Chapter 16: High Renaissance and Mannerism
0.0(0)Studied by 11 people
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Art History
AP Art History
High Renaissance
Mannerism
Holy Roman Empire
Renaissance
Sfumato
Chiaroscuro
Leonardo da Vinci
Micheangelo
Delphic Sybil
The Flood
Last Judgment
School of Athens
Raphael
Venetian High Renaissance
Venus of Urbino
Arcadian
Titian
Entombment
Entombment of Christ
Jacopo da Pontormo
II Gesù façade
Giacomo della Porta
12th
Last updated 8:36 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
Martin Luther
He started a theological and political revolution in Europe in 1517 when he nailed his theses to a church door in Wittenberg, Germany.
2
New cards
Mannerism
\_______'s fundamental principles pit the ideal, natural, and symmetrical against the actual, artificial, and imbalanced.
3
New cards
Council of Trent
At the \_____ (1545–1563), Catholics responded to the Reformation's split with the Counter-Reformation.
4
New cards
Titian
Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire praised \_____.
5
New cards
Leonardo da Vinci
Francis I of France held \_____'s dying body
6
New cards
divino
Michelangelo's biographers dubbed him "\___."
7
New cards
Cosimo I
In 1563, \_____ of Florence founded the first permanent painting college to teach painters and elevate their reputation.
8
New cards
Canvas
a heavy woven material used as the surface of a painting; first widely used in Venice
9
New cards
Sfumato
a painting technique utilized by Leonardo da Vinci, created a hazy look by rendering figures softly.
10
New cards
Chiaroscuro
a gradual transition from light to dark in a painting. Forms are not determined by sharp outlines, but by the meeting of lighter and darker areas
11
New cards
Glazes
thin transparent layers put over a painting to alter the color and build up a rich sonorous effect
12
New cards
Ignudi
nude corner figures on the Sistine Chapel ceiling
13
New cards
Acorns
a motif on the ceiling, were inspired by the crest of the chapel’s patron, Pope Julius II.
14
New cards
Last Supper
a meal shared by Jesus Christ with his apostles the night before his death by crucifixion
15
New cards
Sibyl
a Greco-Roman prophetess whom Christians saw as prefiguring the coming of Jesus Christ
16
New cards
Flood story
as told in Genesis 7 of the Bible, Noah and his family escape rising waters by building an ark and placing two of every animal aboard
17
New cards
La Disputà
Opposite of Raphael's Painting School of Athens.
18
New cards
Arcadian
a simple rural and rustic setting used especially in Venetian paintings of the High Renaissance; named after Arcadia
19
New cards
Arcadia
a district in Greece to which poets and painters have attributed a rural simplicity and an idyllically untroubled world
20
New cards
Cassoni
trunks intended for storage of clothing for a wife’s trousseau seen in the background of the painting.
21
New cards
Entombment
a painting or sculpture depicting Jesus Christ’s burial after his crucifixion
22
New cards
Still life
a painting of a grouping of inanimate objects, such as flowers or fruit
23
New cards
Genre painting
painting in which scenes of everyday life are depicted
24
New cards
ambiguity
Mannerist painting's worth lies in its deliberate \____.
25
New cards

The Last Supper
* Painted by Leonardo da Vinci (1494–1498)
* Painted for the refectory, or dining hall, of an abbey of friars.
* A relationship is drawn between the friars eating and a biblical meal.
* Commissioned by the Sforza family of Milan
* Great drama of the moment | Matthew 26:21 | Matthew 26:26–27
* Painted for the refectory, or dining hall, of an abbey of friars.
* A relationship is drawn between the friars eating and a biblical meal.
