AP Macroeconomics Unit 4
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Just some useful notes for the AP Macro...
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
(4.1) What are financial assets?
Financial assets are written claims where buyers have the right to future incomes from sellers. i.e., loans, bonds, land, homes, cars, etc. Also have different levels of liquidity (how easily they can be turned into cash)
(4.1) Properties of a loan
Loans are both an asset and a liability and are critical to the growth of the aggregate economy.
(4.1) Opportunity cost of holding money?
The opportunity cost of holding money is the interest that money could be earning in an interest-bearing asset, like a bond.
(4.1) What is the relationship between bond prices and interest rates?
There is an inverse relationship between bond prices and interest rates. i.e., Interest Rates↓ means Demand↑ which means Price↑ and vice versa
(4.2) Fisher Equation?
NIR = RIR + Inflation
(4.2) Nominal interest rates vs real interest rates?
Nominal interest rates are charged by banks on loans, but are not adjusted for inflation.
Real interest rates are the real rate of return on investments and loans, and they are adjusted for inflation.
(4.2) Expected vs Actual Inflation
Expected inflation is what banks use to set a nominal interest rate for terms of a customer loan and savings vehicles; Actual inflation is calculated after the loan term is over.
(4.2) Impact of inflation on borrowers and lenders?
Higher unexpected inflation makes the real rate of return on fixed rate savings and loans lower. Thus, when unexpected inflation is higher than anticipated, borrowers are better off and lenders are worse off.
(4.3) Three major functions of money?
Unit of Account (Common Currency)
Store of Value (Money that remains the same or appreciates in purchasing power over time)
Medium of Exchange (Way of exchanging goods/services)
(4.3) Define the money supply (memorize)
M0 = Monetary Base: Currency + bank reserves
M1 = Currency in circulation + demand deposits + savings accounts
M2 = M1 + small-denomination time deposits (like certificate of deposit) + retail money market funds
(4.4) What is fractional reserve banking used for?
Fractional reserve banking is used to create loans, which expands the money supply.
(4.4) What two things are equal to each other a bank balance sheet
Assets (Reserves, Loans) are equal to Liabilities (Demand Deposits)
(4.4) What is the money multiplier
The money multiplier is used to calculate maximum changes in the money supply which can occur through changes in demand deposits.
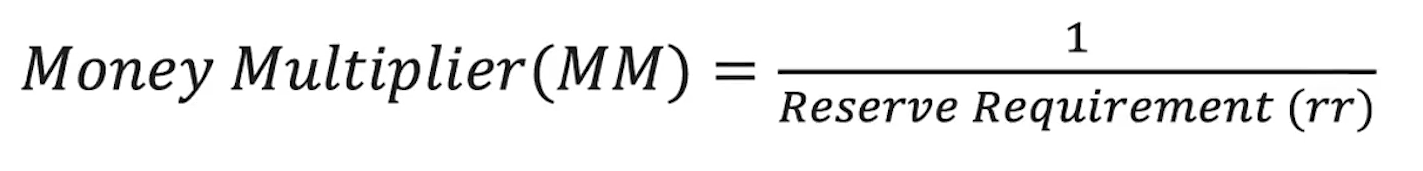
(4.5) What is the relationship between quantity of money and the interest rate in the money market model?
There is an inverse relationship between quantity of money and the interest rate in the money market model
(4.5) What factors shift money demand?
