acids, bases and buffers
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
what is a Bronsted-Lowry acid
a proton donor
Bronsted-Lowry base
proton acceptor
what are conjugate acid-base pairs
2 species that can be interconverted by transfer of a proton
what is an amphoteric substance
acts as an acid and a base
how is water an amphoteric substance
because it can accept a proton to form H30+ and act as a base or it can donate a proton to form OH- and act as an acid
conjugate acid
a base with a hydrogen ion added to it
conjugate base
an acid that has donated its hydrogen
monobasic acid
an acid with one H+ ions like HCL, CH3COOH
dibasic acid
an acid with 2 H+ ions eg H2SO4
example of a tribasic acid
H3PO4
metal carbonate + acid
salt + water + carbon dioxide
metal oxide +acid
salt + water
metal + acid
salt + hydrogen
alkali + acid
salt + water
how to calculate the acid dissociation constant, Ka
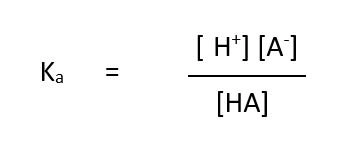
how to find pKa
-logKa
how to find Ka from pKa
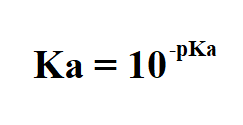
what does the value of Ka indicate
the bigger the value, the stronger the acid
what does the value of pKa indicate
the smaller the value, the stronger the acid