* Commissioned by the Sforza family of Milan
* Great drama of the moment | Matthew 26:21 | Matthew 26:26–27
26
New cards
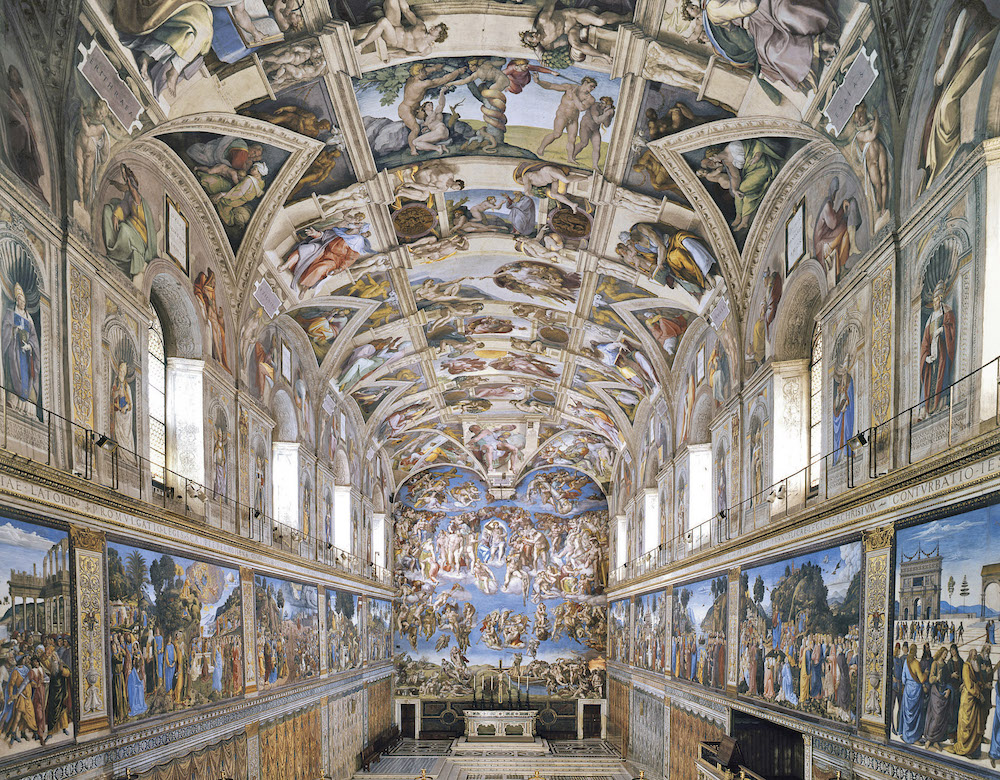

Sistine Chapel ceiling
* By Michelangelo (1508–1512)
* grand and massive figures are meant to be seen from a distance; also a grandeur of the Biblical narrative
* 300 figures on the ceiling, with no two in the same pose
* grand and massive figures are meant to be seen from a distance; also a grandeur of the Biblical narrative
* 300 figures on the ceiling, with no two in the same pose
27
New cards
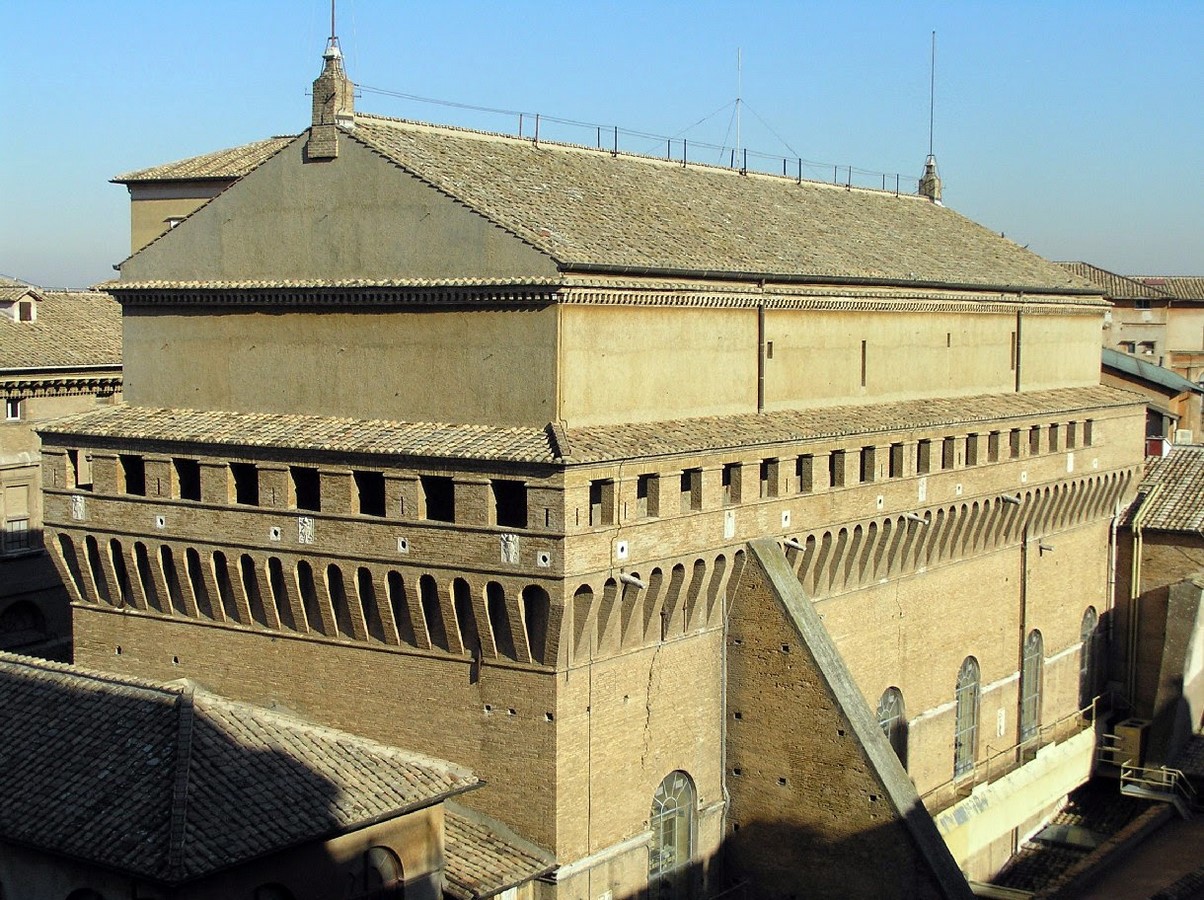

