IRM - Basic Topography of the Upper Respiratory Tract (AP01)
1/64
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What are the functions of the nose?
Respiration
Olfaction
Filtration of dust
Humidification of inspired air
Reception and elimination of secretions
Warms inspired air
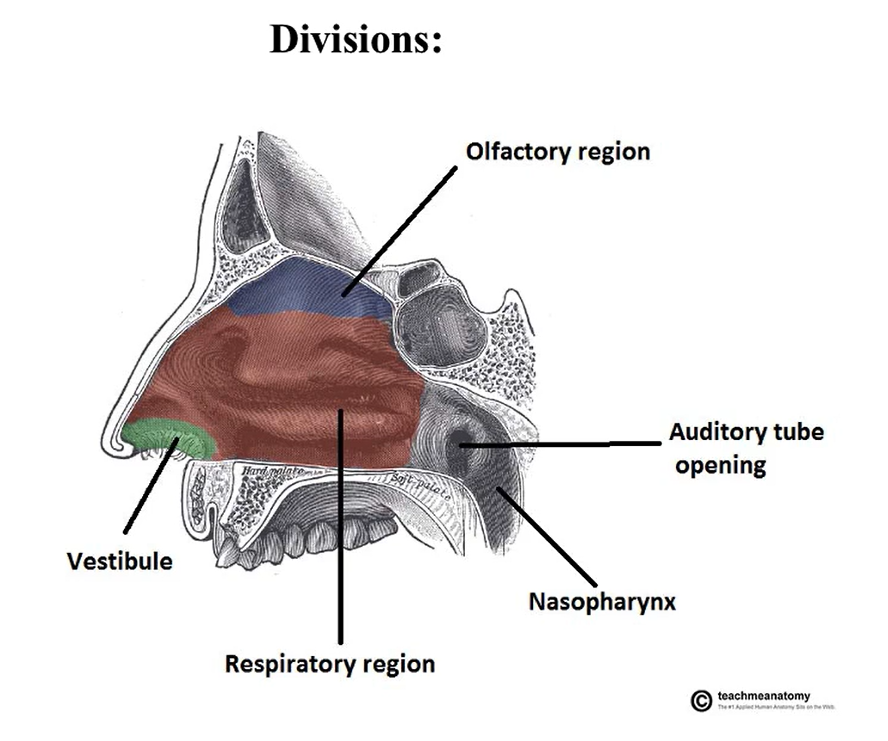
What is the basic shape of the nasal cavity?
Divided into two chambers (left and right) by the nasal septum, which is a medial wall.
What helps to slow the air down in the nasal cavity in order for it to get warmed and filtered?
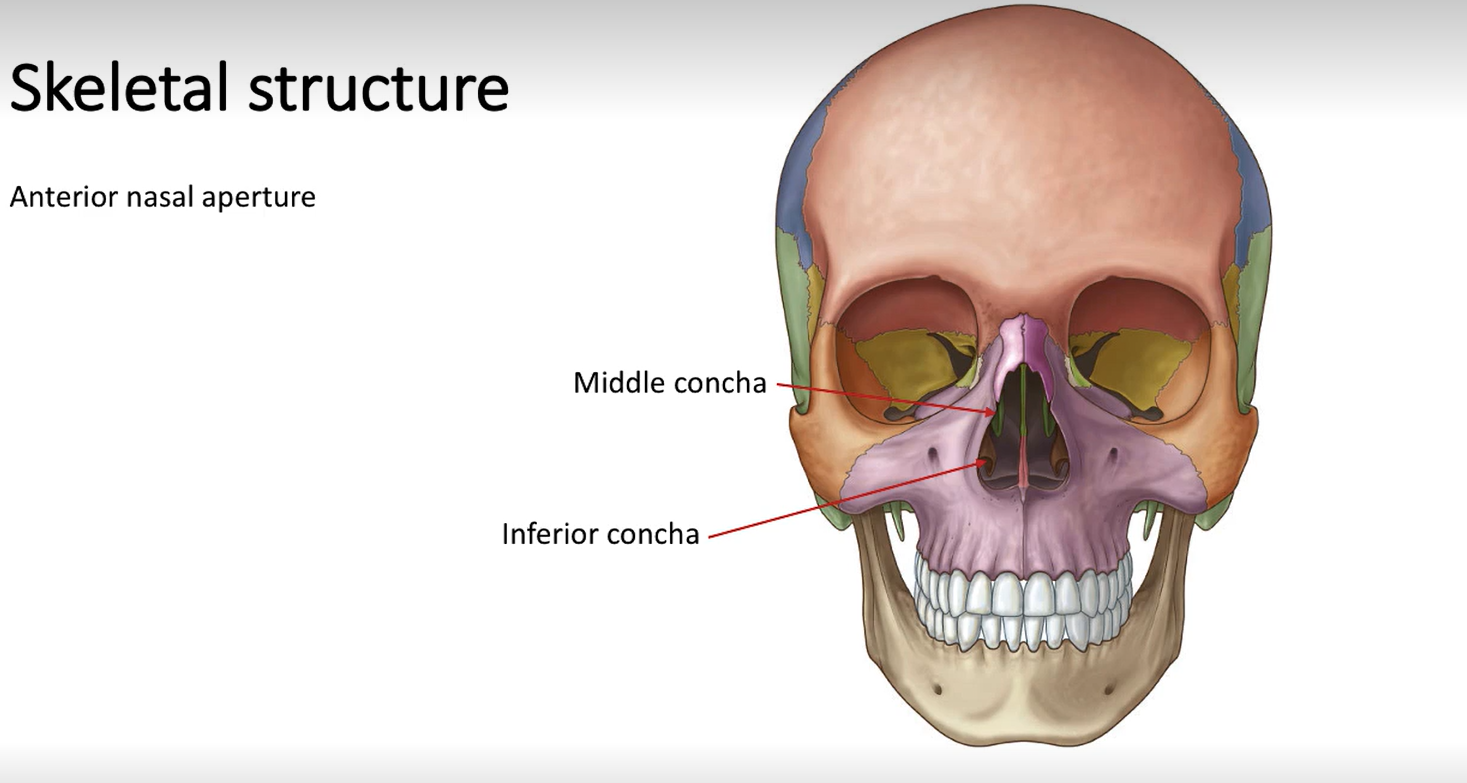
Turbinates/conchae: Superior, middle and inferior conchae
What are the associated spaces underneath the conchae?
