Ap Comp Sci 3.8 Iteration Quiz
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
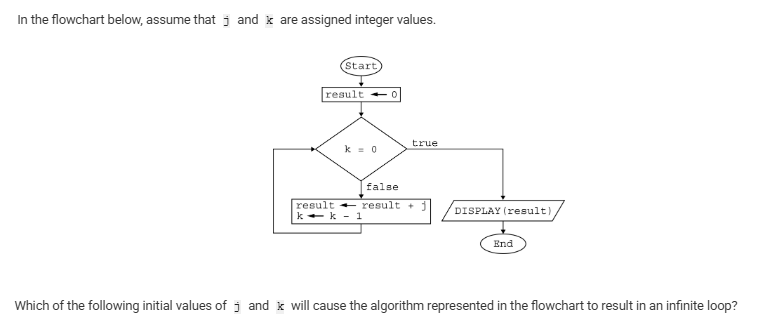
A j = -5, k = 5
B j = 0, k = 5
C j = 5, k = 0
D j = 5, k = -5
D
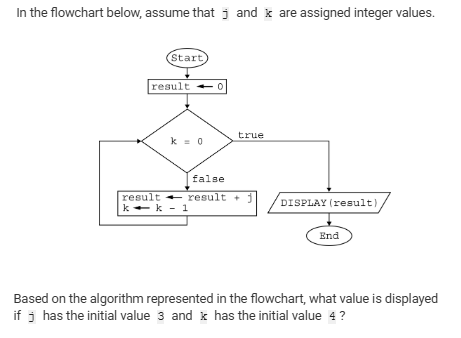
A) 7
B) 9
C) 10
D) 12
D
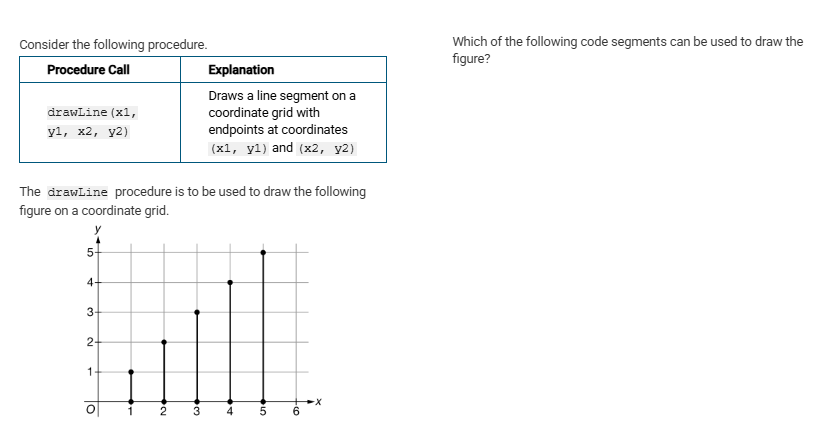
Which of the following code segments can be used to draw the figure?
Responses
A
xVal 1
yVal 0
len 1
REPEAT 5 TIMES
{
drawLine(xVal, yVal, xVal, yVal + len)
xVal xVal + 1
len len + 1
}
B
xVal 1
yVal 0
len 1
REPEAT 5 TIMES
{
drawLine(xVal, yVal, xVal + len, yVal)
yVal yVal + 1
len len + 1
}
C
xVal 5
yVal 0
len 5
REPEAT 5 TIMES
{
drawLine(xVal, yVal, xVal, yVal + len)
xVal xVal - 1
}
D
xVal 5
yVal 0
len 5
REPEAT 5 TIMES
{
drawLine(xVal, yVal, xVal + len, yVal)
yVal yVal - 1
len len - 1
}
A
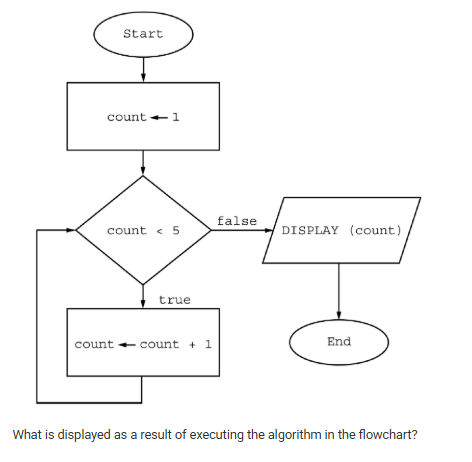
What is displayed as a result of executing the algorithm in the flowchart?
Responses
A
5
B
15
C
1 2 3 4
D
1 2 3 4 5
a
![<p><br></p><p><strong>A</strong></p><p class="choice_paragraph"></p><img src="https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR113799.g16.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center" alt="The figure presents two blocks of code that consist of 8 lines. The second block of code contains nested blocks of code. Line 1: [begin block] n ← 1 [end block] Line 2: [Begin block] REPEAT 3 TIMES [Begin block] Line 3: [begin block] n ← n + 1 [end block] Line 4: [Begin block] REPEAT n TIMES [Begin block] Line 5: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] Line 6: [begin block] ROTATE_LEFT [end block] Line 7: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] Line 8: [begin block] ROTATE_RIGHT [end block] [End block] [End block] [End block] [End block]"><p><strong>B</strong></p><p class="choice_paragraph"></p><img src="https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR113799.g14.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center" alt="The figure presents two blocks of code that consist of 8 lines. The second block of code contains nested blocks of code. Line 1: [begin block] n ← 1 [end block] Line 2: [Begin block] REPEAT 3 TIMES [Begin block] Line 3: [Begin block] REPEAT n TIMES [Begin block] Line 4: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] Line 5: [begin block] ROTATE_LEFT [end block] Line 6: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] Line 7: [begin block] ROTATE_RIGHT [end block] [End block] [End block] Line 8: [begin block] n ← n + 1 [end block] [End block] [End block]"><p><strong>C</strong></p><p class="choice_paragraph"></p><p><strong>D</strong></p><p class="choice_paragraph"></p><img src="https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR113799.g18.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center" alt="The figure presents two blocks of code that consist of 9 lines. The second block of code contains nested blocks of code. Line 1: [begin block] n ← 1 [end block] Line 2: [Begin block] REPEAT 3 TIMES [Begin block] Line 3: [Begin block] REPEAT n TIMES [Begin block] Line 4: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] [End block] [End block] Line 5: [begin block] ROTATE_LEFT [end block] Line 6: [Begin block] REPEAT n TIMES [Begin block] Line 7: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] [End block] [End block] Line 8: [begin block] ROTATE_RIGHT [end block] Line 9: [begin block] n ← n + 1 [end block] [End block] [End block]"><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a66ef1b2-4f0a-4d13-94a2-9791fe7124f8.png)
A
