxic levels of lithium produce nausea, vomiting, muscular tremors, seizures, and even coma
Because of these risks, patients must have regular blood tests to monitor their lithium levels
Most individuals with bipolar disorder appear to require medication to alleviate their symptoms, and psychotherapy alone is not typically considered an option
Treating major depressive disorder
Given the range of suspected causal factors in depression, treatment approaches are equally diverse
Treatment ranges from medical, to cognitive, to behavioural, to simple aerobic exercise, and combinations of these approaches are common
The most popular method for treating major depressive disorder today is the use of medication
The most widely prescribed medication are the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which include popular brands like Prozac and Zoloft
As their name implies, these medications increase serotonin activity at the synapse by interfering with reuptake of the neurotransmitter
As a result, more serotonin is available in the synapse
A number of psychotherapy alternatives are quite successful in alleviating depression and have the added benefit of producing no adverse side effects
One of the most popular approaches is the use of CBT (Cognitive-behavioural therapy)
Treating anxiety disorders
Anxiety disorders, including general anxiety disorder, phobias, and panic disorder, are typically treated by using medication, CBT, or a combination of the two
Anxiety is associated with a heightened level of brain activity because of anticipated danger; consequently, most efforts to medicate anxiety attempt to reduce brain activity, or produce a “tranquilizing” effect
Because GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain, a common method for slowing brain activity is to enhance the effects of GABA
Although these drugs are used occasionally, the antidepressants previously discussed are typically more effective
This result might reflect a common underlying cause for both depression and anxiety
Treating obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)
OCD can be treated with antidepressant medication, CBT, or a combination of both
CBT for OCD involves training the person to anticipate compulsive behaviour and then to engage in a competing behaviour
Meta-analysis shows that CBT is a highly effective approach to treating OCD
Treating body dysmorphic disorders
CBT is particularly helpful in cases of body dysmorphic disorder
In CBT, cognitive restructuring can help the individual think more realistically about perceived physical flaws
Many individuals with this disorder, however, insist on continued treatment by cosmetic surgeons and resist suggestions that they should obtain psychotherapy
Treating post-traumatic stress disorder
PTSD is typically treated using exposure therapy with or without SSRI medications
Because many people with PTSD also develop a variety of substance use disorders, additional treatment addressing these disorders is necessary for full recovery
Treating dissociative identity disorder
The treatment of dissociative identity disorder can be quite controversial, as is the diagnosis of this condition
Some psychotherapists work on the assumption that dissociative identity disorder is a valid diagnostic category that often results from serious trauma, childhood sexual abuse in particular
Treatment is aimed toward integrating the various personalities by first identifying and “working through” the traumatic memories related to the disorder
Hypnosis is commonly used by these therapists to assist in the recovery and resolution of traumatic memories, but this practice is not well advised
Under hypnosis a suggestive person might be vulnerable to the manufacture of false memories, and individuals identified as having dissociative identity disorder appear to be far more suggestible than the general public
Treating somatic symptom disorders
Both biological and psychological treatments are commonly used to treat somatic symptom disorders, which involve physical symptoms such as pain that have no apparent physical basis
Among the best biological treatments for somatic symptom disorders are medication with antidepressants and increases in physical activity
Treating antisocial personality disorder
Finding effective treatments for antisocial personality disorder has a high priority, given the extent of harm individuals in this category inflict upon the rest of society
Effective treatments appear elusive
No known medications specifically reduce antisocial behaviour, although many incarcerated individuals are treated with tranquilizing drugs, including antipsychotic and anticonvulsant medications, to make their aggressive, violent behaviour more manageable
Even if effective medications are discovered, individuals with antisocial personality disorders tend to view themselves as “okay,” and not in need of treatment
Psychological treatments for antisocial personality disorder include learning models that emphasize anger control, social skills, and moral reasoning
Treating borderline personality disorder
No medications are currently approved specifically for the treatment of borderline personality disorder, but medications are frequently prescribed
Among the commonly prescribed medications are antidepressants, antipsychotic medications, mood stabilizers (ex. lithium), anti-anxiety medications, and anticonvulsants
Psychotherapy for borderline personality disorder often takes the form of CBT
In this case, the individual learns to manage stress, emotions, and relationships
In particular, psychotherapists emphasizes skills aimed at reducing the individuals potential for suicidal thinking and behaviour
A therapy specially designed for individuals with BPD, dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT), attempts to address symptoms in the order or their importance: reducing suicidal thoughts, reducing behaviours that interfere with therapy, and finally reducing behaviours that interfere with the quality of life
4 major dimensions of recovery
Health: overcoming disease or managing symptoms by making informed health choices that support both physical and psychological well-being (ex. Abstaining from use of alcohol, illicit drugs, non-prescribed medications for addictions)
Home: a stable safe place to live
Purpose: meaningful daily activities to be independent, earn income, and participate in society (ex. a job, volunteering, family caretaking, creating endeavors)
Community: have relationships for a support system, friendship, love, and hope