Superior, middle and inferior meatuses
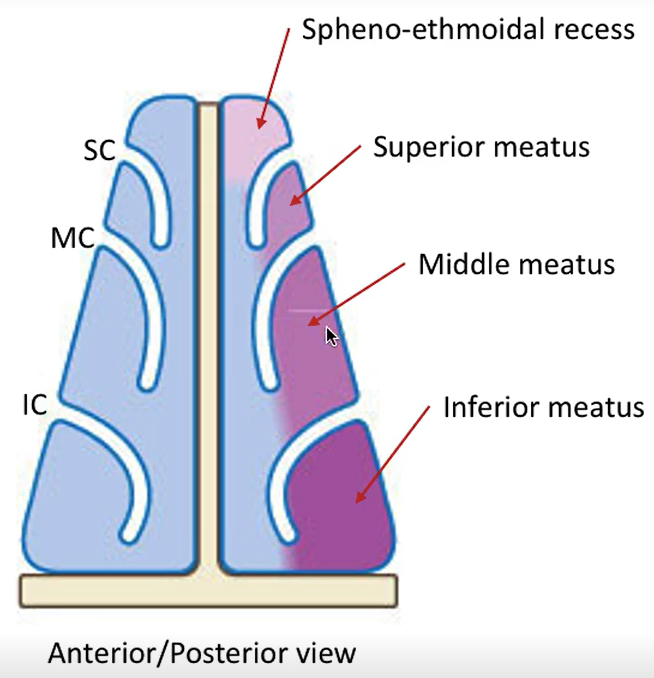
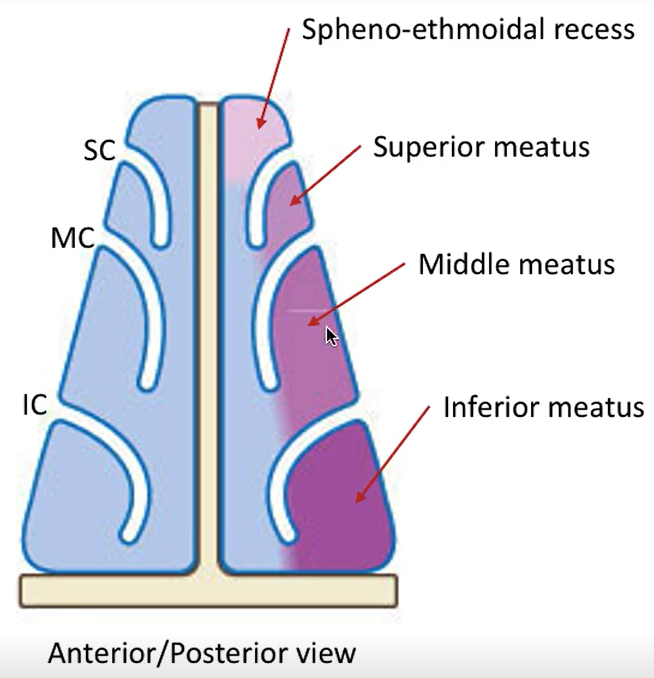
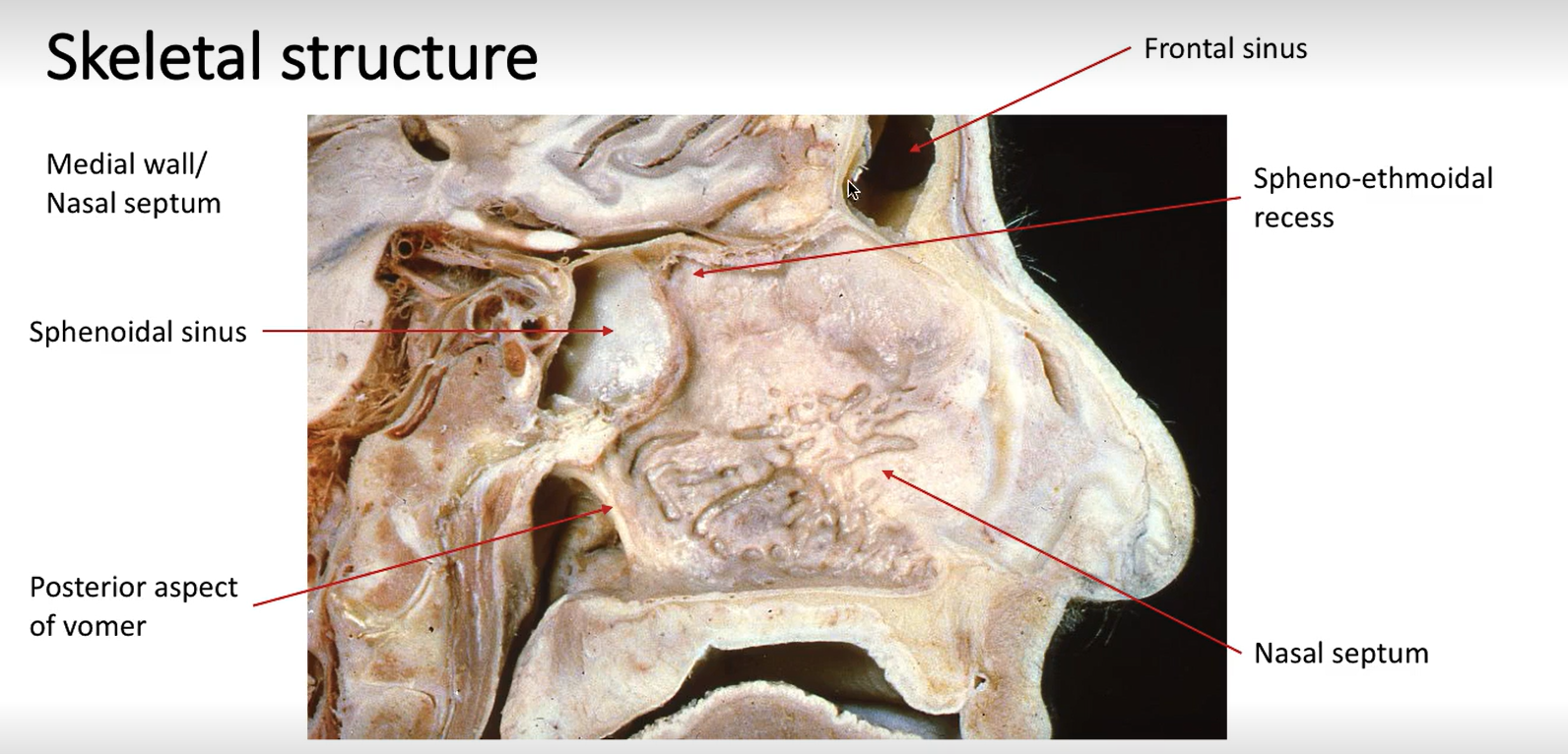
What is the space at the top of the nasal cavity?
Spheno-ethmoidal recess
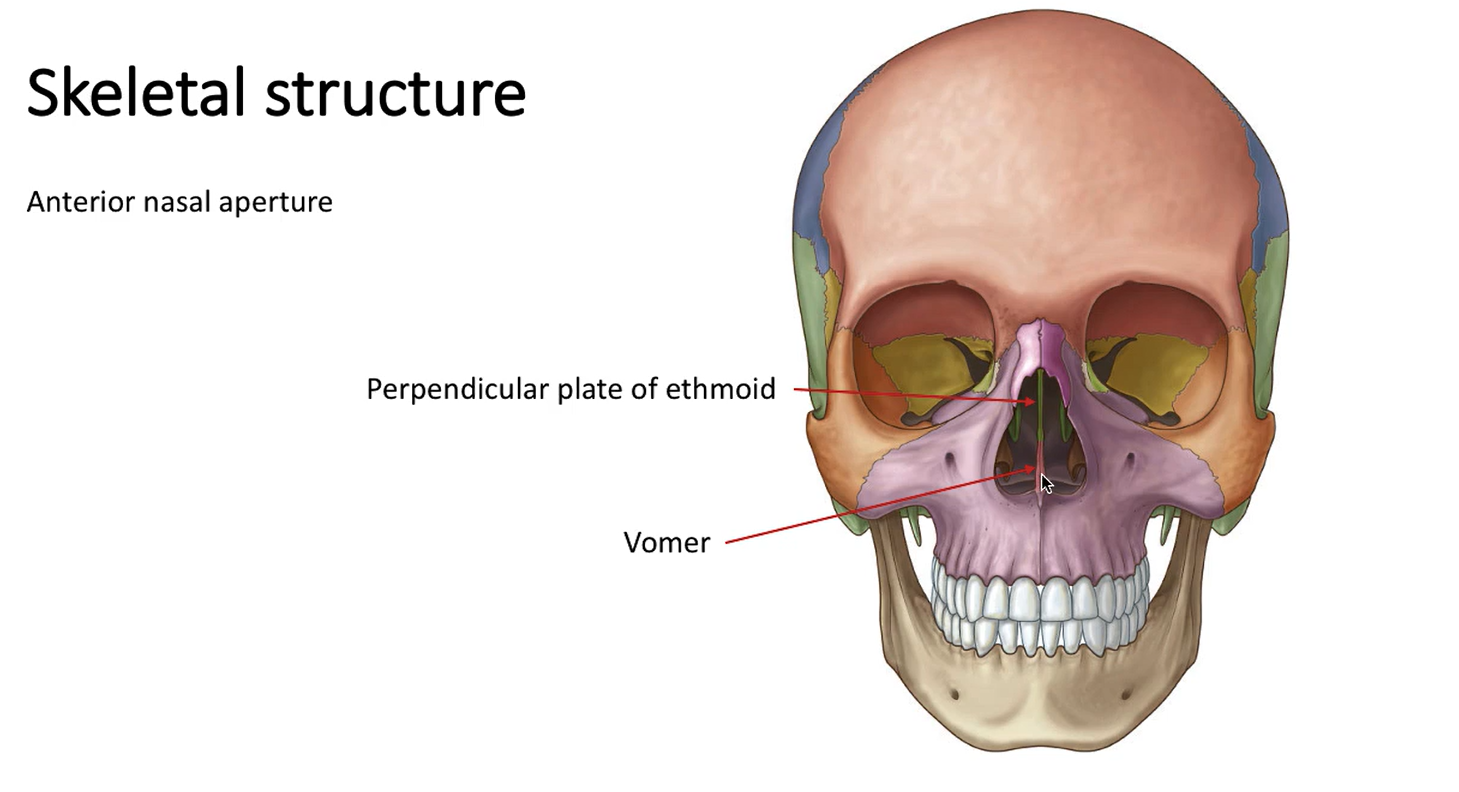
What is the opening at the front of the nasal cavity called?
