Dental Terminology
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
primary/deciduous dentition
baby teeth
permanent/succedaneous dentition
adult teeth
maxillary teeth
upper jaw (teeth 1-16)
mandibular teeth
lower jaw (teeth 16-32)
upper right quadrant
teeth 1-8 (dentist's left)
upper left quadrant
teeth 8-16 (dentist's right)
lower right quadrant
teeth 32-25 (dentist's left)
lower left quadrant
teeth 24-17 (dentist's right)
anterior teeth
towards front of mouth
posterior teeth
towards back of mouth
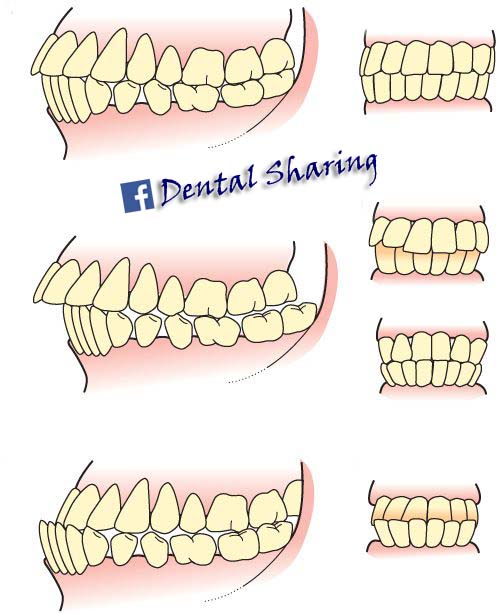
occlusion
the bite/fit between the maxillary and mandibular teeth
central incisors
teeth 8,9 & 25,24
lateral incisors
teeth 7, 10 & 26, 23
canines (cuspids)
teeth 6 11 & 27, 22
first premolars/bicuspids
teeth 5, 12 & 28, 21
second premolars/bicuspids
teeth 4, 13 & 29, 20
first molars
teeth 3, 14 & 30, 19
second molars
teeth 2, 15 & 31, 18
third molars (wisdom teeth)
teeth 1, 16 & 32, 17
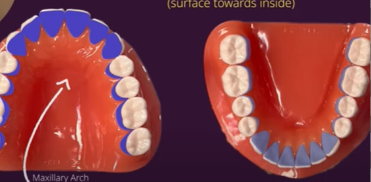
lingual surfaces
side of teeth facing tongue
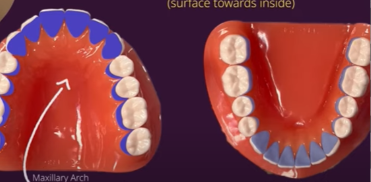
buccal/facial surfaces
side of teeth facing cheeks
labial surfaces
side of teeth touching back of lips
mesial
toward the midline
distal
away from midline
occlusal surfaces
biting surface of posterior teeth
incisal edges
biting surface of anterior teeth
interproximal
area between two teeth
proximal surface
surface that faces the interproximal area (flossing surface)
crown
the visible part of the tooth
root
part of tooth under the gums
gingiva
gum (anchored to the bone)
root canal
center of root
enamel
hard layer that covers crown of the tooth
dentin
softer mineralized connective tissue underneath enamel
pulp
center of the tooth that makes up the root canal
cementum
calcified connective tissue that covers the root
periodontium
supporting structures around tooth composing of the gingiva and periodontal ligaments
periodontal ligaments
fibers that connect the cementum to the bone
gingival margin
gingiva edge that covers the root and touches the crown, has a scalloped shape following the contour of the CEJ
gingival sulcus/crevice/periodontal pocket
the valley between the marginal gingiva and CEJ; usually 3-4mm deep
interdental gingiva/papilla
gingiva between two teeth that cover the triangular gap
alveolar process (mandibular and maxillary process)
bone surrounding tooth
plaque/biofilm
soft mass of oral bacteria
fermentable carbohydrate
broken down by oral bacteria & can build plaque
includes monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, polyols (sugar alcohols)
supragingival
above the gumline
subgingival
below the gumline
calculus/tartar
made up of 70-90% inorganic salts, bacteria easily cling to it and plays a role in carrying periodontal disease
how many primary teeth are there total
20
what teeth are missing from the primary dentition
premolars (bicuspids) & third molars
eruption
when dentition become visible (primary or permanent)
exfoliation
when primary dentition are lost
carious lesion (caries)
cavity/area of decay
occlusal caries
decay on top of the molars
interproximal caries
decay between two teeth
root caries
decay on the root
demineralization occurs when
the enamel is broken down (appears white, the beginning of a cavity)
cavity treatment: almalgam filling is made of
50% mercury + silver, copper, and zinc
cavity treatment: composite filling is made of
made of acrylic (plastic) + powdered glass or ceramic
cavity treatment: crown is made of
usually gold or ceramic
root canal therapy is used when
used when cavity progresses into pulp
inflamed pulp removed
filled with gutta percha (rubbery material)
sealed (often with a crown)
fissure
line groove on occlusal surface
pit
small point indentation on occlusal surface (often the intersection between two fissures)
pit and fissure sealant
protective coating applied to the pits and fissures to protect the occlusal surfaces while chewing to prevent decay
fluoridated water
ingested before permanent dentition erupts to provide strength
fluoride rinse agent