![The figure presents two blocks of code that consist of 8 lines. The second block of code contains nested blocks of code. Line 1: [begin block] n ← 1 [end block] Line 2: [Begin block] REPEAT 3 TIMES [Begin block] Line 3: [begin block] n ← n + 1 [end block] Line 4: [Begin block] REPEAT n TIMES [Begin block] Line 5: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] Line 6: [begin block] ROTATE_LEFT [end block] Line 7: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] Line 8: [begin block] ROTATE_RIGHT [end block] [End block] [End block] [End block] [End block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR113799.g16.png)
B
![The figure presents two blocks of code that consist of 8 lines. The second block of code contains nested blocks of code. Line 1: [begin block] n ← 1 [end block] Line 2: [Begin block] REPEAT 3 TIMES [Begin block] Line 3: [Begin block] REPEAT n TIMES [Begin block] Line 4: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] Line 5: [begin block] ROTATE_LEFT [end block] Line 6: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] Line 7: [begin block] ROTATE_RIGHT [end block] [End block] [End block] Line 8: [begin block] n ← n + 1 [end block] [End block] [End block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR113799.g14.png)
C
D
![The figure presents two blocks of code that consist of 9 lines. The second block of code contains nested blocks of code. Line 1: [begin block] n ← 1 [end block] Line 2: [Begin block] REPEAT 3 TIMES [Begin block] Line 3: [Begin block] REPEAT n TIMES [Begin block] Line 4: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] [End block] [End block] Line 5: [begin block] ROTATE_LEFT [end block] Line 6: [Begin block] REPEAT n TIMES [Begin block] Line 7: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] [End block] [End block] Line 8: [begin block] ROTATE_RIGHT [end block] Line 9: [begin block] n ← n + 1 [end block] [End block] [End block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR113799.g18.png)
d
Which of the following algorithms display all integers between 1 and 20, inclusive, that are not divisible by 3 ?
Select two answers.
A
Step 1:
Set x to 0.
Step 2:
Increment x by 1.
Step 3:
If x is not divisible by 3, then display x.
Step 4:
Repeat steps 2 and 3 until x is 20.
B
Step 1:
Set x to 0.
Step 2: If x is divisible by 3, then display x.Step 3:
Increment x by 1.
Step 4: Repeat steps 2 and 3 until x is greater than 20.
C
Step 1:
Set x to 1.
Step 2: If x is divisible by 3, then do nothing; otherwise display x.Step 3:
Increment x by 1.
Step 4: Repeat steps 2 and 3 until x is 20.
D
Step 1:
Set x to 1.
Step 2: If x is divisible by 3, then do nothing; otherwise display x.Step 3:
Increment x by 1.
Step 4: Repeat steps 2 and 3 until x is greater than 20.
A, D
The following algorithm is intended to determine the average height, in centimeters, of a group of people in a room. Each person has a card, a pencil, and an eraser. Step 2 of the algorithm is missing.
Step 1: All people stand up.
Step 2: (missing step)
Step 3: Each standing person finds another standing person and they form a pair. If a person cannot find an unpaired standing person, that person remains standing and waits until the next opportunity to form pairs.
Step 4: In each pair, one person hands their card to the other person and sits down.
Step 5: At this point, the standing person in each pair is holding two cards. The standing person in each pair replaces the top number on their card with the sum of the top numbers on the two cards and replaces the bottom number on their card with the sum of the bottom numbers on the two cards. The sitting partner’s card is discarded.
Step 6: Repeat steps 3–5 until there is only one person standing.
Step 7: The last person standing divides the top number by the bottom number to determine the average height.
