Understanding Intellectual Disability and Its Implications
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Intellectual Disability
Significant limitations in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior.
Rosa's Law
2010 law reducing stigma around intellectual disability.
IDEA Definition
Subaverage intellectual functioning affecting educational performance.
Onset Criteria
Diagnosis must occur before age 18.
Intellectual Functioning
Ability to reason, plan, and problem-solve.
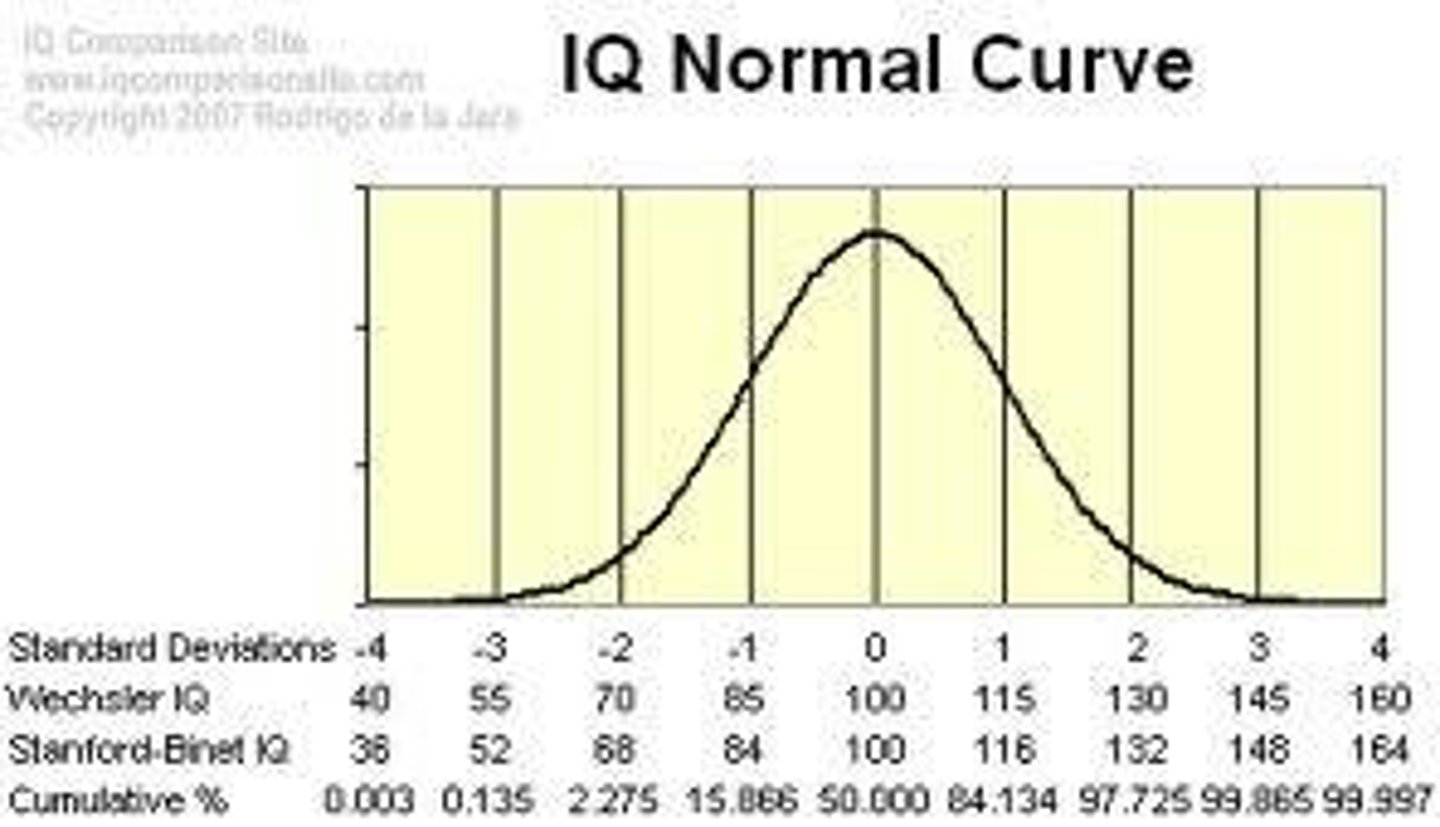
IQ Measurement
Scores 2 standard deviations below mean indicate disability.
Adaptive Behavior
Skills needed for everyday functioning and independence.
Conceptual Skills
Communication, money management, and time understanding.
Social Skills
Interpersonal skills, rule following, and naivete.
Practical Skills
Activities of daily living and health management.
Global Developmental Delay
Temporary diagnosis for children under 5 years old.
Signs of Delay
Indicators of developmental issues at various ages.
Vineland Scales
Assessment tool for evaluating adaptive behavior.
AAIDD
American Association on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities.
Severity Levels
Categorization: mild, moderate, severe, profound.
