Article 3a + 3b - Conditioning and Social Cognitive Theory, Behaviorism
5.0(2)Studied by 4 people
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:20 PM on 3/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
1\. What is the difference between an ill-structured and a well-structured problem? Can you give an example?
**ill-structured problem:** more than one way of finding a solution + multiply possible solution
* example problem: climate change
%%**Well-structured problem**%%**:** easy to identify problem + only on possible solution
* example problem: 2+2=?
* example problem: climate change
%%**Well-structured problem**%%**:** easy to identify problem + only on possible solution
* example problem: 2+2=?
2
New cards
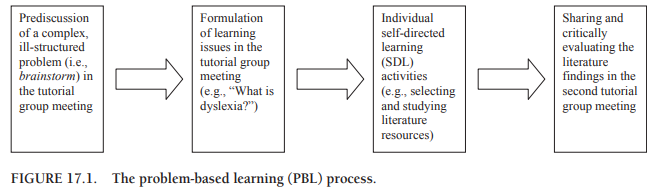
2\. How does the process of problem-based learning (PBL) look like?
create problem -→ present problem → understand problem → combine previous knowledge → find knowledge gap → SDL→ solve it + conclusion
3
New cards
3\. What is the role of the tutor in PBL and what is the “ideal” tutor?
* establish a god problemm → stimulate
* give guidance
* give feedback/evaluate
* be social and cognitive congruent
* *Cognitive congruence:* ability to “frame his or her contributions in a language that is adapted to the level of the students”
*Social congruence:* willingness to be involved with students’ life and learning.
* give guidance
* give feedback/evaluate
* be social and cognitive congruent
* *Cognitive congruence:* ability to “frame his or her contributions in a language that is adapted to the level of the students”
*Social congruence:* willingness to be involved with students’ life and learning.
4
New cards
4\. How critical is the number of students in a (PBL) tutorial group meeting?
small group ( 6-10 students + tutor)
2-3h per session; 2/per week
Why?
* Diverse background yet forester communication and participation
2-3h per session; 2/per week
Why?
* Diverse background yet forester communication and participation
5
New cards
5\. PBL was designed to help students construct an extensive and flexible knowledge base, become effective collaborators, develop effective problem-solving skills, become intrinsically motivated to learn and develop self-directed learning skills (SDL). a. How do students get intrinsically motivated through PBL? b. What role do SDL-skills play in PBL?
a) **Intrinsic motivation?**
* relevant to current existnce
* relevance to future careers
* increased motivation when students have more control over their learning
b) SDL **association with PBL**
* self-study to during new knowledge acquisition
* relevant to current existnce
* relevance to future careers
* increased motivation when students have more control over their learning
b) SDL **association with PBL**
* self-study to during new knowledge acquisition
6
New cards
what is SDL?
SDL→ SELF DIRECTED LEARNING
= the preparedness of a student to engage in learning activities defined by him- or herself, rather than by a teacher
* feeling of being in charge and having an impact !!
= the preparedness of a student to engage in learning activities defined by him- or herself, rather than by a teacher
* feeling of being in charge and having an impact !!
7
New cards
6\. Using “authentic” problems is an important characteristic of PBL. Why does PBL emphasize the use of authentic problems?
* increases intrinsic motivation
* makes knowledge more transferable to real life situation
* makes knowledge more transferable to real life situation
8
New cards
7\. In general, what are the most important features of a well-developed problem in PBL?
* problems must build on **prior knowledge**
* **eliciting discussion**( opposing viewpoints)
* **well structured**( problem can only lead to *one* solution)
* **stimulating SDL**
* **encouraging knowledge integration and transfer**
* **relevance for future profession**
* **eliciting discussion**( opposing viewpoints)
* **well structured**( problem can only lead to *one* solution)
* **stimulating SDL**
* **encouraging knowledge integration and transfer**
* **relevance for future profession**
9
New cards
8\. In traditional forms of education, lectures play a prominent role. What is the perception of lectures within a PBL curriculum?
* lectures should give insight/ inspiration for future profession
10
New cards
9\. It is common practice in a PBL course to use multiple sources to discuss a particular topic. It does not really matter which one is used during self-study. What the rationale using a diversity of sources?
* find similarities and consens in literature
* diffent levels of depth
* identify different perspectives and viewpoints
* stimulate critical thinking an discussions
* makes the problem more authentic to real life
* diffent levels of depth
* identify different perspectives and viewpoints
* stimulate critical thinking an discussions
* makes the problem more authentic to real life
11
New cards
10\. What is the difference between a learning goal and a learning issue in PBL?
the issue is the problem at hand
the learning goal is the knowledge the tutor wants the student to derive from probelm
the learning goal is the knowledge the tutor wants the student to derive from probelm
12
New cards
11\. True or False: Project-based learning is more student centered than PBL.
