Physics #3
4.2(5)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:49 PM on 12/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
Mass
The amount of matter in an object; will not change based on gravity
2
New cards
Weight
A measure of force of gravity on an object; will change based on gravity
3
New cards
Frictional force
The force that resists movement across a surface
4
New cards
Dynamic / kinetic friction
Force of Friction between surfaces in motion; result of surfaces moving over one another.
5
New cards
Static friction
Force of friction between surfaces NOT in motion; result of surfaces adhering to each other; strongest form of friction
6
New cards
Sliding friction
Form of Kinetic/dynamic friction
7
New cards
Rolling friction
Form of Kinetic/dynamic friction; weakest type of friction
8
New cards
Inertia
The tendancy to remain unchanged (Newton’s 1st Law)
9
New cards
Acceleration
The increase (+) or decrease (-) in an object’s motion
10
New cards
Velocity
The direction and a rate at which an object is moving
11
New cards

Explain why the boulder does not move. While there may be a variety of reasons for this, explain how friction is affecting the motion of the boulder.
The boulder will not move across the groud becuase the girl cannot overcome the force of static friction. While the girl applies a force, the rock applies a force back on the girl. Simce the girl cannot overcome the amount of friction, the boulder will not move.
12
New cards
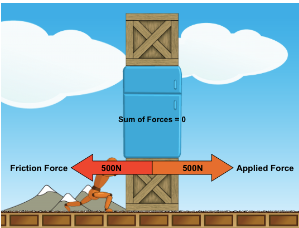
Why is the person not able to move the objects? Include ideas about balanced/unbalanced forces in addition to static friction.
The person is unable to exert a force strong enough to overcome static friction, thus, the object remains stationary (Balanced forces)
13
New cards
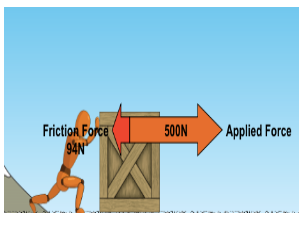
Why is the person able to move the object?
The person is able to exert a force strong enough to overcome static friction, thus, the object moves (Unbalanced forces).
14
New cards
How do you calculate an object’s mass (g) to Newtons (N)?
Divide the mass by 100
15
New cards
How do you calculate an object’s force (N) to mass (g)?
Multiply the force by 100
16
New cards
If a golf ball has a mass of 1211.75 grams, what is the force exerted on it in Newtons?
12.1175 N
17
New cards
If a textbook has a mass of 815.2 grams, what is the force exerted on it in Newtons?
8.152 N
18
New cards
If the force exerted on a pencil bag is 1.125248 N, what is the mass in grams?
112.5248 g
19
New cards
If the force exerted on a desk is 973.787 N, what is the mass in grams?
97378.7 g
20
New cards
Newton's First Law
An object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
21
New cards
Newton's Second Law
The force of an object is the mass multiplied by the acceleration
22
New cards
Newton's Third Law
Every action will have an equal and opposite reaction
23
New cards
How much force is needed to accelerate a 45 kg skier at a rate of 9 m/s?
405 N
24
New cards
What is the acceleration of a 25 kg object pushed with a force of 600 newtons?
24 N
25
New cards
A force of 370 N is applied to an object that accelerates at a rate of 5 m/s. What is the mass of the object?
74 kg
26
New cards
An object has an acceleration of 9 m/s. If the mass of this object were tripled, what would it’s new acceleration (m/s) be?
3 m/s
27
New cards
An object has an acceleration of 10 m/s. If the mass of this object were halved (½), what would it’s new acceleration (m/s) be?
20 m/s
28
New cards
An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s. If the net force was doubled and the mass were halved, what would it’s new acceleration (m/s) be?
32 m/s