PlantCell Organelle and Function, All Cell Organelles and Functions mine
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
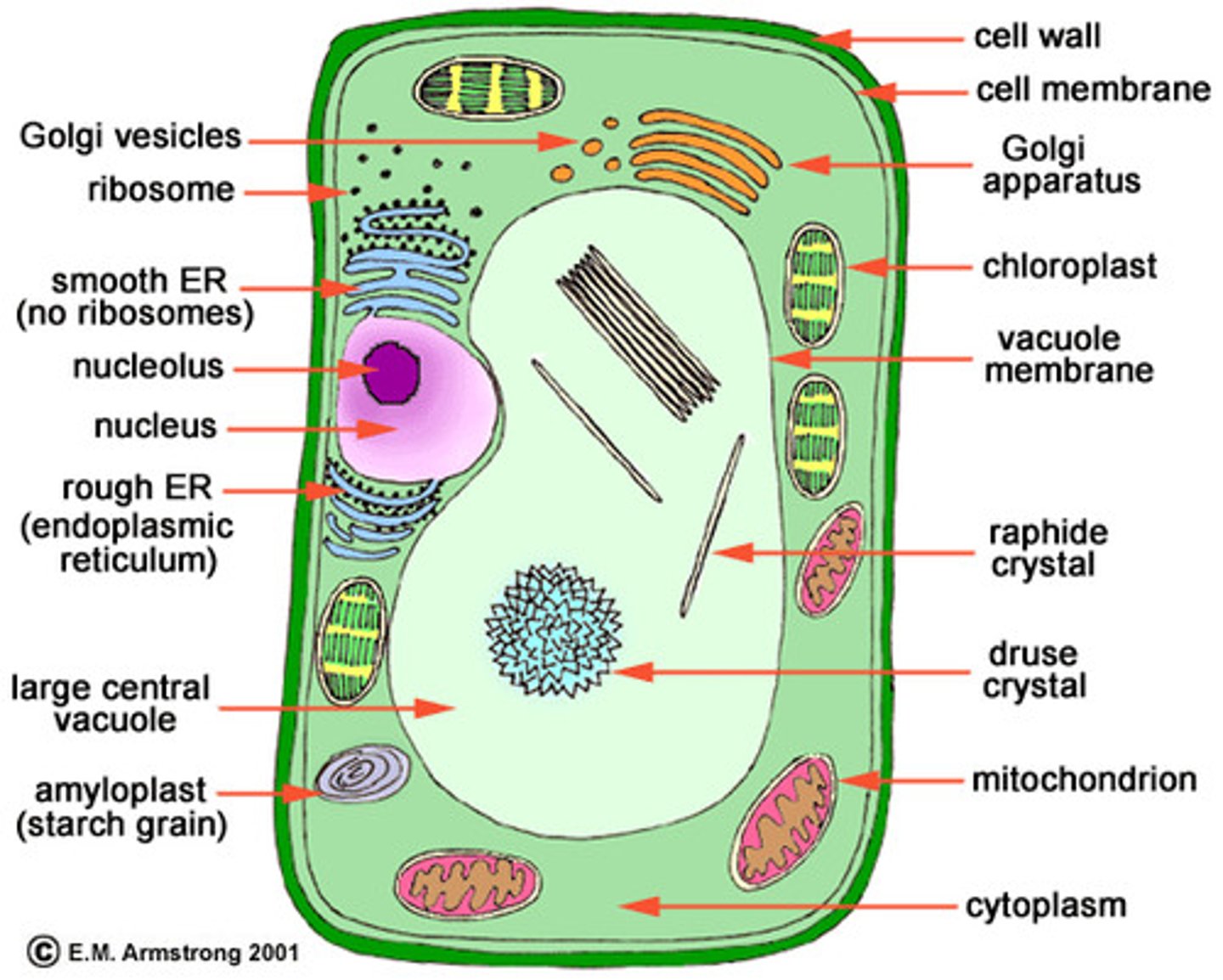
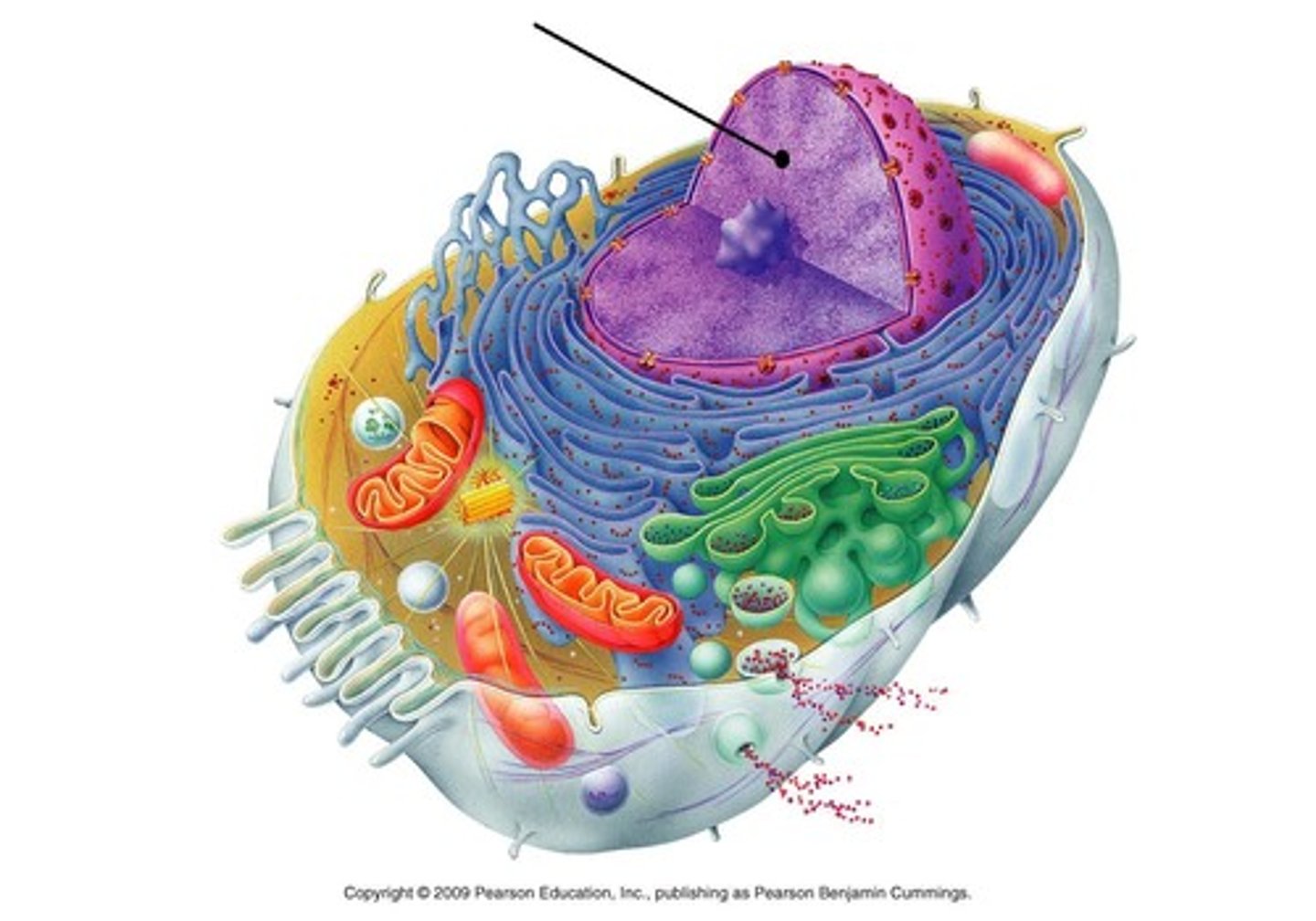
cell membrane
the outermost layer of the cell, determines what goes in/out of cell; protects the cell
nuclear membrane
decides what goes into and out the nucleus, separates genetic material from the rest of the cell