Anterior nasal aperture
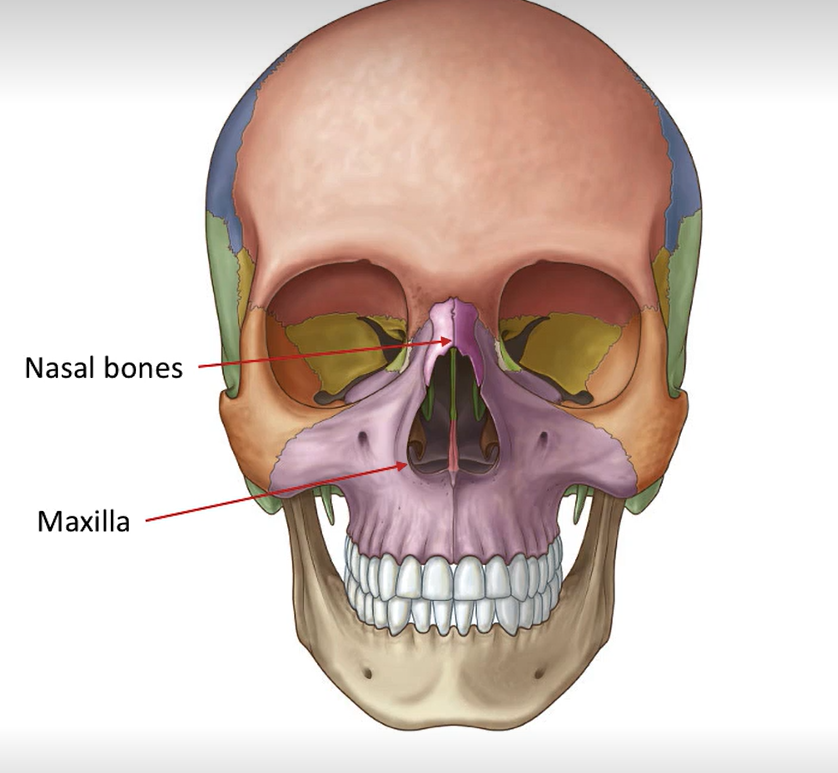
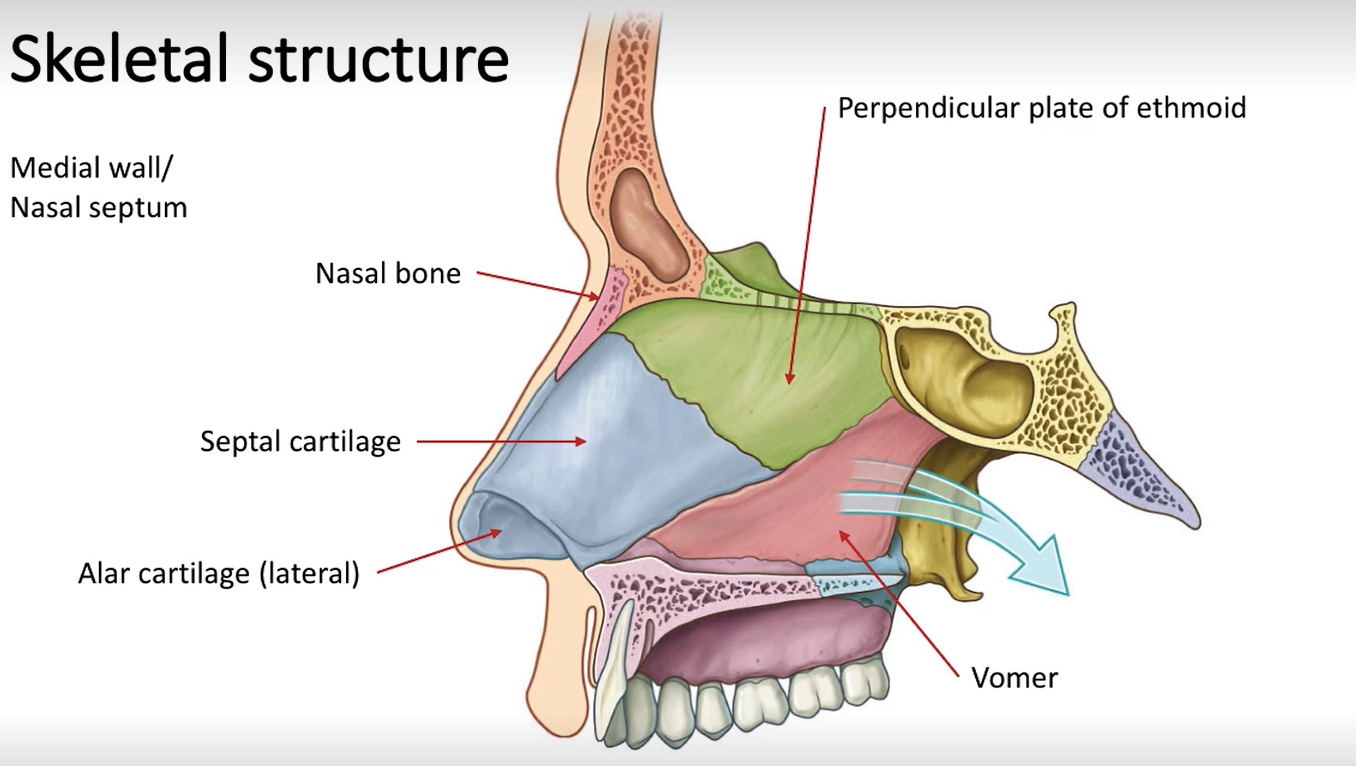
Where are the maxilla and nasal bones located?
Where are the perpendicular plate of ethmoid and vomer found?
