EHS Written Midterm
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
Hemothorax
can be the result of blunt or penetrative trauma to the chest/open or closed injuries
* Early signs and symptoms are the same for shock
* Treatment
* Same for pneumothorax and shock
* Early signs and symptoms are the same for shock
* Treatment
* Same for pneumothorax and shock
2
New cards
Traumatic asphyxia
when severe and sudden compression of the thorax causes a rapid increase in chest pressure
* Signs and symptoms
* bluish/purple discoloration of the face, head, neck, and shoulders
* JVD
* Bloodshot eyes that are protruding from the socket
* Cyanotic and swollen tongue and lips
* Bleeding of conjunctiva
* Treatment
* Emergency care for any chest wounds and shock
* Signs and symptoms
* bluish/purple discoloration of the face, head, neck, and shoulders
* JVD
* Bloodshot eyes that are protruding from the socket
* Cyanotic and swollen tongue and lips
* Bleeding of conjunctiva
* Treatment
* Emergency care for any chest wounds and shock
3
New cards
Cardiac contusion
when the heart is violently compressed between the sternum and spinal column
* Signs and symptoms
* Chest pain/discomfort
* Signs of blunt trauma to the chest (swelling, bruising, crepitation, deformity)
* Tachycardia
* Irregular pulse
* Treatment: rapid transport
* Signs and symptoms
* Chest pain/discomfort
* Signs of blunt trauma to the chest (swelling, bruising, crepitation, deformity)
* Tachycardia
* Irregular pulse
* Treatment: rapid transport
4
New cards
Commotio cordis
sudden cardiac arrest from blunt trauma
* Treatment: CPR and early defibrillation
* Treatment: CPR and early defibrillation
5
New cards
Pericardial tamponade
trauma causes bleeding to the sac surrounding the heart = inward compression of the heart = decreased cardiac output
* Signs and symptoms
* Similar to a tension pneumothorax
* Except breath sounds are normal
* Worsen as pericardial sac fills with more blood
* PVD
* Signs of shock (hypoperfusion)
* Tachycardia
* Decreased BP
* Narrow pulse pressure
* Weak pulses
* Dyspnea
* Cyanosis
* Treatment
* Early recognition
* Rapid transport
* Maintain airway and use NRB
* Signs and symptoms
* Similar to a tension pneumothorax
* Except breath sounds are normal
* Worsen as pericardial sac fills with more blood
* PVD
* Signs of shock (hypoperfusion)
* Tachycardia
* Decreased BP
* Narrow pulse pressure
* Weak pulses
* Dyspnea
* Cyanosis
* Treatment
* Early recognition
* Rapid transport
* Maintain airway and use NRB
6
New cards
Flail Chest
2+ ribs are broken in 2+ places
* Creates a segment of the chest that is unattached to the rest of the rib cage
* Contraindicated
* Placing the patient on the injured side
* Stabilizing patient with devices that compromise chest wall motion
* Ideal treatment: CPAP/positive airway ventilation using BVM
* Used only if the patient shows signs of respiratory distress/failure
* Creates a segment of the chest that is unattached to the rest of the rib cage
* Contraindicated
* Placing the patient on the injured side
* Stabilizing patient with devices that compromise chest wall motion
* Ideal treatment: CPAP/positive airway ventilation using BVM
* Used only if the patient shows signs of respiratory distress/failure
7
New cards
Sucking Chest Wounds
open chest wound that pulls air into the thoracic cavity
* Treatment
* Cover wound with gloved hand
* Dress wound and tape on 3 sides
* Treatment
* Cover wound with gloved hand
* Dress wound and tape on 3 sides
8
New cards
Tension pneumothorax
caused by air leaking into the chest cavity from a damaged lung with no opening through the outer chest
* Signs
* Rapid deterioration
* Severe respiratory distress
* Signs of shock
* Absent breath sounds on one side
* Cyanosis
* Unequal movement of the chest
* Distended neck veins
* Deviation of trachea to the uninjured side
* Treatment
* Early recognition and rapid transport
* Signs
* Rapid deterioration
* Severe respiratory distress
* Signs of shock
* Absent breath sounds on one side
* Cyanosis
* Unequal movement of the chest
* Distended neck veins
* Deviation of trachea to the uninjured side
* Treatment
* Early recognition and rapid transport
9
New cards
Informed consent
\
* Signing documents
* I.e. scheduled surgery
* Signing documents
* I.e. scheduled surgery
10
New cards
Expressed Consent
Doing actions that demonstrate they want to be helped
11
New cards
Implied Consent
If they could make a decision, they would want to be helped
12
New cards
Minor Consent
Parent making decision for the child
13
New cards
Involuntary Consent
\
* Treating someone who doesn't want treatment but needs it
* I.e. suicidal patient
* Treating someone who doesn't want treatment but needs it
* I.e. suicidal patient
14
New cards
eupnea
normal respirations
15
New cards
tachypnea
fast breathing
16
New cards
bradypnea
slow breathing
17
New cards
Biot’s breathing pattern
quick breathing but spaced out
* brain damage
* brain damage
18
New cards
wheezing lung sounds
* lower airway
* need stethoscope
* narrowing/inflammation = bronchiole diameter reduced
* need stethoscope
* narrowing/inflammation = bronchiole diameter reduced
19
New cards
rales/crackles lung sounds
* lower airway
* need stethoscope
* fluid in/around alveoli
* need stethoscope
* fluid in/around alveoli
20
New cards
snoring lung sounds
* upper airway
* dont need stethoscope
* partial obstruction by tongue
* dont need stethoscope
* partial obstruction by tongue
21
New cards
stridor/ crowing lung sounds
* upper airway
* dont need stethoscope
* “crow cawing”
* partial obstruction at larynx
* dont need stethoscope
* “crow cawing”
* partial obstruction at larynx
22
New cards
gurgling lung sounds
* upper airway
* dont need stethoscope
* fluid in airway
* dont need stethoscope
* fluid in airway
23
New cards
rhonchi lung sounds
* lower airway
* need stethoscope
* mucus blocks larger bronchioles
* need stethoscope
* mucus blocks larger bronchioles
24
New cards
cushing’s reflex
\
* Increased intracranial pressure: opposite of shock
* Increased systolic BP
* Decreased pulse
* Decreased respirations
* Increased intracranial pressure: opposite of shock
* Increased systolic BP
* Decreased pulse
* Decreased respirations
25
New cards
Presence of a closed head injury and signs of shock mean?