Which of the following can be used as step 2 so that the algorithm works as intended?
Responses
A
Step 2: Each person writes their height, in centimeters, at the top of the card and writes the number 1 at the bottom of the card.
B
Step 2: Each person writes their height, in centimeters, at the top of the card and writes the number 2 at the bottom of the card.
C
Step 2: Each person writes the number 1 at the top of the card and writes their height, in centimeters, at the bottom of the card.
D
Step 2: Each person writes the number 2 at the top of the card and writes their height, in centimeters, at the bottom of the card.
a
Suppose a large group of people in a room were all born in the same year. Consider the following three algorithms, which are each intended to identify the people in the room who have the earliest birthday based on just the month and day. For example, a person born on February 10 is considered to have an earlier birthday than a person born on March 5. Which of the three algorithms will identify the correct people?
All the people in the room stand up. All standing people form pairs where possible, leaving at most one person not part of a pair. For each pair, the person with the earlier birthday remains standing, while the other person in the pair sits down. If there is a tie, both people sit down. Any individual not part of a pair remains standing. Continue doing this until only one person remains standing. That person has the earliest birthday.
All the people in the room stand up. All standing people form pairs with another standing person that they have not previously been paired with where possible, leaving at most one person not part of a pair. For each pair, the person with the earlier birthday remains standing, while the other person in the pair sits down. If there is a tie, both people in the pair remain standing. Any individual not part of a pair remains standing. Continue doing this until only one person remains standing or all persons standing have the same birthday. Anyone still standing has the earliest birthday.
Beginning with the number 1, ask if anyone was born on that day of any month. Continue with the numbers 2, 3, and so on until a positive response is received. If only one person responds, that person has the earliest birthday. If more than one person responds, determine which person was born in the earliest month, and that person or those persons have the earliest birthday.
Responses
A
I only
B
II only
C
I and II
D
II and III
B
Consider the following code segment.
![The figure presents seven blocks of code that consist of 9 total lines. Throughout the fourth block of code are nested blocks of code. Line 1: [begin block] a ← true [end block] Line 2: [begin block] b ← false [end block] Line 3: [begin block] c ← true [end block] [Begin Block] Line 4: REPEAT UNTIL [begin block] a and b [end block] [Begin Block] Line 5: [begin block] c ← NOT c [end block] Line 6: [begin block] b ← c [end block] [End Block] [End Block] Line 7: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] a [end block] [end block] Line 8: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] b [end block] [end block] Line 9: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] c [end block] [end block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR165486.g01.png)
What is displayed as a result of executing the code segment?
Responses
A
true false false
B
true false true
C
true true false
D
true true true
d
The question below uses a robot in a grid of squares. The robot is represented as a triangle, which is initially in the center square and facing toward the top of the grid.