nucleus
directs cell activities, contains the cell’s DNA
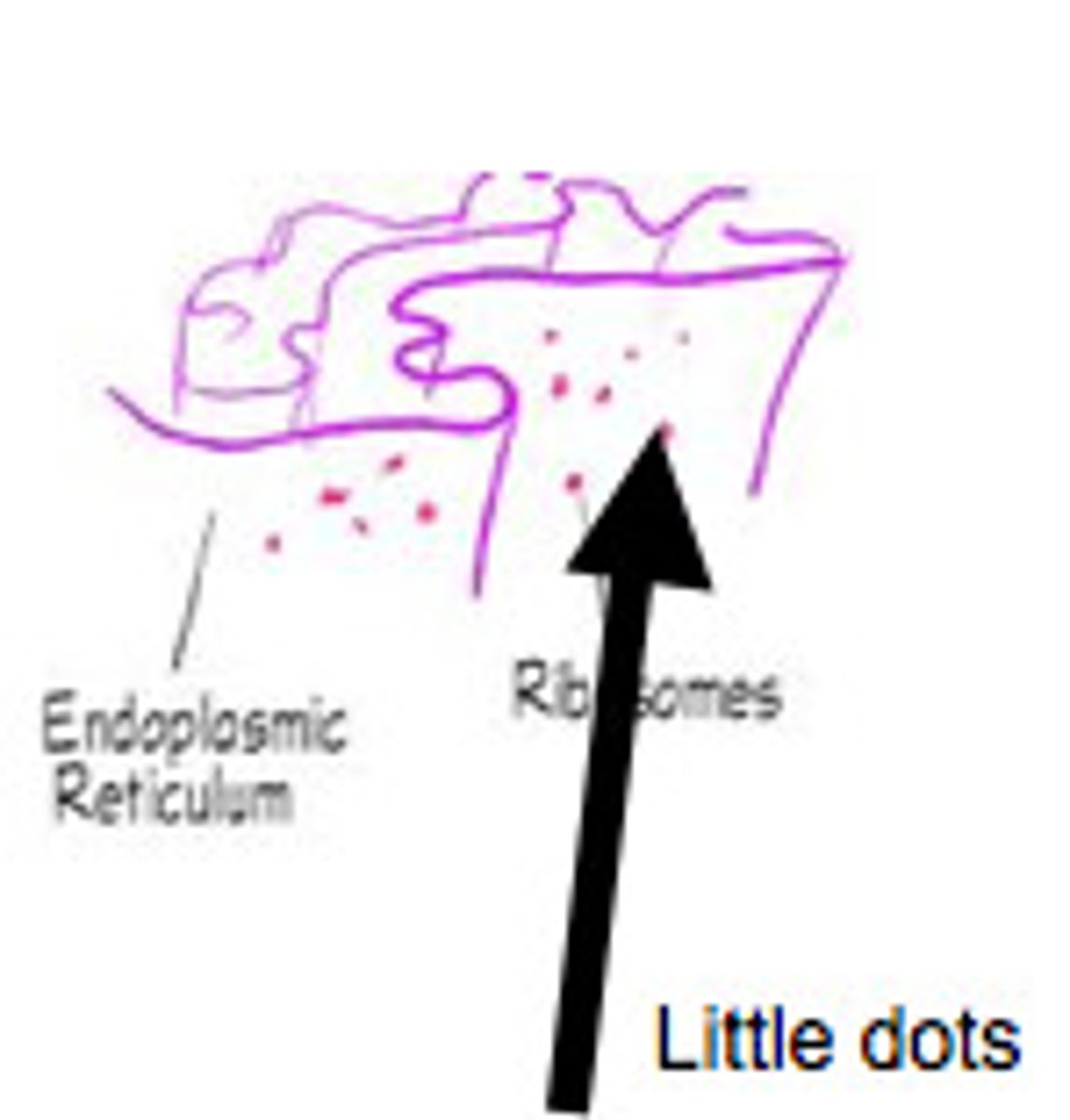
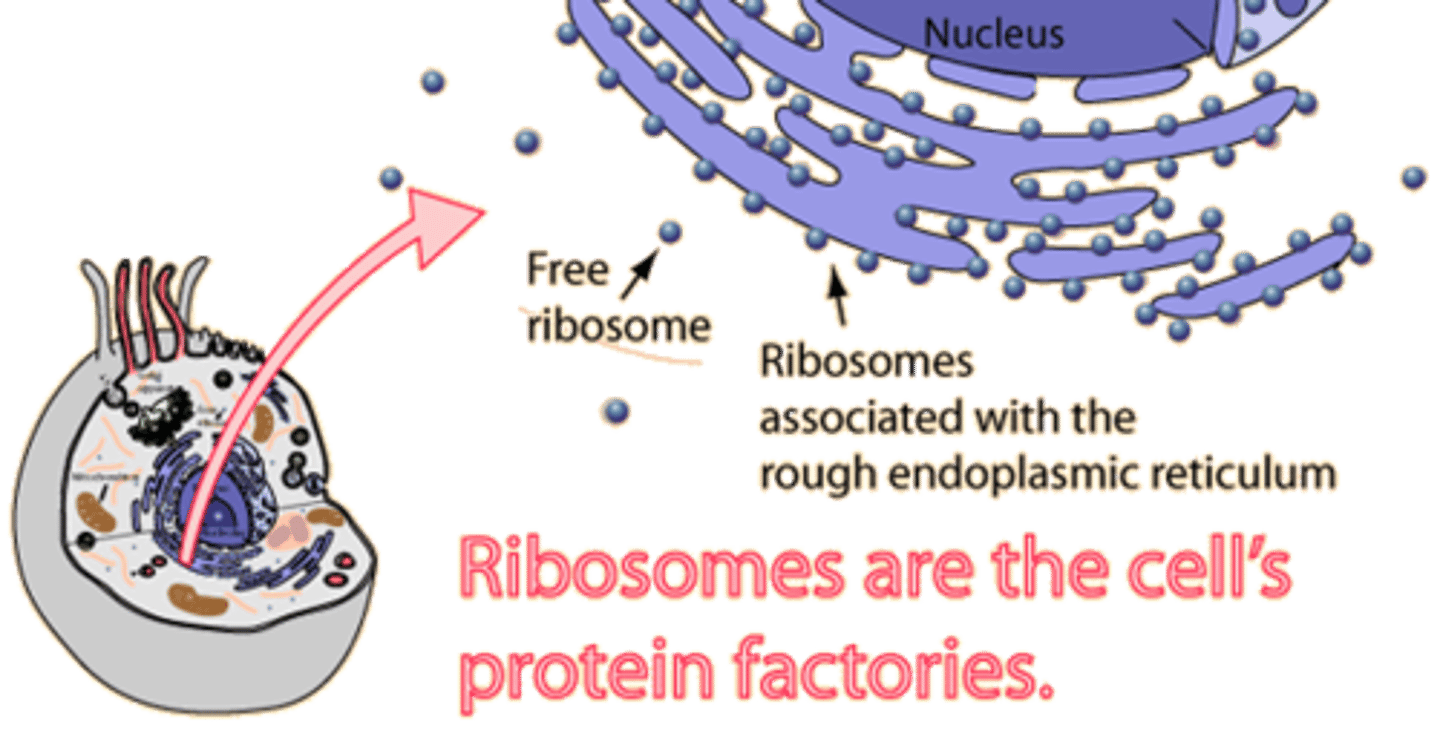
ribosome
makes proteins
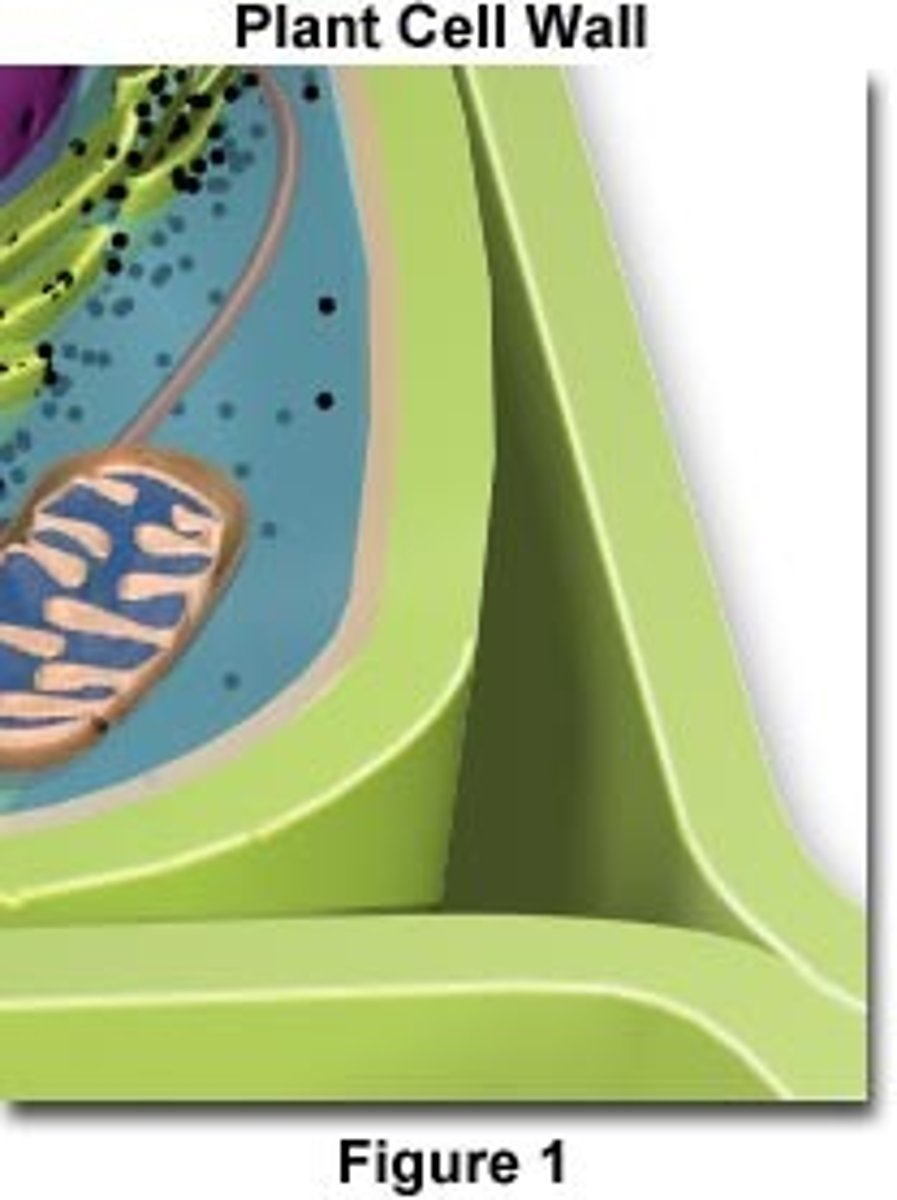
cell wall
made of cellulose, supports structure and protects the plant cell, filter mechanism
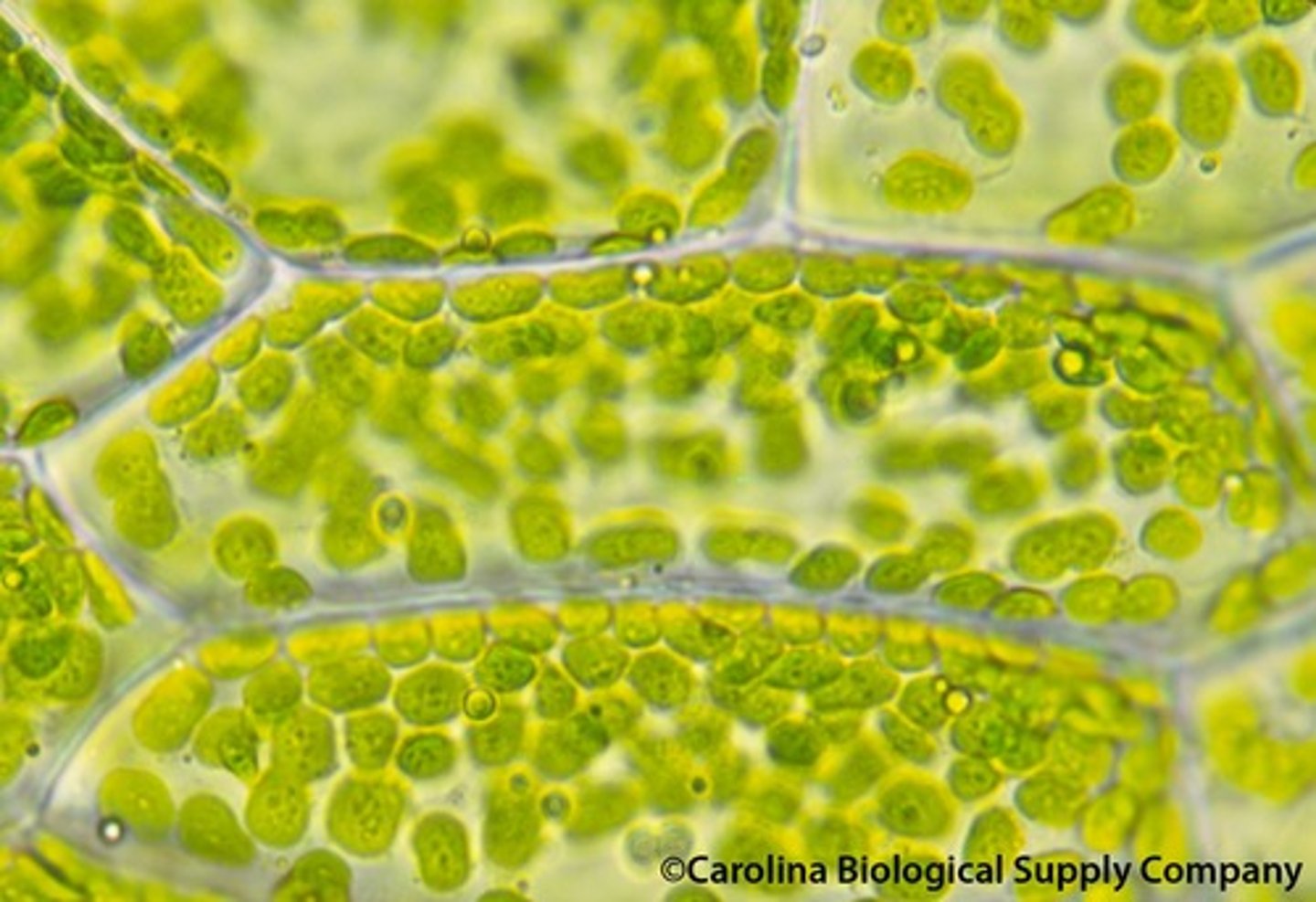