Sistine Chapel
* The chapel is dedicated to the Virgin Mary
* Acorns, a motif on the ceiling, were inspired by the crest of the chapel’s patron, Pope Julius II.
* Acorns, a motif on the ceiling, were inspired by the crest of the chapel’s patron, Pope Julius II.
28
New cards
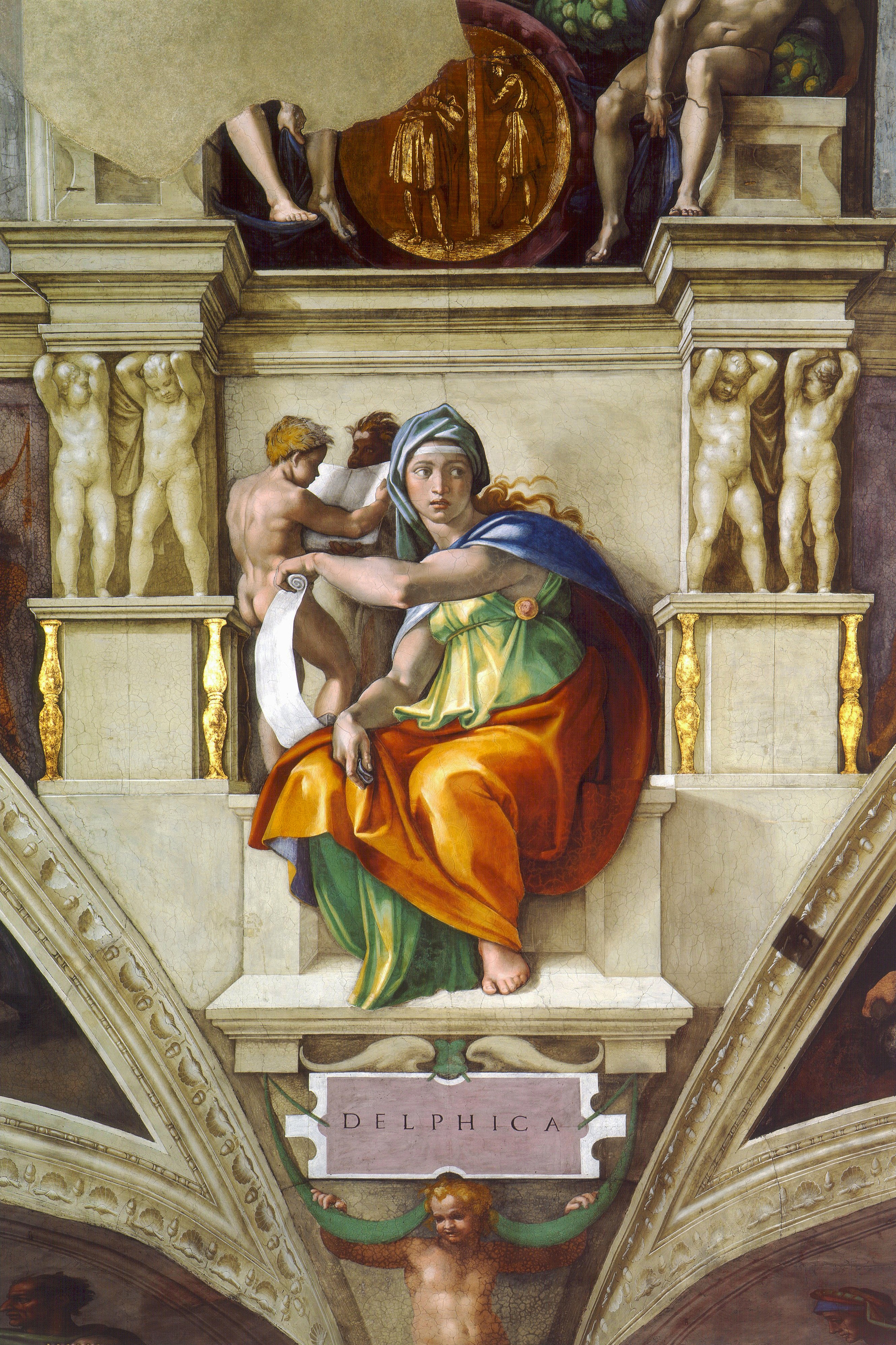

Delphic Sybil
* By Michelangelo (1508–1512)
* There is a dramatic contrapposto positioning of the body.
* Shows a combination of Christian religious and pagan mythological imagery.
* One of five sibyls on the ceiling.
* There is a dramatic contrapposto positioning of the body.