* cushing’s reflex
* another injury present
* another injury present
26
New cards
reasons for splinting
\
* Prevents movement of bone fragments, bone ends, and dislocated joints = reduced chance for further injury
* Reduce pain and minimize common complications from bone and joint injuries
* Prevents movement of bone fragments, bone ends, and dislocated joints = reduced chance for further injury
* Reduce pain and minimize common complications from bone and joint injuries
27
New cards
general splinting rules
\
* Assess CMS
* Cut away clothing to expose injury site
* Place sterile dressing over the open wound
* Align extremity with gentle traction if there is a severe deformity, absent pulses, or cyanosis
* Pad the splint
* Maintain manual traction
* Assess CMS
* Assess CMS
* Cut away clothing to expose injury site
* Place sterile dressing over the open wound
* Align extremity with gentle traction if there is a severe deformity, absent pulses, or cyanosis
* Pad the splint
* Maintain manual traction
* Assess CMS
28
New cards
Types of fractures
\
* Open fracture: fracture with an associated open wound
* Closed fracture: no break in the skin
* Hairline fracture: small crack in the bone that does not create instability
* Open fracture: fracture with an associated open wound
* Closed fracture: no break in the skin
* Hairline fracture: small crack in the bone that does not create instability
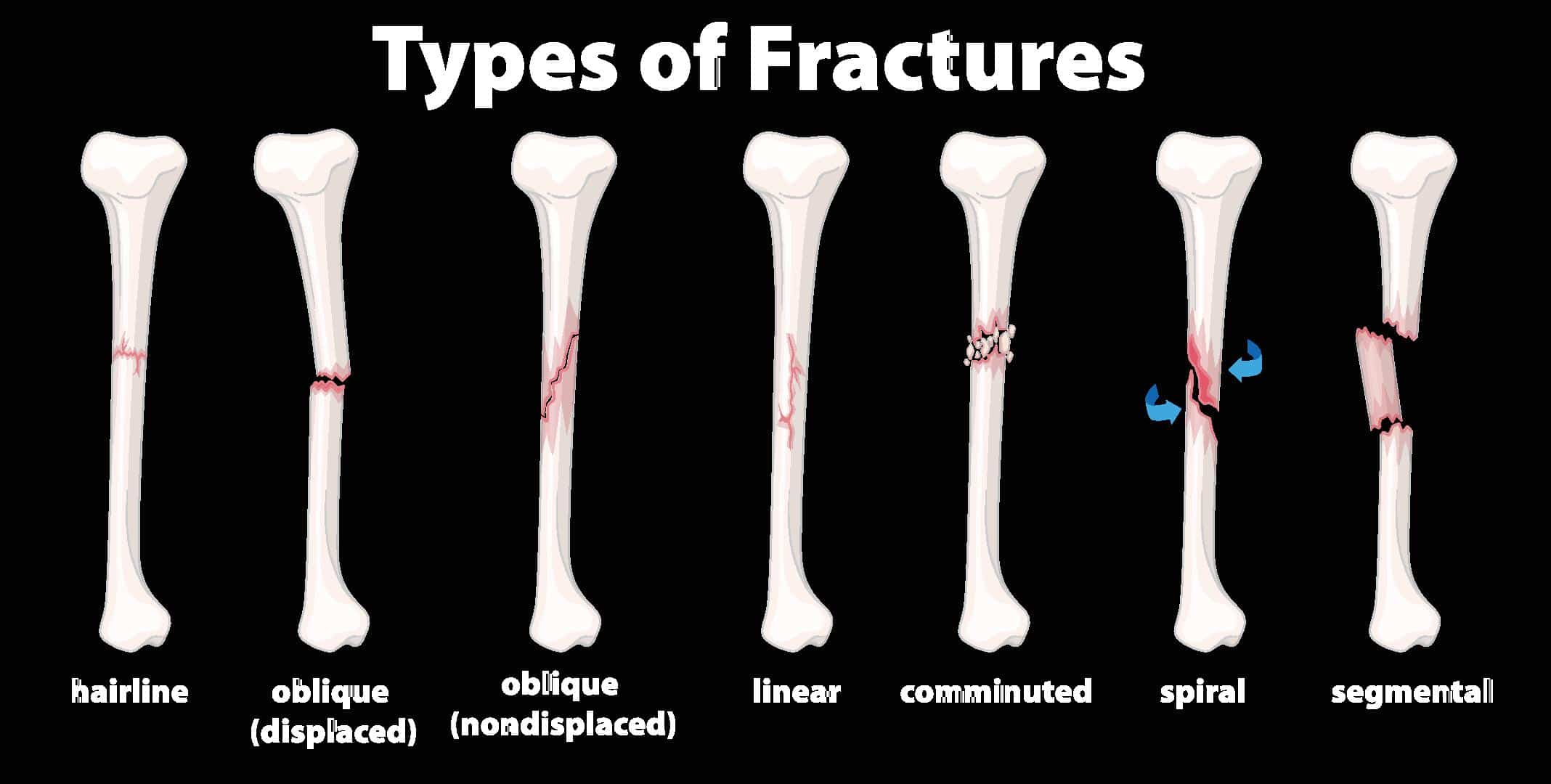
29
New cards
bones
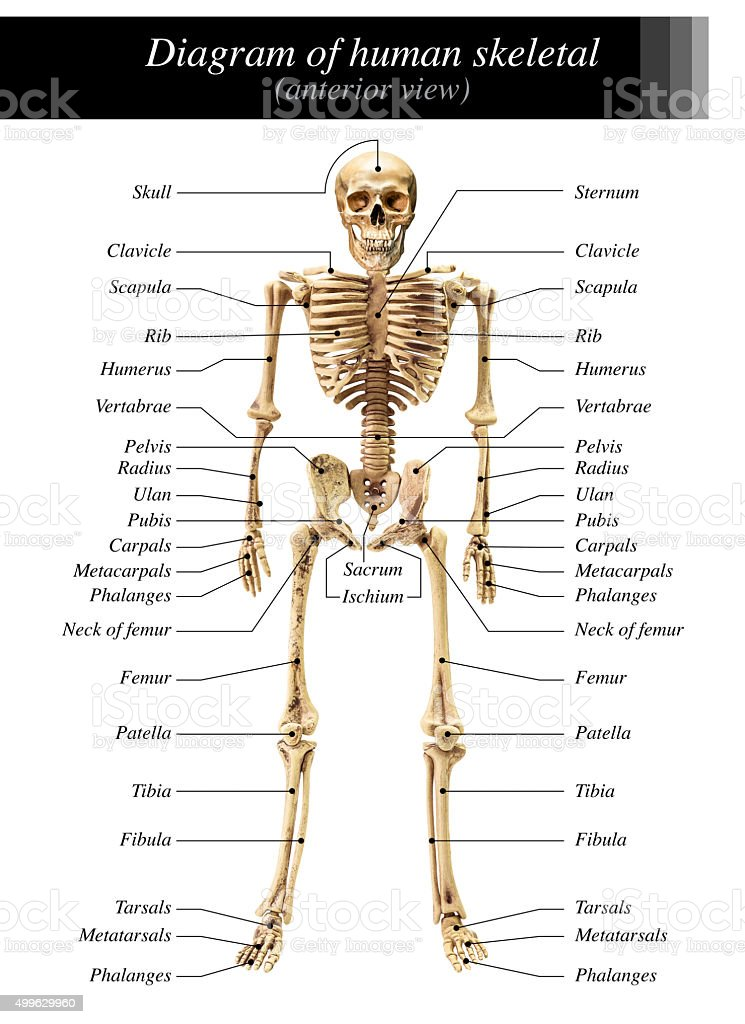
30
New cards
skull bones
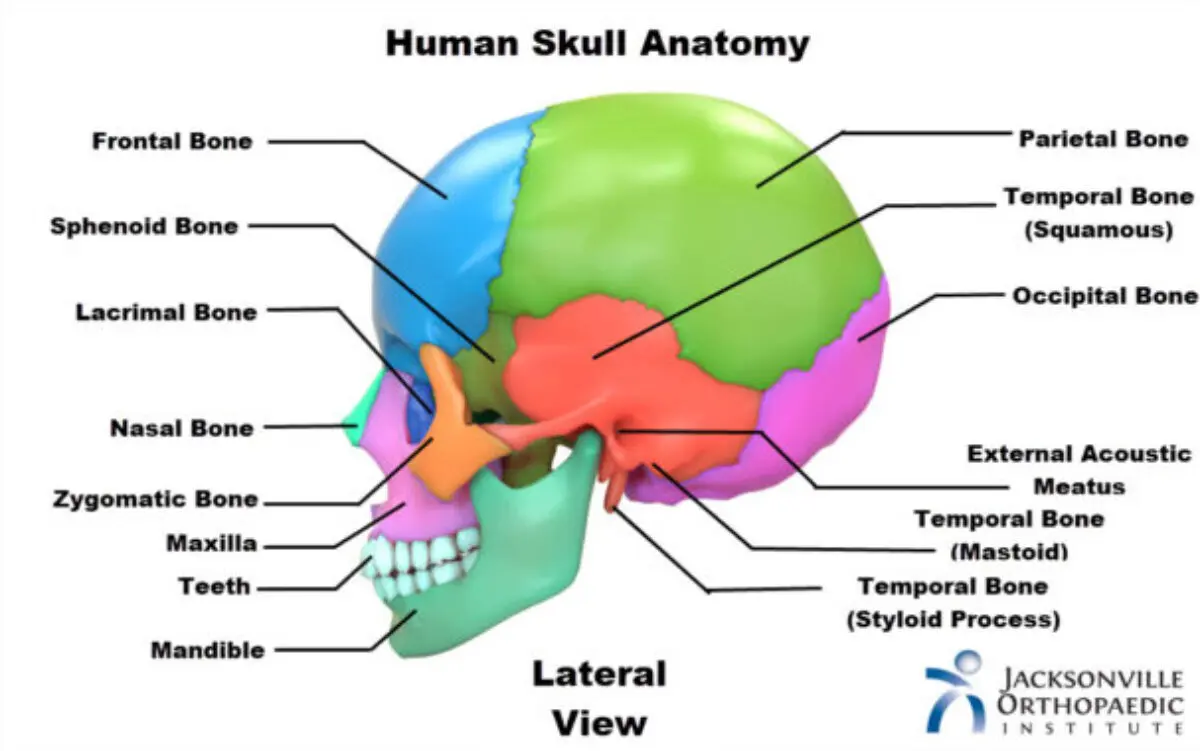
31
New cards
Compensatory shock
\
* Body is able to maintain near-normal blood pressure and perfusion of vital organ
* Blood is shunted away from non-vital areas (i.e. skin and gastrointestinal tract)
* Pulse pressure may be narrowed
* Pulse pressure = systolic - diastolic
* Body is able to maintain near-normal blood pressure and perfusion of vital organ
* Blood is shunted away from non-vital areas (i.e. skin and gastrointestinal tract)
* Pulse pressure may be narrowed
* Pulse pressure = systolic - diastolic
32
New cards
Projectile vomiting is a sign of?
head injury → trauma >:C
33
New cards
suction technique for liquid (blood, vomitus, secretions), food particles, or small objects
suction out
34
New cards
suction technique for thick vomitus, solid objects (teeth, foreign bodies, food)
place pt on side and perform finger sweep
35
New cards
evisceration treatment
\
* Expose the wound
* Position the patient
* Prepare a moist dressing and cover with an occlusive dressing
* Administer high concentration via NRB
* Be prepared to treat for shock
* Expose the wound
* Position the patient
* Prepare a moist dressing and cover with an occlusive dressing