chloroplast
found in plant cells, double membrane organelle that allows photosynthesis to happen; converts sunlight into sugar
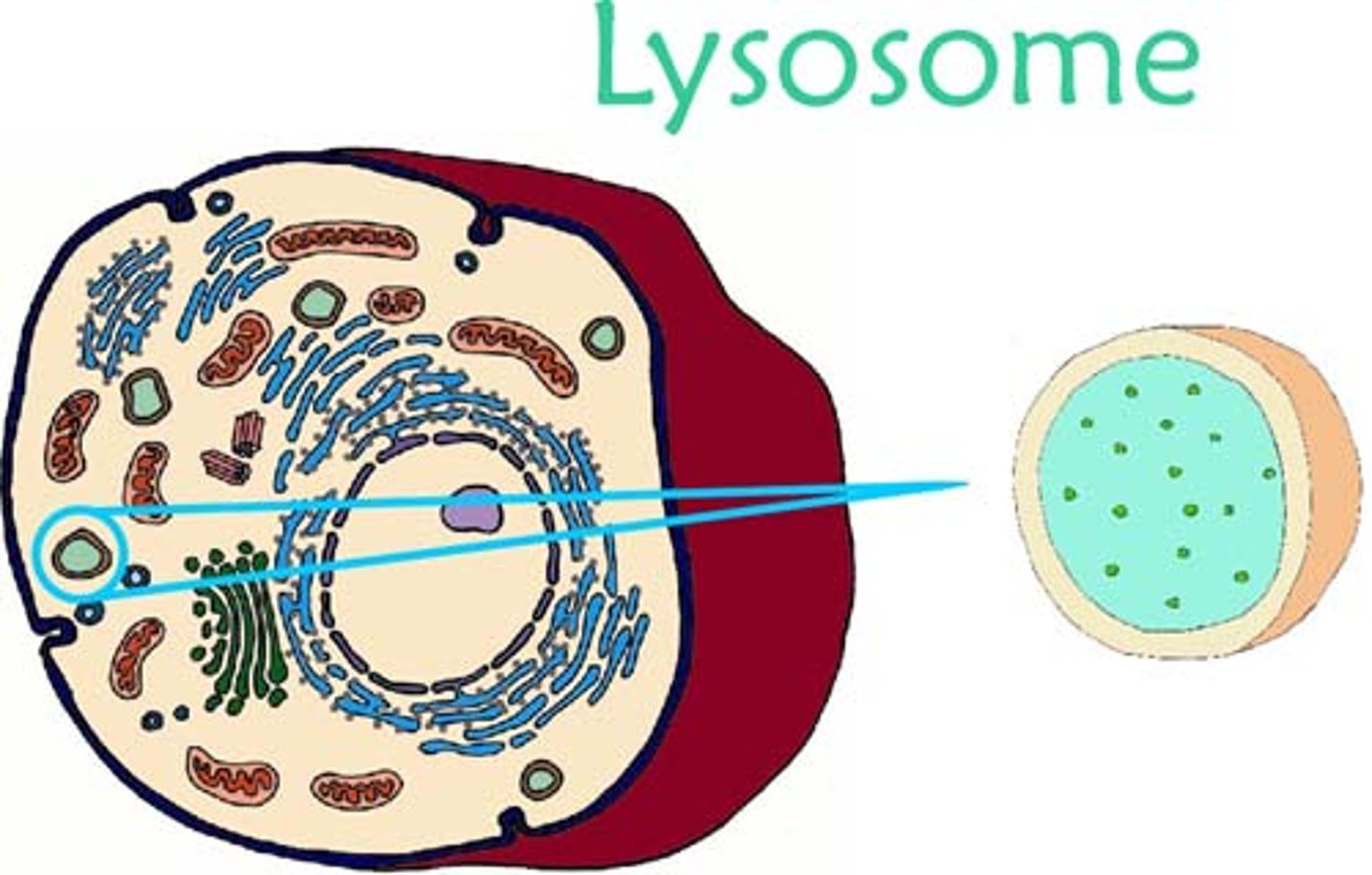
lysosome
destroys unwanted particles, break down/recycle old cell parts, helps white blood cells destroy bacteria
Golgi body
factories in which proteins received from the ER are further processed and sorted for transport.