Aggregate Price Level - P↑ D↑
Real GDP (National Income) - I↑ D↑
Banking Technology - T↑ D↓
*and vice versa
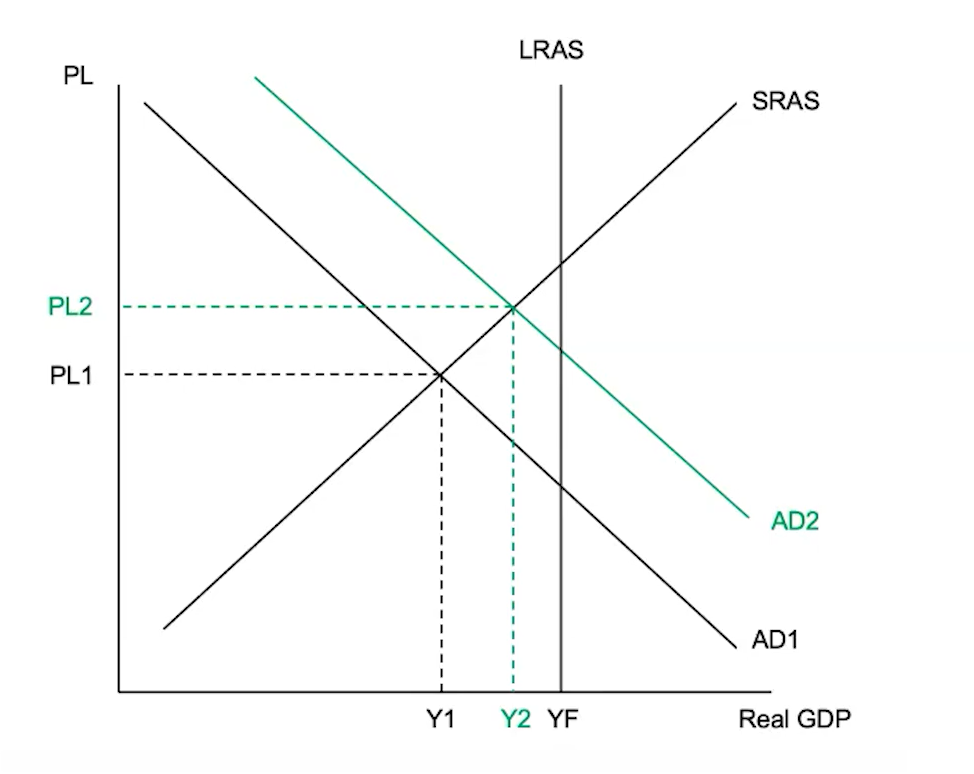
(4.6) How does expansionary monetary policy work?
Expansionary monetary policy is when the central bank decreases the nominal interest rates in the short run to help get an economy out of a recessionary gap
Lower interest rates → Less expensive to borrow → More interest-sensitive spending (investment and consumption) → Increase in AD
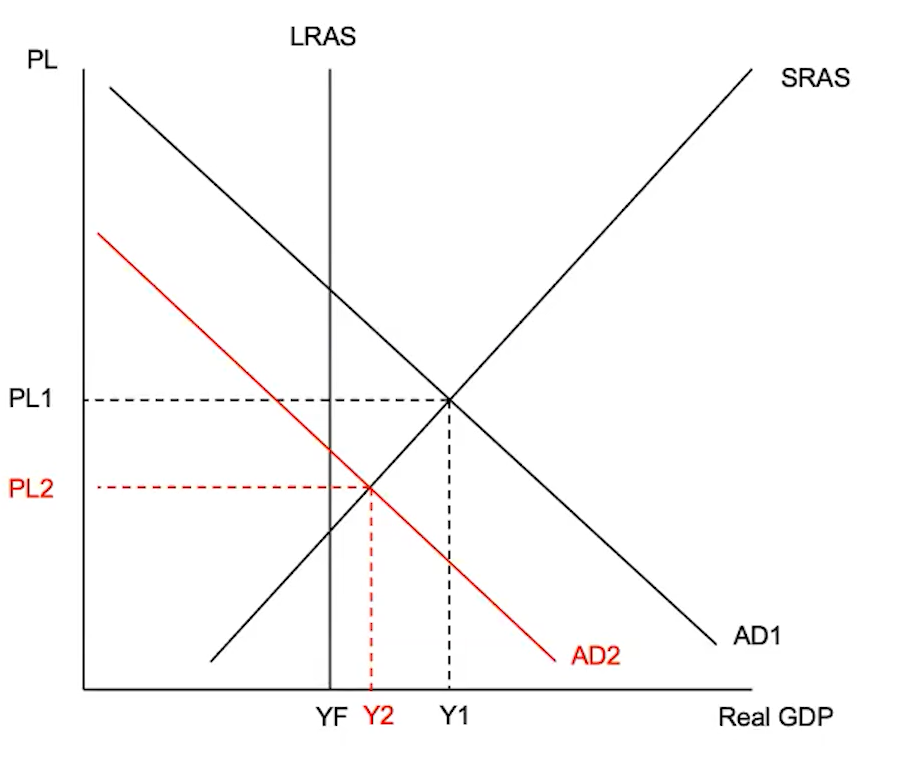
(4.6) How does contractionary monetary policy work?
