Soil science exam #2
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
death by soil
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Primary processes that control soil aeration are best described as
soil water content, rate of O2 consumption, and soil structure (macroporosity)
As a means of characterizing soil water content, percent water-filled pore space reflects
the proportional volume of pore space occupied by water, which cannot exceed 100%
True or false Soil temperatures are insensitive to soil color, since soil temperatures are so strongly influenced by water content.
false, soil color affects heat absorption
Let's imagine that the average snow depth in Brownie's park for February 2025 is 18 inches. If the average snow depth for the same period in 2030 is zero, but air temperatures are similar, what can we expect with respect to soil temperature?
Soil temperature in 2030 will be cooler than in 2025
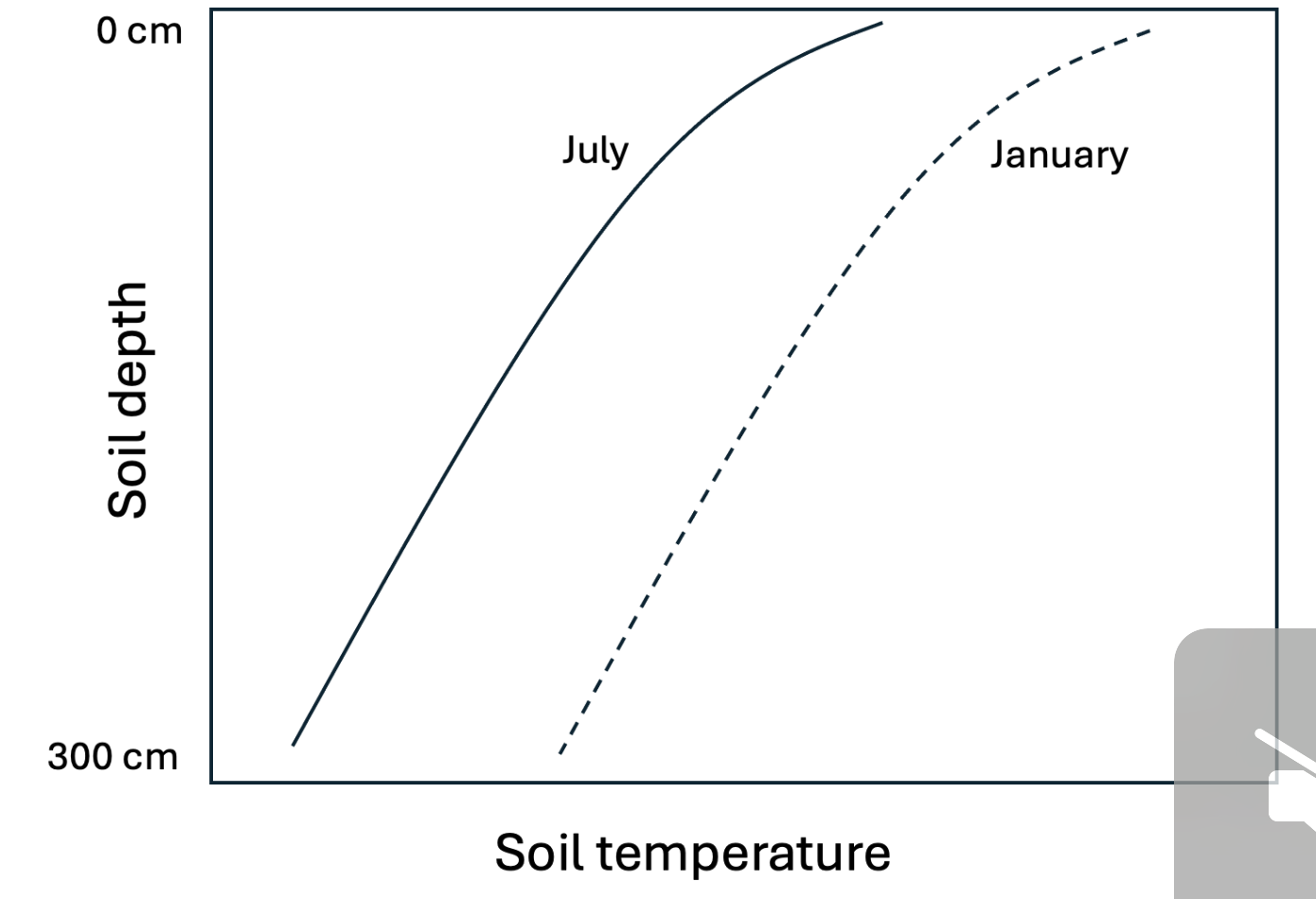
Your friend is studying soil science by trying to draw some of the figures from the lecture slides from memory, and they produce the image below. Help them to identify ways in which their diagram would not likely reflect true soil temperature dynamics in winter and summer in the same, temperate location. Select all reasons that apply (January temperatures are shown with the dashed line; July temperatures with the solid line; warmer temperatures to the right side.)