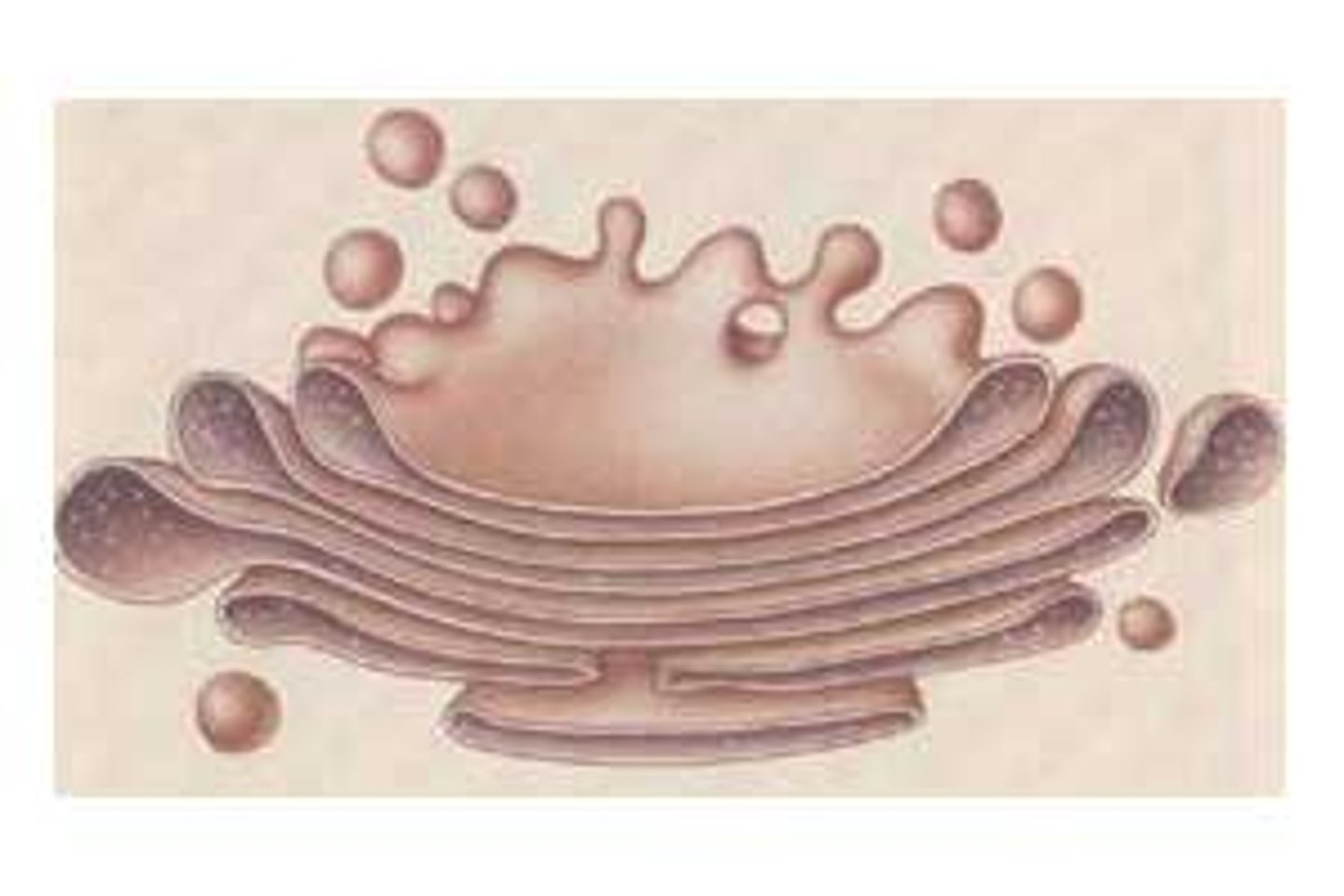
cytoskeleton
Network of protein fibers, is the structural framework for cell shape
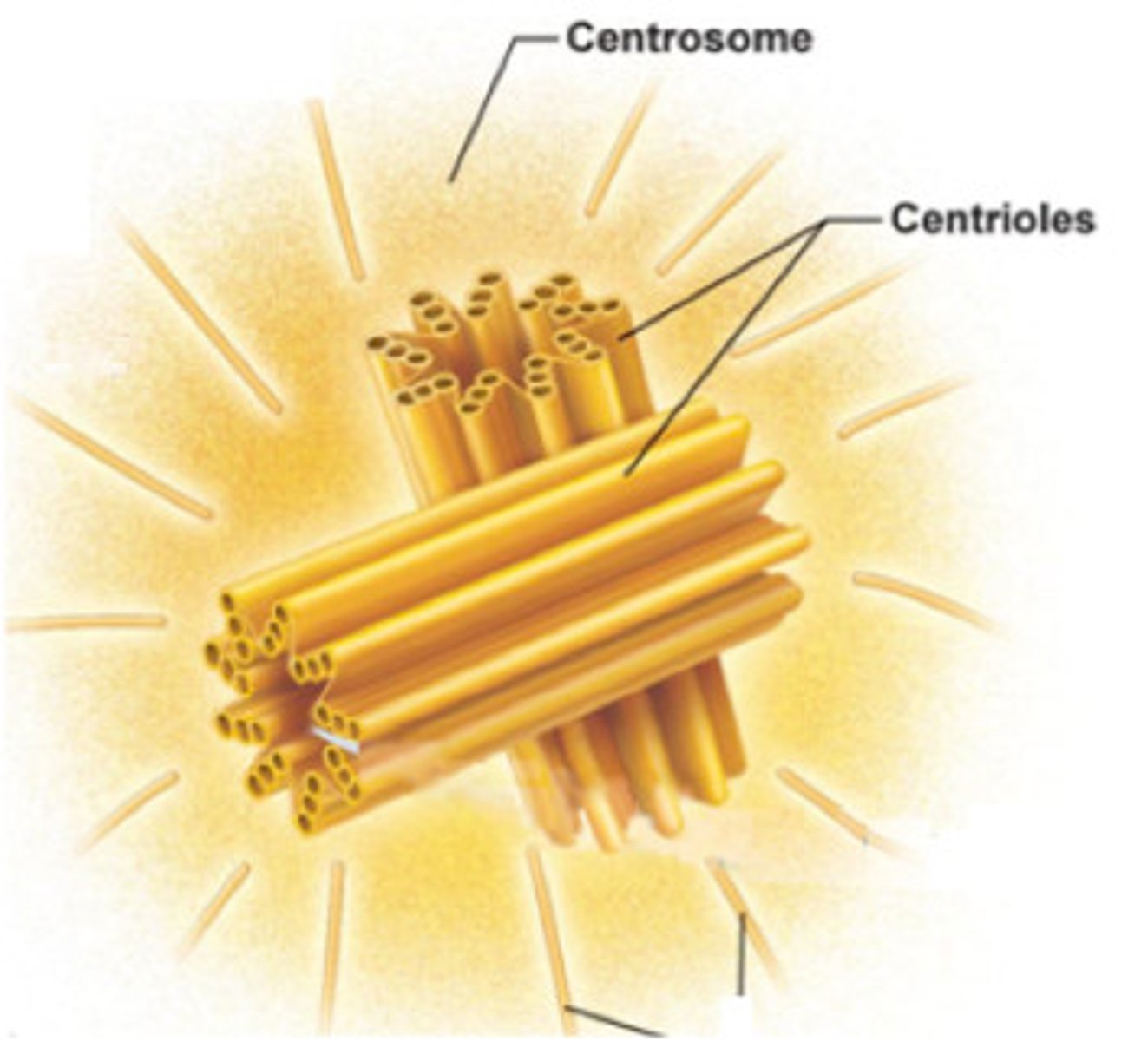
centriole/centrosome
Made from two centrioles. Aids in cell division by separating chromosomes. Helps with cell structure
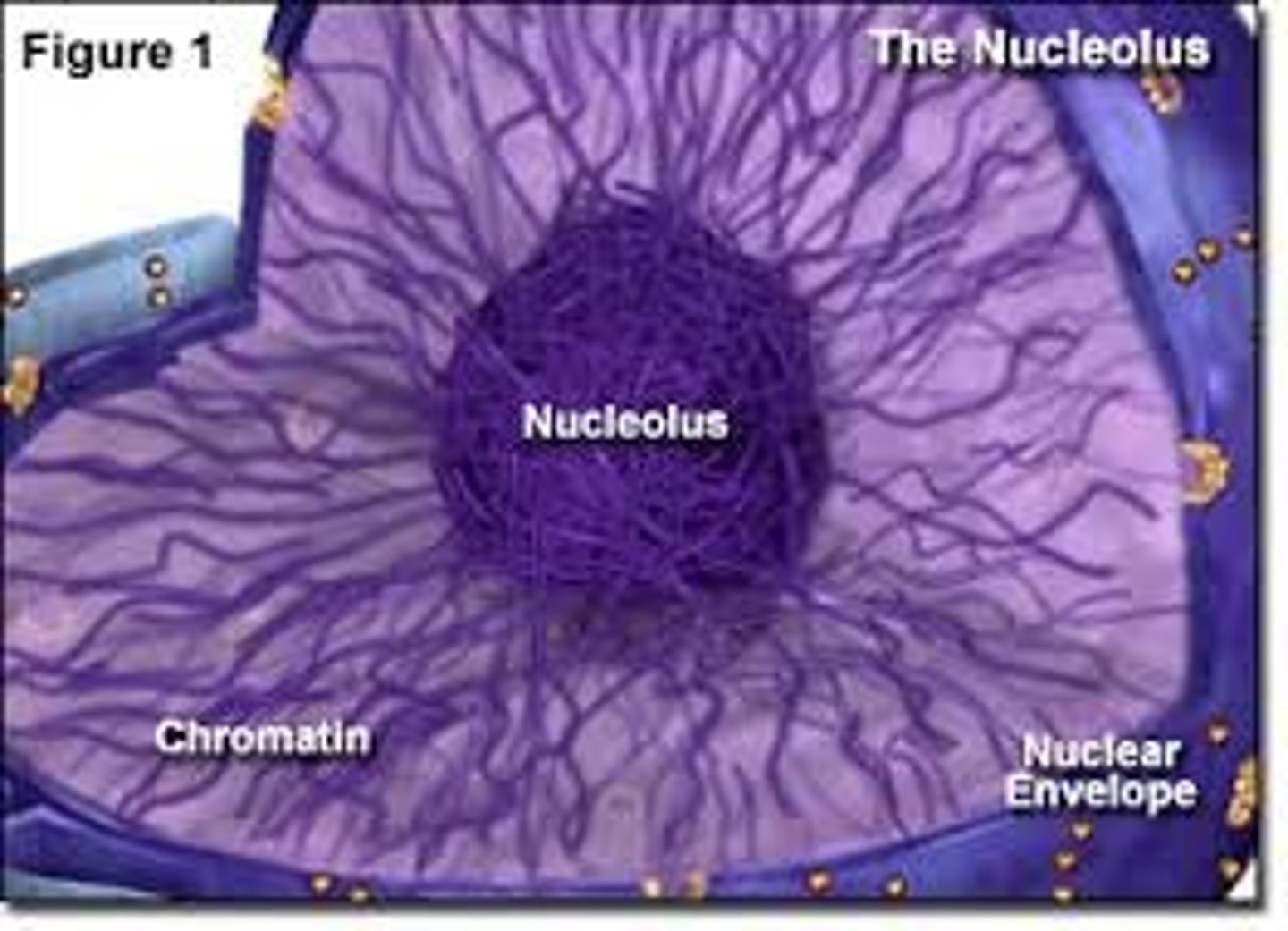
nucleolus