Contractionary monetary policy is when the central bank increases the nominal interest rates in the short run to help get an economy out of an inflationary gap
Higher interest rates → More expensive to borrow → Less interest-sensitive spending (investment and consumption) → Decrease in AD
(4.6) Summary of monetary policy tools
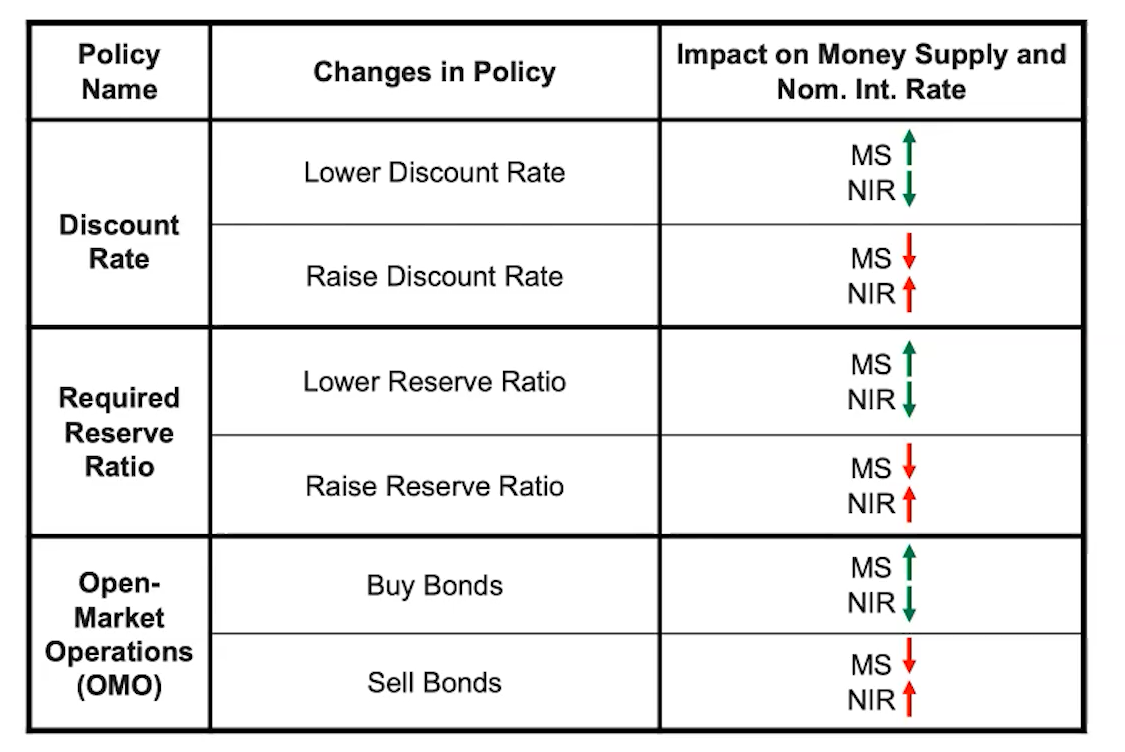
