Astronomy Remove Summer Exam
1/285
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
286 Terms
Diameter of the Earth:
13,000 km
Shape of the Earth:
Oblate Spheroid
Evidence the Earth is round.
Watch a sunset, twice
Measure shadows from 2 places
Look from space
Satellites orbit Earth
Why is the Earth blue?
When light enters Earth atmosphere it is scattered. The scattering of blue light is greater than that of red light.
Three distinguishing features of Earth:
Water
Atmosphere
Life
What is meant by seeing?
Seeing is how wobbly the atmosphere is.
Measure by the Antoniadi Scale:
I = perfect
V = awful
Structure of the Earth:
Inner Core
Outer Core
Mantle
Crust
Most common elements inside Earth:
Iron and nickle
Longitude and Latitude
Longitude = Up
Latitude = Across
Prime Meridian:
Equator:
Longitude of 0
Latitude of 0
ALL LATITUDE LINES
Tropic of Cancer:
Tropic of Capricorn:
Arctic Circle:
Antarctic Circle:
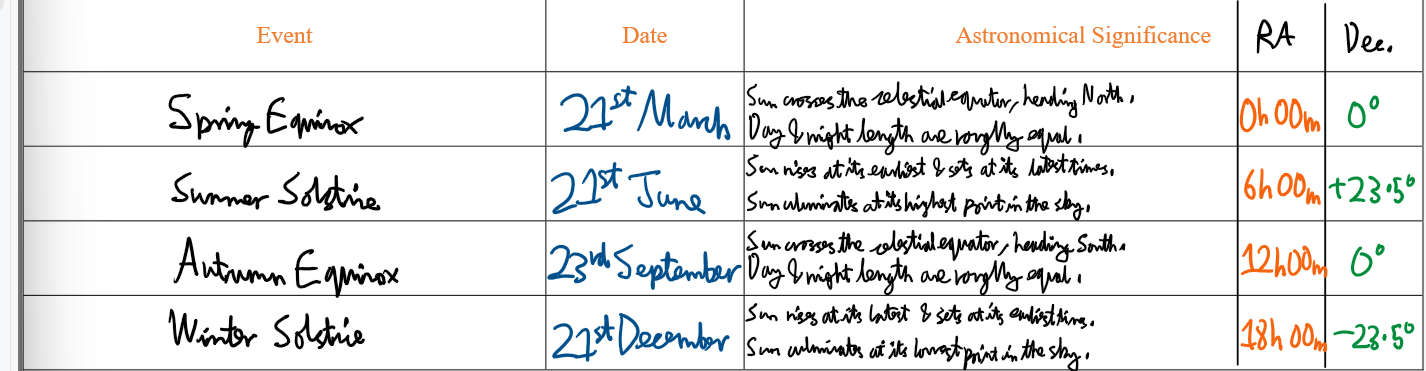
23.5° North
23.5° South
66.6° North
66.6° South
Winter Solstice:
Summer Solstice:
Spring Equinox:
Autumn Equinox:
21st December
21st June
20th March
21st September
Open cluster of stars
Hazy patch of multiple stars.
E.g. Pleiades
Globular Cluster
Halo around the core of a galaxy.
Meteors
(shooting stars)
Dust or rock burning up into the atmosphere.
Meteor Showers
Occurs when the Earth passes through debris.
Comets
Icy rocky objects that come from var within the Solar System.
Nebulae
A remnant of a supernova.
Aurora
Solar flares from the Sun.
Galaxies
Collections of stars, planets, gas and dust.
Optical double stars
Stars that look from Earth as if they are together.
Binary Stars
Stars that are actually close together.
Supernova
An explosion of a high mass star.
What is the difference to the naked eye between planets and stars?
Planets twinkle much less and are always in the same area of sky.
What is the best time to view satellites?
Around sunrise and sunset as they reflect light.
They appear as a moving faint light.
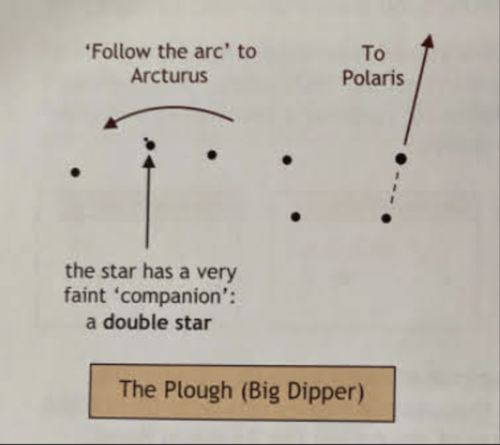
The Plough
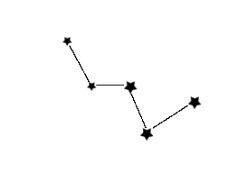
Cassiopeia
Orion
3 stars DOWN to SIRIUS
3 stars UP to ALDEBARAN AND THE PLEIADES

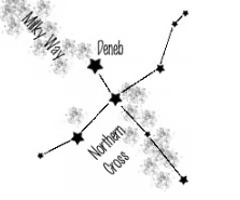
The Summer Triangle
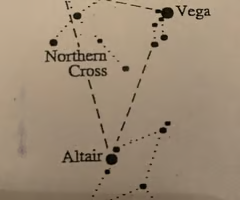
The Northern Cross
Southern Cross

The Great Square of Pegasus
DOWN from bottom right star to FOMALHAUT
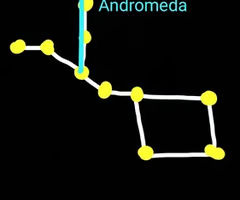
Asterism
The shape we connecting the stars.
Constellation
A patch of sky with borders.
Celestial Sphere
An imaginary 2D sphere surrounding the Earth, on which all celestial objects are located.
Celestial Poles
The projection of the Earth's axis. (NCP and SCP)
Celestial Equator
The projection of the Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere.
The Ecliptic
The Path the Sun appears to take through the sky.