made up of proteins and RNA. Rewrites RNA and combines it with proteins. makes ribosomes
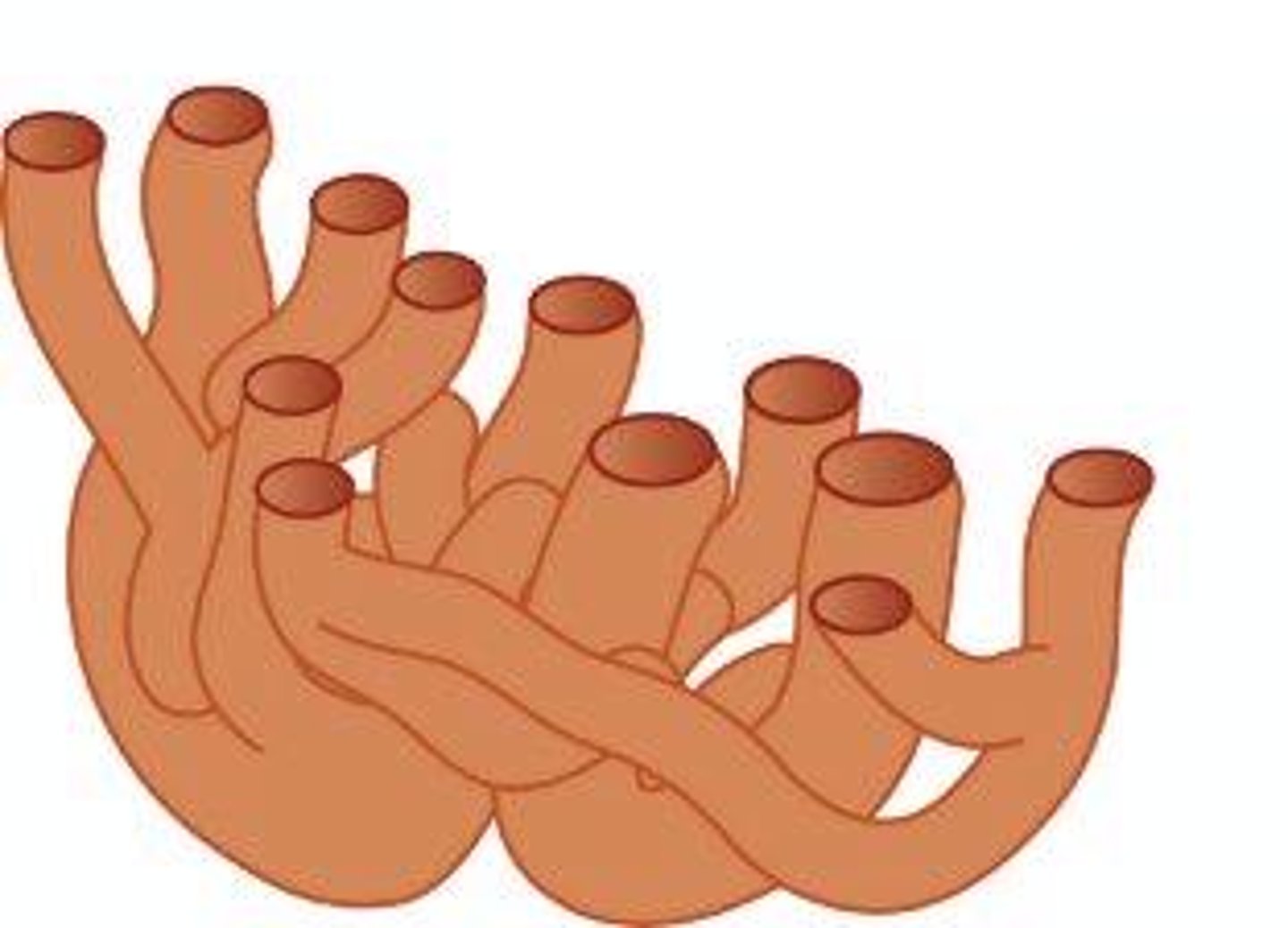
smooth ER
ER which has no ribosomes on it, makes and stores lipids, filters toxins, aids in creating new cell membranes
ribosomes
Two subunits made of RNA and proteins. Make proteins
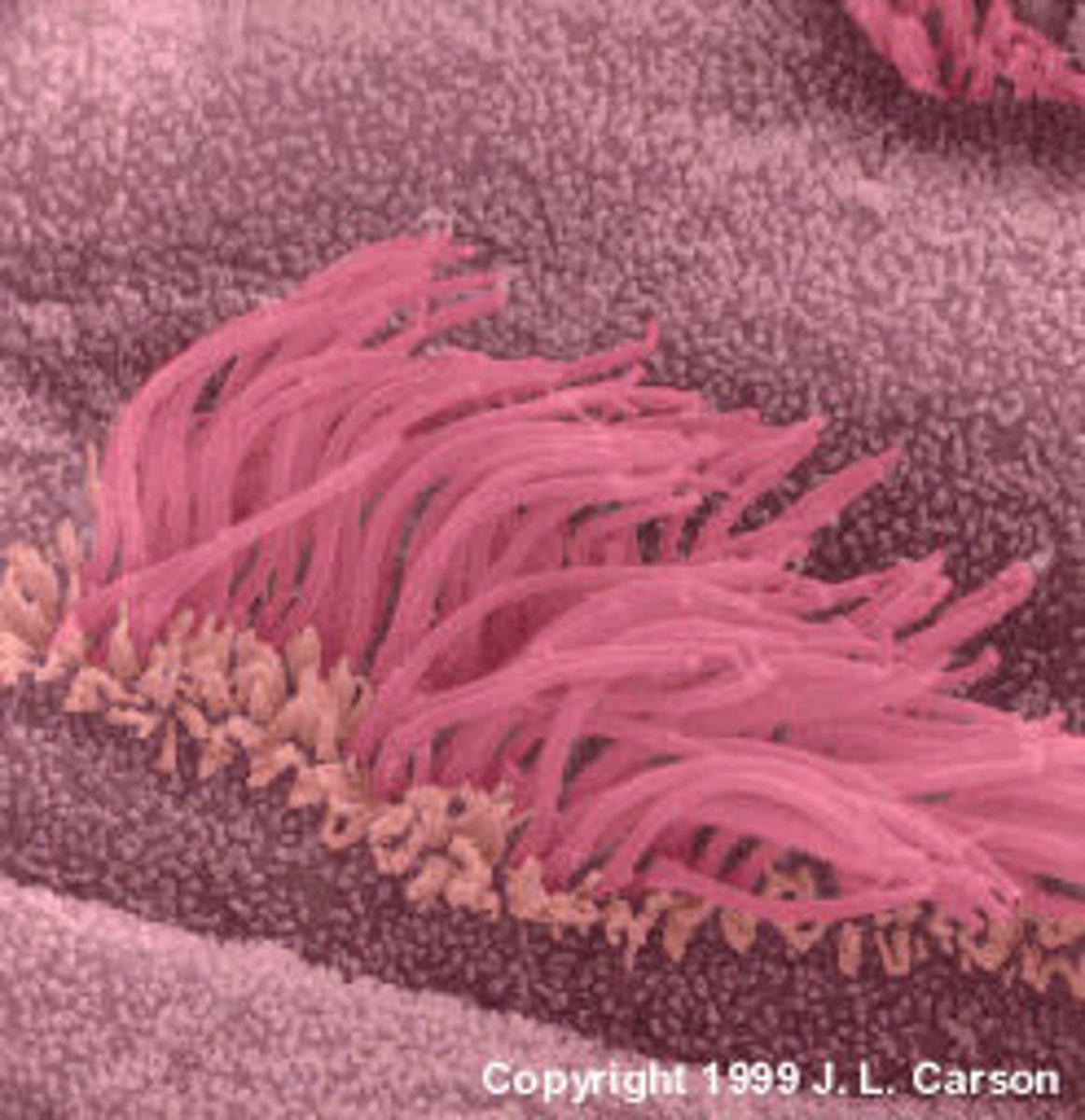
cilia