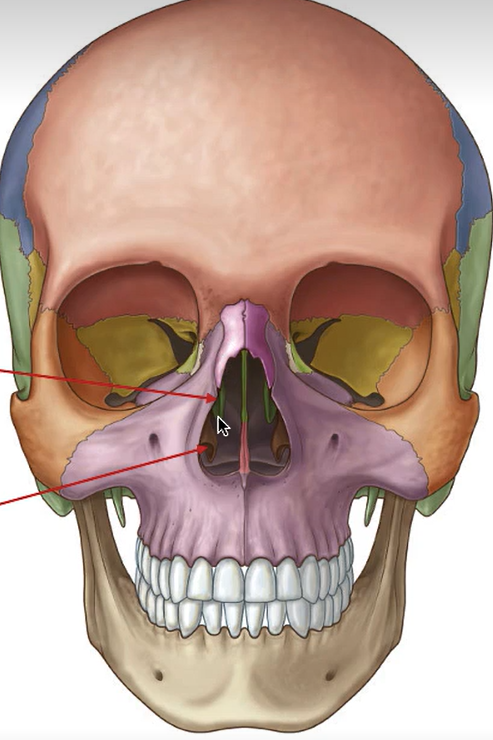
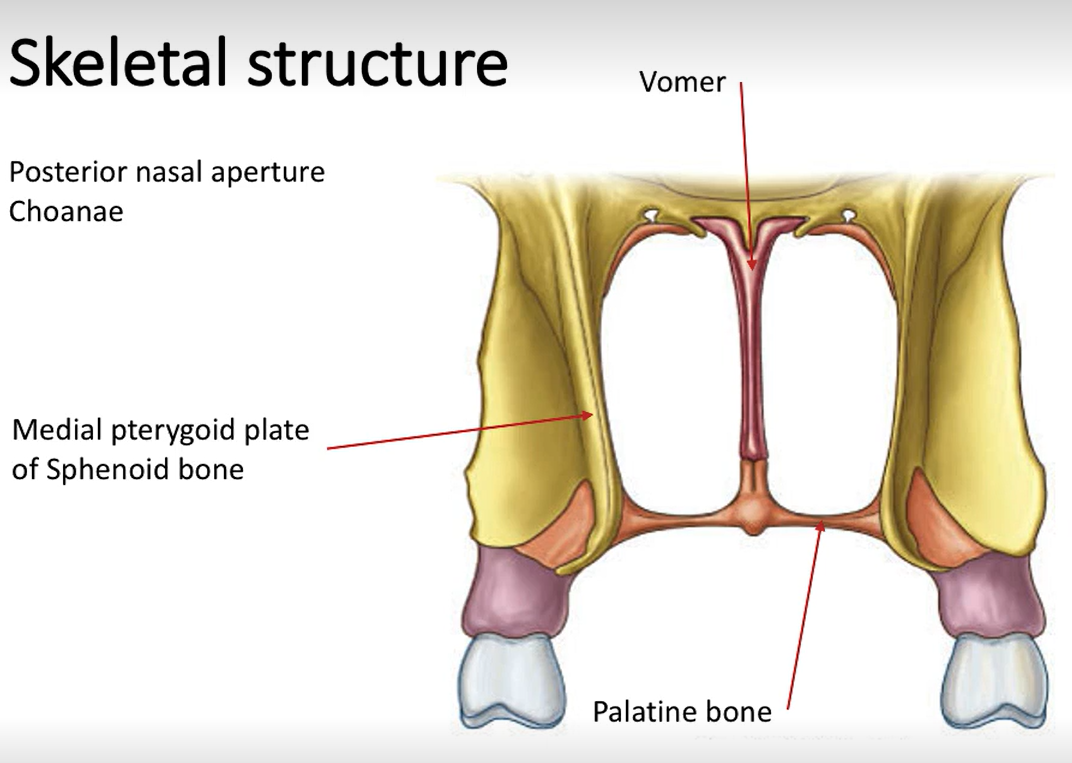
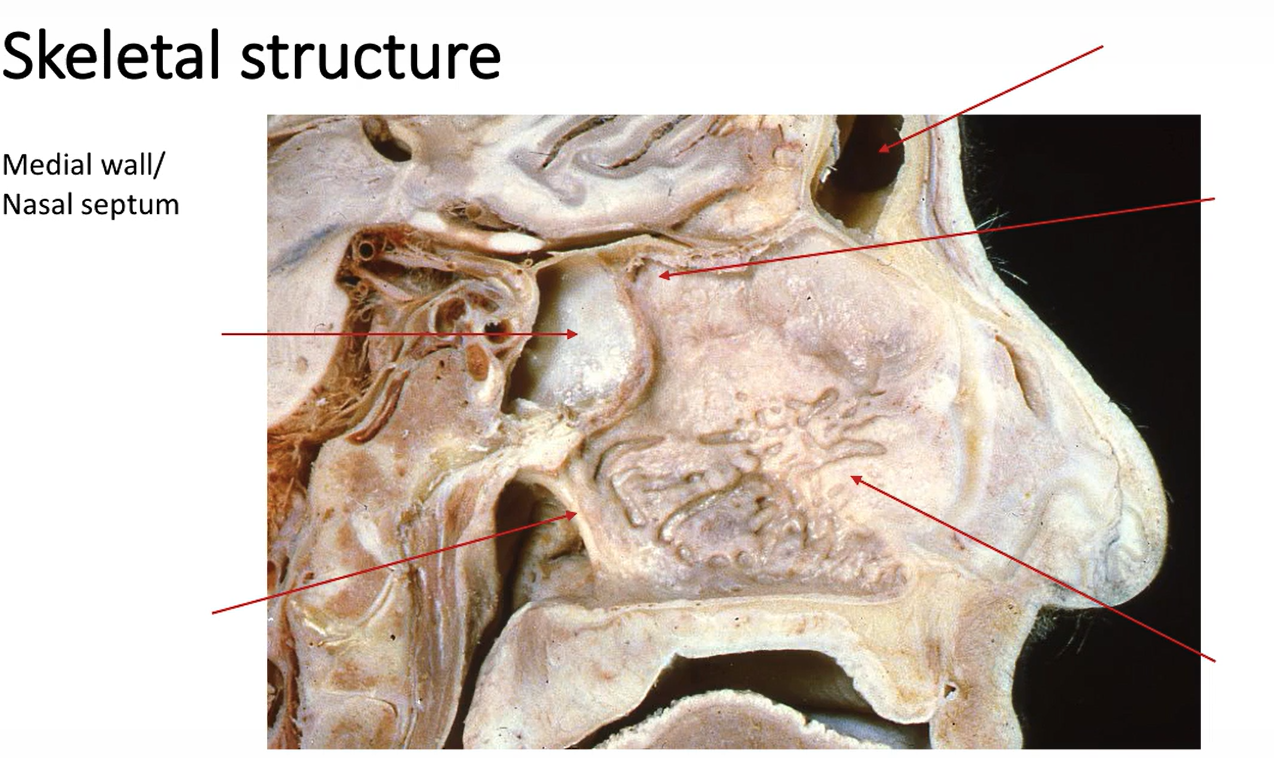
Label these arrows.
Label these arrows.