* Administer high concentration via NRB
* Be prepared to treat for shock
36
New cards
\
* S&S of basilar skull fracture
* S&S of basilar skull fracture
\
* Signs
* Battle’s signs: bruising behind the ear
* Raccoon eyes: bruising under the eyes
* CSF rhinorrhea: CSF leakage from nose
* CSF otorrhea: CSF leakage from ear
* Haemotympanum: blood in ear
* Bump
* Cranial nerve pulses
* Optic nerve problems: optic nerve gets stuck in tract/orbit
* Symptoms
* Signs
* Battle’s signs: bruising behind the ear
* Raccoon eyes: bruising under the eyes
* CSF rhinorrhea: CSF leakage from nose
* CSF otorrhea: CSF leakage from ear
* Haemotympanum: blood in ear
* Bump
* Cranial nerve pulses
* Optic nerve problems: optic nerve gets stuck in tract/orbit
* Symptoms
37
New cards
Glasgow coma scale
\
* 3 minimum, 15 max
* Eye opening
* Spontaneous → 4
* To verbal command → 3
* To pain → 2
* No response → 1
* Verbal response
* Oriented and converses → 5
* Disoriented and converses → 4
* Inappropriate words → 3
* Incomprehensible sounds → 2
* No response → 1
* Motor response
* Obeys verbal commands → 6
* Localizes pain → 5
* Withdraws from pain (flexion) → 4
* Abnormal flexion in response to pain (decorticate rigidity) → 3
* Extension in response to pain (decerebrate rigidity) → 2
* No response → 1
* 3 minimum, 15 max
* Eye opening
* Spontaneous → 4
* To verbal command → 3
* To pain → 2
* No response → 1
* Verbal response
* Oriented and converses → 5
* Disoriented and converses → 4
* Inappropriate words → 3
* Incomprehensible sounds → 2
* No response → 1
* Motor response
* Obeys verbal commands → 6
* Localizes pain → 5
* Withdraws from pain (flexion) → 4
* Abnormal flexion in response to pain (decorticate rigidity) → 3
* Extension in response to pain (decerebrate rigidity) → 2
* No response → 1
38
New cards
Oxygen NC vs. NRB vs. BVM
\
* NC: 1-6 lpm
* NRB: 15 lpm
* BVM: artificial ventilation/respirations + high flow O2
* NC: 1-6 lpm
* NRB: 15 lpm
* BVM: artificial ventilation/respirations + high flow O2
39
New cards
abdominal anatomy
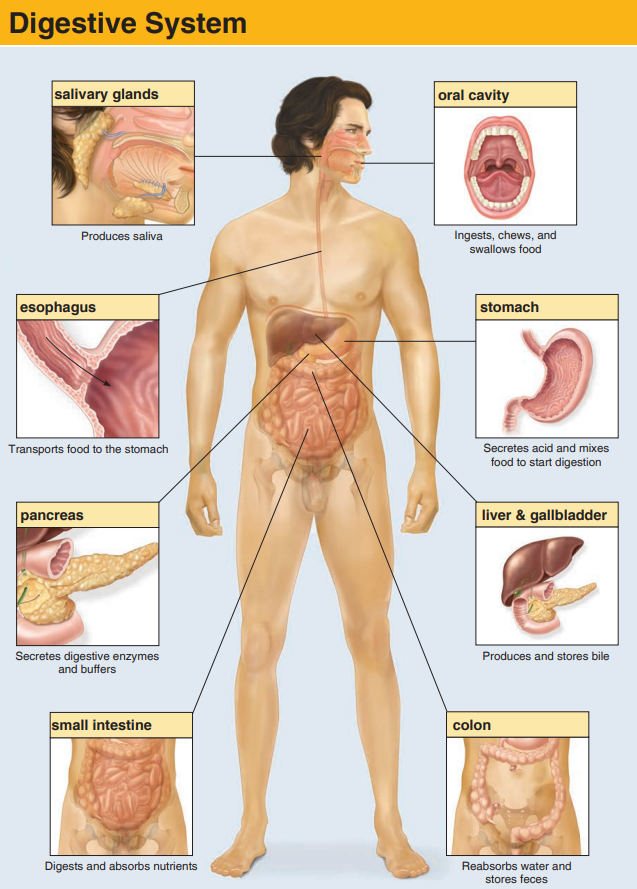
40
New cards
Hollow organs
(hollow) will not bleed but will spill contents into the abdominal cavity
* Stomach
* Gallbladder
* Urinary bladder
* Ureters
* Internal urethra
* Fallopian tubes
* Small intestine
* Large intestine
* Stomach
* Gallbladder
* Urinary bladder
* Ureters
* Internal urethra
* Fallopian tubes
* Small intestine
* Large intestine
41
New cards
Solid organs
major bleeding and severe shock
* Liver
* Spleen
* Pancreas
* Kidneys
* Liver
* Spleen
* Pancreas
* Kidneys
42
New cards
vascular structures
large stationary structures that carry lots of blood
* Abdominal aorta and its branches
* Inferior vena cava
* Abdominal aorta and its branches
* Inferior vena cava
