AP Chemistry - 3.5: Kinetic-Molecular Theory & Graham's Law
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
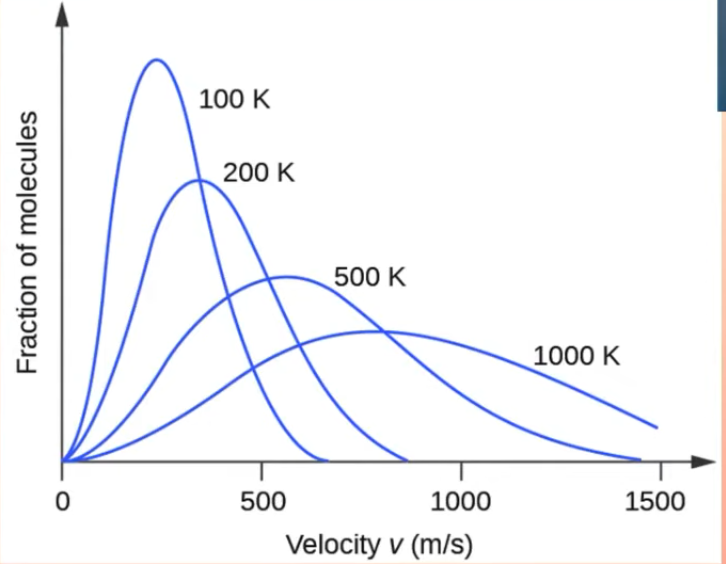
Boltzmann distribution curve
As temperature increases, velocity ____.
increases
As velocity increases, kinetic energy _____.
increases
True or False: Heat and temperature are the same.
False
Temperature
a numerical measure of the average kinetic energy in the molecules of a material
“Which of these molecules has the greatest average kinetic energy?”
Is the same as?
Which of these molecules has the greatest temperature?
Why are Kelvins used in SI regarding temperature and kinetic energy?
As temperature in Kelvins doubles, the kinetic energy also doubles
Heat
form of energy transferred between two systems at different temperatures
Heat synonym
Thermal energy
What is heat measured in
Joules
What does Graham's Law of Effusion simply describe?
the rate at which gas particles move
How is the rate of movement of gas particles related to it’s molecular mass?
Inversely proportional
Graham’s Law of Effusion

A gas with a greater molecular mass will have a ______ rate of movement.
Decreased
Graham’s Law of Effusion - Say it simply
Lighter gases move faster, heavier gases move slower
Effusion
the escaping of molecules through a very tiny hole in a material.
If a tank is rigid, volume increases or decreases?
NONE. Rigid = means volume can not increase
when referring to average molecular speed, which two variables must be considered
Molar Mass, temperature
Highest speed = lowest mm and highest temp