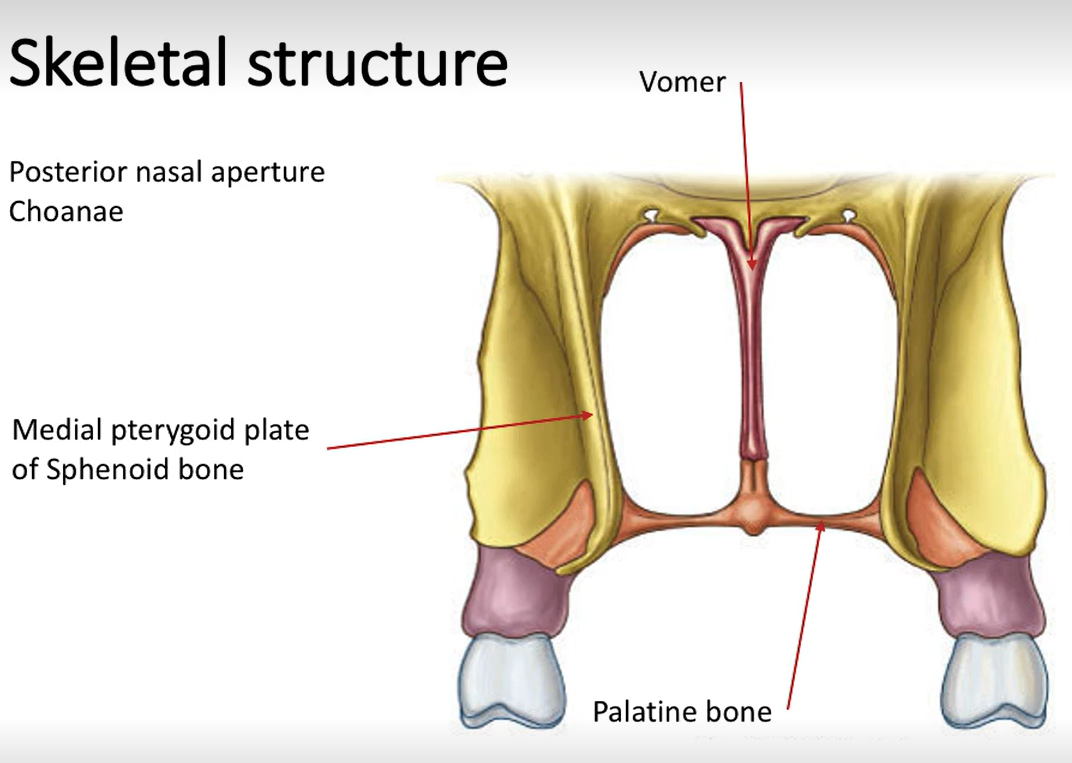
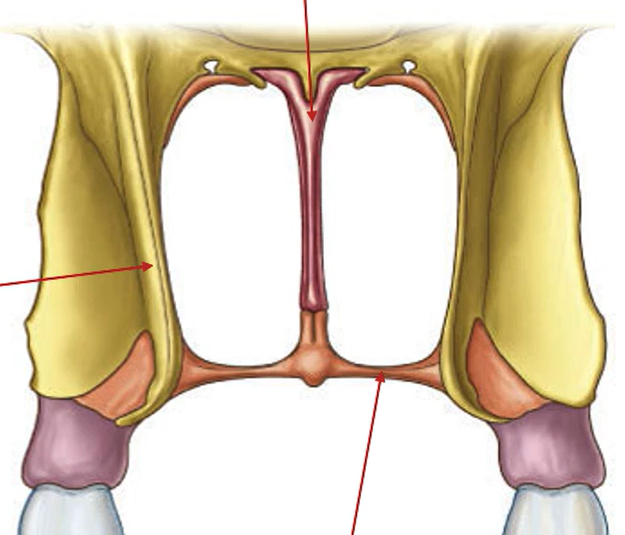
Where are the choanae located?
At the posterior nasal aperture.
Label these arrows.
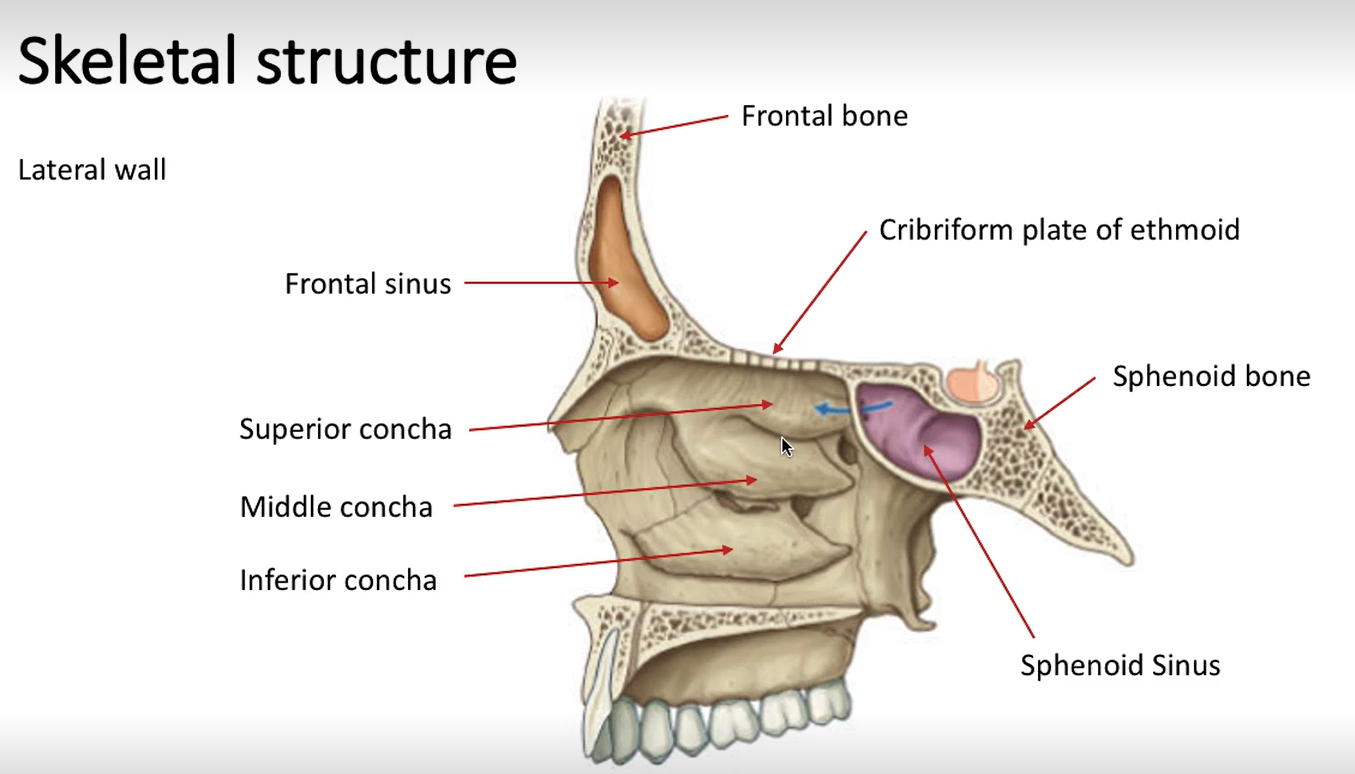
Label these arrows.
Label these arrows.
What are the divisions of the nasal cavity?