* Shows a combination of Christian religious and pagan mythological imagery.
* One of five sibyls on the ceiling.
29
New cards
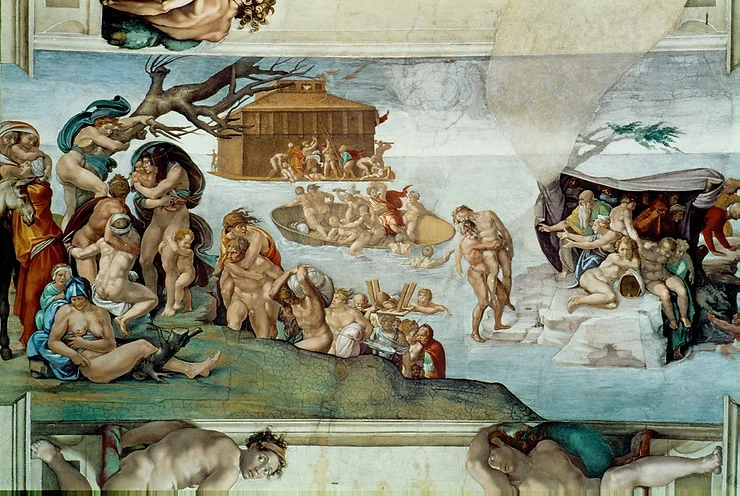

The Flood
* By Micheangelo (1508–1512)
* Sculptural intensity of the figure style.
* More than 60 figures are crowded into the composition.
* Sculptural intensity of the figure style.
* More than 60 figures are crowded into the composition.
30
New cards
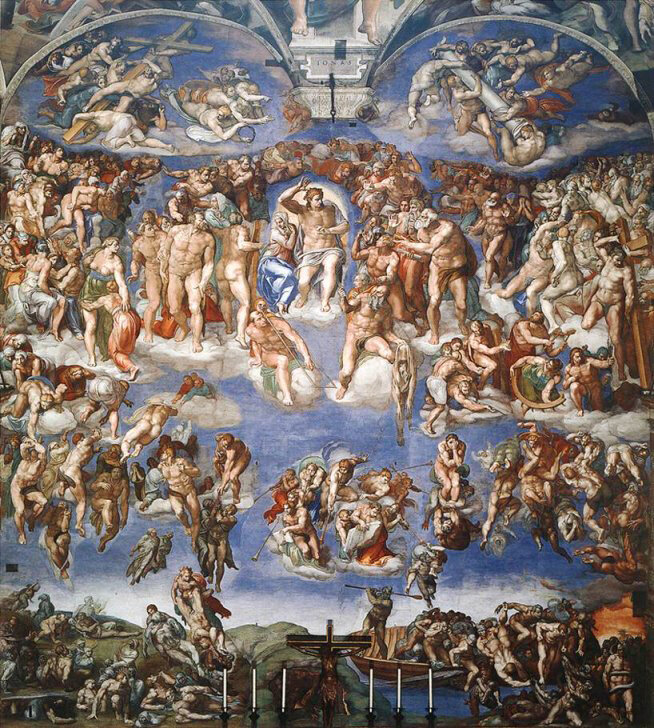

Last Judgment
* By Michelangelo (1536–1541)
* The subject was chosen because of the turbulence in Rome after the sack of the city in 1521.
