CURRENT OF ELECTRICITY
1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Current
rate of flow of charge
Current for __ electrons and __ protons
I = (N q/t ) +….
Current
rate of flow of charge
Direction of Conventional Current
The direction which there is a net flow of positive charge carriers/Opp to the direction of net flow of negative charge carriers
Electric charge
the charge which flows through a given cross section is the product of the steady current and the time
Why does current remain constant along one single conductor?
The amount of charge entering and leaving each junction is the same, do not accumulate or disappear
(charges obey law of conservation, can not be destroyed or created)
Charges when there is no PE applied across in the conductor?
Even if no PE, due to TE they have electrons can move freely and randomly.
They dont travel in a straight line due to collison with one another and atoms in the metal lattice so undergo random motion
—> there is no net flow of charges,no current in conductor
Charges when PD is applied?
an external electric field is set up, electric force acts on the e and so they drift along the conductor in the direction opp to the EF while keeping their random motion
—> net flow of charges, current in the conductor
Derive drift velocity

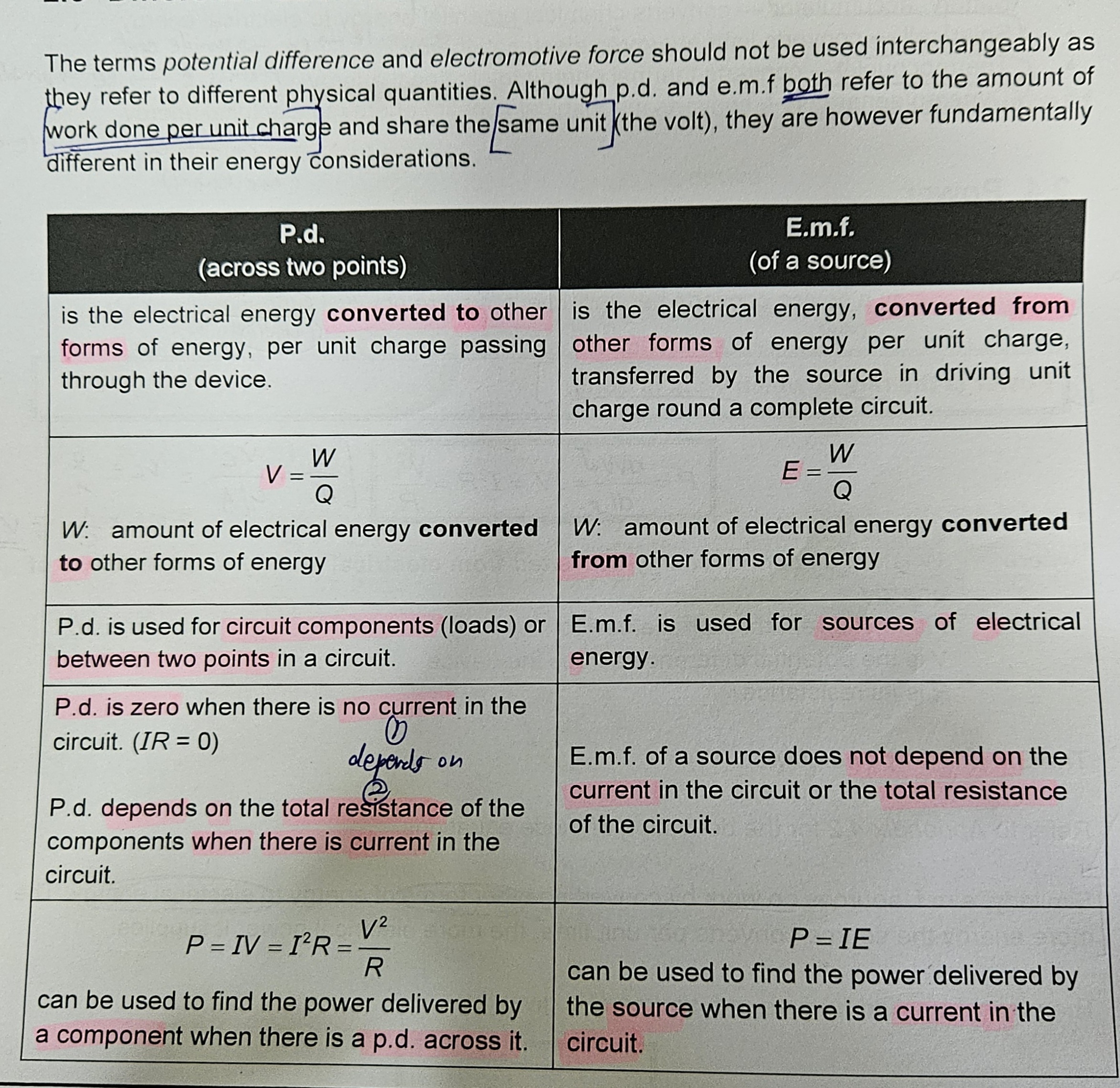
Potential Difference