The Zodiacal Band
The area of the celestial sphere where the planets and moon are located (8 degrees above and below the ecliptic).
Right Ascension
Winter Solstice
Autumn Equinox
Summer Solstice
Spring Equinox
18
12
6
0
Altitude
The angle of elevation of an object above the observer's horizon (0 to 90 degrees)
Azimuth
The bearing of a point directly below an object around the observer's horizon (0 to 360 degrees).
Right Ascension
The angle around the celestial equator.
Declination
The angle above and below the celestial equator.
Meridian
An imaginary line through the observer's sky running from North to South.
Culmination.
When an object transits the meridian.
Zenith
The point directly overhead.
Zenith distance
The distance of an object from the zenith (90 degrees - altitude of object).
Altitude of Polaris =
Observer's Latitude
Altitude of CE =
90 degrees - latitude
Siderial day
23h 56m
Time it takes for Earth to rotate once.
Sydonic day
24h
Time it takes for the Sun to appear in the same place.
How much earlier will a star culminate each successive day?
4 minutes
Local Siderial Time
The Right Ascension currently on the observer's meridian.
Hour Angle =
Local Sidereal Time - Right Ascension
CAN BE NEGATIVE!
Maximum Altitude =
(90 degrees - Altitude of NCP) + declination
Circumpolar
A star that is always visible (above the horizon).
Circumpolar if
90 degrees - declination ≤ latitude of observer
Upper transit =
Lower transit =
Latitude + Polar Distance
Latitude - Polar Distance
Dark Adaption
Dark adapted is when the rods in you eyes become desensitized so that they can see things more fully. It takes 20 minutes to become dark adapted.
Averted Vision
Looking slightly to the side ofa n object to view the object better.
What device can be used to find the altitude of a star?
A clinometer
Sidereal Day
The time it takes for Earth to rotate once on its axis (with respect to the distant stars) 23hr 56m
Synodic Day
The time it takes for the Sun to appear the same place in the sky. 24h 00m
Explain the difference between sidereal and synodic days
By time the Earth has rotated 360 degrees, it has rotated in its orbit.
So, it has to rotate slightly more for the Sun to appear in the same place.
This makes a synodic day 4 minutes longer than a sidereal day.
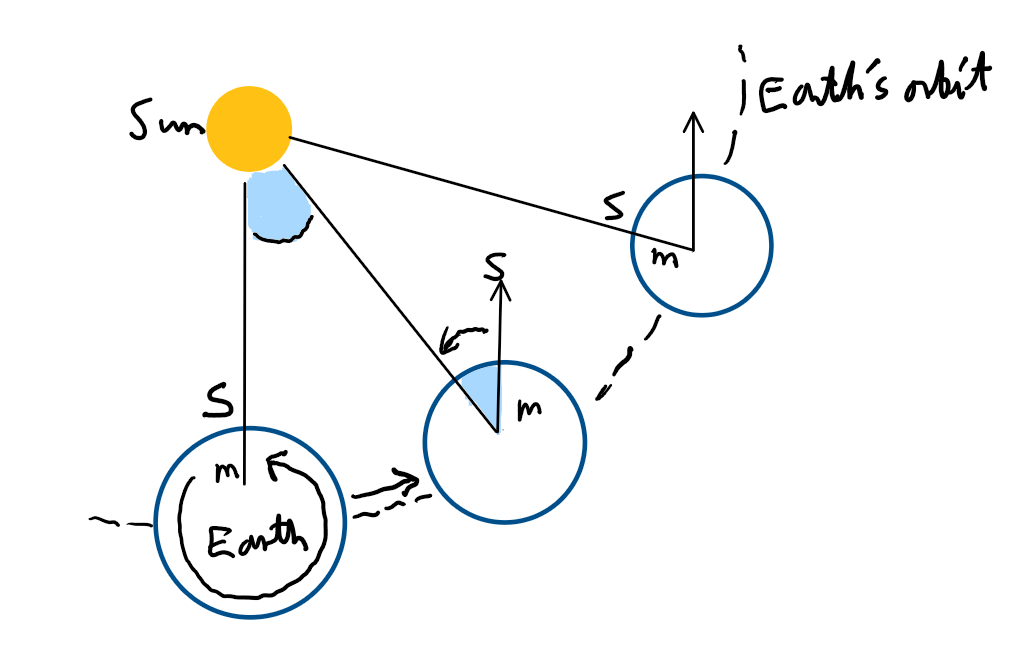
What does this difference mean for the night sky?
Stars rise, set and transit 4 minutes earlier each day.
So, our night-time view changes.
