Developmental Psychology TEST 1 - Armstrong
1/77
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Infancy
0-2 years old. Latin term 'Non-speaking'.
Early childhood
3-5 years old.
Middle childhood
6-12 years old - entry into school.
Puberty
Process leading to sexual maturity - Adolescence.
Development
Occurs on two levels: Qualitative and Quantitative.
Qualitative
A change in quality.
Quantitative
A change in number or amount.
Multidimensional
Development is multidimensional.
Domains of Development
Occurs across 3 domains - physical, cognitive, and social/emotional.
Gains and Losses
Involves Gains and Losses.
Plasticity
Is sometimes Plastic -- compensation.
Contexts of Development
Is influenced by different contexts -- unique combinations of personal and environmental circumstances.
Nature vs Nurture
Nature = genetics/ biology of you; Nurture = environment.
Continuous Development
Slow unfolding of differing abilities over time; not very obvious.
Discontinuous Development
More obvious changes that are less smooth and more abrupt.
Active Development
Children are active in their development, interacting with their environment.
Passive Development
Children are shaped by experience, where things happen to them.
Mechanistic Model
Development won't occur without some outside source - needs an outside influence.
Organismic Model
Development comes from inside - within the organism, motivated to explore.
Stability vs Change
Are we stable in every aspect of development or is there change?
Scientific Method Steps
1. Forming a Research Question; 2. Developing a Hypothesis; 3. Testing the Hypothesis.
Behaviorism
Learning by association - putting things together.
Classical Conditioning
Type of associative learning where two stimuli go together.
Conditioned Response
A learned response (e.g., salivation to the sound of the bell/tuning fork).
Conditioned Stimulus
A stimulus you have learned to respond to (e.g., the noise of the bell/tuning fork).
Ivan Pavlov
Known for Classical Conditioning - 'Pavlov's Dogs' experiment.
Unconditioned stimulus
a stimulus you do not have to learn to respond to (food)
Unconditioned response
response that you don't have to learn (salivation)
Operant Conditioning
another type of associative learning where you learn from a behavior and its consequence
Positive Reinforcement
adding something or presenting something after the behavior to increase the behavior
Negative Reinforcement
taking or removing something away after the behavior to increase the behavior
Negative reinforcer
the thing you want to get rid of or go away
Punishment
the only thing that stops, hinders, or gets rid of a behavior
Discipline
to teach
Positive Punishment
adding something aversive, unpleasant after a behavior to punish it
Negative Punishment
something is removed after the behavior to punish it
Social Cognitive Theory
the theory that emphasizes the importance of thought processes in learning through modeling and observational learning
Modeling
the process of learning by observing others
Jean Piaget's Cognitive-Developmental Theory
a theory that explains cognitive development through stages
Sensorimotor Stage
birth to 2 years: learning through senses and motor experiences
Preoperational Stage
2 to 7 years: the reasoning you have before you can perform operations
Operation
complex, reversible mental task
Cognitive Perspective on Child Development
focuses on how children process information differently at various stages of development
Observational Learning
learning that occurs by watching others and modeling their behavior
Reinforcement
a consequence that strengthens behavior
Aversive consequence
a negative outcome that discourages a behavior
Behavioral modeling
the process of learning behaviors by observing others' actions and consequences
Cognitive abilities
the mental skills that are involved in learning, reasoning, and problem-solving
Formal Operational
Abstractions in thought do not trip you up anymore.
Organization
The tendency to create increasingly complex ways of thinking that incorporate more and more accurate images of reality.
Schemas
Mental structures that we build as we interact with our environment; organized patterns of behavior that a person uses to think about situations and determine how to act in situations.
Adaptation
Made up of two complimentary processes: assimilation and accommodation.
Assimilation
Initial reaction/tendency to new things in our environment; the process of taking new information and trying to make it fit into already existing schemas.
Accommodation
When you alter your schemas/understandings to take in and incorporate new information.
Equilibration
The balance that forces us to stop assimilating and accommodate.
Information-Processing Theory
Involves storage and retrieval of information.
Biological Perspective on Development
Asks questions like 'do we have instinctive behaviors? What purpose do they serve? How do they help us adapt?'
Ecological Systems Theory
A contextual theory that considers all contexts that a child exists in and their impact on the child.
Microsystem
Environments where the child has direct interaction, such as family, school, and neighborhood playground.
Mesosystem
The interaction between elements of the microsystem.
Exosystem
Institutions in the community that affect the child but where the child does not exist.
Macrosystem
Cultural factors that influence the child.
Chronosystem
Changes over time that impact the child.
Sociocultural Perspective
Focuses on the social and cultural influences on development.
ZPD
Zone of Proximal Development; the difference between what a learner can do without help and what they can do with help.