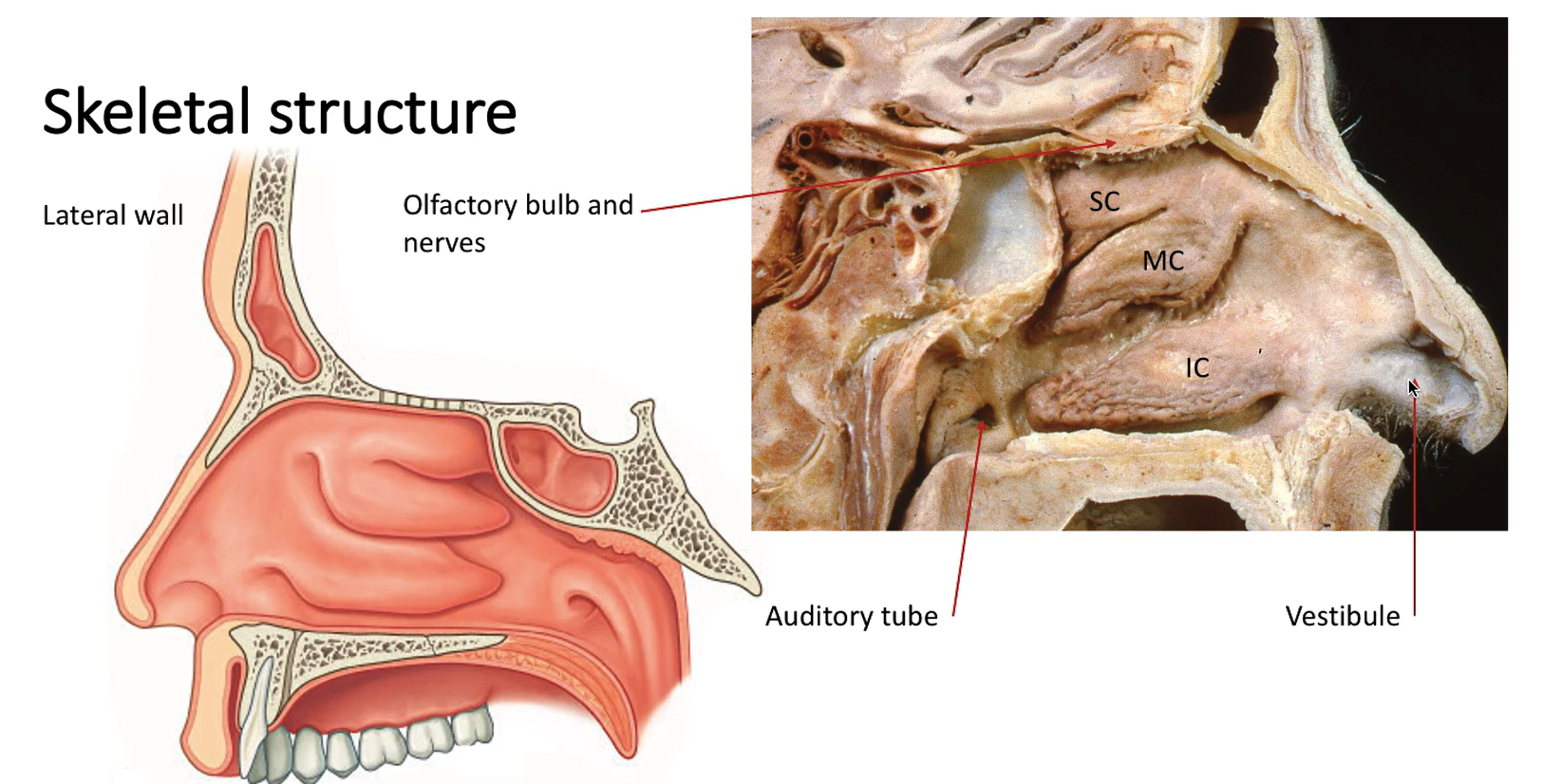
Where is the olfactory bulb/nerves, auditory tube and vestibule located in a cadaver?
What are the subdivisions of the pharynx? (from superior to inferior)
Nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx
What is the location of the nasopharynx?
Posterior to nasal cavity
Superior to soft palate
What are the contents of the nasopharynx?
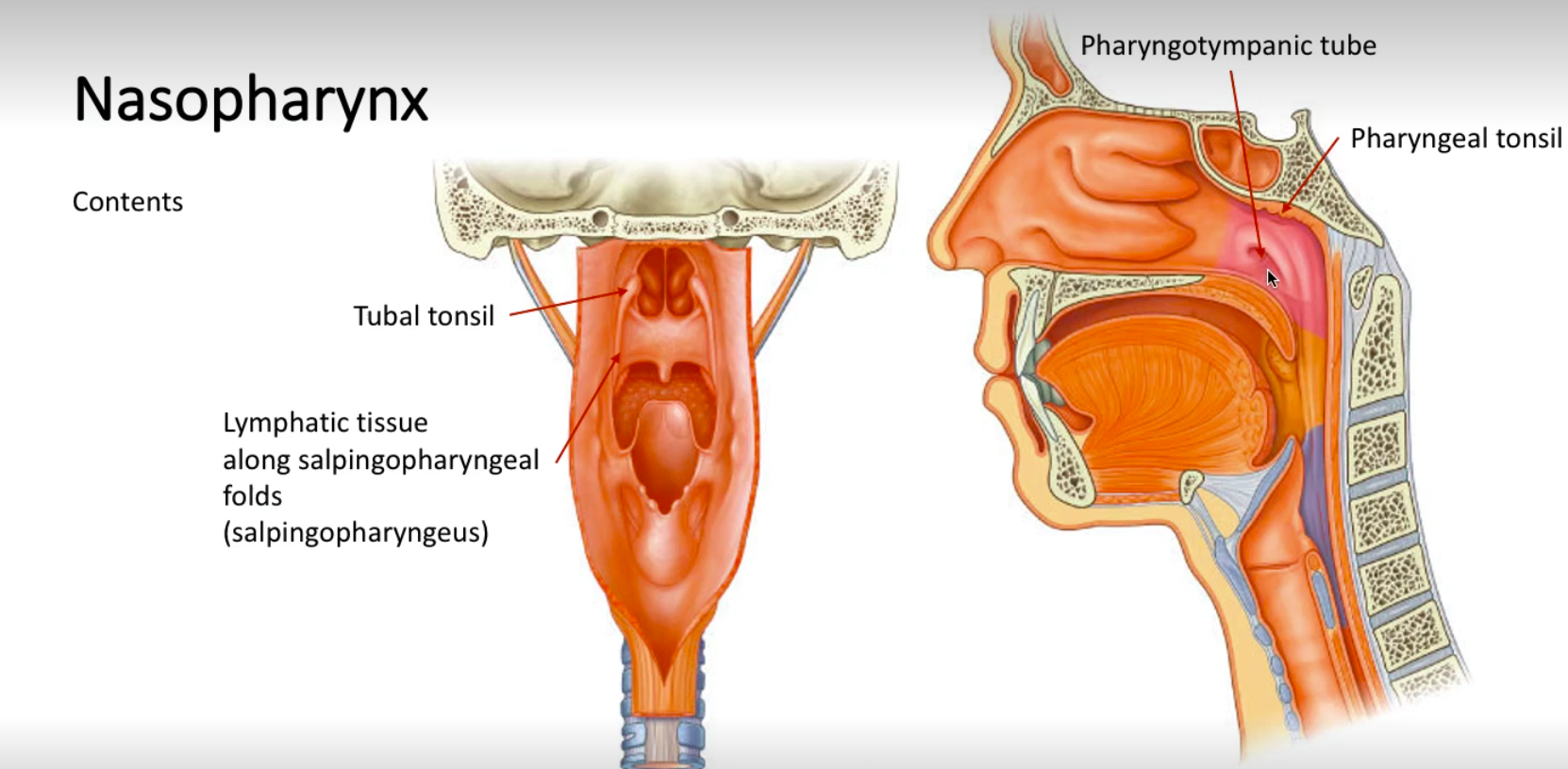
What is the function of the pharyngotymapnic tubes (eustachian tubes)?
Connects the middle ear cavity to the nasopharynx.
Responsible for equalising air pressure between atmosphere and middle ear.
Tensor veli palatini muscles contract when swallowing or yawning, causing it to open and allow air to enter.
What is the location of the oropharynx?
Inferior to soft palate
Superior to base of tongue
Medial to palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches
Posterior to the oral cavity
What is Waldeyer’s ring?
The ring of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx.
What are the components of Waldeyer’s ring?
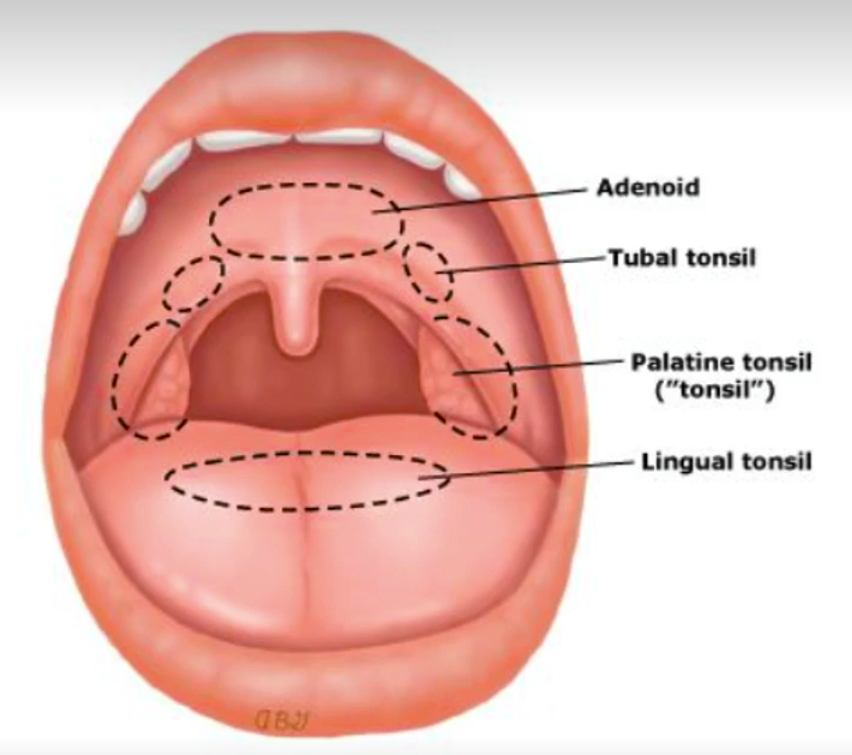
What are the functions of Waldeyer’s ring?