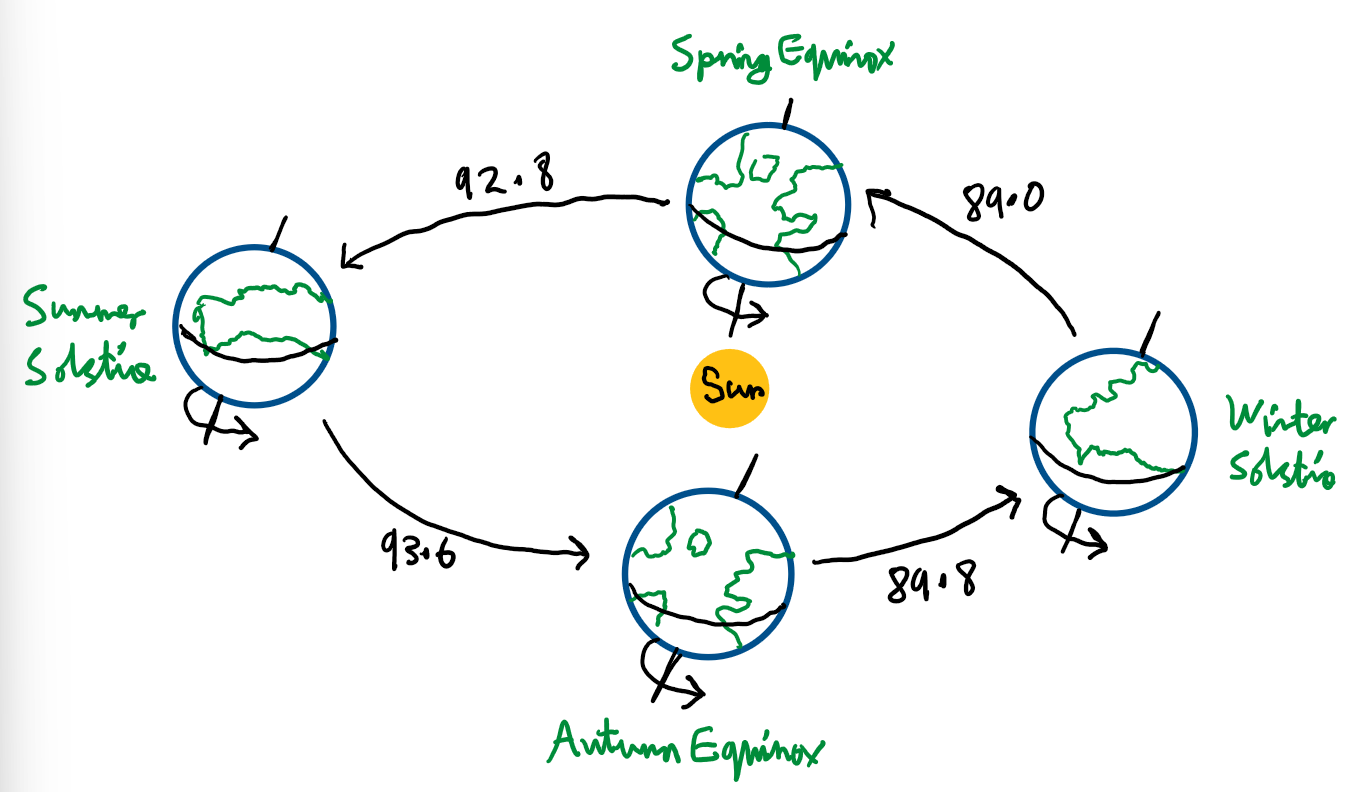
Explain why sunset and sunrise times change over the course of a year:
It is due to Earth’s offset axis.
Equinoxes and Solstices information table:
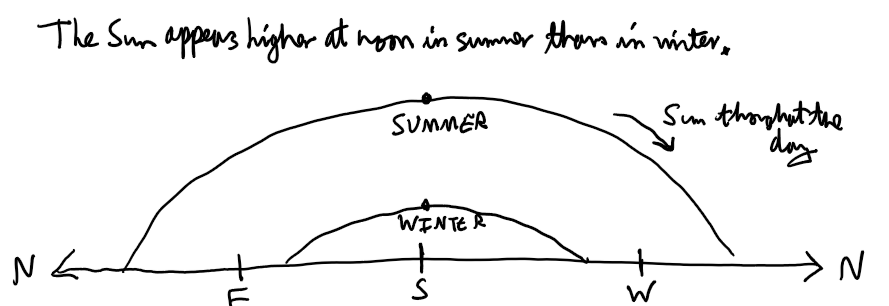
How does the Sun’s apparent motion vary over the course of a year?
What is the difference between a planet’s sidereal and synodic time?
Depends on how far the planet moves in a year.
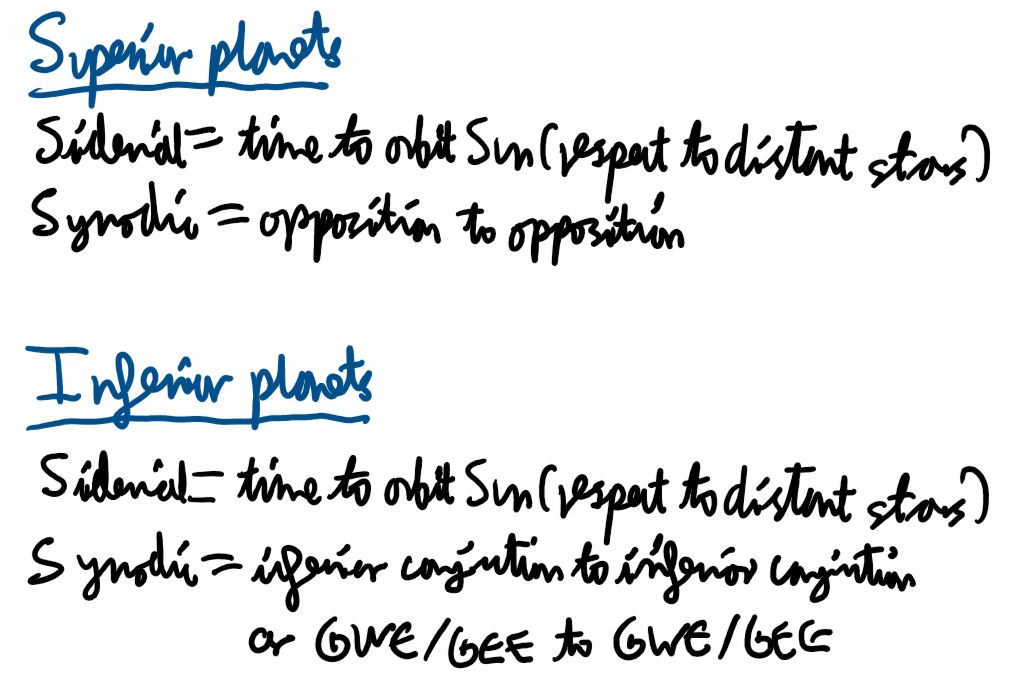
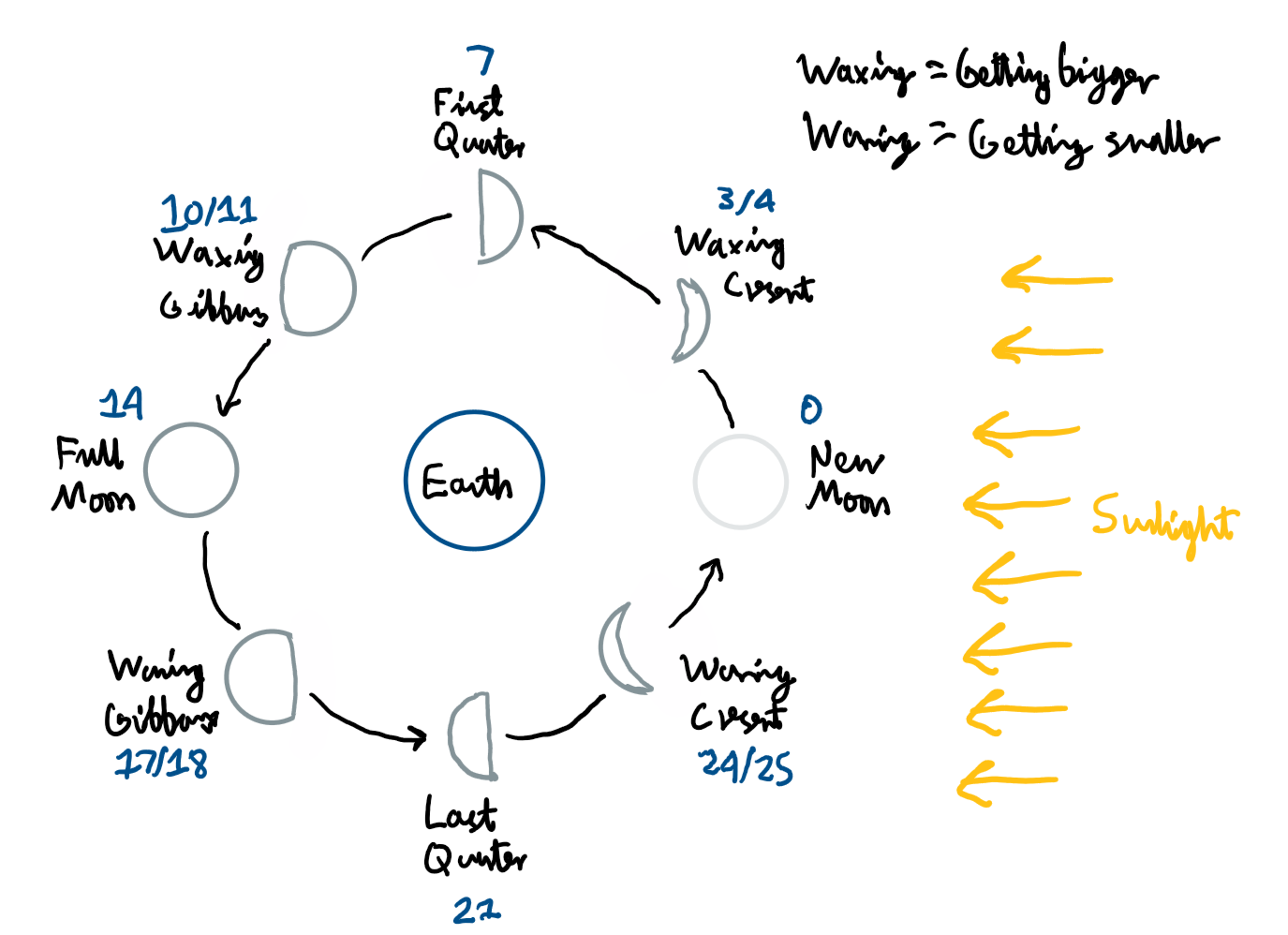
What are the various phases of the Moon?