* Spiraling composition is a reaction against the High Renaissance harmony
* Pope Paul III was the patron.
* The subject was chosen because of the turbulence in Rome after the sack of the city in 1521.
* Spiraling composition is a reaction against the High Renaissance harmony
* Pope Paul III was the patron.
31
New cards
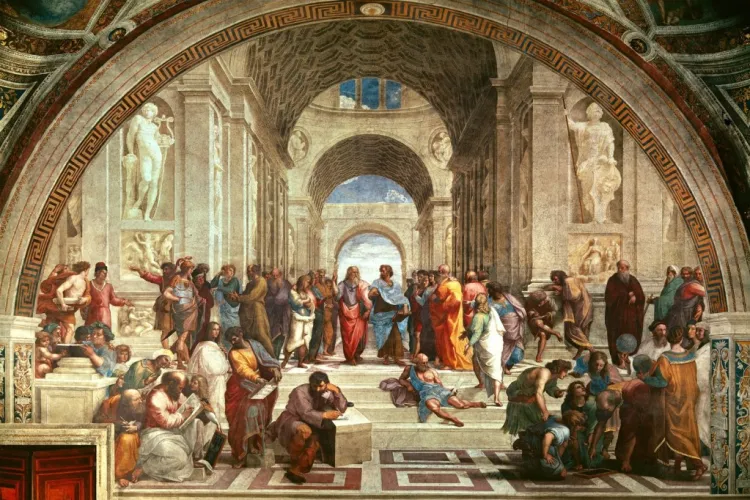

School of Athens
* By Raphael (1509–1511)
* Commissioned by Pope Julius II to decorate his library.
* Painting originally called Philosophy
* Opposite this work is a Raphael painting called La Disputà,
* Commissioned by Pope Julius II to decorate his library.
* Painting originally called Philosophy
* Opposite this work is a Raphael painting called La Disputà,
32
New cards
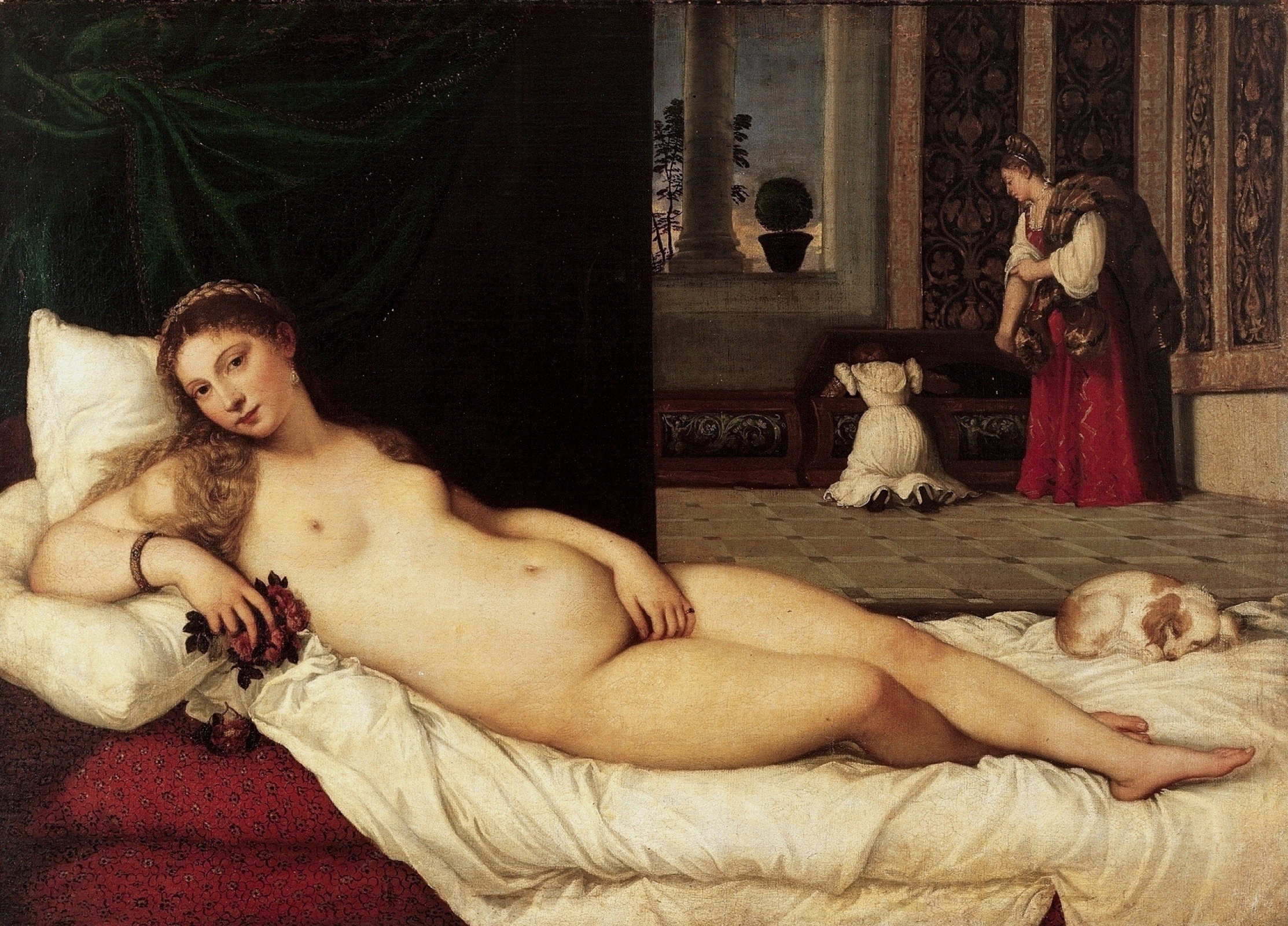
Venus of Urbino
* By Titian (1538)
* May have been commissioned by the Duke of Urbino as a wedding painting.
* Oil painted in layers; glazes achieve rich color.