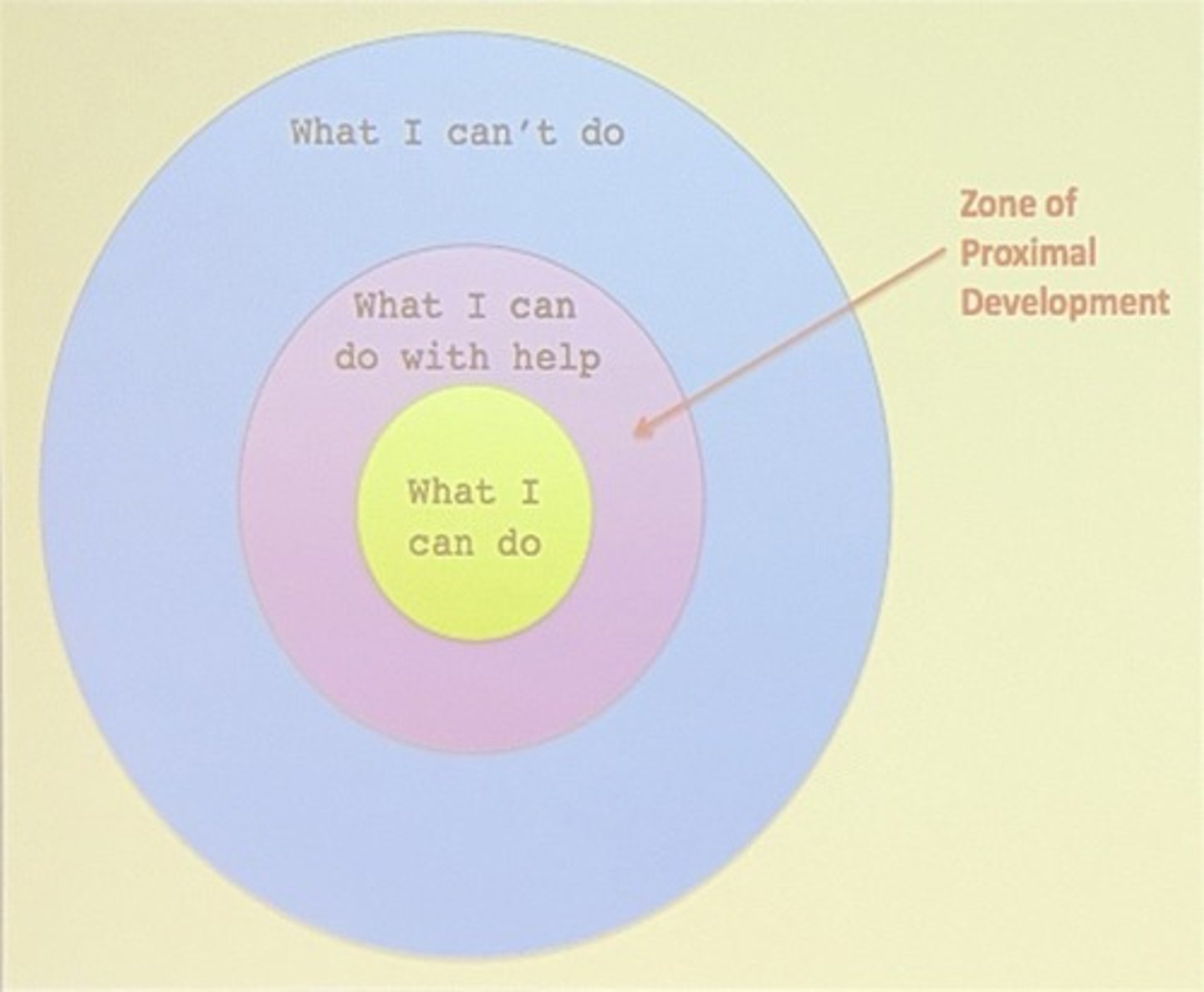
Scaffolding
Support given to a learner that is tailored to their needs with the intention of helping them achieve their learning goals.
Chromosomes
Structures within cells that contain DNA and genetic information.
Zygote
A new cell formed from the union of a sperm and an ovum; a fertilized egg.
Twins
Monozygotic (one fertilized egg split) and Dizygotic (two eggs).
Dominant Traits
Traits that are expressed when at least one dominant allele is present.
Recessive Traits
Traits that are expressed only when two recessive alleles are present.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene; can be homozygous (same traits) or heterozygous (different traits).
Chromosomal Abnormalities
Genetic disorders caused by changes in chromosome structure or number.
Down Syndrome
A genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21.
XYY Syndrome
A genetic condition in which a male has an extra Y chromosome.
Klinefelter Syndrome
A genetic condition in which a male has an extra X chromosome.
Turner Syndrome
A genetic condition in which a female is partly or completely missing an X chromosome.
Fragile X Syndrome
A genetic condition causing intellectual disability, behavioral issues, and various physical features.