Responsible for blocking and filtering air going through the ear, nose, etc.
Part of the immune system
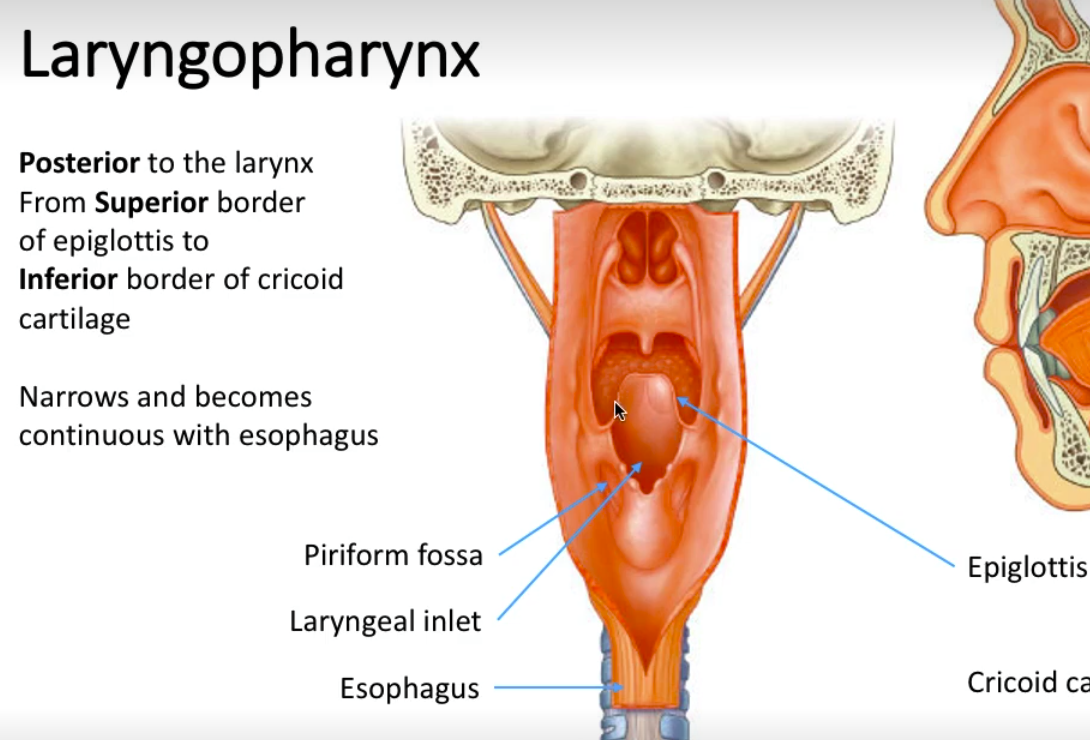
What is the location of the laryngopharynx?
Posterior to the larynx
From superior border of epiglottis to inferior border of cricoid cartilage
It narrows and becomes continuous with esophagus
How does air reach the airways in the laryngopharynx?
Via the laryngeal inlet
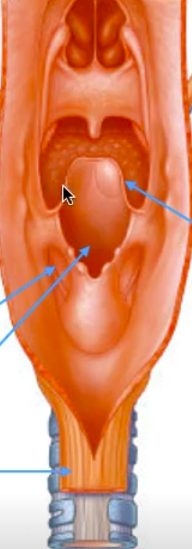
Label these arrows.
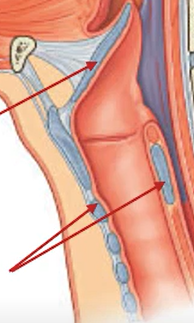
Label these arrows.
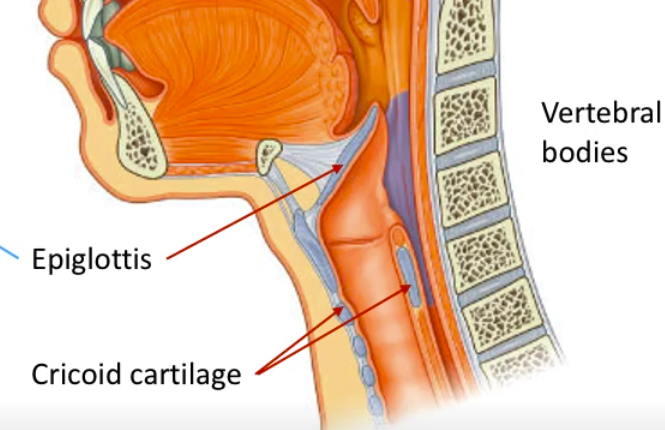
What are the three constrictor muscles of the pharynx?
Superior, middle and inferior constrictors
Where are the pharyngeal tubercle and the pharyngeal raphe located?
What does the superior constrictor muscle attach to?
Superiorly: pharyngeal tubercle (occipital bone), base of skull via pharyngobasilar fascia
Posteriorly: pharyngeal raphe
Anteriorly: pterygoid hamulus, pterygomandibular raphe, mandible and side of tongue
What does the middle constrictor muscle attach to?
Posteriorly: pharyngeal raphe
Anteriorly: inferior end of stylohyoid ligament, greater and lesser horns of hyoid bone
What does the inferior constrictor muscle attach to?
Posteriorly: pharyngeal raphe
Encircles junction between pharynx and oesophagus
Anteriorly: oblique line of thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage
What is the motor innervation for constrictor muscles of the pharynx?
Innervation by the pharyngeal plexus, which is a combination of branches of mainly the vagus nerve (CN X) as well as the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).
What are the longitudinal muscles of the pharynx?
Stylopharyngeus, salpingopharyngeus and palatopharyngeus
Where are the longitudinal muscles of the pharynx located?
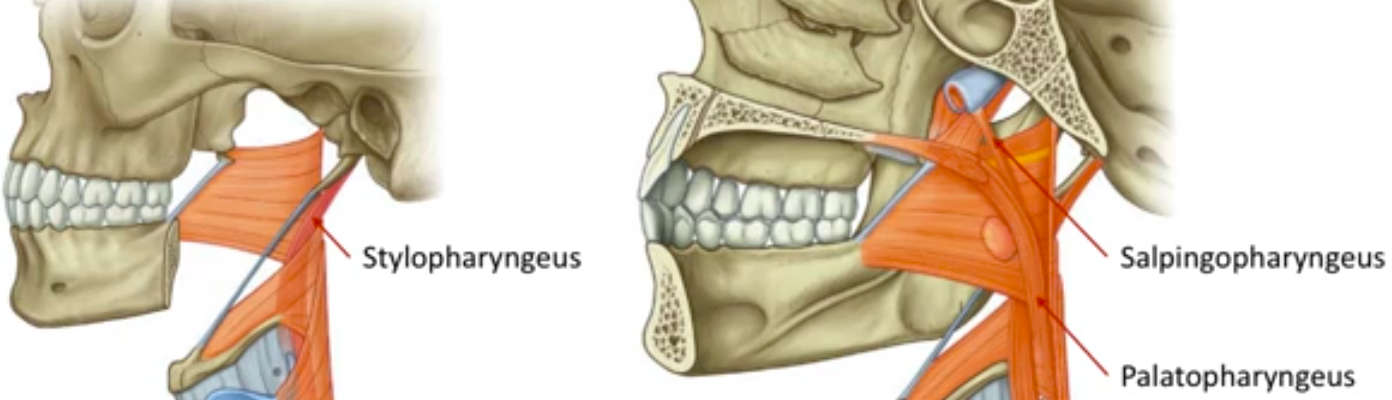
How are the longitudinal muscles of the pharynx innervated?