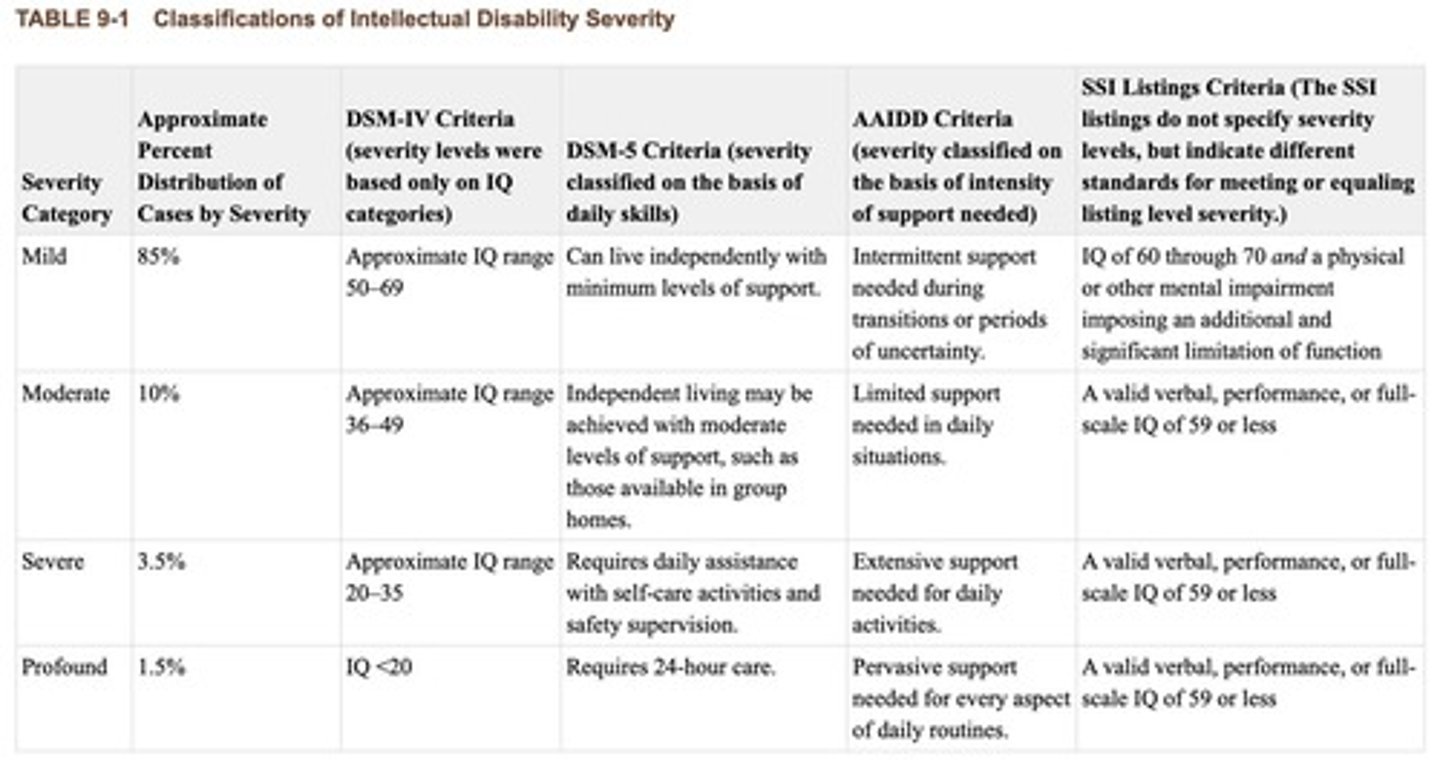
Support Levels
Intermittent, limited, extensive, pervasive support needs.
Etiology of ID
Hundreds of causes; often unknown for mild ID.
Mild ID Causes
Environmental factors like socioeconomic status and neglect.
Severe ID Causes
Biological origins with multiple associated impairments.
Genetic Disorders
Single gene disorders causing intellectual disabilities.
Down Syndrome
Trisomy 21, a common chromosomal disorder.
Prenatal Environmental Influences
Substance exposure affecting brain development.
Perinatal Influences
Mechanical birth injuries impacting brain health.
Postnatal Influences
Trauma or infections causing brain injury.
Incidence of ID
3rd largest disability category in West Virginia.
Global Prevalence
1-3% of the global population affected by ID.
Social Determinants of Health
Conditions affecting health and risk of diagnosis.
Access to Quality Health Care
Essential for identifying health issues early.
BEST Method
Multifaceted approach for high-risk infant monitoring.
Comprehensive Developmental Evaluation
Assessment involving psychologists and social workers.
IFSP/IEP
Plans addressing individual strengths for children.
Early Intervention
Critical for developing vocational skills in children.
Social and Community Support
Peer interactions influence developmental outcomes positively.
Built Environment
Physical spaces affecting community health and behaviors.
Adaptive Behavior Limitations
Skills needed for independent living assessed.
Mild Intellectual Disability (ID)
Learning challenges; may be employable with support.
Moderate Intellectual Disability (ID)
Slower language development; requires educational support.
Severe Intellectual Disability (ID)
High support needed for communication and daily tasks.
Profound Intellectual Disability (ID)
Limited communication; dependent on caregivers.
Course and Prognosis
Lifelong condition; outcomes vary by individual factors.
Life Expectancy in Mild ID
Similar to general population; generally nonprogressive.
Typical Medical Intervention
Focus on co-occurring conditions, not eliminating ID.
Behavior Management Techniques
Adapt strategies based on cognitive age.
Vocational Skills Support
Job coaches enhance independence and community living.
Recreational Skills Resources
Includes Special Olympics and Disability Action Center.
Client Factors Affected by ID
Values, beliefs, body functions, and structures impacted.
Performance Skills Impacted
Daily living skills affected by individual capabilities.
Interventions for ID
Tailored activities to support individual strengths.
Community Involvement
Encourages use of public transportation for access.
Behavioral Problems Assessment
Evaluate behaviors based on cognitive rather than age.
Psychotropic Medications
Used for mental health issues in individuals with ID.
Neuromuscular Dysfunction Treatment
Botox for spasticity in cerebral palsy cases.
Long-term Teaching
Supports skill acquisition in individuals with ID.
Socialization Importance
Participating in social experiences fosters success.
Environmental Modifications
Adjustments to support individual needs and reduce distractions.