The following code segment is used to move the robot in the grid.
count 1
REPEAT 4 TIMES
{
REPEAT count TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
ROTATE_LEFT()
count count + 1
}
Which of the following code segments will move the robot from the center square along the same path as the code segment above?
Responses
A
count 0
REPEAT 4 TIMES
{
count count + 1
REPEAT count TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
ROTATE_LEFT()
}
B
count 0
REPEAT 4 TIMES
{
count count + 1
ROTATE_LEFT()
REPEAT count TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
}
C
count 0
REPEAT 4 TIMES
{
REPEAT count TIMES
{
ROTATE_LEFT()
}
MOVE_FORWARD()
count count + 1
}
D
count 0
REPEAT 4 TIMES
{
ROTATE_LEFT()
REPEAT count TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
count count + 1
}
a
The following question uses a robot in a grid of squares. The robot is represented by a triangle, which is initially facing right.

Consider the following procedure.
![The figure presents a block of code that consists of 7 lines. Throughout the code there are nested blocks of code, as follows. [Begin Block] Line 1: PROCEDURE botStepper [begin block] n [end block] [Begin Block] Line 2: [Begin Block] REPEAT n TIMES [Begin Block] Line 3: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] [End Block] [End Block] Line 4: [begin block] ROTATE_LEFT [end block] [Begin Block] Line 5: REPEAT n TIMES [Begin Block] Line 6: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] [End block] [End Block] Line 7: [begin block] ROTATE_RIGHT [end block] [End Block] [End Block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR155114.g42.png)
Which of the following code segments will move the robot to the gray square along the path indicated by the arrows?
Responses
A
![The figure presents two lines of code. Throughout the code there are nested blocks of code, as follows. Line 1: [begin block] botStepper [begin block] 2 [end block] [end block] Line 2: [begin block] botStepper [begin block] 3 [end block] [end block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR155114.g35.png)
B
![The figure presents two lines of code. Throughout the code there are nested blocks of code, as follows. Line 1: [begin block] botStepper [begin block] 3 [end block] [end block] Line 2: [begin block] botStepper [begin block] 4 [end block] [end block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR155114.g37.png)
C
![The figure presents three lines of code. Throughout the code there are nested blocks of code, as follows. Line 1: [begin block] botStepper [begin block] 2 [end block] [end block] Line 2: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] Line 3: [begin block] botStepper [begin block] 3 [end block] [end block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR155114.g39.png)
D
![The figure presents three lines of code. Throughout the code there are nested blocks of code, as follows. Line 1: [begin block] botStepper [begin block] 3 [end block] [end block] Line 2: [begin block] MOVE_FORWARD [end block] Line 3: [begin block] botStepper [begin block] 4 [end block] [end block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR155114.g41.png)
c
An algorithm is intended to display the following output.
red red blue red red blue red red blue
Which of the following code segments can be used to display the intended output?
Responses
A
![The figure presents one block of code that consists of 4 total lines. Throughout the block of code there are nested blocks of code. [Begin Block] Line 1: REPEAT 2 TIMES [Begin Block] [Begin Block] Line 2: REPEAT 3 TIMES [Begin Block] Line 3: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] “red” [end block] [end block] [End Block] [End Block] Line 4: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] “blue” [end block] [end block] [End Block] [End Block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR029383.g20.png)
B
![The figure presents one block of code that consists of 4 total lines. Throughout the block of code there are nested blocks of code. [Begin Block] Line 1: REPEAT 2 TIMES [Begin Block] [Begin Block] Line 2: REPEAT 3 TIMES [Begin Block] Line 3: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] “blue” [end block] [End block] [End Block] [End Block] Line 4: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] “red” [end block] [end block] [End Block] [End Block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR029383.g22.png)
C
![The figure presents one block of code that consists of 4 total lines. Throughout the block of code there are nested blocks of code. [Begin Block] Line 1: REPEAT 3 TIMES [Begin Block] [Begin Block] Line 2: REPEAT 2 TIMES [Begin Block] Line 3: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] “red” [end block] [end block] [End Block] [End Block] Line 4: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] “blue” [end block] [end block] [End Block] [End Block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR029383.g24.png)
D
![The figure presents two blocks of code that consist of 4 total lines. Throughout the first block of code there are nested blocks of code. [Begin Block] Line 1: REPEAT 3 TIMES [Begin Block] [Begin Block] Line 2: REPEAT 2 TIMES [Begin Block] Line 3: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] “blue” [end block] [end block] [End Block] [End Block] Line 4: [begin block] DISPLAY [begin block] “red” [end block] [end block] [End Block] [End Block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR029383.g26.png)
c
Consider the following program code.