contains sodium monofluorophosphate or stannous fluoride to prevent decay
sodium monofluorophosphate
Na₂PO₃F, releases fluoride (F⁻) to remineralize teeth
dissociates into 2 sodium (Na+) cations and monofluorophosphate (PO₃F²⁻) anions
in lower pH conditions, monofluorophosphate (PO₃F²⁻) dissociates into fluoride (F⁻) anions and orthophosphate (PO₄³⁻)
stannous fluoride
SnF₂
acidulated phosphate fluoride (APF)
a gel or foam that releases fluoride ions in an acidic solution to rapidly be absorbed by the enamel
should not be used for patients with porcelain (glass ionomer) restorations
neutral sodium fluoride
NaF has a neutral pH and can be used on patients with glass based restorations
fluoride varnish
provides decay prevention, often used after cleaning
5% sodium fluoride in a resin base (like colophony/rosin or polyurethane) with solvents (alcohol)
sometimes with xylitol, flavorings, and calcium phosphate
expectorate
to spit out
disclosing agent
a pigment that sticks to plaque to highlight areas that need better cleaning
oral prophylaxis
professional dental cleaning that removes plaque, calculus, and stains
full mouth series (FMX)
18+ close up x-rays of the teeth and its roots for spotting cavities and gum disease
panoramic image
single broad x-ray of the jawbones, sinuses, and temporomandibular joints (TMJ)
gingivitis
inflammation of the gingival margin characterized by redness or swelling resulting from plaque remaining around the gingival margin and interproximal area
erythemic
red
edematous
swollen
in vitro
in laboratory
in vivo
in humans
causes of gingivitis
poor oral hygiene
gingival abrasion
stress
general illness
uncontrolled diabetes
smoking
hormonal changes (pregnancy/puberty)
gingivitis treatment options
sulcular cleaning
stannous fluoride toothpaste
pulsing tools (i.e waterpik)
mouth rinses
periodontal disease
irreversible damage to supporting structures such as loss of alveolar bone
clinical attachment loss (CAL)
loss of periodontal gum, bone, and fibers
how to calculate CAL
periodontal pocket depth + gingival recession
or
CEJ to base of the periodontal pocket
cervix/cementoenamel junction (CEJ)
boundary between the crown and cementum
how to calculate radiographic bone loss (RBL)
(distance from CEJ to alveolar bone crest) divided by (root length) x 100
alveolar bone crest (ABC)
highest point of bone surrounding the tooth
root apex
tip of the root
stage I periodontitis (in terms of CAL, RBL, tooth loss)
CAL: 1-2mm
RBL: coronal third (less than 15%)
tooth loss: none
stage II periodontitis (in terms of CAL, RBL, tooth loss)
CAL: 3-4mm
RBL: coronal third (15-33%)
tooth loss: none
stage III periodontitis (in terms of CAL, RBL, tooth loss)
CAL: at least 5mm
RBL: extending to middle third of root and beyond
tooth loss: at least 4
stage IV periodontitis (in terms of CAL, RBL, tooth loss)
CAL: at least 5mm
RBL: extending to middle third of root and beyond
tooth loss: at least 5
grade A: slow rate periodontitis
CAL or RBL: no loss over 5 years
(RBL)/age: less than 0.25
smoking: none
HbA1c: normoglycemic/non diabetic
grade b: moderate rate periodontitis
CAL or RBL: at least 2mm over 5 years
(RBL)/age: 0.25 to 1
smoking: up to 10 cigarettes a day
HbA1c: up to 7.0%
grade c: rapid rate periodontitis
CAL or RBL: more than 2mm over 5 years
(RBL)/age: more than 1
smoking: more than 10 cigarettes a day
HbA1c: at least 7.0%
HbA1c
hemoglobin A1c test measures the average amount of glucose attatched to hemoglobin in your red blood cells over the past few months
step 1 in staging and grading periodontitis: initial case overview
full mouth probing
full mouth radiographs
note missing teeth
step 2: staging - for stage I to stage II (mild to moderate) periodontitis
confirm CAL
rule out non-periodontitis causes of CAL such as
cervical restorations
caries
root fractures
trauma
determine maximum CAL
step 2: staging - for stage III to stage IV (moderate to severe) periodontitis
determine maximum CAL or RBL
confirm RBL patterns
assess tooth loss due to periodontitis
evaluate case complexity factors