(4.6) Is the required reserve ratio applicable in open market operations
The required reserve ratio is not applicable in open market operations
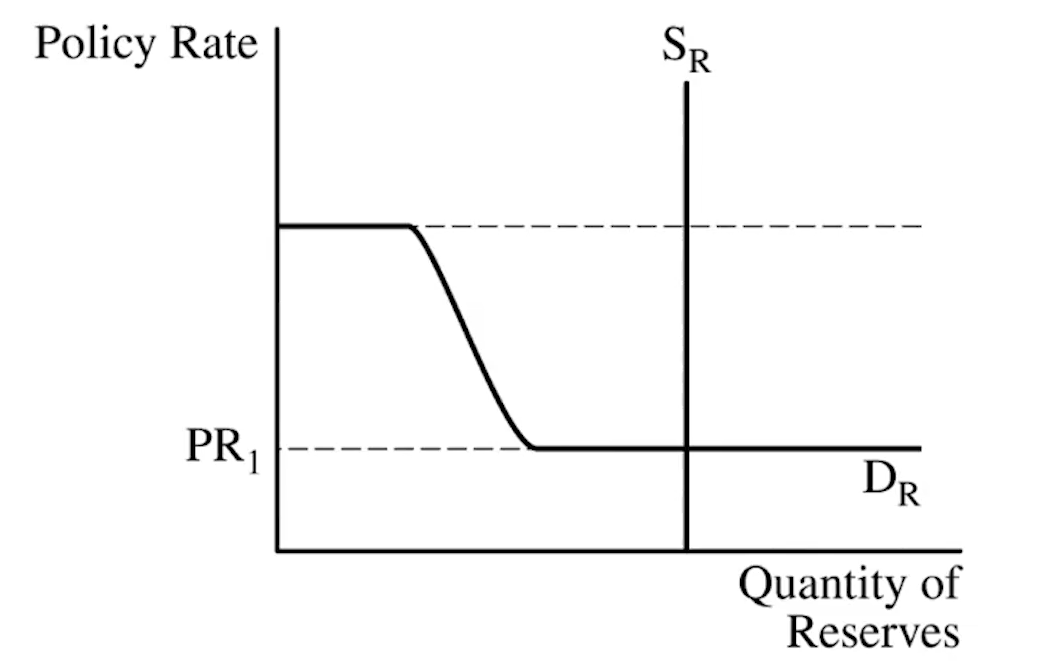
(4.6) Reserve Model Market Graph
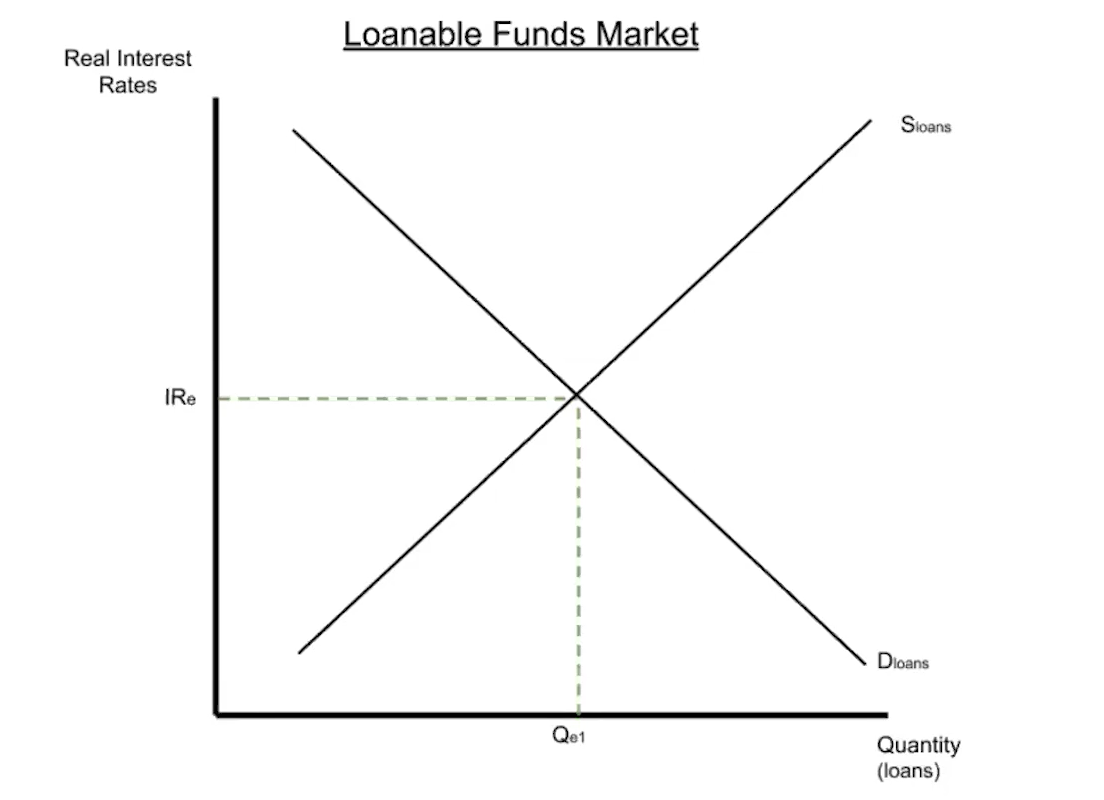
(4.7) Loanable Funds Market Graph
Note that loanable funds market focuses on real interest rate (NIR - I), not nominal interest rate because they take place over long periods of time.
