ICT - Storage Devices and Media
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Last updated 11:24 PM on 3/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
A Storage Media
A hardware device that can store data examples:
* Magnetic tape
* CD
* Pen Drive
* Hard Drive
* SSD
* Magnetic tape
* CD
* Pen Drive
* Hard Drive
* SSD
2
New cards
A storage device
A hardware device that reads/writes data and stores it in the storage media. Example:
* CD ROM
* CD ROM
3
New cards
The three main types of storages
* Magnetic
* Optical
* Solid state
* Optical
* Solid state
4
New cards
Data transfer rate
The time is takes a storage device to put data (write) to the storage media
5
New cards
Data access rate/time
The time it takes storage device to get data (read) on a storage device
6
New cards
Latency
The time it takes the storage device to a read/write on a storage media simultaneously. The programs like MS Word is an example of this
7
New cards
Magnetic HDD
Cost: Medium
Capacity: High
Durability: Medium
Reliability: Medium
Portability: Medium
Speed: Medium
\
\
Capacity: High
Durability: Medium
Reliability: Medium
Portability: Medium
Speed: Medium
\
\

8
New cards
SSD
Cost: High
Capacity: Medium
Durability: High
Reliability: High
Portability: High
Speed: High
Capacity: Medium
Durability: High
Reliability: High
Portability: High
Speed: High

9
New cards
Optical Media
Cost: Very Low
Capacity: Very Low
Durability: Medium
Reliability: Low
Portability: Very High
Speed: Slow
Capacity: Very Low
Durability: Medium
Reliability: Low
Portability: Very High
Speed: Slow

10
New cards
MAGNETIC TAPE DRIVES definition
* Coated @@plastic@@ in a magnetic layer (iron oxide)
* Data is written to the tape using a read/write head in a serial sequence and is read in serial order
* Data is written to the tape using a read/write head in a serial sequence and is read in serial order
11
New cards
MAGNETIC TAPE DRIVES uses
\
* Batch processing applications like bills
* Backup for a large amount of data
* Archiving large amounts of data
* Batch processing applications like bills
* Backup for a large amount of data
* Archiving large amounts of data
12
New cards
MAGNETIC TAPE DRIVES + & -
__**Advantage**__
* Inexpensive
* Don’t damage easily
* Huge data capacity
* Data transfer rate fast
__**Disadvantage**__
* Data access time is slow
* More than one tape is needed to update the master
* They are affected by magnetic fields
* Inexpensive
* Don’t damage easily
* Huge data capacity
* Data transfer rate fast
__**Disadvantage**__
* Data access time is slow
* More than one tape is needed to update the master
* They are affected by magnetic fields
13
New cards
HARD DISK DRIVES (HDD) definition
* Platter is made up of @@glass or aluminium@@ and coated in iron oxide.
* An @@actuator@@ triggers the @@arm to move the head@@ to read/write data on the platter
* Data on the platter is stored in tracks, tracks are grouped on sectors
* An @@actuator@@ triggers the @@arm to move the head@@ to read/write data on the platter
* Data on the platter is stored in tracks, tracks are grouped on sectors
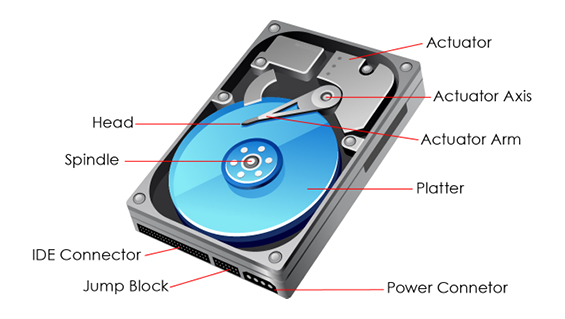
14
New cards
HARD DISK DRIVES (HDD) uses
\
* Store operating system
* Store application software
* Used in real-time systems like robots
* Used in file servers
* Store operating system
* Store application software
* Used in real-time systems like robots
* Used in file servers
15
New cards
HARD DISK DRIVES (HDD) + & -
__**Advantage**__
* Fast data transfer rate and fast access time to data
* Large memory capacity
__**Disadvantage**__
* Can be easily damaged from incorrect shutdown
* Many moving parts can affect reliability
* Read/write can be noisy because of the moving parts
* Fast data transfer rate and fast access time to data
* Large memory capacity
__**Disadvantage**__
* Can be easily damaged from incorrect shutdown
* Many moving parts can affect reliability
* Read/write can be noisy because of the moving parts
16
New cards
OPTICAL MEDIA (CD & DVD) definition
* CD & DVD are Optical Media that are read/written from Optical Storage Media
* Uses a red laser light to burn data onto the surface of the disk
* DVD uses dual-layering.
