Week 5: Nucleic Acids, Transcription, Gel Electrophoresis, Southern Blots
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PAL 5: 5a
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
The strands in a double helix of DNA are:
A) complementary.
B) All of these choices are correct.
C) parallel.
D) held together via ionic bonds.
A) complementary.
Which statement is true of DNA?
A) Successive nucleotides in a strand are connected by phosphodiester bonds.
B) The percentage of the purine A always equals the percentage of the purine G.
C) A phosphate group in a nucleotide is attached to the 5' carbon in ribose.
D) It is used by ribosomes for translation.
E) A purine always forms a complementary base pair with another purine.
A) Successive nucleotides in a strand are connected by phosphodiester bonds.
In a double-stranded DNA molecule, the strands are said to be antiparallel because:
A) each purine of one strand pairs with a pyrimidine of another
B) one strand runs in 5' to 3' direction and the other in 3' to 5'
C) they form an uneven pair of grooves on the outside of the molecule
D) only one of them is a template strand.
B) one strand runs in 5' to 3' direction and the other in 3' to 5'
In a DNA strand, 3'-5' phosphodiester bonds are:
A) Present to help link two nitrogenous bases.
B) Not present.
C) Present to help link two ribose molecules together.
D) None of the answer choices is correct.
E) Present to help link two nucleotides together.
E) Present to help link two nucleotides together.
Which statement about RNA is correct?
A) RNA molecules are typically longer than DNA molecules.
B) The nucleotide at the 5' end of an RNA molecule is typically a nucleoside bisphosphate.
C) RNA is usually found in double-stranded form, like DNA.
D) RNA molecules are synthesized with no defined direction.
E) RNA molecules are capable of evolving an enzymatic activity over time.
E) RNA molecules are capable of evolving an enzymatic activity over time.
Which example correctly lists the components necessary for eukaryotic transcription?
A) ribosomes, general transcription factors, DNA, and RNA nucleotides
B) DNA polymerase, general transcription factors, DNA, and DNA nucleotides
C) RNA polymerase, general transcription factors, DNA, and RNA nucleotides A
D) RNA polymerase, general transcription factors, DNA, and DNA nucleotides
C) RNA polymerase, general transcription factors, DNA, and RNA nucleotides A
T/F: Whichever DNA strand is transcribed, the RNA polymerase reads the template strand from 5' to 3'.
False
In eukaryotes, where do general transcription initiation factors bind?
A) Terminators
B) RNA Polymerases
C) 5' UTRs
D) Promoters
E) Enhancers
D) Promoters
Transcription continues until:
A) a terminator sequence is encountered.
B) there are no more available nucleotides.
C) the promoter for another gene is encountered
D) all bases in the DNA are copied.
E) a transcription factor signals the end of the gene.
A) a terminator sequence is encountered.
Different polypeptides can be made from a single gene thanks to:
A) the removal of different introns.
B) the existence of multiple promoters in a single gene
C) consecutive translation.
D) the double stranded nature of DNA.
A) the removal of different introns.
RNA processing occurs in the:
A) nucleus and cytoplasm.
B) nucleus.
C) plasma membrane.
D) Golgi apparatus.
B) nucleus.
Alternative splicing means that:
A) a given mRNA sequence could be translated in different ways.
B) different spliced forms contain different combinations of exons.
C) some transcripts are spliced correctly and others incorrectly
D) some transcripts are spliced while others are not.
B) different spliced forms contain different combinations of exons.
An intron is:
A) part of an RNA transcript that is not present in the DNA template'
B) a polypeptide that is excised out of a larger protein post-translationally.
C) an RNA sequence that is removed during the processing of an RNA molecule in the nucleus.
D) a type of transfer RNA.
E) part of an intact, mature mRNA that leaves the nucleus.
C) an RNA sequence that is removed during the processing of an RNA molecule in the nucleus.
In gel electrophoresis, how would a DNA molecule that is negatively charged compare to another DNA molecule that is negatively charged?
A) They'd travel in opposite directions.
B) Not enough information is provided.
C) They'd travel the same distance.
D) They'd travel different distances.
B) Not enough information is provided.
T/F: In gel electrophoresis, DNA fragments migrate toward the positive pole of the electric field.
True
A Southern blot is a technique that allows us to:
A) detect the presence of an RNA sequence of interest.
B) detect the presence of a protein of interest.
C) detect the presence of a DNA sequence of interest.
D) None of the other answer options is correct.
C) detect the presence of a DNA sequence of interest.