Organelles that extend from the surface of nearly all mammalian cells. They move a cell or group of cells or to help transport fluid or materials past them
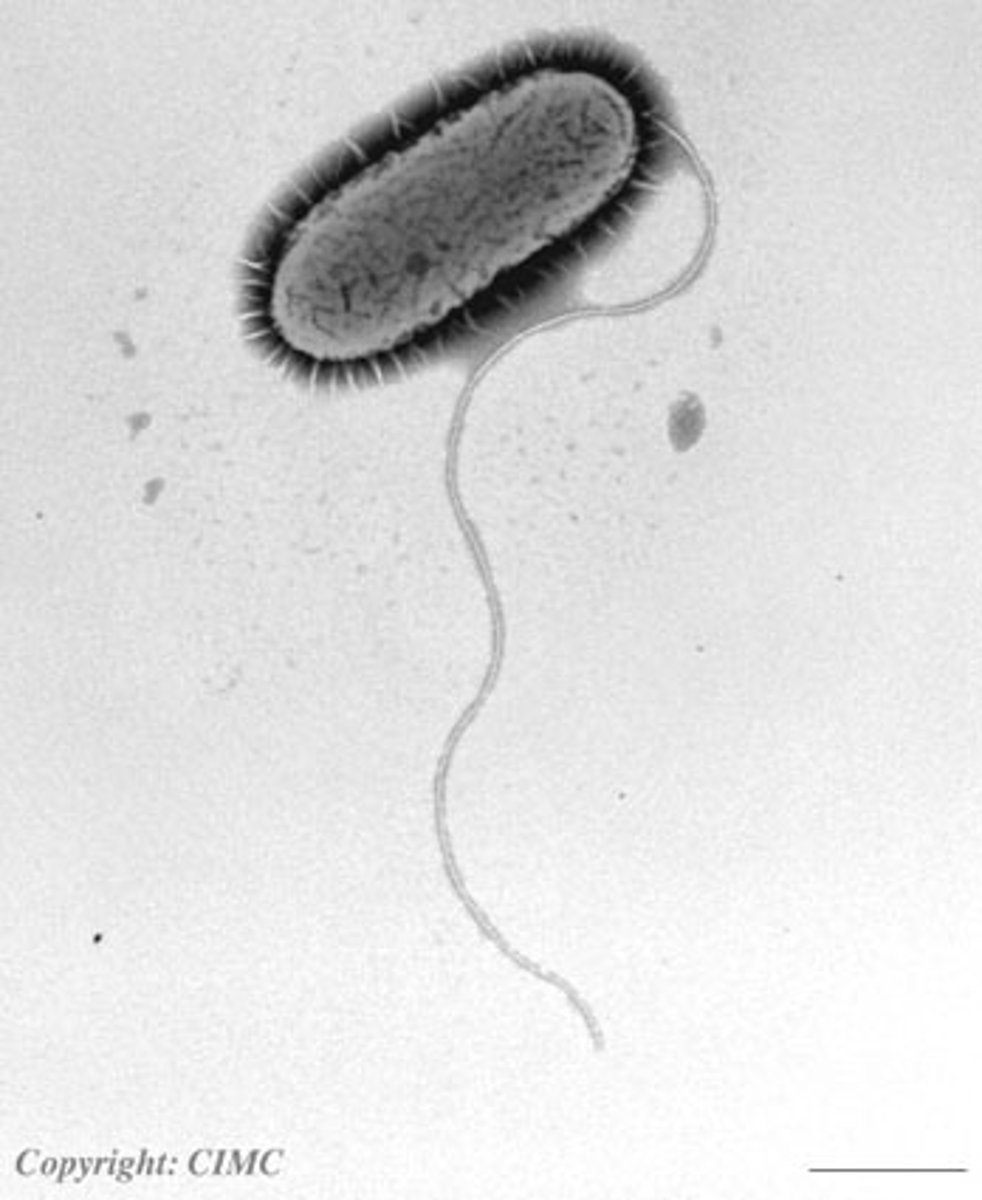
flagella
whip, tail like appenage that propels the cell along
chromatin
efficiently package DNA into a small volume
centriole
Small set of microtubules arranged in a certain way. Help in the formation of the spindle fibers.