the PD between 2 points in a circuit is the electrical energy converted to other form of energy per unit charge when charges pass from from one point to another
Electromotice force
EMF of a source is the electrical energy converted from other forms of energy per unit charge delivered by the source in driving unit charge around a circuit
Power
rate at which work is done
Differences between PD and EMF
Resistance
Of a conductor is defined as the ratio of the PD across the conductor to the current through it
(Not thr grad of the tangent, draw to origin)
(phy qnty of matter that opposes the flow of electric charge, if higher means lower mobility of electric charge in the matter)
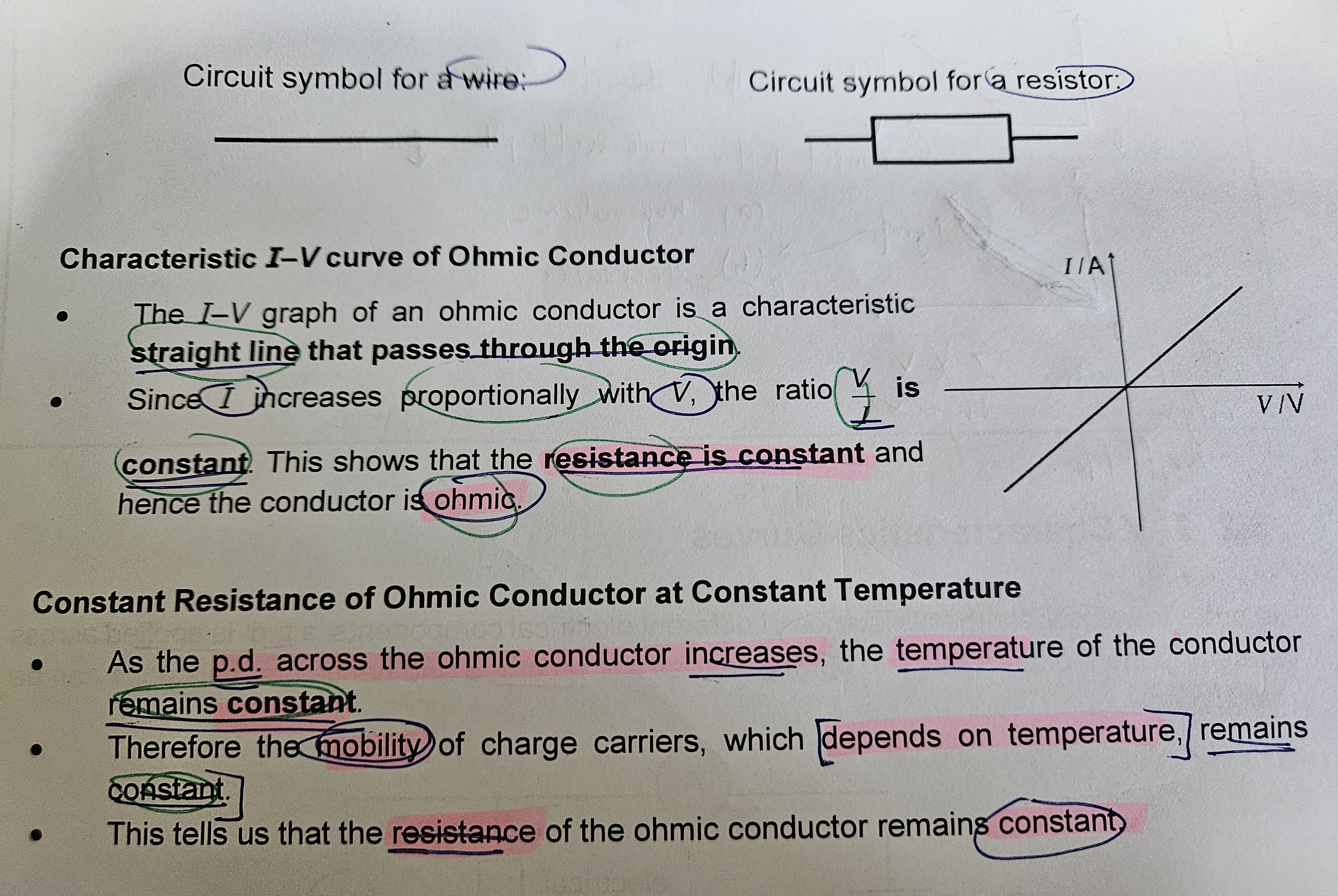
Ohm's Law
