P1: Investigating motion on an inclined runway
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Independent variable
height of the ramp
Dependent variable
average speed of the marble down the ramp
Controlled variable
surface of the ramp
Apparatus
Wooden ramp about 120 cm long
Blocks of wood from about 5 cm high to about 15 cm high
Metre stick – to measure height of block and distance on runway
Pencil
Stopwatch
Marble
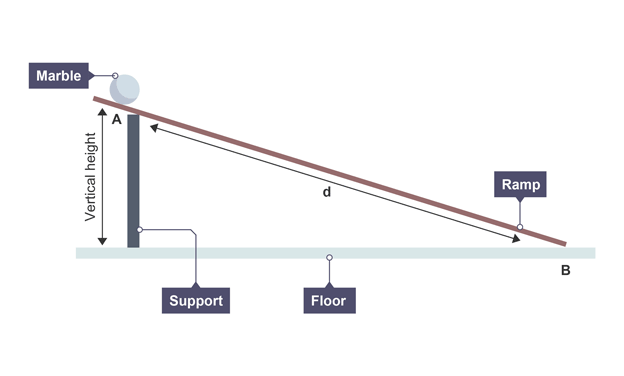
Method
Set up ramp against wooden block
Using ruler, draw two pencil lines in the ramp, one at top and other at the bottom
Measure the distance, x between these two lines (1m)
Measure the height of the ramp, h
Allow marble to roll down ramp, starting from rest at upper line and finishing at lower line
For each height h, time motion three times using stop watch and record the results in table
Calculate average time, t
Average speed is equal to x/t
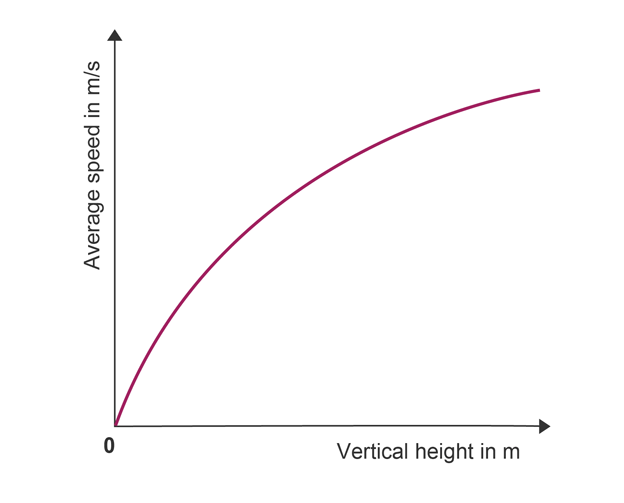
Graph
average speed (y axis)
height, h (x axis)
line of best fit is curve through origin of decreasing gradient
shows average speed is not proportional to h, but increases non-linear
Results
as height of runway increases, average speed will also increase
Justification
as height increases GPE of marble will also increase
when moves down GPE is converted to kinetic energy
a greater amount of kinetic energy at bottom will have greater speed
Error
main error is reaction time using the stop clock
Safety
make sure the marble doesn’t fall on to the floor
secure the runway with a clamp
wear safety goggles