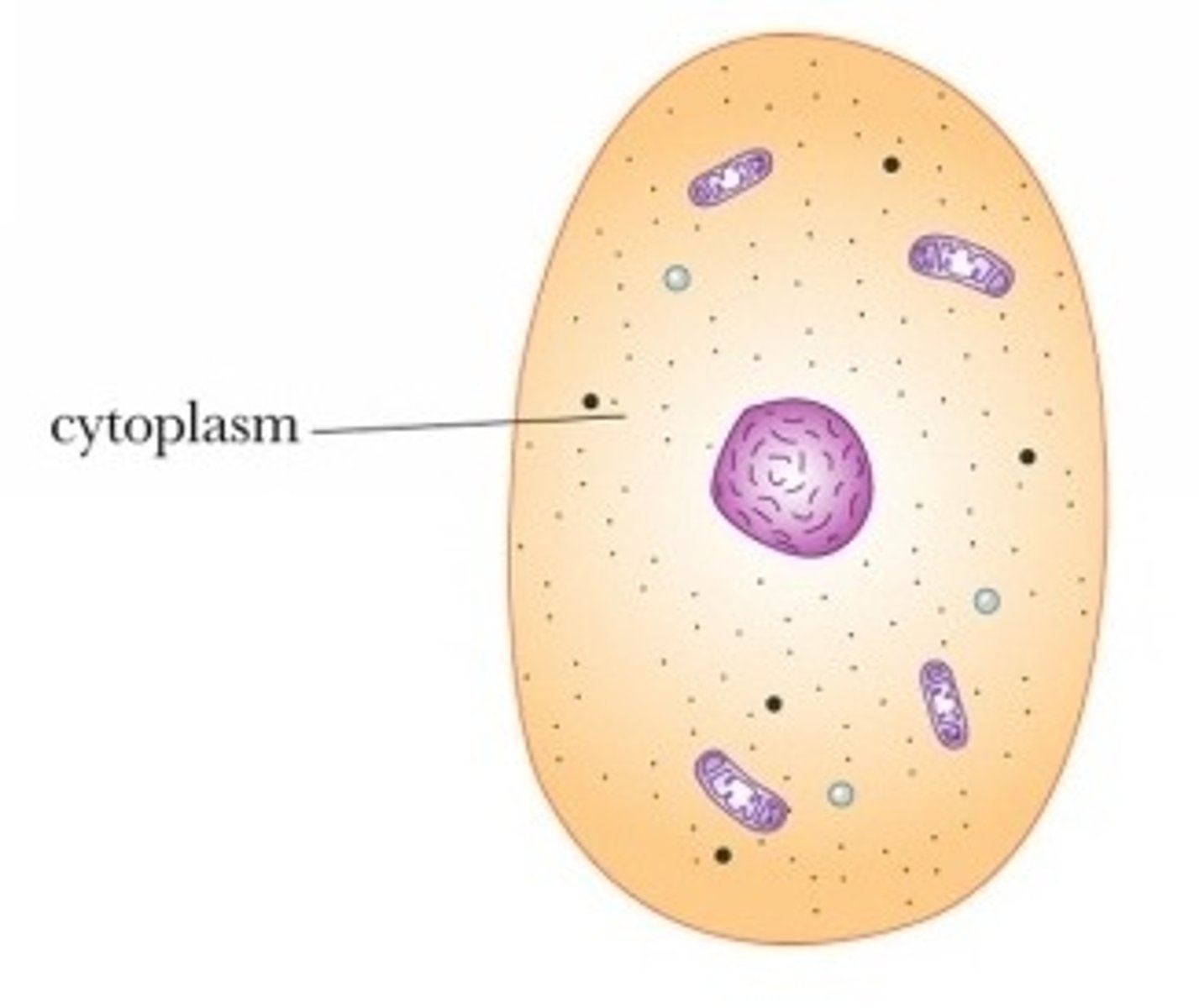
cytoplasm
The jelly-like material in the cell. Holds the internal components of cells in place. Moves materials around the cell
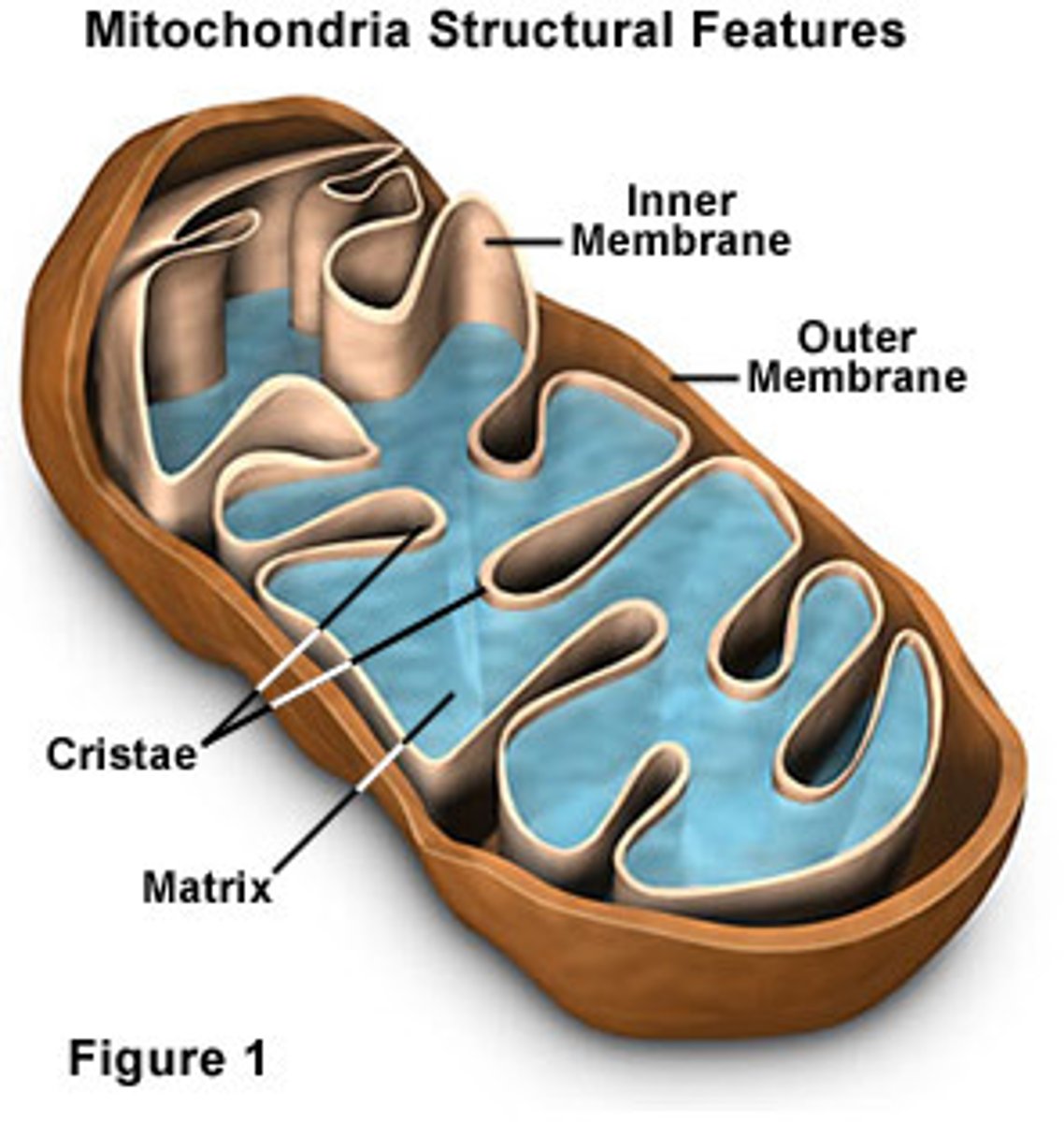
mitochondria
“powerhouse” of the cell; breaks down sugar to make energy
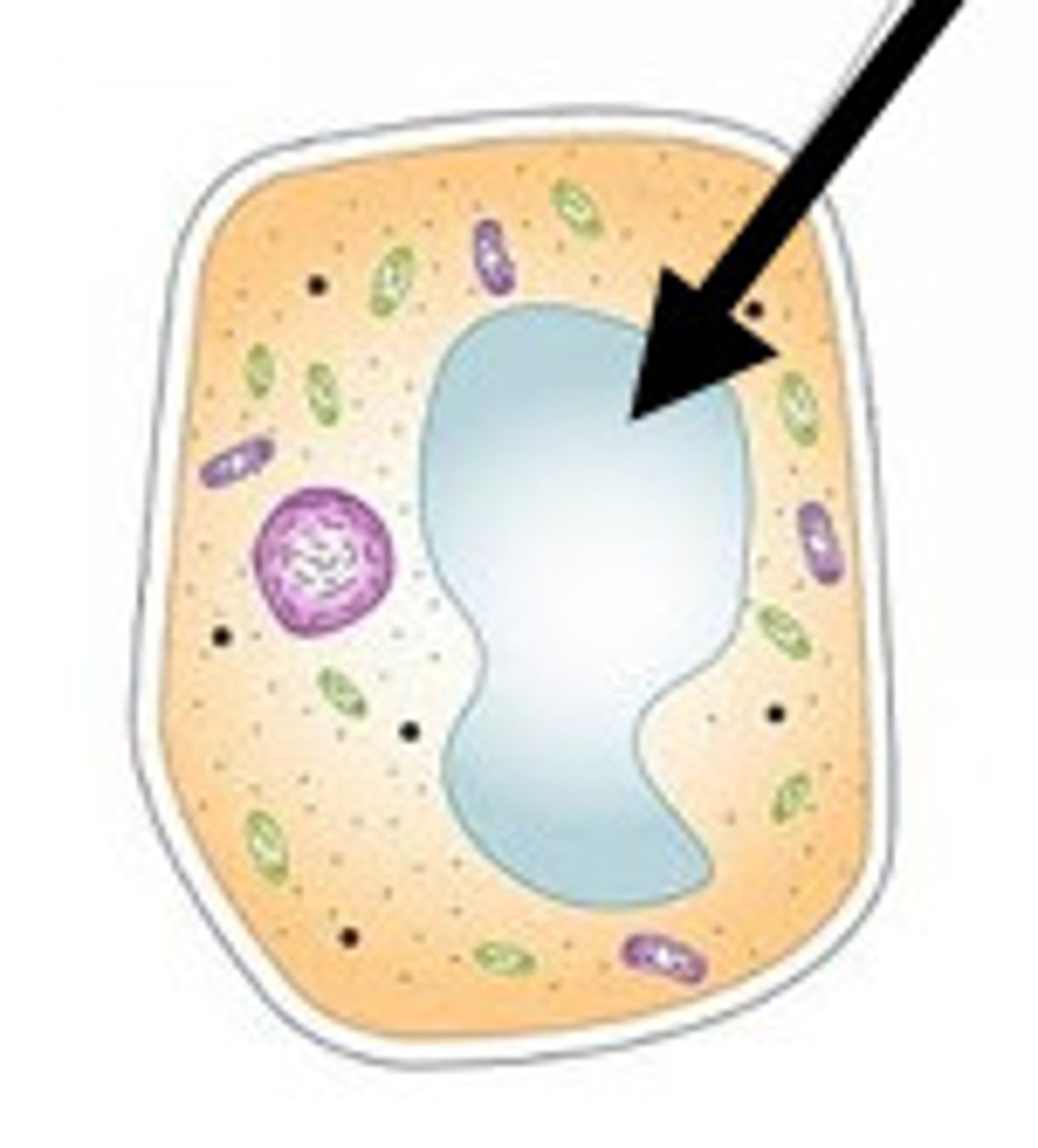
central vacuole
found in plant cells, large membrane-bound vesicle. involved with storage, cell growth, digestion, waste disposal.