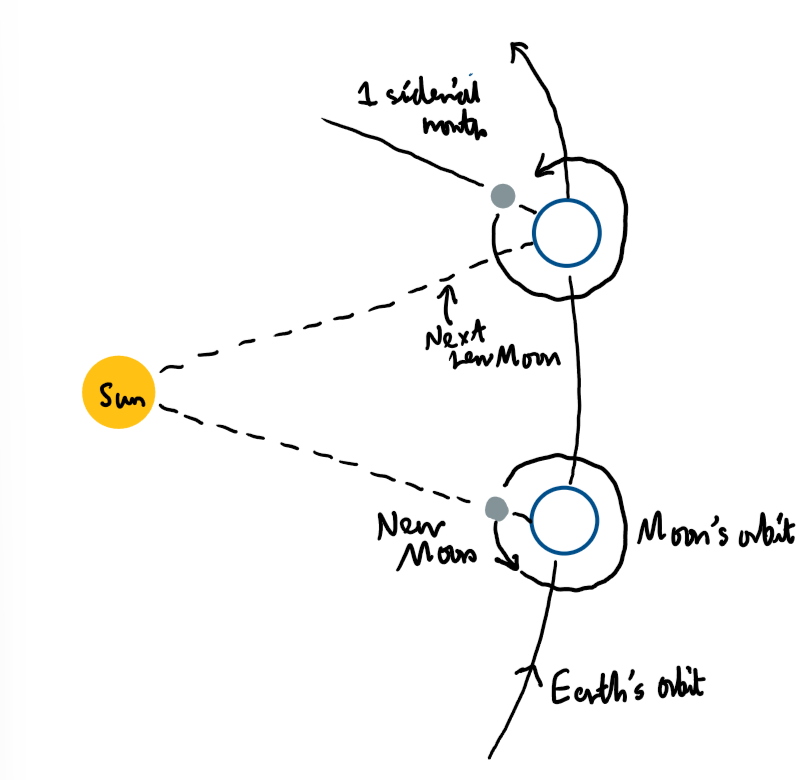
What is a sidereal month?
How long it takes the Moon to go round the Earth once. 27.3 days
How long does it take the Moon to rotate?
27.3 days - same a sidereal month - only ever see one side
What is a synodic month?
How long it takes the Moon to get back to the same phase (e.g Full Moon to full Moon) 29.5 days
Explain the difference between a sidereal and synodic month:
The Earth has moved round the Sun slightly more so the Moon has to go a bit further.
What is Apparent Solar Time (AST)?