Which of the following best describes the result of running the program code?
Responses
A
The number 0 is displayed.
B
The number 6 is displayed.
C
The number 10 is displayed.
D
Nothing is displayed; the program results in an infinite loop.
d
The question below uses a robot in a grid of squares. The robot is represented as a triangle, which is initially in the bottom-left square of the grid and facing toward the top of the grid.

Code for the procedure Mystery is shown below. Assume that the parameter p has been assigned a positive integer value (e.g., 1, 2, 3, …).

Which of the following shows a possible result of calling the procedure?
Responses
A

B

C

D

A
Directions: For the question or incomplete statement below, two of the suggested answers are correct. For this question, you must select both correct choices to earn credit. No partial credit will be earned if only one correct choice is selected. Select the two that are best in each case.
The question below uses a robot in a grid of squares. The robot is represented as a triangle, which is initially in the bottom-right square of the grid and facing toward the top of the grid.

Which of the following code segments can be used to move the robot to the gray square?
Select two answers.
response - correct
Responses
A

B

C

D

A, C
Consider the following code segment.

Which of the following replacements for <MISSING CONDITION> will result in an infinite loop?
Responses
A
j = 6
B
j ≥ 6
C
j = 7
D
j > 7
a
Consider the following procedure.
Procedure Call | Explanation |
drawCircle(xPos, yPos, rad) | Draws a circle on a coordinate grid with center (xPos, yPos) and radius rad |
The drawCircle procedure is to be used to draw the following figure on a coordinate grid.

Which of the following code segments can be used to draw the figure?
Select two answers.
response - correct
Responses
A
x 4
y 1
r 0
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
drawCircle(x, y, r)
r r + 1
y y + 1
}
B
x 4
y 1
r 0
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
r r + 1
y y + 1
drawCircle(x, y, r)
}
C
x 4
y 4
r 3
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
drawCircle(x, y, r)
y y - 1
r r - 1
}
D
x 4
y 4
r 3
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
y y - 1
r r - 1
drawCircle(x, y, r)
}
B, C
Consider the following program.

Which of the following describes the result of executing the program?
Responses
A
The program displays the sum of the even integers from 0 to 10.
B
The program displays the sum of the even integers from 0 to 20.
C
The program displays the sum of the odd integers from 1 to 9.
D
The program displays the sum of the odd integers from 1 to 19.
D

A

B

C

D

C
In the following procedure, the parameter n is an integer greater than 2.
![The figure presents a block of code that consists of 7 lines. Throughout the code there are nested blocks of code, as follows. [Begin Block] Line 1: PROCEDURE compute [begin block] n [end block] [Begin Block] Line 2: [begin block] result ← 1 [end block] Line 3: [begin block] j ← 2 [end block] [Begin Block] Line 4: REPEAT UNTIL [begin block] j ˃ 2 [end block] [Begin Block] Line 5: [begin block] result ← result + j [end block] Line 6: [begin block] j ← j + 1 [end block] [End Block] [End Block] Line 7: [begin block] RETURN [begin block] result [end block] [end block] [End Block] [End Block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VH904396.g02.png)
Which of the following best describes the value returned by the procedure?
Responses
A
The procedure returns nothing because it will not terminate.
B
The procedure returns the value of 2 * n.
C
The procedure returns the value of n * n.
D
The procedure returns the sum of the integers from 1 to n.
D
The following question uses a robot in a grid of squares. The robot is represented as a triangle, which is initially in the bottom left square of the grid and facing right.

Consider the following code segment, which moves the robot in the grid.

Which of the following shows the location of the robot after running the code segment?
Responses
A

B

C

D

A
The grid below contains a robot represented as a triangle, initially facing right. The robot can move into a white or gray square but cannot move into a black region.

