AP Chemistry - Kahoot Questions Chapter 4
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is Beer's Law?
A = εbc
A=Ɛbc, what is b?
path length or cell width
What mass of NH4Cl is needed to prepare 500.0 mL of a 0.187 M solution.
5.00 g
How much concentrated 12M hydrochloric acid is needed to prepare 100. mL of a 2.0 M solution?
17 mL
What is the pOH of a solution in which [H3O+] = 2.6 x 10-6 M?
8.41
In a Beer's law graph, what does the slope of the linear relationship equal if b = 1.0 cm?
molar absorptivity
What is the M of 100 mL of NaOH sol'n if it takes 20.0 mL of 2.5 M H3PO4 to neutralize it?
1.5M
What is a limiting reactant?
reactant that determines the amount of product formed
How do you calculate percent yield?
experimental yield/theoretical yield x 100
The theoretical yield of a chemical reaction is
the max. amount of product formed ideally
Actual yield must be determined by:
experimentation
What is the molarity of 2 mol solute dissolved in 500 mL solvent?
4 M
To prepare a solution with specific molarity, which container should be used to fill and mix to the final volume?
volumetric flask
Which term describes a stepwise dilution of a substance in solution?
Serial dilution
The [H3O+] in a solution with pH 2.36.
4.4 X 10-3 M
The pH of a solution at 25°C in which [OH-] = 3.9 X 10-5 M is:
9.59
What is the Acid-Base titration equation?
#H+ x MA x VA = MB x VB x #OH-
The point during a titration where the indicator's color change is noticed.
end point
The equivalence point is:
When stoichiometric amounts of acid and base have reacted
The equivalence point is where.....
moles acid = moles base
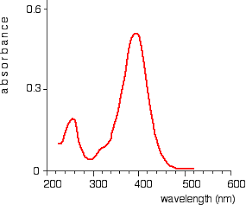
Optimum wavelength to use for spectrophotometry here?
400 nm
Beer's Law says
the absorbance of a colored solution is related to its concentration