The time measured by direct observation of the Sun or as shown on a sundial.
The place the Sun is in the sky.
What is meant by ‘Mean Sun’?
Imaginary Sun
Moves uniformly along the celestial equator
Moves at a constant rate of apparent motion
Completes its annual course in the same time the real Sun takes
What is the Equation of Time?

How does the Equation of Time vary over the year?
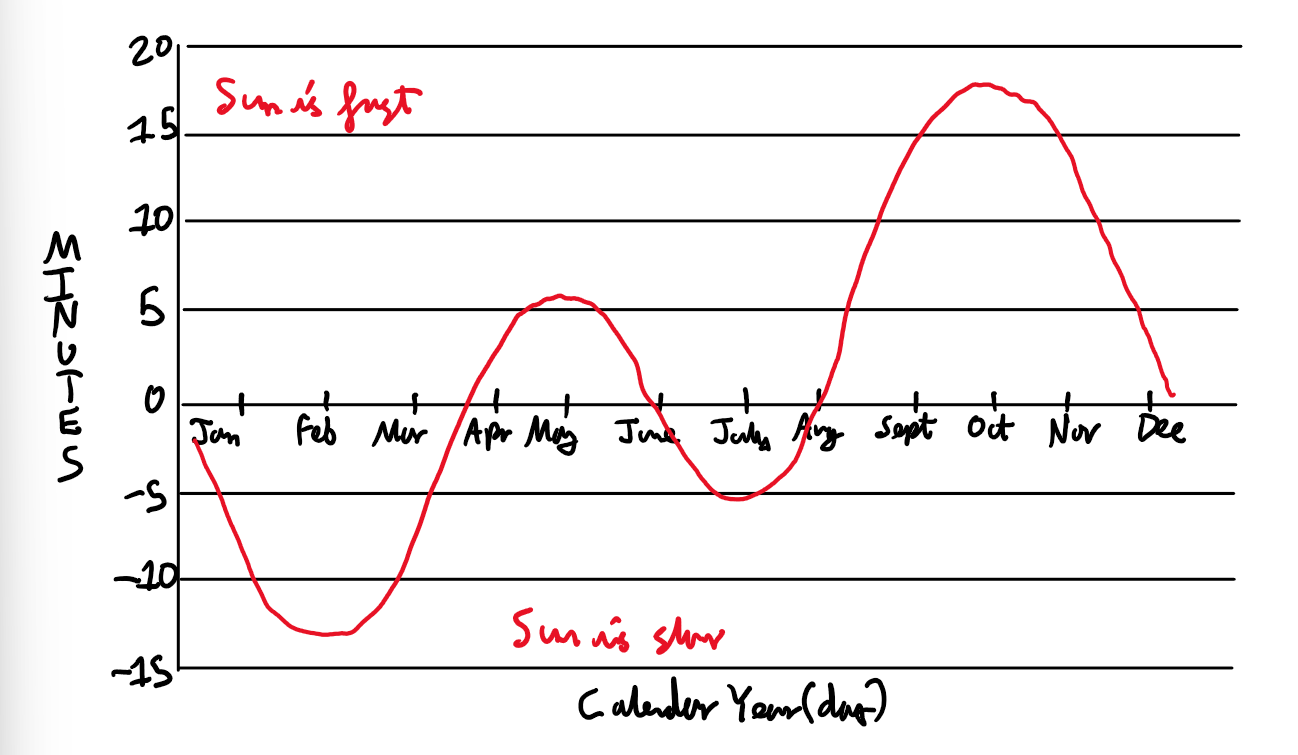
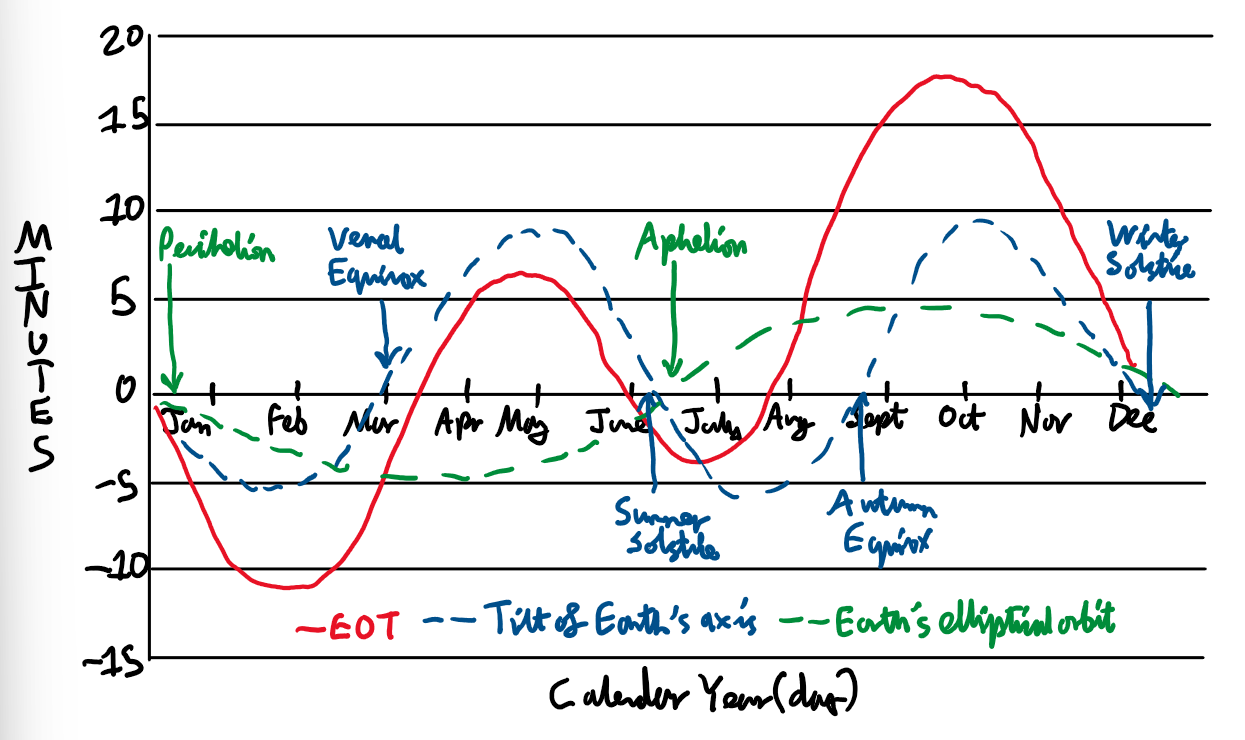
Explain the variation in the Equation of Time?