The code segment below uses the procedure GoalReached, which evaluates to true if the robot is in the gray square and evaluates to false otherwise.
REPEAT UNTIL (GoalReached ())
{
<MISSING CODE>
}
Which of the following replacements for <MISSING CODE> can be used to move the robot to the gray square?
Responses
A
REPEAT UNTIL (CAN_MOVE (forward) = false)
{
ROTATE_RIGHT ()
}
MOVE_FORWARD ()
B
REPEAT UNTIL (CAN_MOVE (forward) = false)
{
MOVE_FORWARD ()
}
ROTATE_RIGHT ()
C
REPEAT UNTIL (CAN_MOVE (right))
{
ROTATE_RIGHT ()
}
MOVE_FORWARD ()
D
REPEAT UNTIL (CAN_MOVE (right))
{
MOVE_FORWARD ()
}
ROTATE_RIGHT ()
B
The following code segment is intended to remove all duplicate elements in the list myList. The procedure does not work as intended.
j LENGTH(myList)
REPEAT UNTIL(j = 1)
{
IF(myList[j] = myList[j - 1])
{
REMOVE(myList, j)
}
j j - 1
}
For which of the following contents of myList will the procedure NOT produce the intended results?
Select two answers.
response - correct
Responses
A
[10, 10, 20, 20, 10, 10]
B
[30, 30, 30, 10, 20, 20]
C
[30, 50, 40, 10, 20, 40]
D
[50, 50, 50, 50, 50, 50]
A, C
Consider the following code segment.
![The figure presents three blocks of code that consist of 5 total lines. Throughout the third block of code are nested blocks of code. Line 1: [begin block] x ← 0 [end block] Line 2: [begin block] result ← 0 [end block] [Begin Block] Line 3: REPEAT UNTIL [begin block] x is greater than 5 [end block] [Begin Block] Line 4: [begin block] result ← result plus x [end block] Line 5: [begin block] x ← x plus 1 [end block] [End Block] [End Block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR167044.g02.png)
What is the value of result after the code segment is executed?
Responses
A
6
B
10
C
15
D
21
C
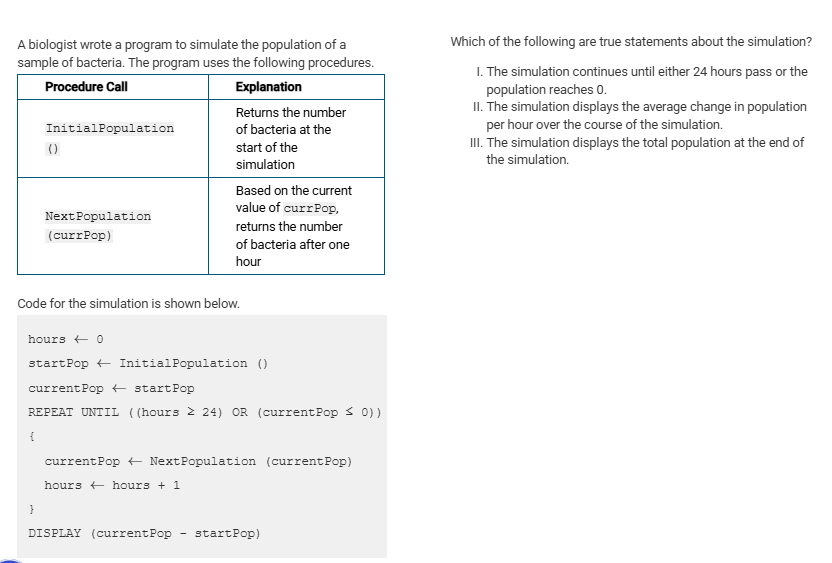
A
I only
B
II only
C
III only
D
I and II
A
There are 32 students standing in a classroom. Two different algorithms are given for finding the average height of the students.
Algorithm A
Step 1: All students stand.
Step 2: A randomly selected student writes his or her height on a card and is seated.
Step 3: A randomly selected standing student adds his or her height to the value on the card, records the new value on the card, and is seated. The previous value on the card is erased.
Step 4: Repeat step 3 until no students remain standing.
Step 5: The sum on the card is divided by 32. The result is given to the teacher.
Algorithm B
Step 1: All students stand.
Step 2: Each student is given a card. Each student writes his or her height on the card.
Step 3: Standing students form random pairs at the same time. Each pair adds the numbers written on their cards and writes the result on one student’s card; the other student is seated. The previous value on the card is erased.
Step 4: Repeat step 3 until one student remains standing.
Step 5: The sum on the last student’s card is divided by 32. The result is given to the teacher.
Which of the following statements is true?
Responses
A
Algorithm A always calculates the correct average, but Algorithm B does not.
B
Algorithm B always calculates the correct average, but Algorithm A does not.
C
Both Algorithm A and Algorithm B always calculate the correct average.
D
Neither Algorithm A nor Algorithm B calculates the correct average.
C
The algorithm below is used to simulate the results of flipping a coin 4 times. Consider the goal of determining whether the simulation resulted in an equal number of heads and tails.
Step 1: Initialize the variables heads_counter and flip_counter to 0.
Step 2: A variable coin_flip is randomly assigned a value of either 0 or 1. If coin_flip has the value 0, the coin flip result is heads, so heads_counter is incremented by 1.
Step 3: Increment the value of flip_counter by 1.
Step 4: Repeat steps 2 and 3 until flip_counter equals 4.
Following execution of the algorithm, which of the following expressions indicates that the simulation resulted in an equal number of heads and tails?
Responses
A
coin_flip = 1
B
flip_counter = 1
C
flip_counter = 2
D
heads_counter = 2
D
Consider the following program.
![The figure presents four blocks of code that consist of 6 lines. Throughout the third and fourth blocks of code there are nested blocks of code. Line 1: [begin block] val ← 0 [end block] Line 2: [begin block] sum ← 0 [end block] [Begin Block] Line 3: REPEAT 10 TIMES [Begin Block] Line 4: [begin block] val ← val + 2 [end block] Line 5: [begin block] sum ← sum + val [end block] [End Block] [End Block] Line 6: [Begin Block] DISPLAY [begin block] sum [end block] [End Block]](https://assets.learnosity.com/organisations/537/VR012544.g03.png)
Which of the following describes the result of executing the program?
Responses
A
The program displays the sum of the even integers from 2 to 10.
B
The program displays the sum of the even integers from 2 to 20.
C
The program displays the sum of the odd integers from 1 to 9.
D
The program displays the sum of the odd integers from 1 to 19.
B
The following grid contains a robot represented as a triangle, which is initially facing toward the top of the grid. The robot can move into a white or gray square but cannot move into a black region.