43
New cards
tort
civil wrong that causes harm or injury to another person
44
New cards
assault
willful threat to inflict harm on a patient
* Does not have to be physical
* Does not have to be physical
45
New cards
battery
touching a patient unlawfully without his consent
46
New cards
Negligence
no intent to do any harm to the patient but breaches the duty to act
1) duty of care
2) breach
3) causation
4) damages
1) duty of care
2) breach
3) causation
4) damages
47
New cards
eye anatomy
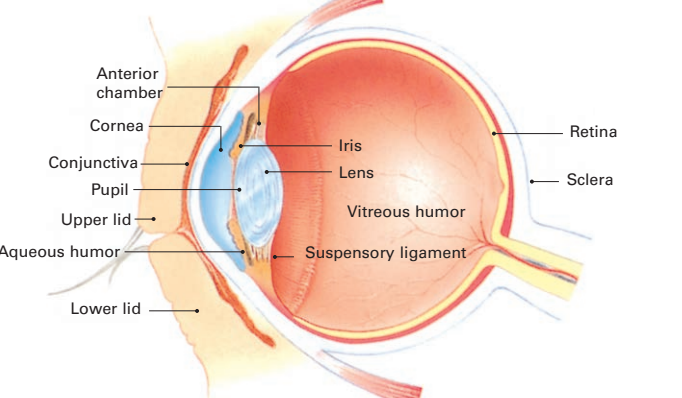
48
New cards
orbital fracture S&S
\
* Diplopia: double vision
* Decrease in vision
* Loss of sensation above the eyebrow, over the cheek, upper lip
* Nasal discharge
* Tenderness to palpate
* Bony step-off
* Patient is unable to follow finger upward
* Diplopia: double vision
* Decrease in vision
* Loss of sensation above the eyebrow, over the cheek, upper lip
* Nasal discharge
* Tenderness to palpate
* Bony step-off
* Patient is unable to follow finger upward
49
New cards
lid injury S&S
\
* Control bleeding with light pressure from a dressing
* Cover lid with gauze soaked in saline
* Control bleeding with light pressure from a dressing
* Cover lid with gauze soaked in saline
50
New cards
globe injury S&S
\
* Best treated at the hospital
* Apply patches lightly to both eyes
* No cold packs
* Best treated at the hospital
* Apply patches lightly to both eyes
* No cold packs
51
New cards
corneal injury S&S
\
* Flush with sterile water/saline
* Do not attempt to remove object if flushing is not effective
* Place eye patch and transport
* Flush with sterile water/saline
* Do not attempt to remove object if flushing is not effective
* Place eye patch and transport
52
New cards
Chemical eye burns S&S
\
* Immediately irrigate with water/saline and continue for at least 20 min/arrival at the hospital
* Contacts must be removed
* Immediately irrigate with water/saline and continue for at least 20 min/arrival at the hospital
* Contacts must be removed
53
New cards
impaled object in the eye/extruded eyeball S&S
\
* Stabilize object/extruded eyeball
* Cover both eyes
* Stabilize object/extruded eyeball
* Cover both eyes
54
New cards
Types of Hypovolemic Shock
(inadequate volume)
* Hemorrhagic shock: loss of RBC
* Non-hemorrhagic shock: loss of fluid without RBC
* Hemorrhagic shock: loss of RBC
* Non-hemorrhagic shock: loss of fluid without RBC
55
New cards
Types of Distributive Shock
(inadequate vessel tone)
* Septic shock
* Anaphylactic shock
* Psychogenic shock
* Neurogenic shock
* Septic shock
* Anaphylactic shock
* Psychogenic shock
* Neurogenic shock
56
New cards
septic shock
infection = vessels cant contract
57
New cards
anaphylactic shock