how to find pH
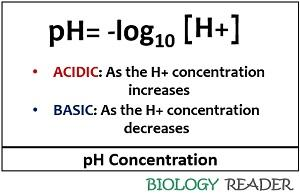
how to find H+ concentration

how to find Kw, the ionic product of water
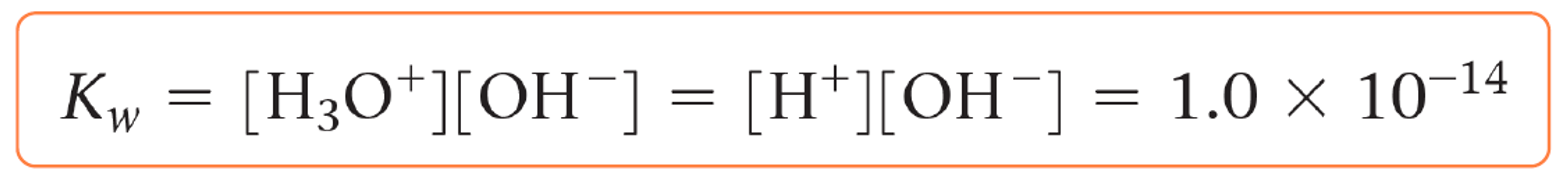
what is Kw at 298K
1.00 × 10^-14 mol² dm^-6
kw in pure water
[H+] = [OH-] so
Kw = [H+]²
what happens to Kw if you increase temperature
equilibrium will shift to the right and [H+] will increase meaning Kw will also increase —- pH of H20 decrease at temperature increases
what are 2 approximations for calculating pH of weal monobasic acids
approximation 1 : [H+(eqm)] = [A-(eqm)] —> assumption that all of the H+ comes from the acid and not the dissociation of water
approximation 2 : [HA(eqm)]= [HA(start)] —> assumption that the dissociation of weak acid is so strong that when eqm is reached the [HA] is unchanged
Ka for weak acids in aqueous solutions
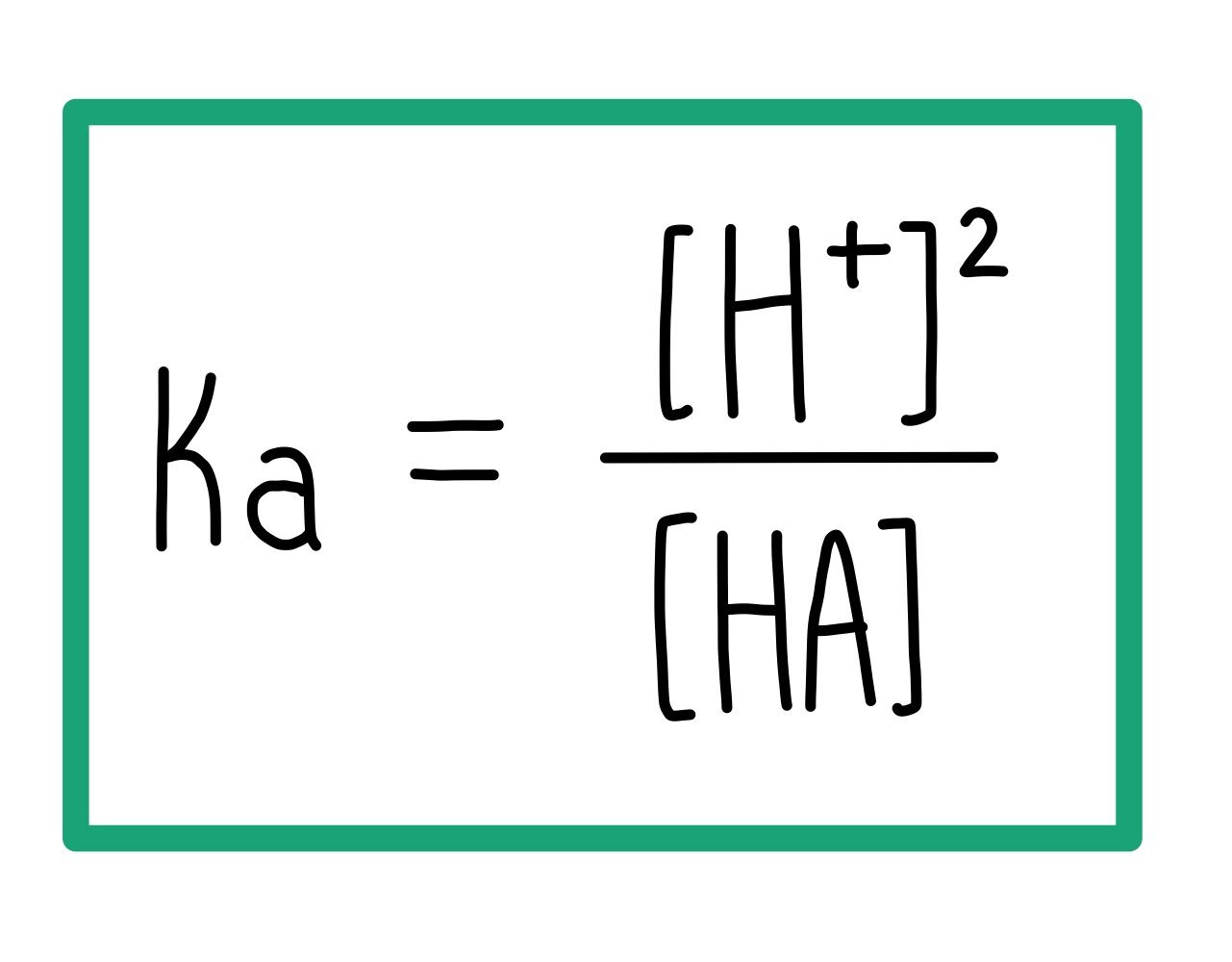
what is a buffer solution
a system that minimises pH changed when small amounts of an acid or a base are added
what are the 2 components of a buffer solution
the weak acid, HA, removes added alkali
the conjugate base, A-, removes added acid
formation of buffer solution from a weak acid and its salt