(4.8) Disequilibrium in the Loanable Funds Market
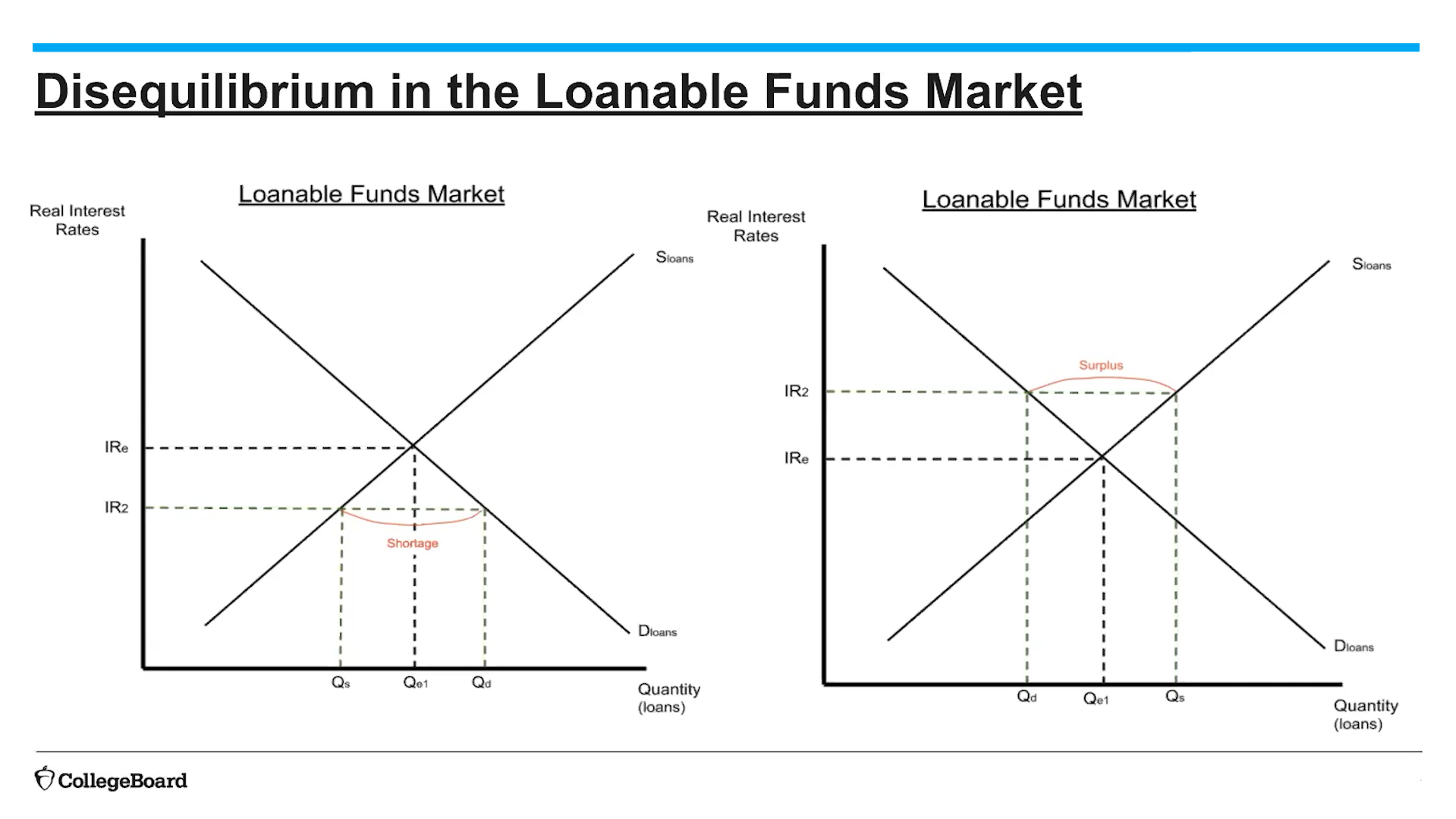
(4.8) What shifts supply and demand of loanable funds?
Changes in savers behavior will shift supply of loanable funds
Changes in return on investment will impact demand on loanable funds