A template DNA strand contains the sequence 3'-GATAGCCT-5'. The corresponding sequence in the RNA transcript is:
A) 5'-AGGCTATC-3'
B) 5'-CUAUCGGA-3'
C) 5'-AGGCUAUC-3'
D0 5'-CTATCGGA-3'
B) 5'-CUAUCGGA-3'
A template DNA strand contains the sequence 5'-ACGGTCTA-3'. The corresponding sequence in the RNA transcript is:
A) 5'-UAGACCGU-3'
B) 5'-TGCCAGAT-3'
C) 5'-TAGACCGT-3'
D) 5'-UGCCAGAU-3'
A) 5'-UAGACCGU-3'
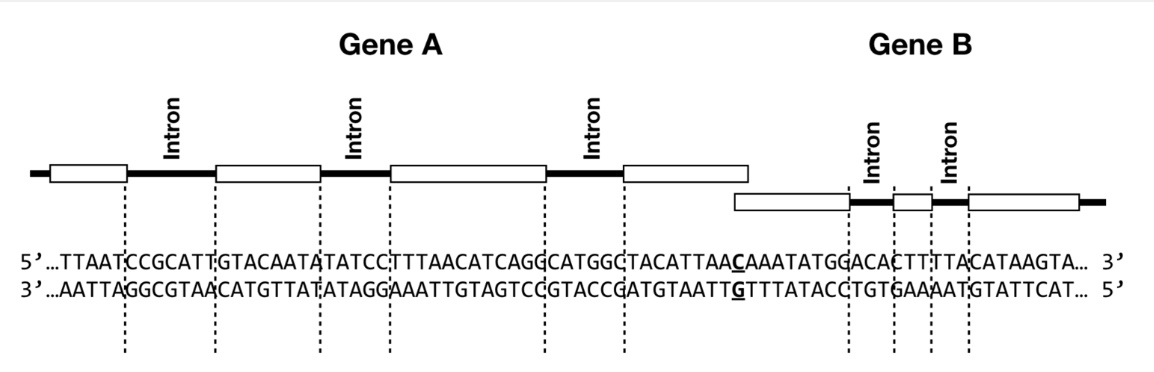
The figure below depicts two eukaryotic genes, Gene A and Gene B. For each gene, exons are depicted as white boxes, and introns are indicated by lines. The corresponding DNA sequence is shown below the gene diagrams. The bolded and underlined base pair represents the +1 transcription start site for each gene. The three dots on either side of the DNA sequence indicate that this DNA sequence can be assumed to extend beyond this figure on both sides. Use this figure to answer the following questions.
T/F: You would expect to find a long stretch of adenosines (a polyA tail) to the right of the figure in the DNA sequence for Gene B.
False
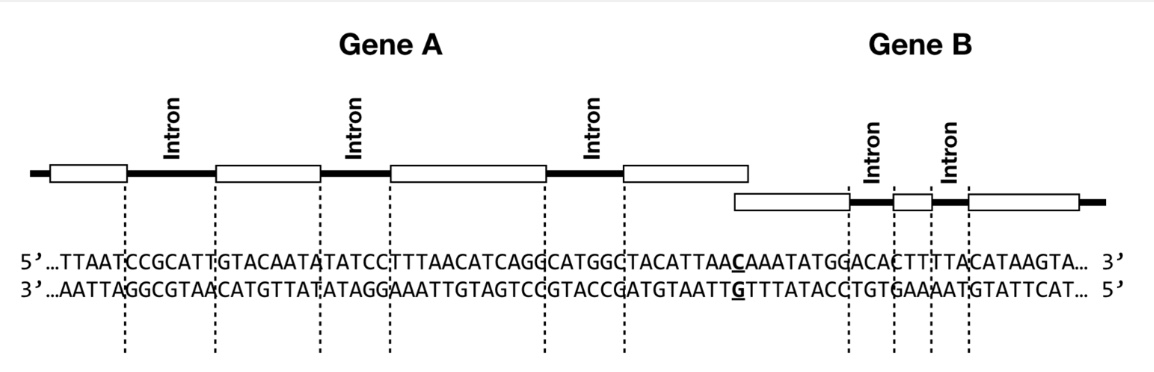
The figure below depicts two eukaryotic genes, Gene A and Gene B. For each gene, exons are depicted as white boxes, and introns are indicated by lines. The corresponding DNA sequence is shown below the gene diagrams. The bolded and underlined base pair represents the +1 transcription start site for each gene. The three dots on either side of the DNA sequence indicate that this DNA sequence can be assumed to extend beyond this figure on both sides. Use this figure to answer the following questions.