Which of the following code segments can be used to move the robot to the gray square?
Responses
A
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
REPEAT 2 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
B
REPEAT 8 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
C
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
ROTATE_LEFT()
REPEAT 2 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
ROTATE_LEFT()
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
D
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
ROTATE_LEFT()
REPEAT 2 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
ROTATE_RIGHT()
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
}
D
The following grid contains a robot represented as a triangle, which is initially facing right.

The following code segment is intended to move the robot to the gray square.
<MISSING STATEMENT>
{
REPEAT 4 TIMES
{
MOVE_FORWARD()
ROTATE_RIGHT()
}
ROTATE_LEFT()
MOVE_FORWARD()
ROTATE_RIGHT()
}
Which of the following can be used as a replacement for <MISSING STATEMENT> so that the code segment works as intended?
Responses
A
REPEAT 1 TIMES
B
REPEAT 2 TIMES
C
REPEAT 3 TIMES
D
REPEAT 4 TIMES
B
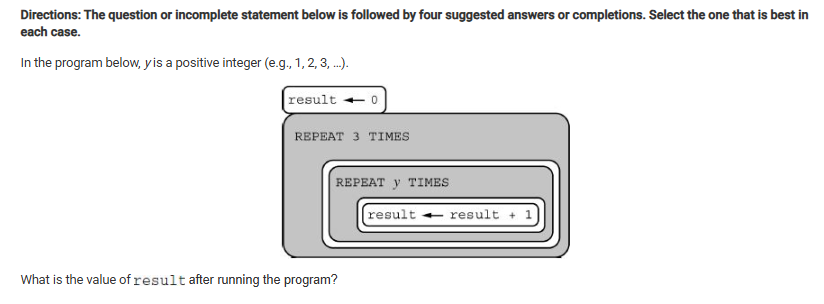
A
y + 3
B
3y
C
D
B