States that the current through a metallic conductor is directly proportional to the PD across it under constant physical conditions (temp, pressure, humidity, mechanical stress)
I prop V
*obey the law = ohmic conductor where R us constant with increasing pressure so straight line graph passing through origin
OHMIC CONDUCTORS
eg. wire/resistors
FILAMENT LAMP

THERMISTOR

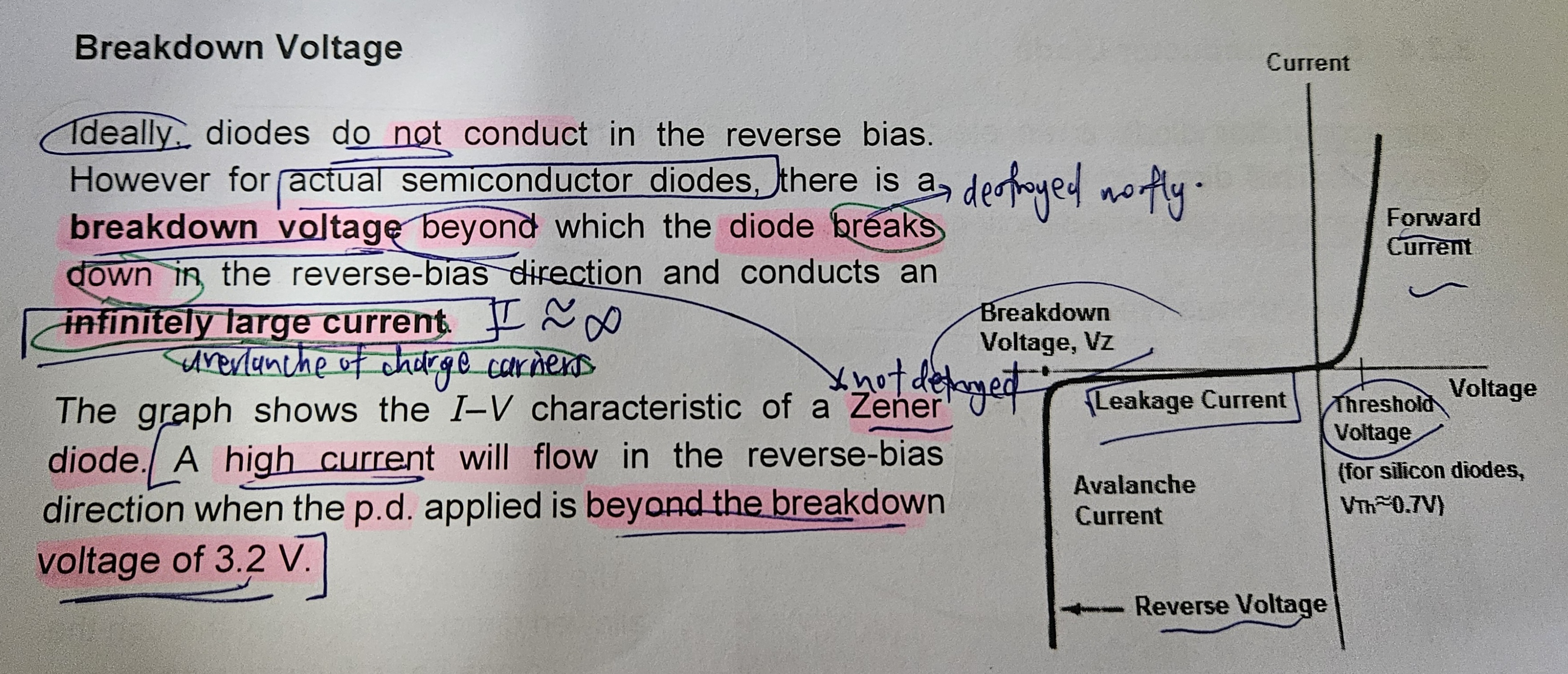
SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE
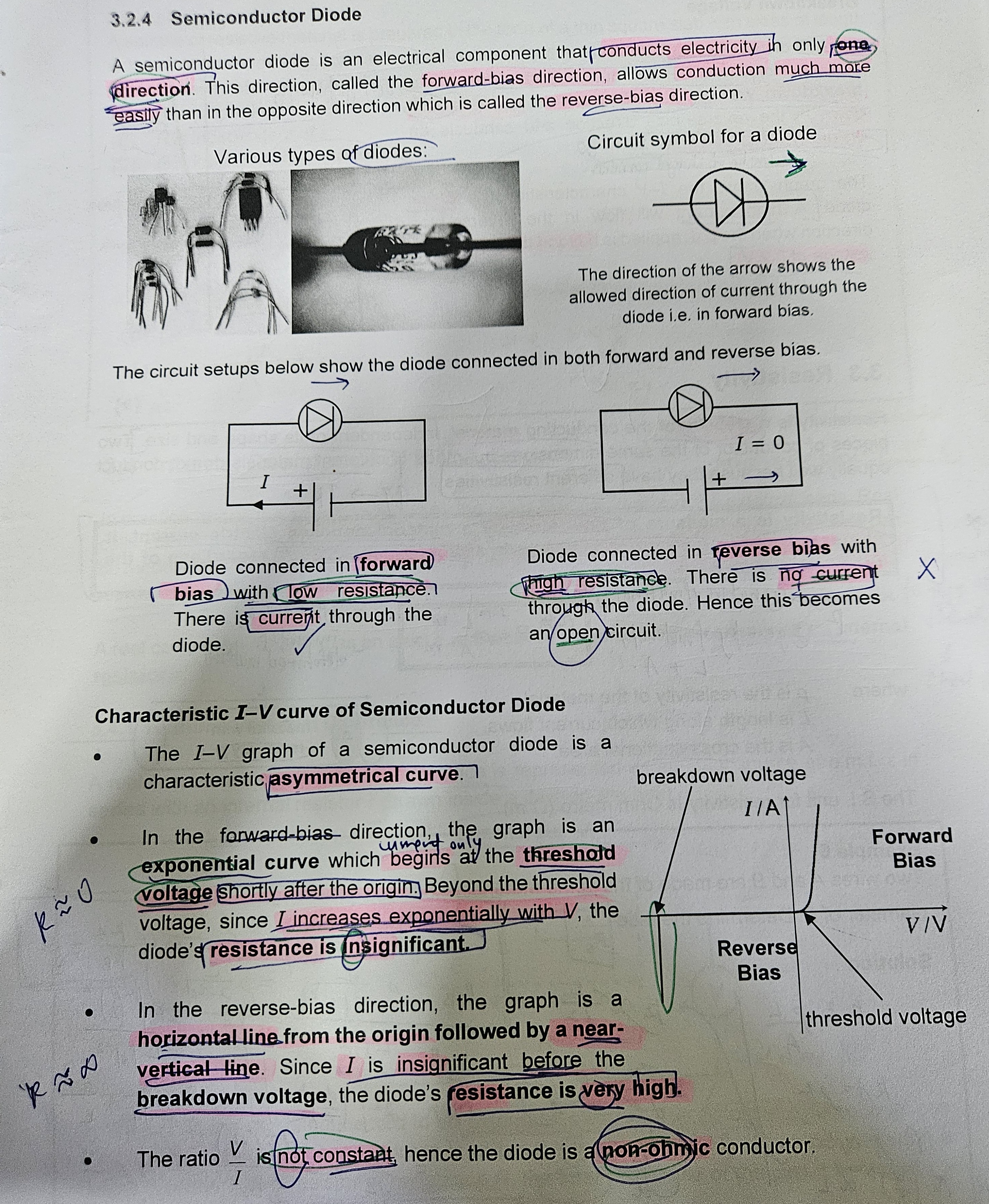
BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE
Resistivity
A measure of how strongly a material opposes electric current. It characterises the resistance of materials at a fixed temperature of the materials dimensions.