chemicals released in anaphylactic reaction = vasodilation and increased capillary permeability
58
New cards
Psychogenic shock
sudden nervous system reaction = temporary vascular dilation = drop in BP = fainting
59
New cards
Neurogenic shock
muscles in blood vessels are cut of from nerve impulses = no contraction
60
New cards
inadequate pump function
* Cardiogenic shock: something wrong with the heart
* Obstructive shock: something blocking heart function
* Obstructive shock: something blocking heart function
61
New cards
complete spinal cord injury
total loss of motor and sensory function below level of injury
62
New cards
incomplete spinal cord injuries types
spinal cord is injured but not completely through all 3 major tracts (motor, light touch, pain tracts)
* central cord syndrome
* anterior cord syndrom
* brown-sequard syndrom
* central cord syndrome
* anterior cord syndrom
* brown-sequard syndrom
63
New cards
central cord syndrome
middle of the spinal cord is injured = weakness/paralysis and loss of pain sensation to the upper extremities but good function in the lower extremities
64
New cards
anterior cord syndrome
loss of sensation to pain and motor function below site of injury but able to feel light touch
65
New cards
Brown-Sequard syndrom
loss of motor and sensation below injury, but the effects differ on each side of body
* I.e. patient loses motor and light touch on right side but loses pain sensation on left side
* I.e. patient loses motor and light touch on right side but loses pain sensation on left side
66
New cards
position of comfort for abdominal injuries
supine with legs bent at the knees
* If injury to lower extremities, hips, pelvis, or spine is not suspected
* If injury to lower extremities, hips, pelvis, or spine is not suspected
67
New cards
Mechanics of lifting and moving
* Keep the weight of the object as close to the body as possible
* To move a heavy object, use the leg, hip, and gluteal muscles plus contracted abdominal muscles
* “Stack”: shoulders, hips, feet as one unit
* Reduce the height/distance through which the object must be moved
* To move a heavy object, use the leg, hip, and gluteal muscles plus contracted abdominal muscles
* “Stack”: shoulders, hips, feet as one unit
* Reduce the height/distance through which the object must be moved
68
New cards
portable stretcher
standard stretcher
69
New cards
stair chair
used in narrow spaces, small elevators, stairways
70
New cards
Backboard
* Short backboards: immobilize noncritical sitting patients before moving them
* Full body vacuum mattress
* Full body vacuum mattress
71
New cards
Scoop stretcher
advantage is that it can be used in confined areas that are too small for conventional stretchers
72
New cards
reeves
rapid spine motion restriction in tight spaces