1 | In July, surface soils should generally be warmer than deeper soil. |
2 | Temperatures throughout the soil profile should generally be cooler in January than in July. |
Wetland plants overcome O2 limitations by
developing aerenchyma, which are specialized tissues that allow for gas exchange between water and plant
T or F Due to uptake of CO2 by plant roots, concentration of CO2 in soil pore spaces is much lower than that of the atmosphere.
false, Anerobic respiration causes CO2 to increase in pore spaces compared to atmosphere
You install some soil temperature sensors at 2 cm and 100 cm depths in your backyard in midsummer (hot days and cool nights). The sensor readings are as follows:
midnight:
2 cm: 25 C
100 cm: 27 C
midday:
2 cm: 25 C
100 cm: 38 C
Are your soil temperature sensors installed properly?
No, the 100 cm fluctuation is unreasonably large compared to the 2 cm fluctuation. Sensors may have been switched.
The influence of tillage system on soil warming in the spring is important to consider because
crop seeds have a minimum temperature for germination
Evapotranspiration represents the difference between the two most important processes of water loss from land (evaporation and transpiration).
False, because evapotranspiration actually refers to the sum of evaporation and transpiration, meaning it represents the combined water loss from land through both processes, not the difference between them
The best definition of a soil colloid is:
Small soil particles with large surface area permass
What is the best description of a 2:1 silicate clay?
Layers of octahedral sheets, sandwiched by tetrahedral sheets, which can be either expanding or nonexpanding
Which of the processes below is an example of isomorphic substitution:
a structural aluminum cation in a dioctahedral sheet is replaced with a magnesium cation
True or false Higher pH conditions tend to lead to more negative charges in pH-dependent charge sites, which lead to greater cation exchange capacity.
true
true or false Organic colloids have a high pH-dependent charge.
true
Hydration of cations influences:
their effective radii, and therefore how easily they are replaced in cation exchange, because bigger cations are not as tightly bonded
The three types of soil acidity are
active, exchangeable, and residual
True or false The influence of additions of H+ to soil on active acidity can be buffered by various soil processes, including protonation of soil colloids.
True
Two different soils both receive long-term fertilization, using ammonium-based fertilizers. One soil exhibits a greater reduction in pH than the other. This difference is likely due to:
all of the above, since all of the above may influence buffering capacity
The purpose of lime application to soil is to
Raise soil pH, because it neutralizes soil acidity due to the carbonate and hydroxide ions it releases The carbonate ions react with hydrogen ions in the soil solution, forming water and carbon dioxide gas.
It's important to consider aluminum for soil pH because
Aluminum hydrolyzes in soil solution, releasing hydrogen ions and contributing to soil acidity.
What is a salt?
A compound that forms when an acid reacts with a base, typically dissolving into cations and anions in soil solution
true or false Irrigation water derived from ground water can contain dissolved salts.
True
How are cations vs. anions distinguished?
By their charge
true or false Once an ion has been absorbed to a soil surface, it can be exchanged with a different ion in soil solution.
True
Which of the following best describes the concept of acidity?
Acidity is a measure of the concentration of H⁺ (protons) in a solution