It is due to a combination of the tilt of the Earth’s axis and Earth’s elliptical orbit.
Labelled Image of a sundial:
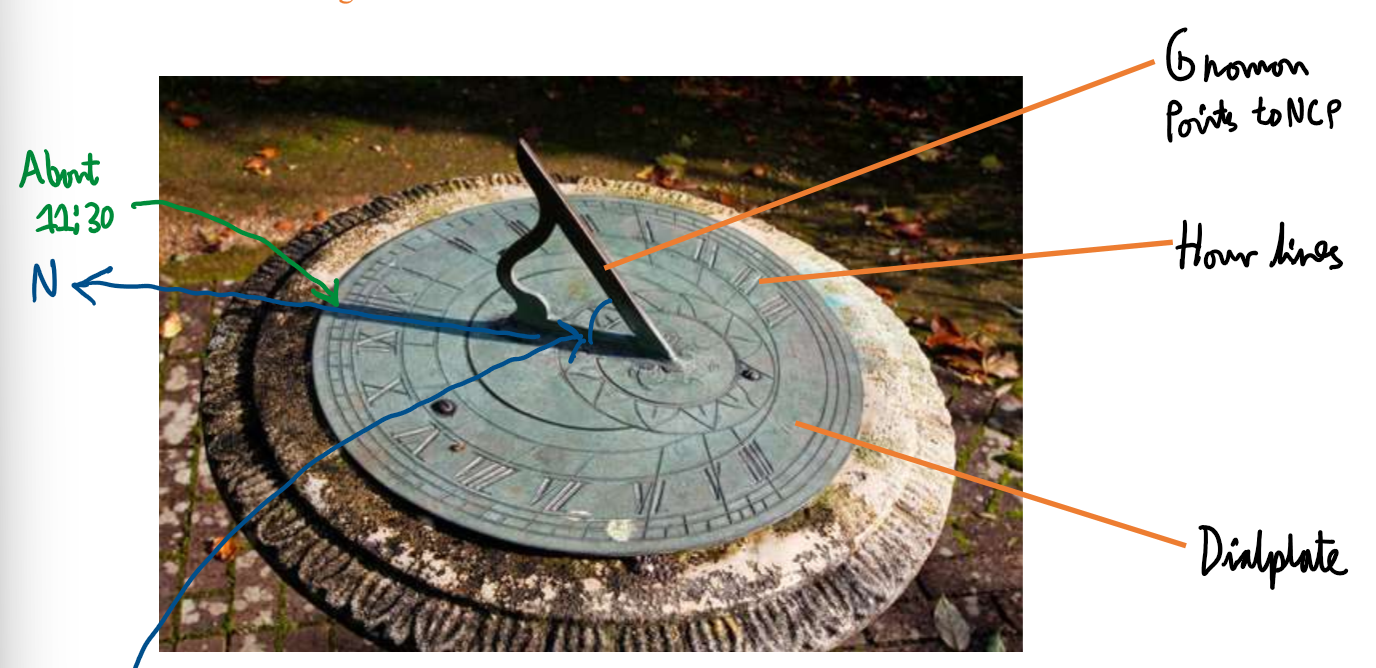

Describe how to set up a sundial:
Altitude of NCP must equal latitude of observer.
Must face in the right direction and be on level ground
Wait for a sunny day
Read of the edge of the shadow
Describe how to use shadow stick observations to find the time of local noon:

Describe how to determine longitude from your shadow stick data:
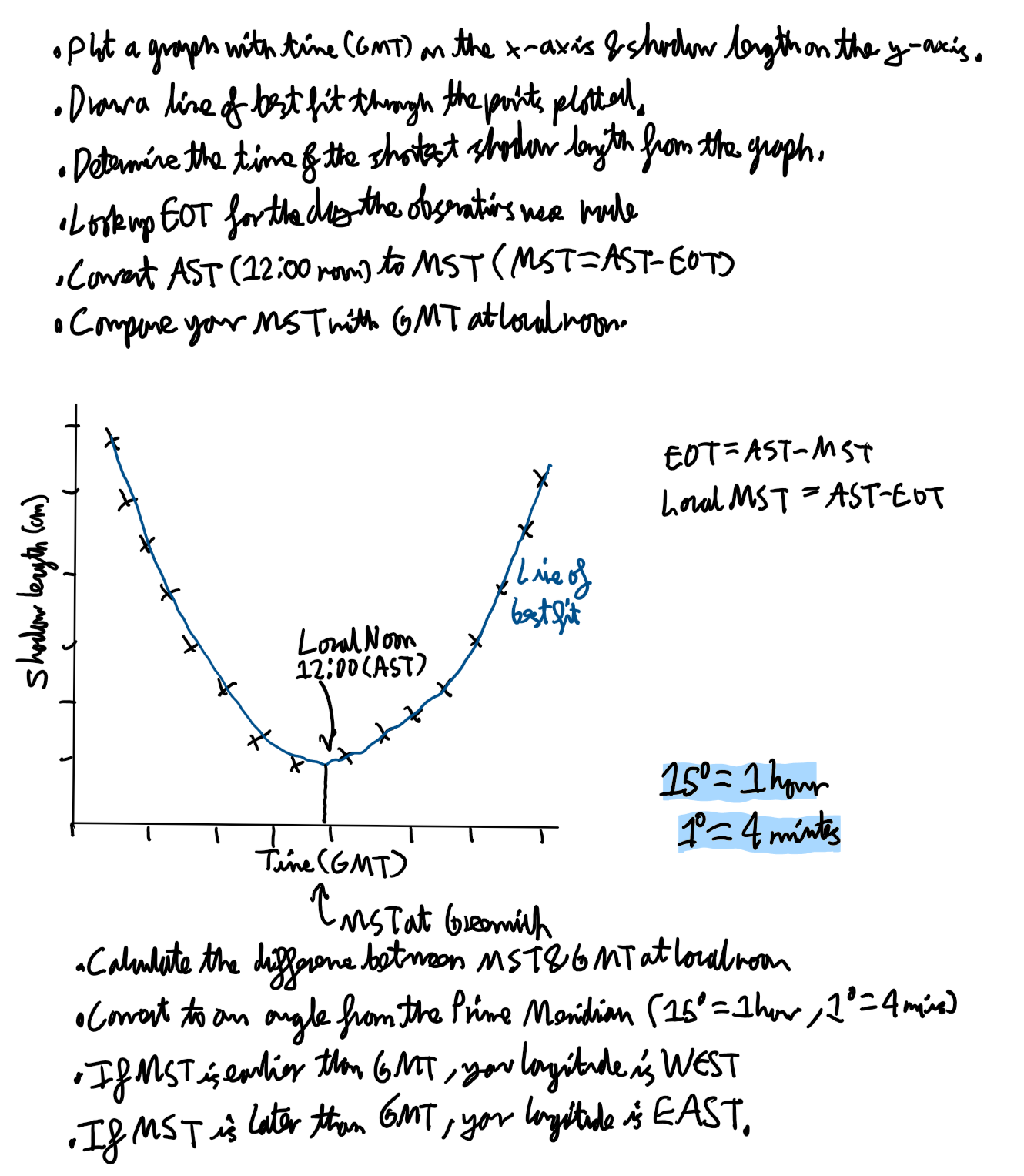
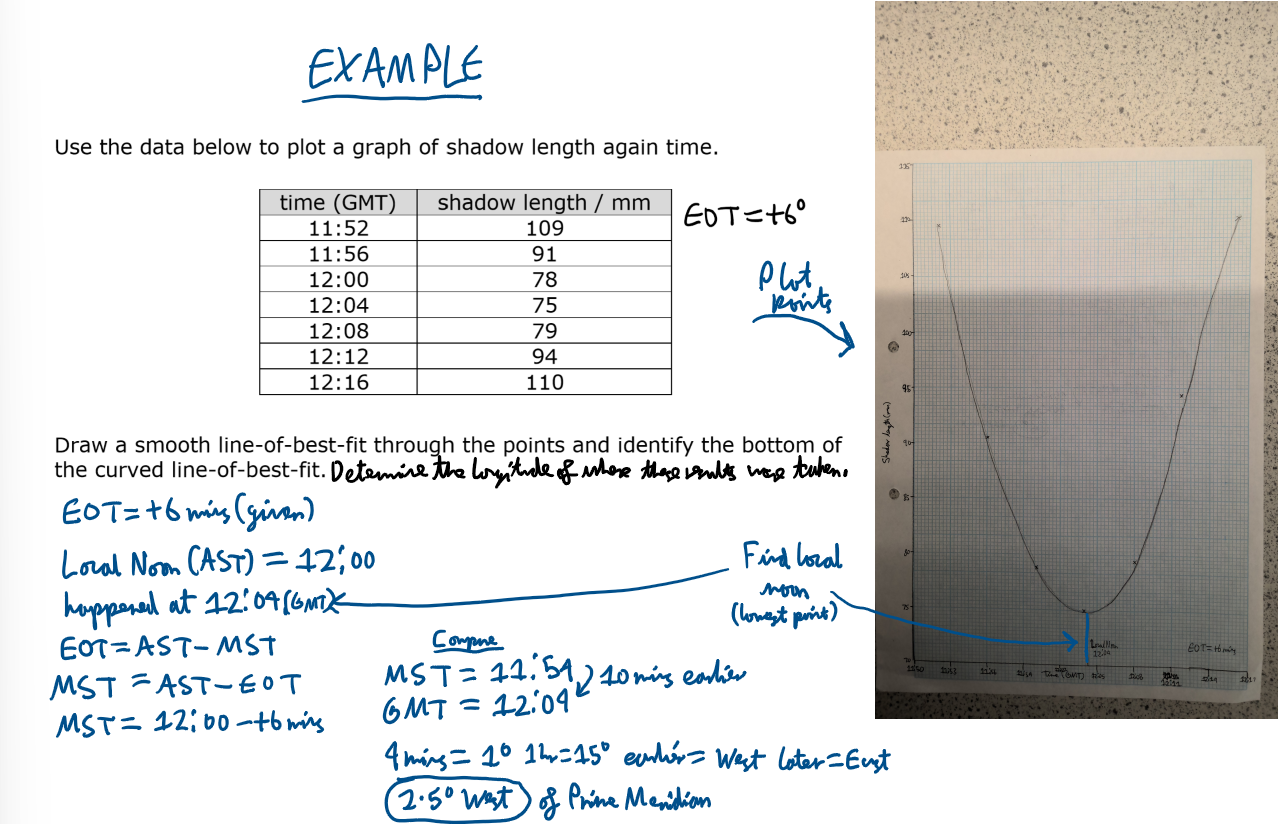
Example of determining longitude from shadow stick data:
What is an analemma?
Movement of the Sun over the course of a year.

Local time is earlier…
Local time is later…
further West
further East
What is the prime meridian?
The line of longitude that passes through Greenwich with 0 degrees of longitude.
Set up in 1884.
What is Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)?
The timezone at 0 degrees longitude that all other time zones are based off of. Same as UTC.
What is a timezone?
One of 24, 15 degree wide zones on the globe where a certain time is used.
