Anaerobic respiration
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
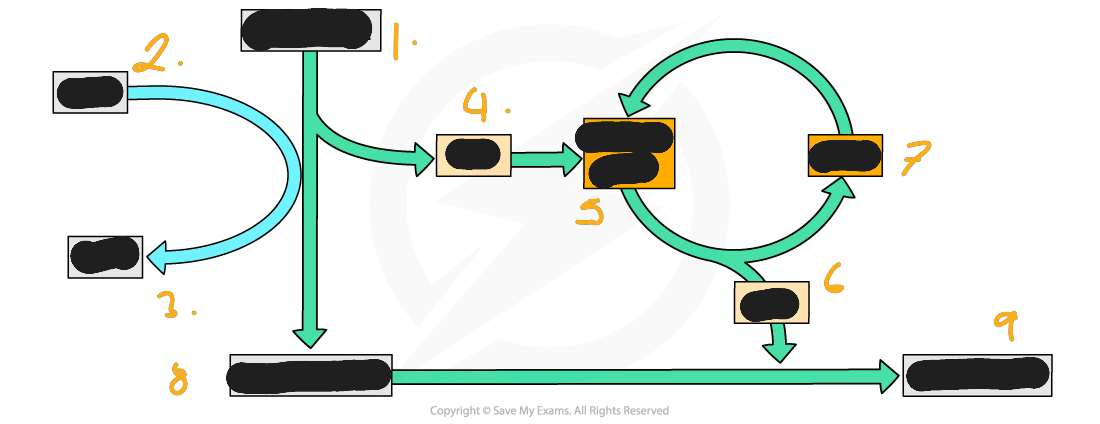
glucose the makes triose phosphate
ADP
ATP
2H
NADH +H+
2H
NAD
pyruvate
lactate
describe the process of anaerobic respiration in animals
Animals and bacteria the extra step converts pyruvate to lactate (or lactic acid). This is a reduction, so the NADH is oxidised meaning NAD is regenerated, to be used in glycolysis. The reaction is reversible, so the energy remaining in the lactate molecule can be retrieved when oxygen becomes available and the lactate is oxidised via the rest of aerobic respiration
The bacteria used to make yogurt use this reaction, as do muscle cells and red blood cells in humans.
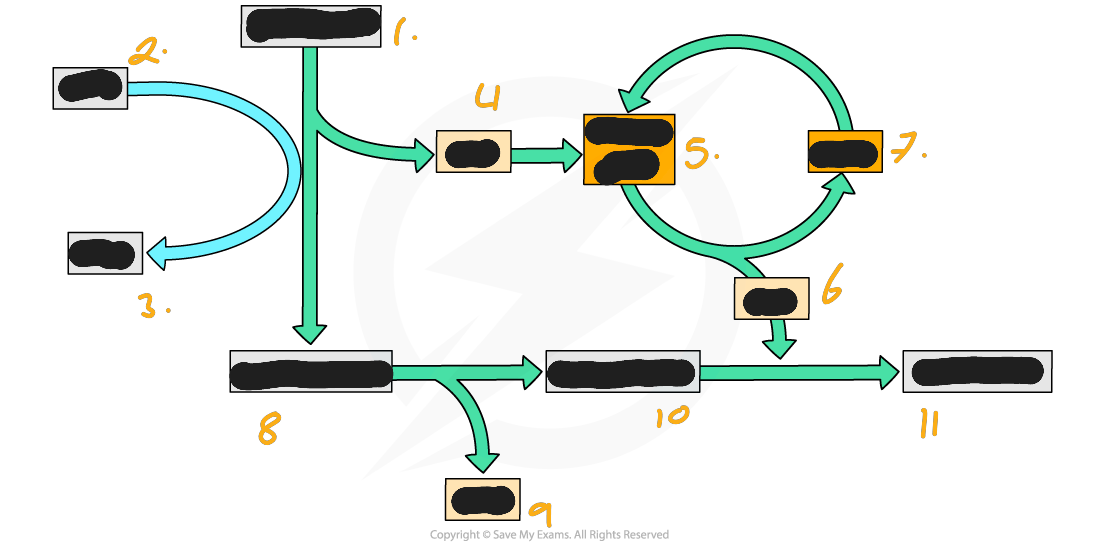
glucose which gets converted into triose phosphate
ADP
ATP
2H
NADH + H+
2H
NAD
pyruvate
CO2
ethanal
ethanol
describe the processes of anaerobic respiration in fungi and plants
In plants and fungi the extra steps converts pyruvate to ethanol. This is also a reduction, so NADH is used and NAD is regenerated, to be used in glycolysis. Ethanol is a two-carbon compound and carbon dioxide is also formed. This means the reaction is irreversible, so the energy in the ethanol cannot be retrieved by the cells.
|
Ethanolic anaerobic respiration is also known as fermentation, and we make use of fermentation in yeast to make ethanol in beer and wine.
why cant anaerobic respiration be sustained in animals
As it causes muscle cramp and fatigue
what causes the muscle fatigue
Lactic acid is a fairly strong acid so it lowers the pH in muscles cells, which slows enzymes therefore production of ATP and this contributes to muscle fatigue and cramp.
How many ATP per glucose are made in both plants+ fungi and animals+ bacteria
2
how many NADH are made in plants+ fungi and animals+ bacteria
In anaerobic respiration, the two NADH molecules produced during glycolysis are converted back to NAD+ so glycolysis can continue. Therefore, the net production of NADH in anaerobic respiration is zero.
where do both these processes occur
cytoplasm
what’s is another name for anaerobic respiration in fungi or plants
fermentation
when do animals respire anaerobically
strenuous exercise
what happens after this strenuous exercise
The Latic acid diffuses out of the cells and into the blood stream. The lactate is soluble. And is passes through the liver and oxidised back into pyruvate and then quickly broken down. We continue to breath more deeply and frequently in order to take in extra oxygen to repay the oxygen debt ( the amount of oxygen needed to break down the lactic acid)
describe how a sprinter is able to produce enough energy to run 100m without enough O2

what happens to lactate after its stopped being produced.
After exercise, when lactate is no longer being produced, lactate remains in the blood.
It is transported in the blood to the liver, where it is broken down.
In the liver, lactate is converted back into pyruvate.
This conversion involves oxidation of lactate and the production of reduced NAD (NADH).
The pyruvate is then oxidised further.
It enters the Krebs cycle, where it is fully broken down.
This process requires extra oxygen, which is why it contributes to oxygen debt after exercise.
As a result of aerobic respiration, carbon dioxide and water are produced.