73
New cards
Electrical burn
* Produced by electrical current flow in the body
* High voltage electricity
* Entry and exit wound: everything in between is damaged
* High voltage electricity
* Entry and exit wound: everything in between is damaged
74
New cards
Chemical burns
* Produced by acids, alkalis, and other heat-generating chemicals
* Severity is dependent on
* Type of chemical
* Chemical concentration
* Duration of exposure to the chemical
* Treatment: immediately flush area with saline
* Severity is dependent on
* Type of chemical
* Chemical concentration
* Duration of exposure to the chemical
* Treatment: immediately flush area with saline
75
New cards
Thermal burns
* Associated with heat applied to the body
* Severity is dependent on
* Time exposed to the heat source
* Temperature of the heat
* Potential for inhalation injury
* Severity is dependent on
* Time exposed to the heat source
* Temperature of the heat
* Potential for inhalation injury
76
New cards
Flame burn
caused by flame :/
77
New cards
Contact burn
* Touching something hot
* E.g. touching a stove
* E.g. touching a stove
78
New cards
Scald burn
caused by hot liquid, superficial
79
New cards
flash burn
* Something explodes and flashes
* Lighting a fire with too much gas
* Lighting a fire with too much gas
80
New cards
other types of burns
* steam burn
* gas burn
* chemical burns
* gas burn
* chemical burns
81
New cards
Rules of Nines
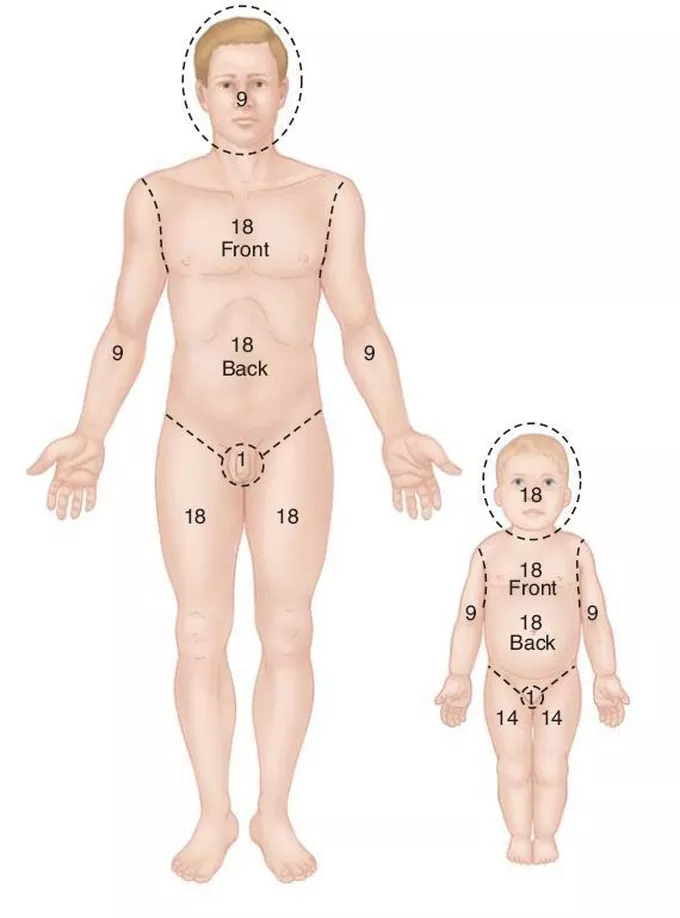
82
New cards
Voluntary muscles (skeletal)
\
* Most are attached at one or both ends of the skeleton
* Muscles become shorter and thicker = muscle contraction
* Most are attached at one or both ends of the skeleton
* Muscles become shorter and thicker = muscle contraction
83
New cards
Involuntary muscles (smooth)
* Found in walls of organs
* Help move food through digestive system
* Help move food through digestive system
84
New cards
Cardiac
Only found in walls of the heart
85
New cards
When does an EMT straighten a fracture?
* Severe deformity
* Distal extremity is cyanotic or lacks pulses
* Distal extremity is cyanotic or lacks pulses
86
New cards
What joints should an EMT not attempt to straighten a deformity?
* Wrist
* Elbow
* Knee
* Hip
* Shoulder
* \*major nerves are arteries are close to these joints\*
* Elbow
* Knee
* Hip
* Shoulder
* \*major nerves are arteries are close to these joints\*
87
New cards
central pulses
* Carotid
* Femoral
* Femoral
88
New cards
peripheral pulses
* Radial
* Brachial
* Posterior tibial
* Dorsalis pedis
* Brachial
* Posterior tibial
* Dorsalis pedis
89
New cards
On-line medical direction
EMS provider and physician communicate directly in real time providing immediate feedback
90
New cards
On-scene medical direction