TRUE
**Project-based learning** is more student focused → students come up with their own projects related to the probelm
**Project-based learning** is more student focused → students come up with their own projects related to the probelm
13
New cards
12\. Case-based learning is also related to PBL. What is however the most important difference?
case based learning presets the needed knowlge before the porblem is adressed
14
New cards
13\. Many studies have been conducted to investigate the effectiveness of PBL (compared to traditional forms of education). Why is this type of research so difficult?
* PBL is still has a very vague definition → difficult to test
* having control groups performed worse in an academic setting is unethical
* Measurement of learning outcomes an be different to traditional learning outcomes
* Small sample sizes: PBL is often implemented in small groups, which can make it difficult to obtain large sample sizes for research studies
* having control groups performed worse in an academic setting is unethical
* Measurement of learning outcomes an be different to traditional learning outcomes
* Small sample sizes: PBL is often implemented in small groups, which can make it difficult to obtain large sample sizes for research studies
15
New cards
15\. How do Kirschner, Sweller, and Clark define direct instructional guidance and learning?
@@**instructional guidance**@@ as a form of instruction that involves presenting learners with information or skills they need to acquire in a step-by-step manner.
* best for novice
* best for novice
16
New cards
16\. According to Kirschner and colleagues, there are two main assumptions underlying programs using minimal guidance. Briefly discuss these two assumptions
1. Learners can discover for themselves what they need to know
2. Instruction hinders the development of creative thinking and problem-solving skills
17
New cards
17\. Our cognitive architecture plays a prominent role in the ideas of Kirschner and colleagues. Why do they think that minimal guidance is not in line with our cognitive architecture?
We base our cognitive architecture on the fact that working memory capacity is very limited. Limit guidance overwhelms our working memory due to other cofounding factors that have nothing to do with transporting information into our long term memory
18
New cards
18\. True or False: using minimal guidance will always lead to inferior performance compared to direct instruction.
FALSE
direct instruction will always give better result than minmial guidance approch
direct instruction will always give better result than minmial guidance approch
19
New cards
20\. What is the worked-example effect and why is it effective?
worked examples are highly guided problems that help students better than inquiry-based approaches “phenomenon where providing learners with a series of worked examples, or step-by-step solutions to problems, can enhance their ability to solve similar problems on their own.”
20
New cards
21\. When does the worked-example effect turn into a redundancy effect?
**the redundancy effet** is when students are given “extra/unnecessary” information in addition to a worker probeln it results in worse performance (overload/distracion of working memory)
21
New cards
22\. Provide an example of the expertise reversal effect
the erxpertise reversal effect states that instructional methods which ar eused for novices do not necceraly work for experts
* example: giving a lot of guidance is goo for novices but can be worse ( promoting dependence) for experts
* example: giving a lot of guidance is goo for novices but can be worse ( promoting dependence) for experts
22
New cards
23\. PBL was introduced in the sixties in medical education. Was this a coincidence?
PBL was developed as **a response to the traditional lecture-based approach** to medical education, which was seen as ineffective in preparing medical students for **real-life clinical practice**.Thus, PBL was a deliberate attempt to **transform medical education** and respond to the **changing demands of the healthcare system**
23
New cards
24\. Kirschner and colleagues argue that PBL is more costly. Loyens and colleagues argue it is not. Who is right?
* it all depends on the materials used for PBL
* more guidance could also mean more time/teaching of instructer → more cost
* PBL is more motivating → fewer dropout rates → better money investment
* more guidance could also mean more time/teaching of instructer → more cost
* PBL is more motivating → fewer dropout rates → better money investment
24
New cards
25\. Based on research by Patel and colleagues, Kirschner et al. argue: “… something in PBL may hinder the development of the forward reasoning pattern” (p83). Critically reflect upon this statement.
**Forward reasoning:**
* stuffy nose + cough → corona
**Backward reasoning**
* corona ? → stuffy nose ✅+ cough ✅
\
\
\
* stuffy nose + cough → corona
**Backward reasoning**
* corona ? → stuffy nose ✅+ cough ✅
\
\
\
25
New cards
26\. Summary question. One after the other student provides an argument in favor or against instruction using minimal guidance (i.e., 1st pos, 2nd neg, 3rd pos, 4th neg, etc.)
PRO PBL
* PBL seems more relevant to the future profession
* PBL stimulates critical thinking
ANTI-PBL
* more guided approaches are easier on the working memory
* PBL is not good for noviences
* PBL seems more relevant to the future profession
* PBL stimulates critical thinking
ANTI-PBL
* more guided approaches are easier on the working memory
* PBL is not good for noviences
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
PSYC 362 (Behavioral Neuroscience) - Sleep, Drinking/Ingestion, & Learning
236Updated 1205d ago0.0(0)
PSYC 362 (Behavioral Neuroscience) - Sleep, Drinking/Ingestion, & Learning
236Updated 1205d ago0.0(0)