T/F: The promoter sequence for Gene B is located to the right of the figure.
False
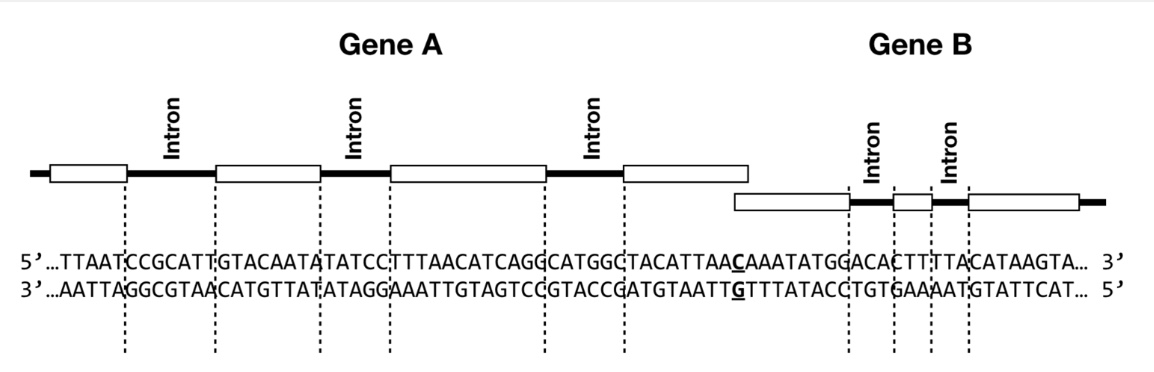
The figure below depicts two eukaryotic genes, Gene A and Gene B. For each gene, exons are depicted as white boxes, and introns are indicated by lines. The corresponding DNA sequence is shown below the gene diagrams. The bolded and underlined base pair represents the +1 transcription start site for each gene. The three dots on either side of the DNA sequence indicate that this DNA sequence can be assumed to extend beyond this figure on both sides. Use this figure to answer the following questions.
T/F: The template strand for Gene A is the top strand as shown in this diagram.
True
If you made a change in the promoter sequence in the DNA that inactivates the promoter, what would happen at the RNA level?
A) Nothing, the RNA would be made as usual.
B) The mutation of the DNA would be carried through to the RNA sequence.
C) The RNA polymerase would not be able to recognize and bind the DNA, so no RNA would be made.
D) The DNA helicase would not be able to recognize and bind the DNA, so the RNA would not be made.
C) The RNA polymerase would not be able to recognize and bind the DNA, so no RNA would be made.

For the following questions, refer to the diagram below which shows a short region of a double-stranded DNA molecule. The horizontal lines indicate the DNA backbones. The numbered boxes refer to potential transcription start sites. The top strand is the template strand for sites 1 and 2, and the bottom strand is the template strand for sites 3 and 4.
What would be the first 12 nucleotides of the RNA molecule if transcription started at start site 1?
A) 5'–CGCAUUUGGCAU–3'
B) 5'–UAUGCCCAAUGC–3'
C) 5'–CUACGGGUUACG–3'
D) 5'–GCAUUGGGCAUA–3'
E) 5'–CGUAACCCGUAG–3'
F) 5'–AUGCCAAAUGCG–3'
B) 5'–UAUGCCCAAUGC–3'

For the following questions, refer to the diagram below which shows a short region of a double-stranded DNA molecule. The horizontal lines indicate the DNA backbones. The numbered boxes refer to potential transcription start sites. The top strand is the template strand for sites 1 and 2, and the bottom strand is the template strand for sites 3 and 4.
What would be the first 12 nucleotides of the RNA molecule if transcription started at start site 4?
A) 5'–CGCAUUUGGCAU–3'
B) 5'–GCAUUGGGCAUA–3'
C) 5'–UAUGCCCAAUGC–3'
D) B5'–AUGCCAAAUGCG–3'
E) 5'–CUACGGGUUACG–3'
F) 5'–CGUAACCCGUAG–3'
F) 5'–CGUAACCCGUAG–3'

For the following questions, refer to the diagram below which shows a short region of a double-stranded DNA molecule. The horizontal lines indicate the DNA backbones. The numbered boxes refer to potential transcription start sites. The top strand is the template strand for sites 1 and 2, and the bottom strand is the template strand for sites 3 and 4.
Which transcription start site would result in an RNA transcript in which the first 12 positions were 5'–CGCAUUUGGCAU–3'?
A) Start site 2
B) Start site 1
C) Start site 4
D) Start site 3
A) Start site 2
An organism's genomic DNA is analyzed and found to contain 28% cytosine. What percentage of that organism's DNA is adenine?