(affected by impurities/deformed material)
INTERNAL resistance of EMF source

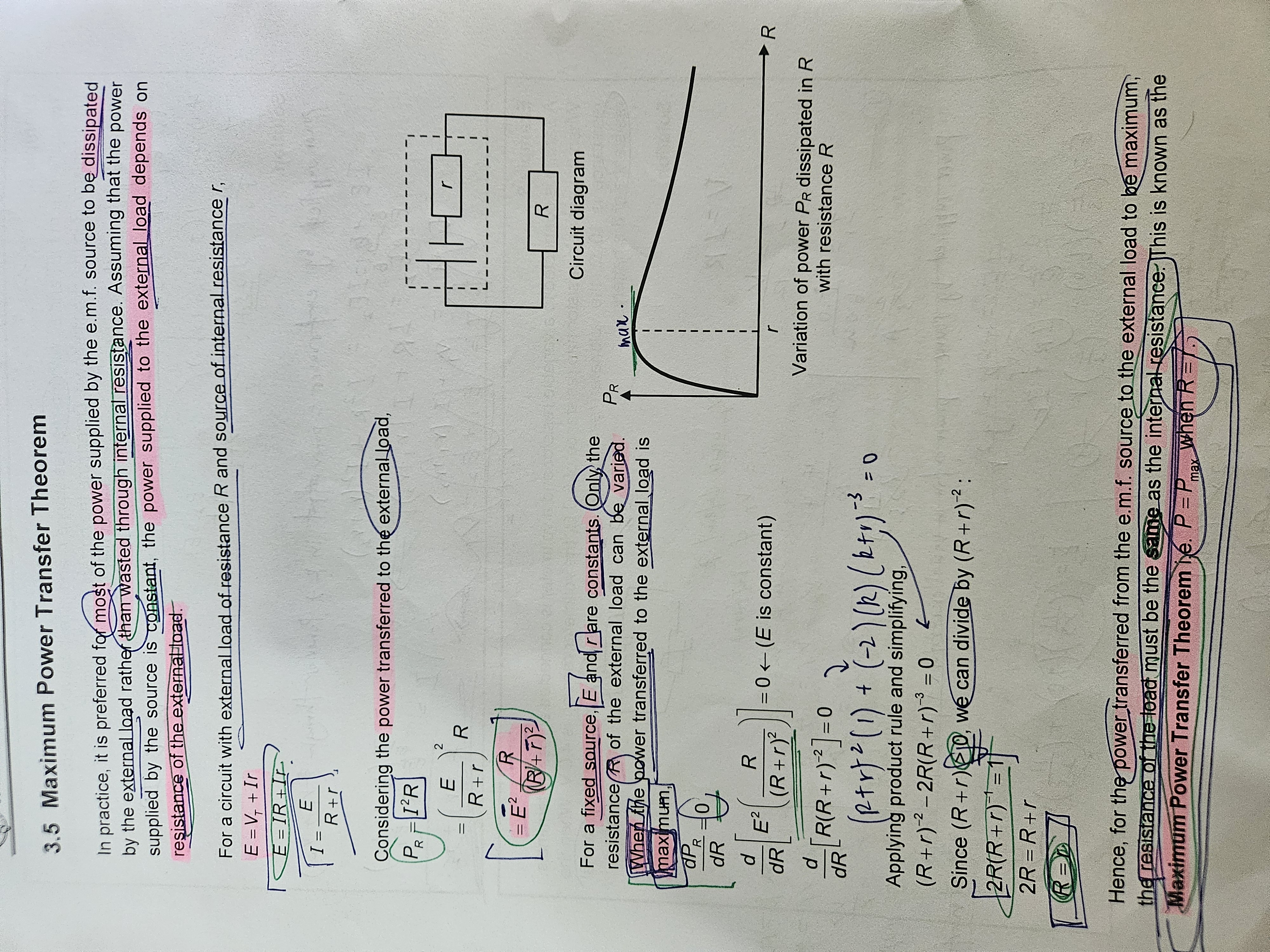
Maximum Power Trasnfer Theorem
When R = r