mix a solution of ethanoic acid with a solution of one of its salts
when added to water, the salt will completely dissociate
formation of a buffer solution by partial neutralisation of the weak acid
add aq solution of an alkali like NaOH, to an excess of the weak acid
the weak acid is partially neutralised by the alkali forming the conjugate base, some weak acid is left unreacted
the solution now contains salt of the weak acid and any unreacted weak acid
how does a conjugate base remove added acid
[H+] increases
H+ ions react with conjugate base, A-
the eqm position shift to the left, removing most H+ ions
how does a weak acid remove added alkali
[OH-] increases
the small concentration of H+ ions react with the OH-
HA dissociates, shifting eqm position to the right, to restore most of the H+ ions lost
what does the pH of a buffer solution depend on
the pKa value of the weak acid
the ratio of conc of the weak acid and its conjugate base
how to find pH of a buffer solution
then sub into the Ph formula
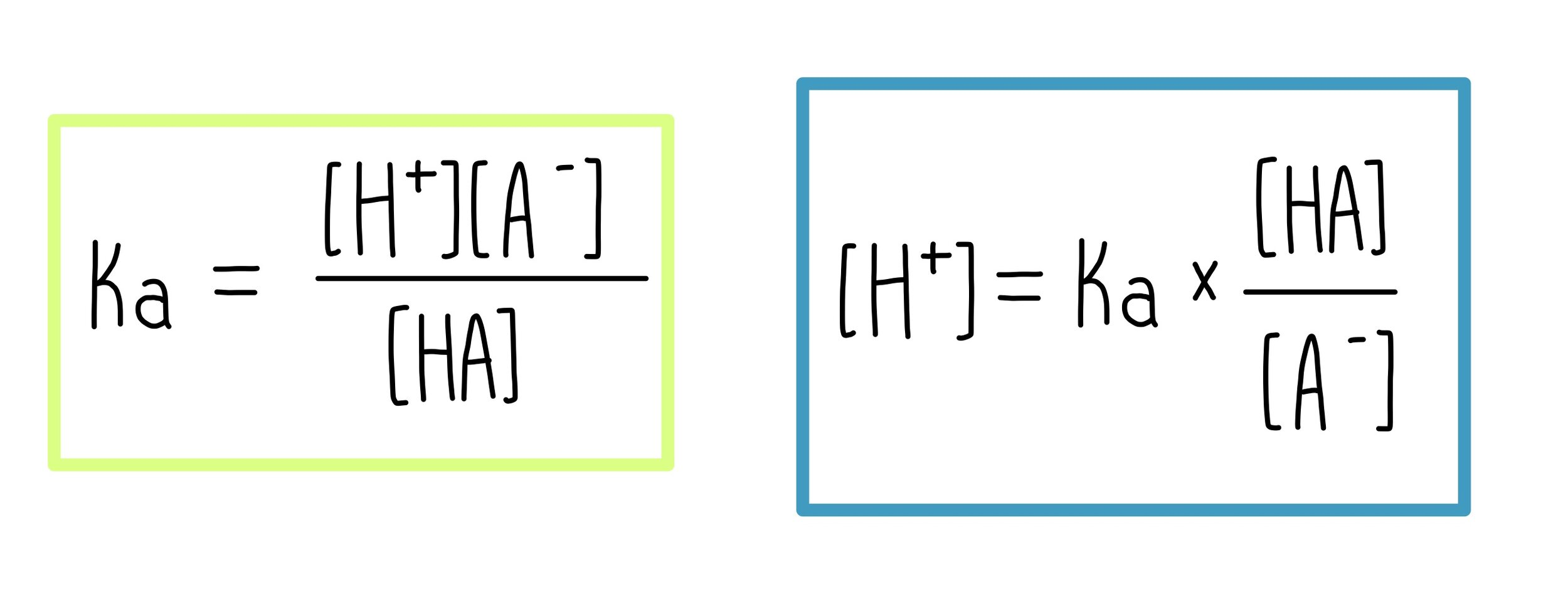
what is the pH range of blood
7.35-7.45
what happens if the pH of blood falls/rises too much
falls below 7.35- develop acidosis
rises above 7.45 - develop alkalosis