AP Psych Review
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
confirmation bias
favoring information that confirms your beliefs
hindsight bias
believing events were predictable after they happened
reliability
consistency of measurement
validity
accuracy of a test in measuring what it is supposed to measure
The American Psychological Association (APA)
leading scientific and professional organization representing psychology in the US
wording effect
changes in responses caused by word choices in questions
social desirability bias
a tendency to give socially approved answers
third variable problems
a counting variable that influences both variables of interest
confounding variable
variable that might influence the experiment’s outcome unexpectedly
operational defintions
clear, precise descriptions of variables
random assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance
experimenter bias
when researchers’ expectations influence the outcome of a study
representative sample
a sample that accurately reflects the characteristics of the population as a whole
random sample
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
sample bias
errors that occur in the sample selection leading to non-representative
measure of central tendency
a number that describes the center of a data set (mean, median, mode)
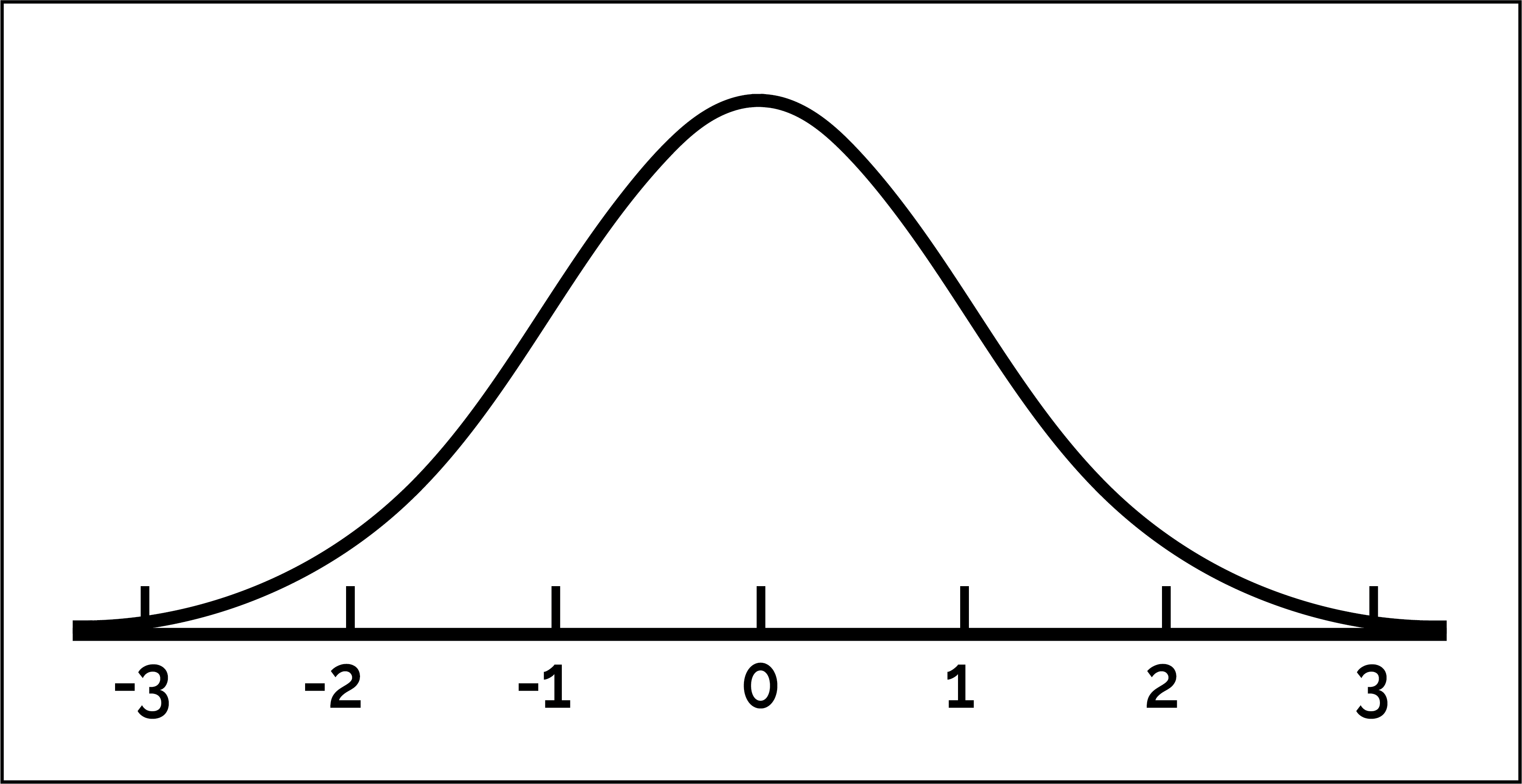
normal curve
a symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many types of data
regression to the mean
tendency for extreme scores to fall back toward the average
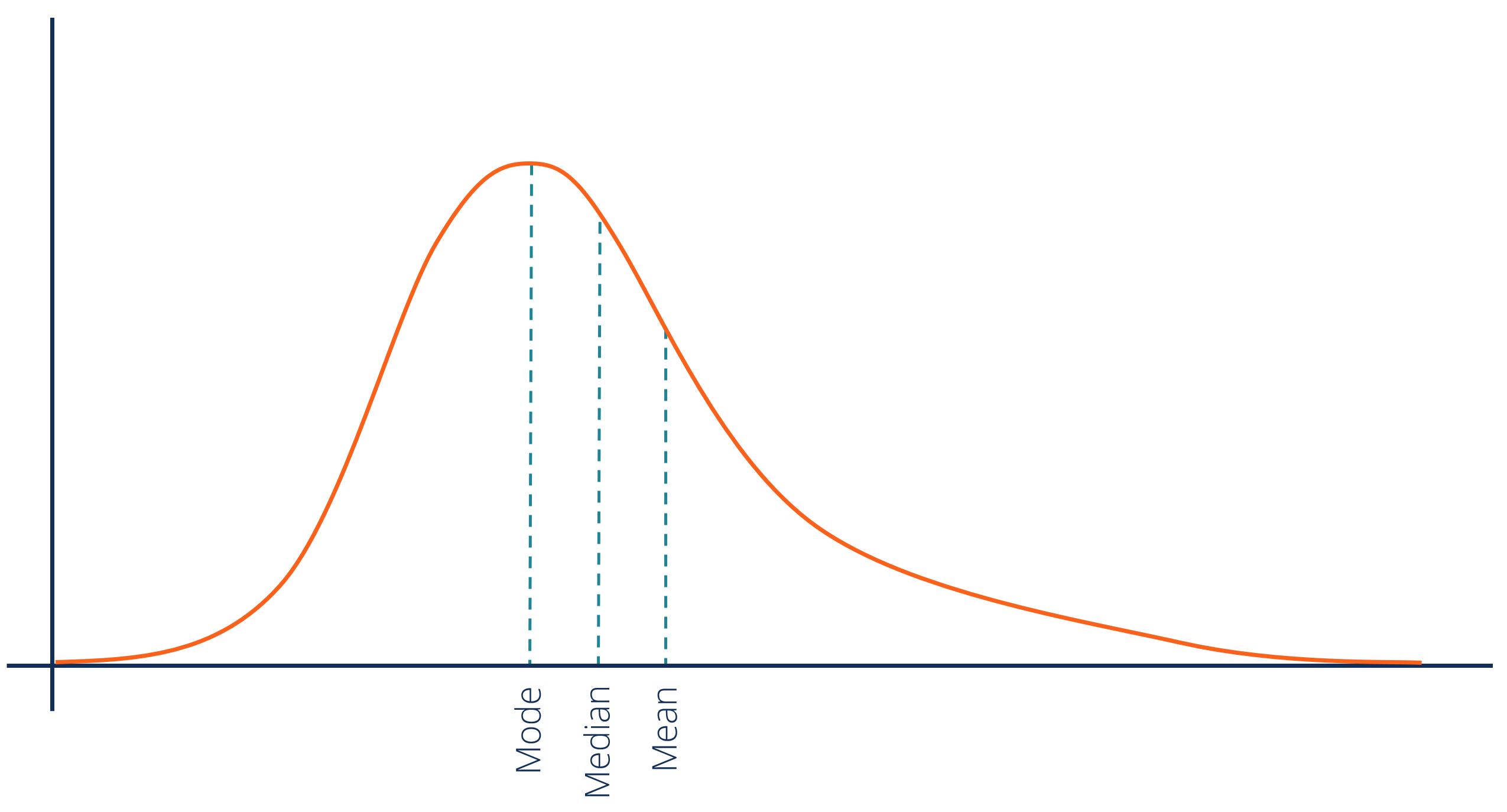
positive skew
when a distribution includes more low scores
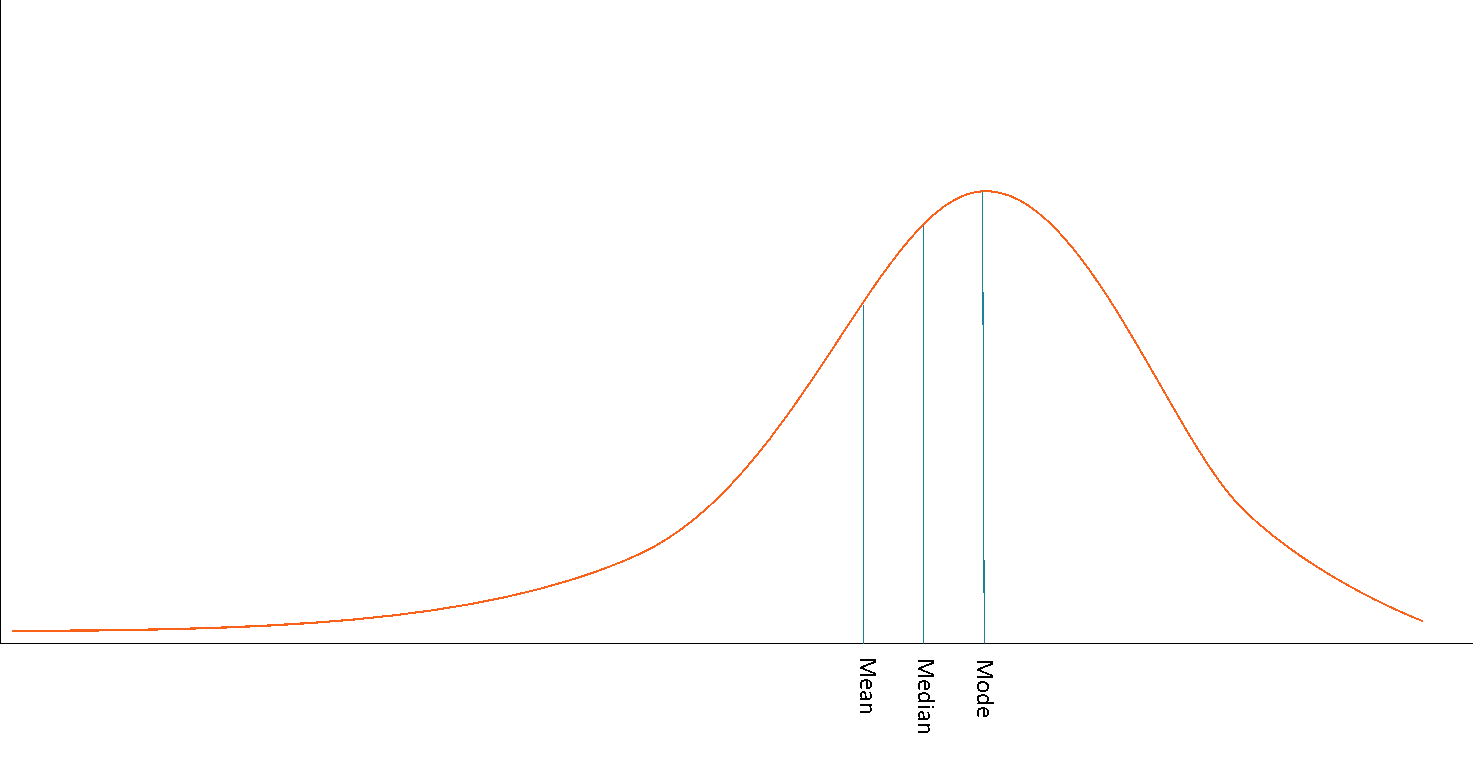
negative skew
when a distribution includes more high scores
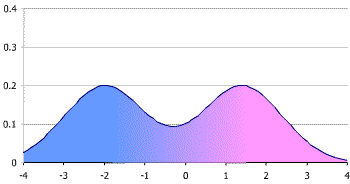
bimodal distribution
a distribution with two different modes which may appear as distinct peaks
statistical significance
the likelihood that a result or relationship is caused by something other than mere chance
effect sizes
a quantitative measure of the magnitude of the experimental effect
meta analysis
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
Institutional Review Boards (IRB)
groups that review research to ensure that ethical standards are met
acquisition
the initial stage in classical conditioning; the phase associating a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus so that the neutral stimulus comes to elicit a conditioned response
higher-order conditioning
a procedure in which the conditioned stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neural stimulus, creating a second