A) 56%
B) 44%
C) 22%
D) 28%
E) 78%
C) 22%
Imagine you have discovered a new species of bacteria. To begin your investigation of this organism, you run an assay on the total nucleotide content of the bacterial DNA. The thymine content of DNA from the bacterial cells is 40%. You also run an assay on the total nucleotide content of E. coli, another species of bacterium. The thymine content of DNA from E. coli is 24%.
T/F: the DNA from your new bacterial species will denature at a higher temperature than the DNA from E. coli.
False
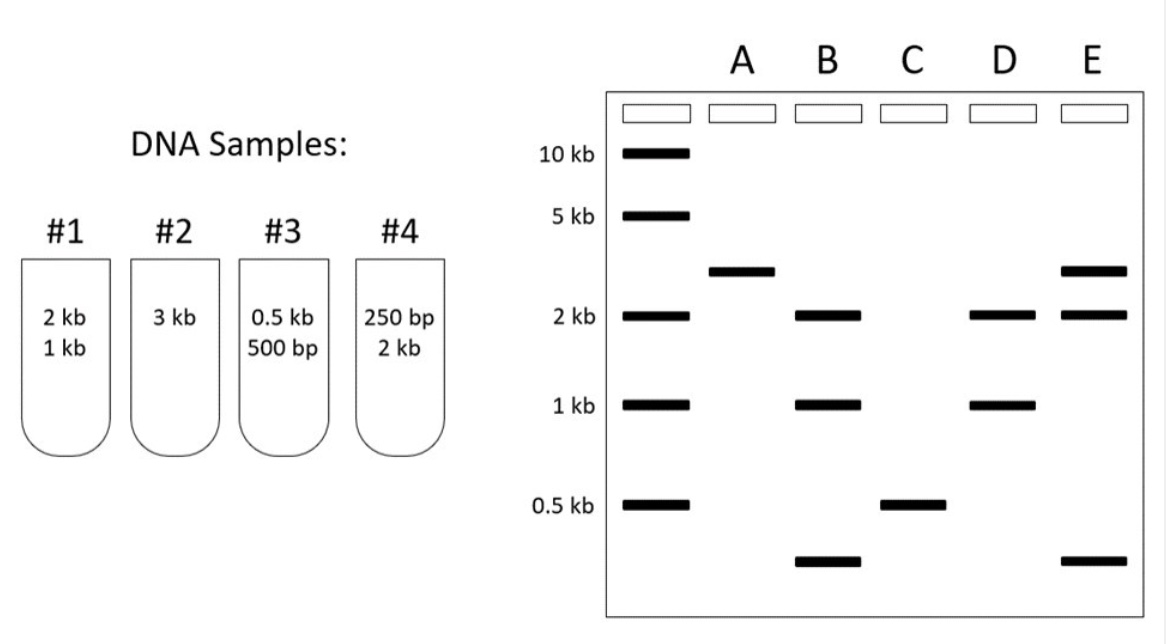
You are running four different DNA samples (#1, #2, #3, #4) on a gel. For each of the following questions, determine which lane on the gel (A-E) shows the results you would predict to observe.