feedback and medical direction regarding the diagnosis, condition, and emergency care provided by the physician who is on-scene with crew
91
New cards
off-line medical direction
following local protocol
92
New cards
stages of grief
* Denial: not me.
* Anger: why me?
* Bargaining: okay, but first let me…
* Depression: okay, but I haven't…
* Acceptance: okay, I am not afraid
* Anger: why me?
* Bargaining: okay, but first let me…
* Depression: okay, but I haven't…
* Acceptance: okay, I am not afraid
93
New cards
3 meninges
layers of tissue that enclose the brain, brainstem, and spinal cord (outer to inner)
* Dura mater
* Arachnoid
* Pia mater
* Dura mater
* Arachnoid
* Pia mater
94
New cards
CSF
produced and circulated throughout the brain
* cushions/protects
* Combats infection
* Cleanses brain and spinal cord
* cushions/protects
* Combats infection
* Cleanses brain and spinal cord
95
New cards
Scene safety
* Be sure to not approach scenes that appear unsafe, can call the police or get someone to make the scene safe first
* When knocking on the door, stand to the side of the door and on the side w/ the door handle
* If someone answers the door with a weapon, can run away if you feel unsafe
* ALWAYS PROTECT YOU AND YOUR PARTNER FIRST
* When knocking on the door, stand to the side of the door and on the side w/ the door handle
* If someone answers the door with a weapon, can run away if you feel unsafe
* ALWAYS PROTECT YOU AND YOUR PARTNER FIRST
96
New cards
vehicle
* Do have stop at bus stops when the sign is out
* Careful when driving through intersections, where most accidents happen
* Do not trust other people’s cars to stop, drive in a way that is not going to hurt people
* Ambulances can pass in no passing lanes, proceed past a stop sign/red light only having made sure it is safe to do so, can make sounds and have lights to warn people, can go above the speed limit (safely)
* Make sure to check the ambulance after every call to stock and make sure all equipment that is needed is there
* Careful when driving through intersections, where most accidents happen
* Do not trust other people’s cars to stop, drive in a way that is not going to hurt people
* Ambulances can pass in no passing lanes, proceed past a stop sign/red light only having made sure it is safe to do so, can make sounds and have lights to warn people, can go above the speed limit (safely)
* Make sure to check the ambulance after every call to stock and make sure all equipment that is needed is there
97
New cards
Five rights of medication administration
* Right patient
* Right medication
* Right route
* Right dose
* Right date (time)
* Right medication
* Right route
* Right dose
* Right date (time)
98
New cards
START Triage
