2.8 - The role of money and financial markets
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
^^**How would you define the term ‘Money’?**^^
* Anything that is generally accepted as a **means of payment** for goods and services.
It consists of notes and coins which are regarded as *legal tender* and bank deposits in the form of both current and savings accounts.
It consists of notes and coins which are regarded as *legal tender* and bank deposits in the form of both current and savings accounts.
2
New cards
^^What are the following are money?^^
* bank notes
* coins
* saving accounts
* current accounts
* coins
* saving accounts
* current accounts
3
New cards
^^What are the following are not money?^^
* debit cards
* credit cards
* credit cards
4
New cards
^^Why is cash a useful means of payment?^^
* holds value
* widely accepted
* Clear as to how much is being paid
* Easy to understand
* widely accepted
* Clear as to how much is being paid
* Easy to understand
5
New cards
^^What is the first function of money?^^
1. **A medium of exchange**
* Money enables goods and services to be **exchanged**, **transactions to be settled** and **debts to be paid**
* Money avoids the problems of barter, principally the ‘***double coincidence of wants***’
* Barter is inefficient and would suppress specialisation and the division of labour
6
New cards
^^What does **‘double coincidence of wants’** ?^^
**Double coincidence of wants** means what one person wants to sell and buy must coincide with what some other person wants to buy and sell.
\
\
7
New cards
*What is the second function of money?*
2. **Store of value**: this can refer to any asset whose “value” can be used now or used in the future i.e. its value can be retrieved at a later date.
Money performs this function, because it allows purchasing power to be transferred from the present to the future. This means that people can save now to fund spending at a later date
8
New cards
*What is the third function of money?*
3. __**Unit of Account**__
* **This refers to anything that allows the value of something to be expressed in an understandable way, that allows the value of items to be compared**
9
New cards
*What are the requirements of money?*
Money has to be:
\
* **durable**
* **portable**
* **divisible**
* **Complex enough to prevent people making counterfeit versions**
* **Accepted by everyone**
* **Limited in quantity**
\
* **durable**
* **portable**
* **divisible**
* **Complex enough to prevent people making counterfeit versions**
* **Accepted by everyone**
* **Limited in quantity**
10
New cards
*What do debit cards, credit cards and cheques allow?*
Debit cards, credit cards and cheques allow money in the form of bank deposits in current accounts to be transferred between buyers and sellers.
11
New cards
*Debit cards - Explain the differences between debit and credit cards?*
* You cannot buy the product or service if you do not have enough money on your account!
* There is no charge to the seller for accepting these cards in payment.
* Anyone is eligible to open a bank account
\n
* There is no charge to the seller for accepting these cards in payment.
* Anyone is eligible to open a bank account
\n
12
New cards
*Credit cards - Explain the differences between debit and credit cards?*
* If you cannot pay it all back you are **charged interest** on the amount outstanding.
* Can only qualify when you are 18
* Need a regular source of income
* sellers are charged for accepting these cards in payment
\\n
* Can only qualify when you are 18
* Need a regular source of income
* sellers are charged for accepting these cards in payment
\\n
13
New cards
*What is the spectrum of liquidity? and How does it look on a line?*
The **spectrum of liquidity** shows **how close money is to cash**, and therefore how easy to use as payment for goods and services, or liquid, it is.
\n
\n
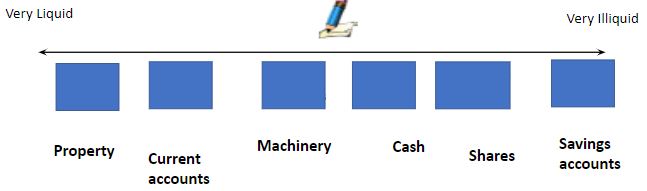
14
New cards
*Explain the term the medium of exchange?*
Anything that sets the standard of value of goods and services acceptable to all parties involved in a transaction
15
New cards
*Explain the term financial sector?*
Consists of financial organisations and their products and involves the flow of capital.
16
New cards
the role of the financial sector for the **economy**
* the financial sector helps consumers, firms and governments to carry out economic activities → helps the market to work
\
* It involves the lending and borrowing of money through, for example bank and building societies
\
* Banks and building societies enable people who do not need to use money now, savers, to provide it for those who need it now borrowers.
\
* This allows for supply of money, from savers, to equal demand for money, from borrowers
\
* It involves the lending and borrowing of money through, for example bank and building societies
\
* Banks and building societies enable people who do not need to use money now, savers, to provide it for those who need it now borrowers.
\
* This allows for supply of money, from savers, to equal demand for money, from borrowers
17
New cards
Case study - The role of the financial sector in the **UK**
* Enables people to borrow money
* Provides advice to consumers and firms
* Facilitates the exchange of goods and services.
* Enables people to save money
* Provides advice to consumers and firms
* Facilitates the exchange of goods and services.
* Enables people to save money
18
New cards
Explain the term banks?
Financial institutions licensed to receive deposits and make loans.
19
New cards
Core functions of commercial banks
1. **Accepting deposits (savings)** from customers and in many cases will pay interest on them.
2. **Lending money** to individuals or firms who wish to borrow. Interest will have to be paid.
3. Providing an efficient **means of payment** and **transferring funds** between different economic agents.
\
(provide foreign currencies for firms & individuals)
\
20
New cards
Investment banks
These help firms with specialist needs:
\
* in mergers and takeovers
* underwriting share issues
\
* in mergers and takeovers
* underwriting share issues
21
New cards
Explain the term building societies?
mutual financial organisations that is owned by their members.
* Its primary objectives are to receive deposits from its members to purchase property.
\n
* Its primary objectives are to receive deposits from its members to purchase property.
\n
22
New cards
Core functions of building societies
* They are a type of mutual organisations where the firm is **owned by its members who are savers with them.**
* Provide a limited range of services mainly savings and mortgages
* less likely to take risks
* support homebuyers by giving mortgages
* Provide a limited range of services mainly savings and mortgages
* less likely to take risks
* support homebuyers by giving mortgages
23
New cards
__**3 Main roles of financial sector**__
1. Credit Provision
1. Credit Provision
**Without credit economic activity would be limited**. Although the provision of credit has **allowed people to live beyond their means and run up very large debts**, they provide a valuable way to allow consumers to buy now and pay later
24
New cards
__**3 Main roles of financial sector**__
2. Liquid Provision
\
2. Liquid Provision
\
Liquidity refers to how easy it is to turn an asset into cash. **Banks are the main providers of liquidity to households and businesses, and this allows the economy to continue to function** when faced with unexpected demands for cash
25
New cards
__**3 Main roles of financial sector**__
3. Risk Management
\
3. Risk Management
\
Financial institutions **allow both individuals and businesses to take risks**.
Professional finance managers will also take savings from a customer and invest the money into a range of different companies so that the saver does not lose all of their money if one fails.
Professional finance managers will also take savings from a customer and invest the money into a range of different companies so that the saver does not lose all of their money if one fails.