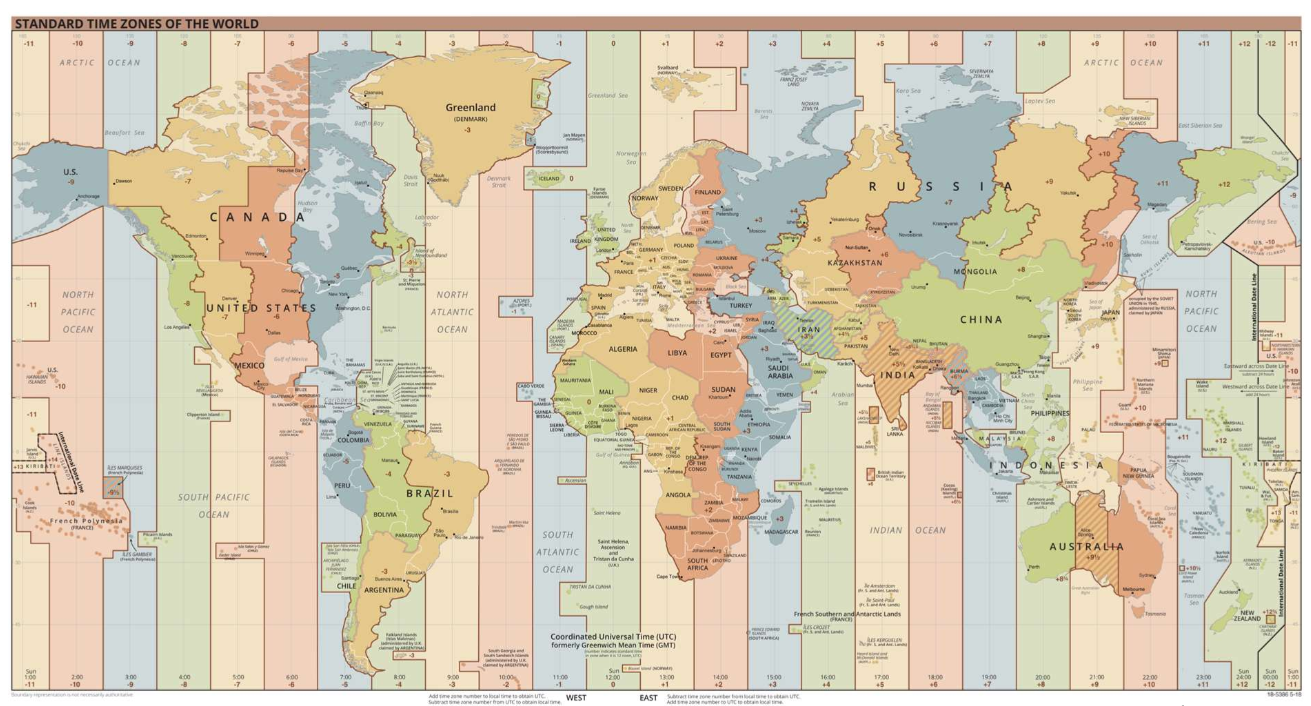
Why are time zones needed?
They are needed to standardise time particularly for travel purposes.
What is one astronomical method for determining longitude?

What is another astronomical method for determining longitude?

What was the breakthrough invention that was a solution to the longitude problem?
The chronometer invented by John Harrison in 1759.
It was the first device to accurately keep time at sea.
What is the horological method of determining longitude?
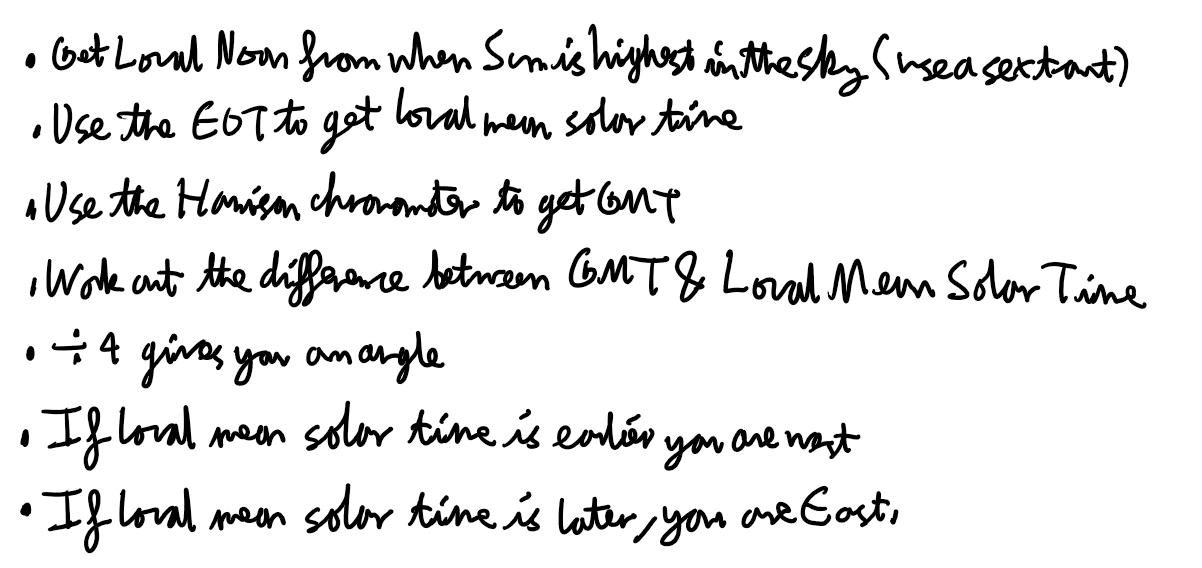
Difference between a planet and dwarf planet
Dwarf planets have not cleared the neighborhood around their orbit and are not satellites.
Dwarf Planet Examples
Ceres
Pluto
Eris
Small Solar System Objects (SSSOs)
All other objects except satellites orbiting the Sun.
SSSO Examples
Meteoroids
Asteroids
Comets
Kuiper Belt Objects
Oort Cloud Objects
Inferior/Superior Planets
Planets closer/ further from the Sun compared to Earth.