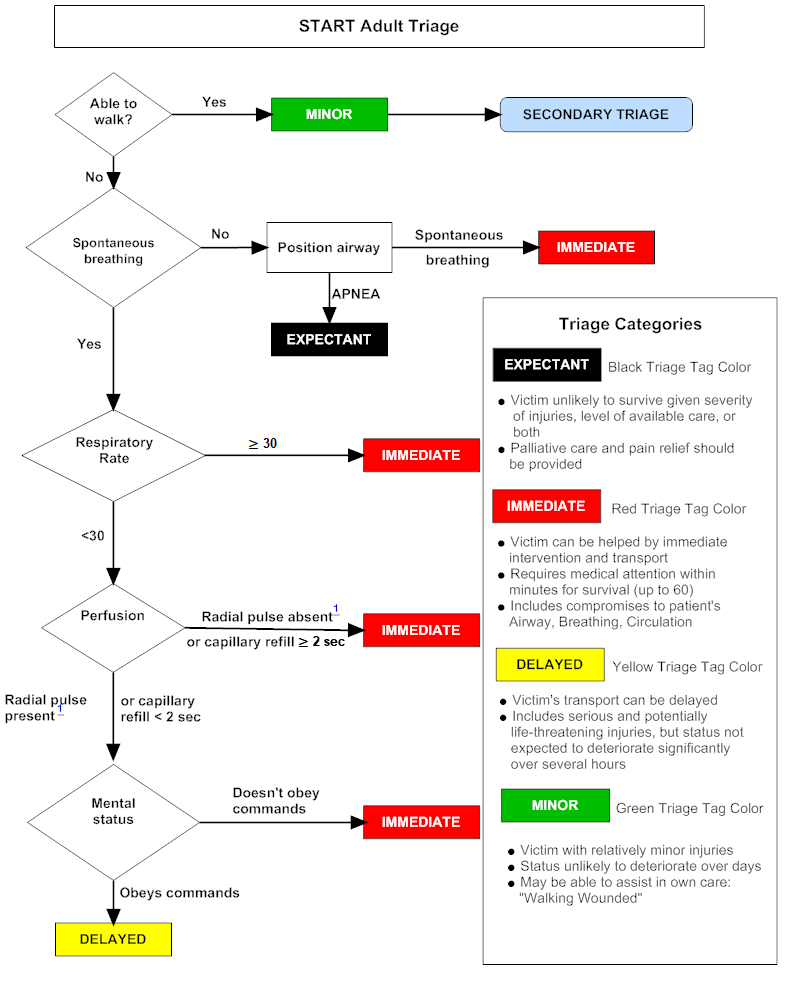
99
New cards
C-Spine injury S&S
* MOI = car accidents, falls in adults that are greater than 20 feet, when force was applied to the body
* Not only looking for neurological deficits, can be physical symptoms
* Signs = crepitus in the cervical spine region, pt cannot move their neck w/out pain, fails C-spine clearance test, unconscious after traumatic MOI
* Symptoms = neck pain, impaired coordination/balance, difficulty breathing, loss of bladder control
* Not only looking for neurological deficits, can be physical symptoms
* Signs = crepitus in the cervical spine region, pt cannot move their neck w/out pain, fails C-spine clearance test, unconscious after traumatic MOI
* Symptoms = neck pain, impaired coordination/balance, difficulty breathing, loss of bladder control
100
New cards
kinematics of trauma
* Science of analyzing mechanisms of injury (MOI)
* Kinetics = deals with the movement of bodies and VELOCITY is super important
* Faster change in speed results in more force extended
* Impacts = energy is absorbed
* Can be through a vehicle, body, organ
* In falls, the impact is transmitter through the body and skeletal system
* In penetrating = the velocity determines the damage
* In blast injuries = there is a pressure wave, blast wave, patient displacement, then take care of HAZMAT
* In crashes = look where the majority of the damage to car was done
* Front = look at the up and over pathway and down and under pathway
* Rear = the head and neck will be pushed back
* Lateral = the patient endured the brunt of the impact, injuries everywhere
* Rollover = multisystem trauma if not restrained
* Pedestrian = extent of injury depends on where the person was hit (still a priority one)
* Motorcycle = impact can be angular, head-on, involve ejection from vehicle
* Kinetics = deals with the movement of bodies and VELOCITY is super important
* Faster change in speed results in more force extended
* Impacts = energy is absorbed
* Can be through a vehicle, body, organ
* In falls, the impact is transmitter through the body and skeletal system
* In penetrating = the velocity determines the damage
* In blast injuries = there is a pressure wave, blast wave, patient displacement, then take care of HAZMAT
* In crashes = look where the majority of the damage to car was done
* Front = look at the up and over pathway and down and under pathway
* Rear = the head and neck will be pushed back
* Lateral = the patient endured the brunt of the impact, injuries everywhere
* Rollover = multisystem trauma if not restrained
* Pedestrian = extent of injury depends on where the person was hit (still a priority one)
* Motorcycle = impact can be angular, head-on, involve ejection from vehicle