Stylopharyngeus innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).
Salpingopharyngeus and palatopharyngeus are innervated by pharyngeal plexus, in particular the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve.
What is the stylopharyngeus associated with?
Runs from styloid process to thyroid cartilage
What is the salpingopharyngeus associated with?
Runs from the cartilage of pharyngotympanic tube and unites with palatopharyngeus
What is the palatopharyngeus associated with?
Runs from hard plate and palatine aponeurosis to the thyroid cartilage and oesophagus.
Where are nosebleeds likely to occur from?
Kiesselbach’s area, which contains anastomosing arteries.
What are the branches of the internal carotid artery?
Anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries
What are the branches of the external carotid artery?
Sphenopalatine artery
Greater palatine artery
Superior labial artery
Maxillary artery
What are the sites of venous drainage from the nasal cavity?
Anteriorly to facial vein
Posteriorly to pterygoid venous plexus
Superiorly to cavernous sinus
What provides general sensation to the nasal cavity?
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V):
Anterior and superior part of nasal cavity - sensation supplied by ophthalmic (V1) division
Posterior and inferior part of nasal cavity - sensation supplied by maxillary (V2) division
What is the function of the sinuses in general at the nasal cavity?
To reduce the weightening of the skull
What are all the sinuses of the cavity lined with?
Mucosa
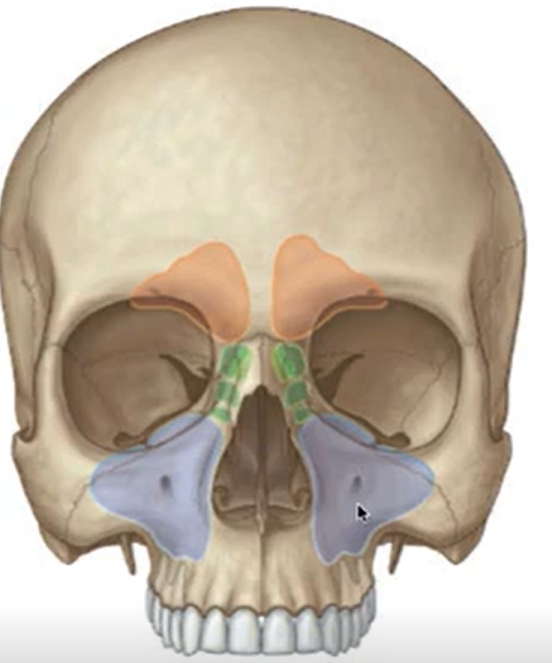
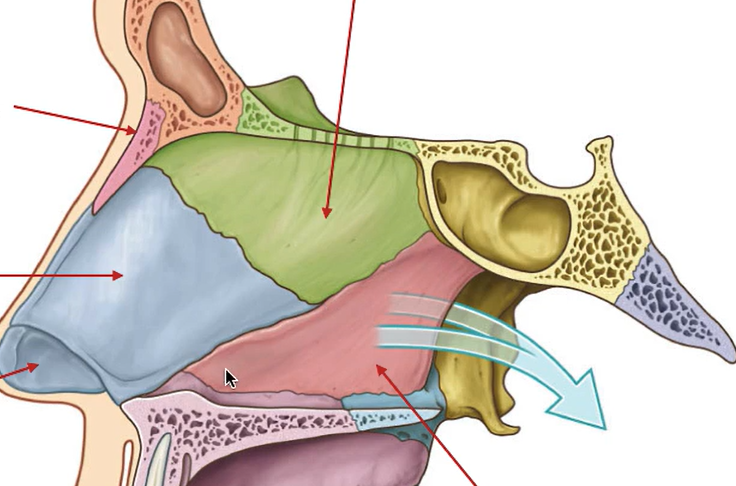
What are the three sinuses shown here?
Orange - frontal sinus
Green - ethmoidal sinus (air cells)
Blue - maxillary sinus
What does the spheno-ethmoidal recess do?
It drains posterior ethmoid cells and sphenoidal sinuses into superior meatus.
What does the middle meatus do?
It drains the middle ethmoidal cells, maxillary sinus and frontal sinus.
What does the inferior meatus do?
It drains the nasolacrimal duct, which drains tears from the ocular surface.
What bone(s) make up the floor of the nasal cavities?
Palatine process of the maxilla
What bone(s) make up the roof of the nasal cavities?
Ethmoid bone and sphenoid bone
What bone(s) make up the lateral and medial walls of the nasal cavities?
Medial - perpendicular plate of ethmoid, vomer
Lateral - lacrimal bone and frontal process of maxilla
What is the significance of the paranasal sinuses in relation to the respiratory system?
They are lined with mucosal cells which produce and secrete mucus.
They also drain air into the nasal cavities.
Why must microorganisms and particulates be removed from the inspired air and how is this achieved?
What fluid can leave the nose after trauma to the roof of the nasal cavity?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
What clinical signs might you find with a base of skull fracture?
Infections
Seizures
Bleeding around the brain
What are some initial treatments that can reduce bleeding?
Pinching the nose
What leads to sinusitis?
Infection of the paranasal sinus epithelium and a subsequent build-up of infected material.
Which sinus is particularly susceptible to sinusitis and why?
Maxillary sinus as it is the only sinus that is located inferior to the nose.
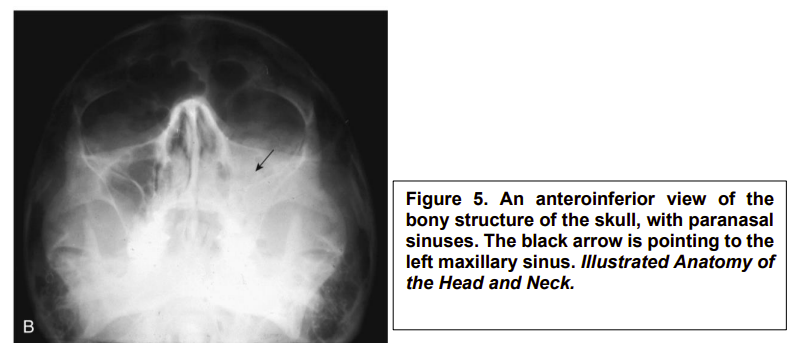
What imaging technique has been used here?
X-ray
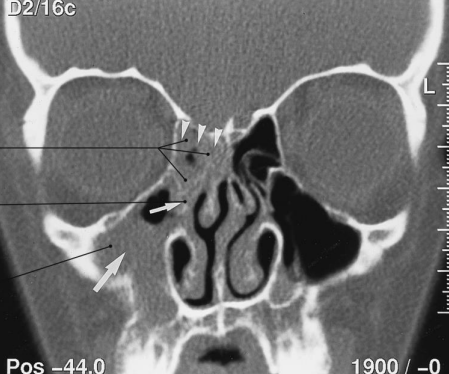
What imaging technique has been used here?
CT scan
What specific tonsillar tissues are located in the nasopharynx?
Adenoid tonsils and tubal tonsils.
What is an adenoidectomy? When might it be performed?
Surgical removal of adenoid tonsils.
Performed in cases of recurring sinusitis.