Lane that shows the results of running Sample #3 only:
A) Lane B
B) Lane E
C) Lane D
D) Lane A
E) Lane C
E) Lane C
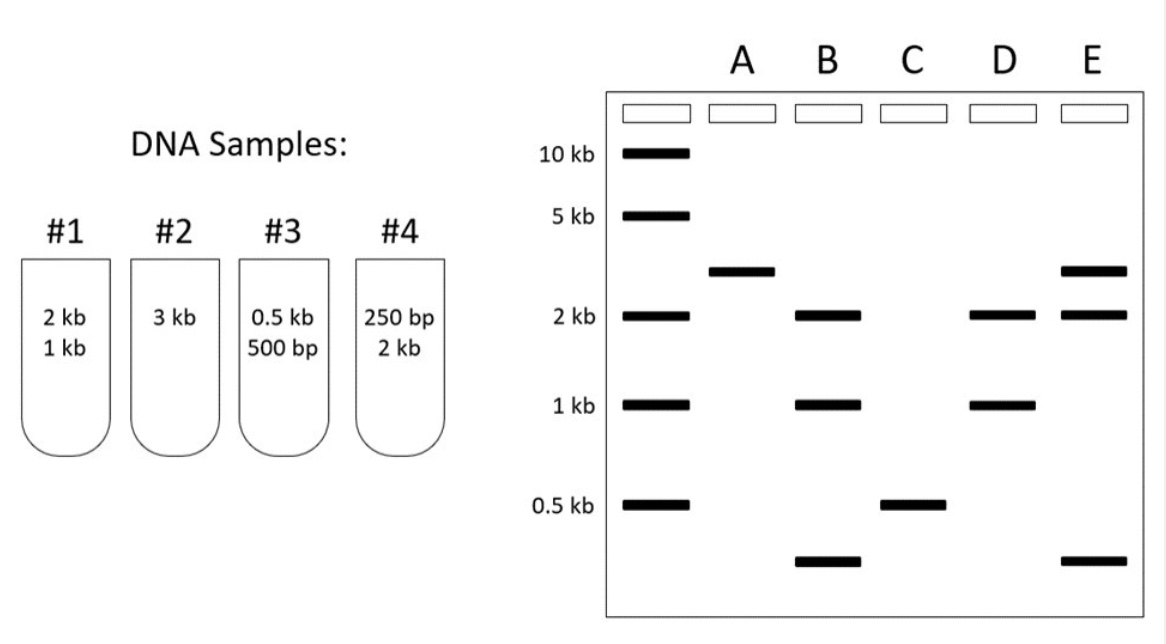
You are running four different DNA samples (#1, #2, #3, #4) on a gel. For each of the following questions, determine which lane on the gel (A-E) shows the results you would predict to observe.
Lane that shows the results of running Sample #1 and Sample #4 together:
A) Lane D
B) Lane B
C) Lane C
D) Lane E
E) Lane A
B) Lane B
A double-stranded DNA molecule, only part of which is shown, is being transcribed. If the molecule is transcribed from left to right, one of the nucleotides shown in bold red font would be the first transcribed in this small molecule.
5′–AATGCCGTAGATTGCAAA–3′
3′–TTACGGCATCTAACGTTT–5′
Which sequence is the correct RNA produced from the transcription of this DNA molecule?
A) 3′–AAUGCCGUAGAUUGCAAA–5′
B) 3′–UUACGGCAUCTAACGUUU–5′
C) 5′–UUACGGCAUCTAACGUUU–3′
D) 5′–AAUGCCGUAGAUUGCAAA–3′
D) 5′–AAUGCCGUAGAUUGCAAA–3′
![<p>Each of the questions below describes a different mutation that could occur in a eukaryotic gene. Determine which RNA gel below [A, B, C, or D] you would be most likely to observe as a consequence of each mutation. On each gel, “WT” is the normal wild type version of the mature mRNA and “MUT” is the mutated version of the mature mRNA. Answer choices may be used more than once or not at all.</p><p>Gel that would most likely result from a mutation that prevents the spliceosome from recognizing an intron:</p><p>A) Gel A</p><p>B) Gel B</p><p>C) Gel C</p><p>D) Gel D</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c88ce914-c3e5-4d12-bbd0-7445fa3a0505.jpg)
Each of the questions below describes a different mutation that could occur in a eukaryotic gene. Determine which RNA gel below [A, B, C, or D] you would be most likely to observe as a consequence of each mutation. On each gel, “WT” is the normal wild type version of the mature mRNA and “MUT” is the mutated version of the mature mRNA. Answer choices may be used more than once or not at all.
Gel that would most likely result from a mutation that prevents the spliceosome from recognizing an intron:
A) Gel A
B) Gel B
C) Gel C
D) Gel D
B) Gel B
![<p>Each of the questions below describes a different mutation that could occur in a eukaryotic gene. Determine which RNA gel below [A, B, C, or D] you would be most likely to observe as a consequence of each mutation. On each gel, “WT” is the normal wild type version of the mature mRNA and “MUT” is the mutated version of the mature mRNA. Answer choices may be used more than once or not at all.</p><p>Gel that would most likely result from a mutation in the promoter that prevents a general transcription factor from binding:</p><p>A) Gel D</p><p>B) Gel B </p><p>C) Gel A</p><p>D) Gel C</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dd05647a-494a-4c41-9f34-50ddf71ebe16.jpg)
Each of the questions below describes a different mutation that could occur in a eukaryotic gene. Determine which RNA gel below [A, B, C, or D] you would be most likely to observe as a consequence of each mutation. On each gel, “WT” is the normal wild type version of the mature mRNA and “MUT” is the mutated version of the mature mRNA. Answer choices may be used more than once or not at all.
Gel that would most likely result from a mutation in the promoter that prevents a general transcription factor from binding:
A) Gel D
B) Gel B
C) Gel A
D) Gel C
A) Gel D