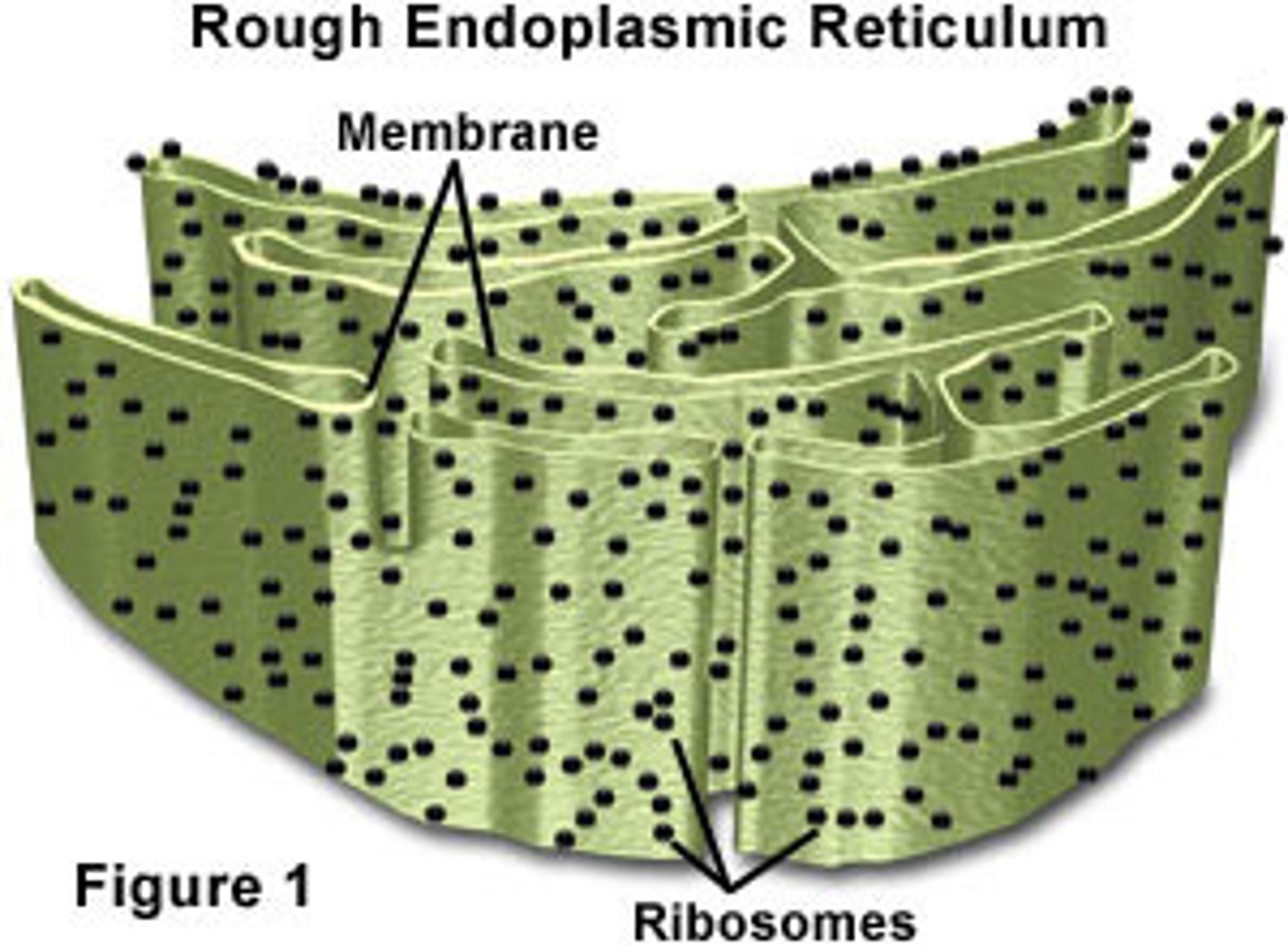
rough ER
ER covered in ribosomes, responsible for the assembly of proteins and transportation
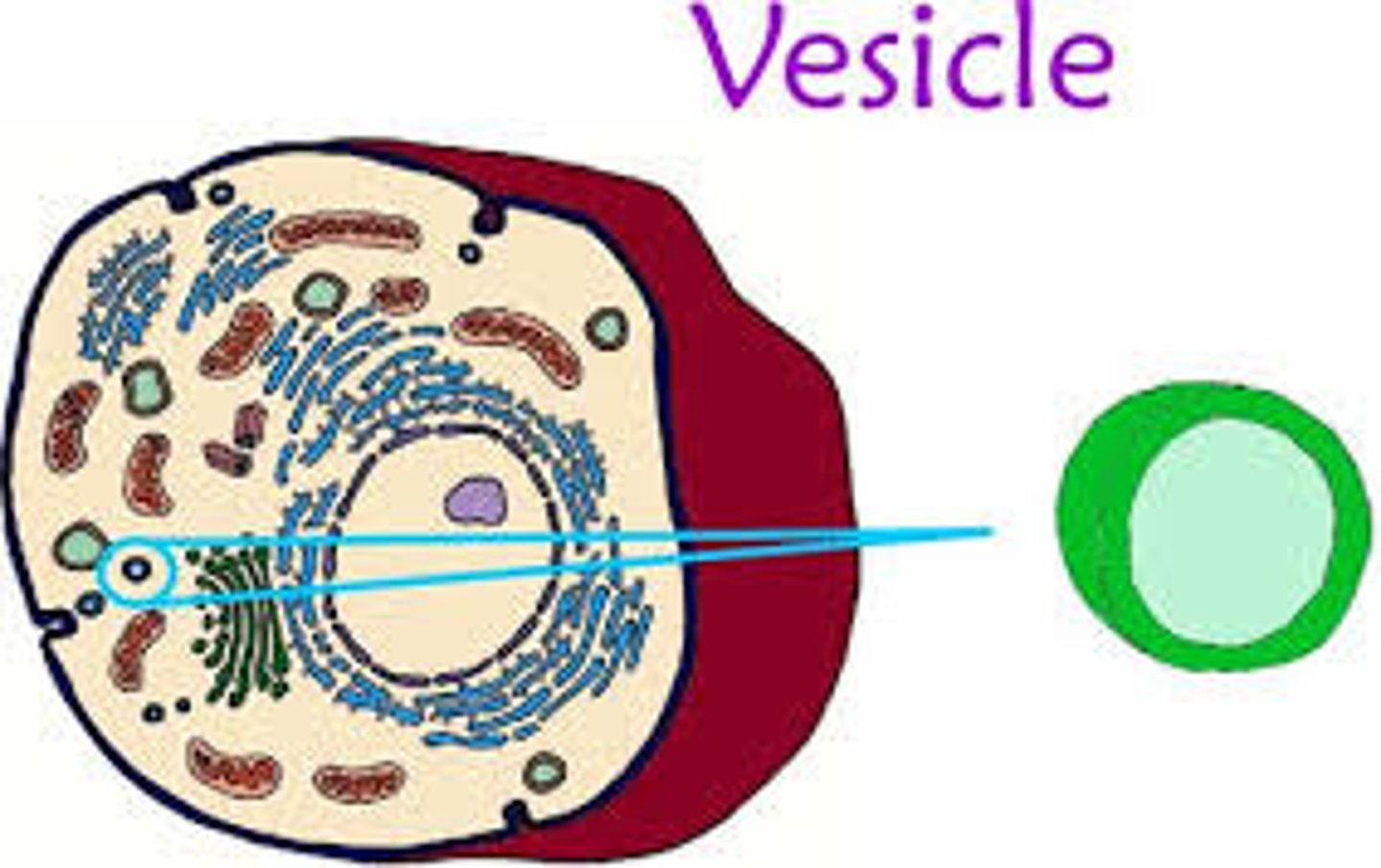
vesicle
fluid enclosed by lipid bilayer. moves molecules between locations inside the cell
pili
appendages that allow bacteria to attach to each other and to transfer DNA
peroxisome
breaks down toxic hydrogen peroxide, aids in digestion of lipids
DNA
heredity material found in nearly all cells, codes for the production of proteins, found in the nucleus
RNA
single-stranded, carries DNA’s genetic code to ribosomes in order to create proteins
vacuole
found in animal cells, stores food, water, or waste materials
contractile vacuole
found in amoeba (eukaryotic) and unicellular algae, brings in and expels water as needed to regulate osmosis
capsule
extra polypeptide coating outside of the cell wall
chlorophyll
the green pigment found in chloroplasts