* A disc that is @@“RW” means you can erase and then reuse@@ the rewritable disc by burning data into it again.
* A disk that is only @@R means we can burn data to it only once.@@ For example CD-R, DVD-RW
* A disk that has only ROM to it means we cannot write any data onto it. We can only read the data on it. Example: DVD-ROM
* Uses a red laser light to burn data onto the surface of the disk
* DVD uses dual-layering.
* A disc that is @@“RW” means you can erase and then reuse@@ the rewritable disc by burning data into it again.
* A disk that is only @@R means we can burn data to it only once.@@ For example CD-R, DVD-RW
* A disk that has only ROM to it means we cannot write any data onto it. We can only read the data on it. Example: DVD-ROM
17
New cards
OPTICAL MEDIA (CD & DVD) uses
__**CD-R & DVD-R**__
* Used when recording at home music or films
* Stores data for later use
__**CD-RW & DVD-RW**__
* Used to record television program (can be done over and over again)
* Used in CCTV system
* Used for backup
* Used when recording at home music or films
* Stores data for later use
__**CD-RW & DVD-RW**__
* Used to record television program (can be done over and over again)
* Used in CCTV system
* Used for backup
18
New cards
OPTICAL MEDIA (CD & DVD) + & -
__**Advantage**__
* Cheaper medium than RW
* Behaves like ROM
* Can be written more than once
* Can use different file formats
* More useful than R optical drives
__**Disadvantage**__
* Can only be recorded once
* Not all devices can read –R
* It is expensive
* Possible to accidentally override data on the media.
* Cheaper medium than RW
* Behaves like ROM
* Can be written more than once
* Can use different file formats
* More useful than R optical drives
__**Disadvantage**__
* Can only be recorded once
* Not all devices can read –R
* It is expensive
* Possible to accidentally override data on the media.
19
New cards
OPTICAL MEDIA (Blu-ray Disk) definition
* Uses a Blu-ray optical storage device to read/write data to disc that uses a blue laser to burn data to disc.
* Stores up to @@5 times more data than a normal DVD@@
* Comes with an @@automatic encryption@@ which helps to prevent data
* Data transfer is @@36Mbps compare to DVD which is 10Mbps@@
* A @@dual layer Blu-ray can store up to 50GB (20hrs) of HD movie@@
* Stores up to @@5 times more data than a normal DVD@@
* Comes with an @@automatic encryption@@ which helps to prevent data
* Data transfer is @@36Mbps compare to DVD which is 10Mbps@@
* A @@dual layer Blu-ray can store up to 50GB (20hrs) of HD movie@@
20
New cards
OPTICAL MEDIA (Blu-ray Disk) uses
* Home video @@consoles@@
* Storing and playing back @@high definition movies@@
* Used for storage or backup of hard disk drives
* Camcorders use it to record and store movies
* Storing and playing back @@high definition movies@@
* Used for storage or backup of hard disk drives
* Camcorders use it to record and store movies
21
New cards
OPTICAL MEDIA (Blu-ray Disk) +& -
__**Advantage**__
* Very large storage capacity
* Very fast data transfer
* Greater data access speed than most optical devices
* Comes with automatic secure encryption which helps prevent privacy and copyright infringement
__**Disadvantage**__
* Relatively expensive technology and disc
* Encryption problems
* Introduction of HD DVD players has reduce the demand for Blu-ray
* Very large storage capacity
* Very fast data transfer
* Greater data access speed than most optical devices
* Comes with automatic secure encryption which helps prevent privacy and copyright infringement
__**Disadvantage**__
* Relatively expensive technology and disc
* Encryption problems
* Introduction of HD DVD players has reduce the demand for Blu-ray
22
New cards
Solid State Drive (SSD) do not use?