* May have been commissioned by the Duke of Urbino as a wedding painting.
* Oil painted in layers; glazes achieve rich color.
33
New cards

Entombment of Christ
* By Jacopo da Pontormo (1525–1528)
* It is placed over the altar of a family chapel near the right front entrance of Santa Felicità in Florence.
* The composition and Mannerist style may reflect the instability in European politics brought on by the Protestant Reformation.
* It is placed over the altar of a family chapel near the right front entrance of Santa Felicità in Florence.
* The composition and Mannerist style may reflect the instability in European politics brought on by the Protestant Reformation.
34
New cards
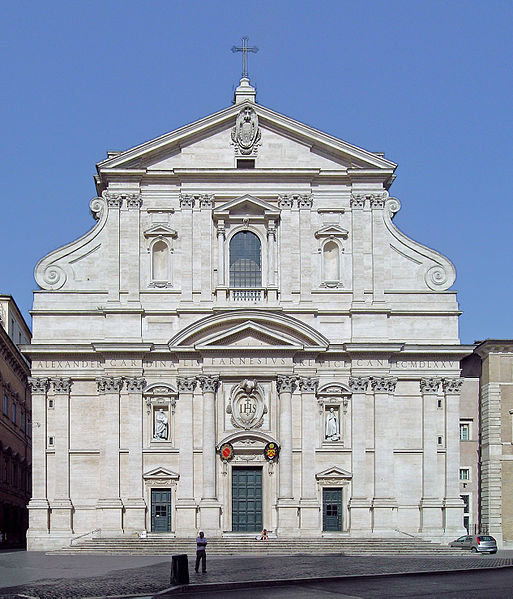

II Gesù
* By Giacomo della Porta (1568–1584)
* Principal church of the Jesuit order.
* Jesuits are seen as the defenders of Counter-Reformation ideals.
* Principal church of the Jesuit order.
* Jesuits are seen as the defenders of Counter-Reformation ideals.