* Actuators
* No magnetic or moving parts, removing latency
•Flash memory or flash drives are most used type of SSD
•NAND is a type of flash memory that reduces erase and write times lower than hard drive, and requires less chip area per cell, which allows for more storage density and lower cost
* No magnetic or moving parts, removing latency
•Flash memory or flash drives are most used type of SSD
•NAND is a type of flash memory that reduces erase and write times lower than hard drive, and requires less chip area per cell, which allows for more storage density and lower cost
23
New cards
How is data stored on SSD drives?
* Data is stored by controlling the movements of electrons within NAND chips. The positive charge on the control gate attracts the electrons from the channel into the floating gate, where they become trapped by the oxide layer that surrounds the floating gate
* Data will be used whether or not the flash device has power, making the SSD non-volatile and rewritable
* SSD must be used once a year
* Data will be used whether or not the flash device has power, making the SSD non-volatile and rewritable
* SSD must be used once a year
24
New cards
HDD vs SSD
__**HDD**__
Speed: slower
Lifespan: longer
Cost: cheaper
Mechanics:
Durability: fragile
Best for: storing extra data ex. movies, photos, documents
__**SSD**__
Speed: slower
Lifespan: longer
Cost: cheaper
Mechanics:
Durability: fragile
Best for: storing extra data ex. movies, photos, documents
Speed: slower
Lifespan: longer
Cost: cheaper
Mechanics:
Durability: fragile
Best for: storing extra data ex. movies, photos, documents
__**SSD**__
Speed: slower
Lifespan: longer
Cost: cheaper
Mechanics:
Durability: fragile
Best for: storing extra data ex. movies, photos, documents
25
New cards
\
Solid State Drive (SSD) uses
Solid State Drive (SSD) uses
Can be used to perform the same functions as HDD including running applications and operating systems. They store files also. Mostly used in modern laptops and smart devices like phones and tablets
26
New cards
Solid State Drive (SSD) +
* More reliable
* Have much faster speed
* Low power consumption
* Cooler than HDD
* Faster data access rate
* Faster data transfer rate
* Have much faster speed
* Low power consumption
* Cooler than HDD
* Faster data access rate
* Faster data transfer rate
27
New cards
Solid State Drive (SSD) -
Most SSD can accept write up to 20GB per day over a 3 year period (SSD Endurance). It means, services that need more write capacity like servers and cloud storage are not recommended to use SSD
28
New cards
Pen Drive (USB Flash Drive, Memory Stick)1.
Connect to the computer through USB port.
Used for smaller backups and transfer of files. Note: All solid state devices are flash drives
Can be used as a security device to prevent software piracy (Dongle)
Used for smaller backups and transfer of files. Note: All solid state devices are flash drives
Can be used as a security device to prevent software piracy (Dongle)
29
New cards
Pen Drive (USB Flash Drive, Memory Stick)2.
* Very compact and portable
* Very robust (strong)
* Does not require additional software to work on devices
* They are not effected by magnetic field
* Very robust (strong)
* Does not require additional software to work on devices
* They are not effected by magnetic field
30
New cards
\
\
Pen Drive (USB Flash Drive, Memory Stick)3.
\
Pen Drive (USB Flash Drive, Memory Stick)3.
* Cannot write protect the files on the drive
* Easy to lose
* Incorrect removal from a computer can cause a read/write error which can corrupt data on the drive
* Easy to lose
* Incorrect removal from a computer can cause a read/write error which can corrupt data on the drive
31
New cards
**Memory Cards +**
* SD cards – very small with high capacity. Mostly used in portable devices like phones and digital video recorders. Example MicroSD
* XD cards - design for digital cameras. Some are just card readers used with MicroSD
* CFast cards – used with high ends digital cameras. Does not need battery to access files
* Memory cards are used to store smart devices
* XD cards - design for digital cameras. Some are just card readers used with MicroSD
* CFast cards – used with high ends digital cameras. Does not need battery to access files
* Memory cards are used to store smart devices