AP Psych Sensation & Perception
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
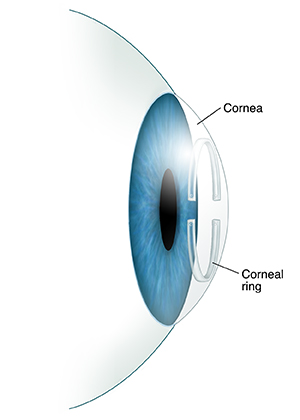
Cornea
- Transparent, dome-like structure on the front part of the eye
- Gives eye focusing or refracting power
- Gives eye focusing or refracting power
2
New cards
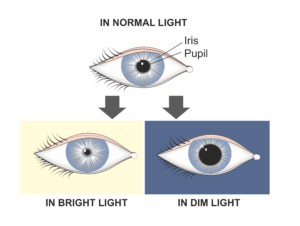
Pupil
- Adjustable opening in the center of the eye where light enters
- Controls amount of light entering eyes
- Controls amount of light entering eyes
3
New cards
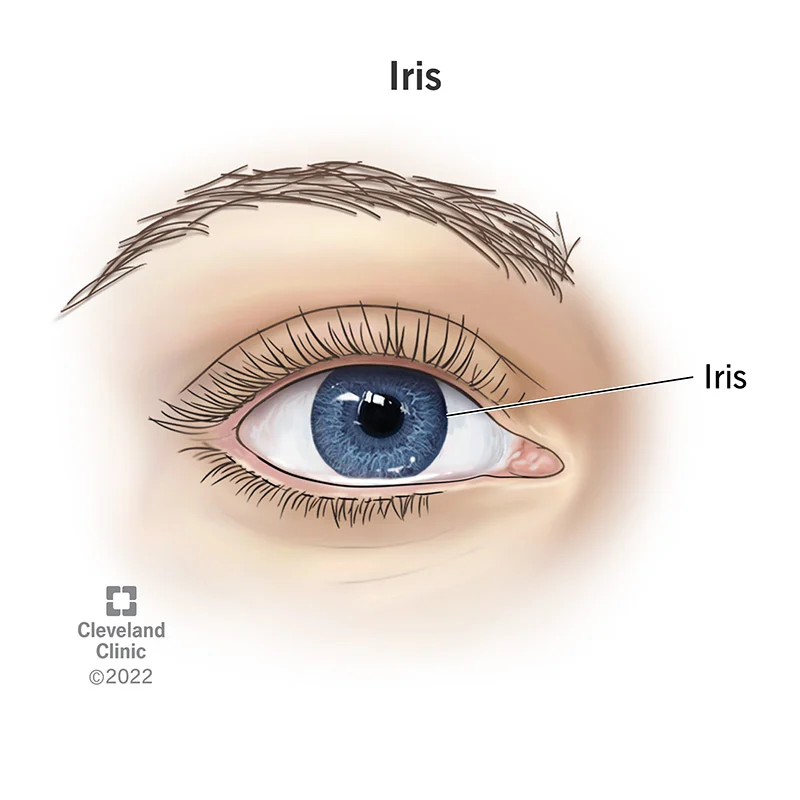
Iris
- Forms colored portion of the eye around the pupil
- Controls size of pupil opening
- Controls size of pupil opening
4
New cards
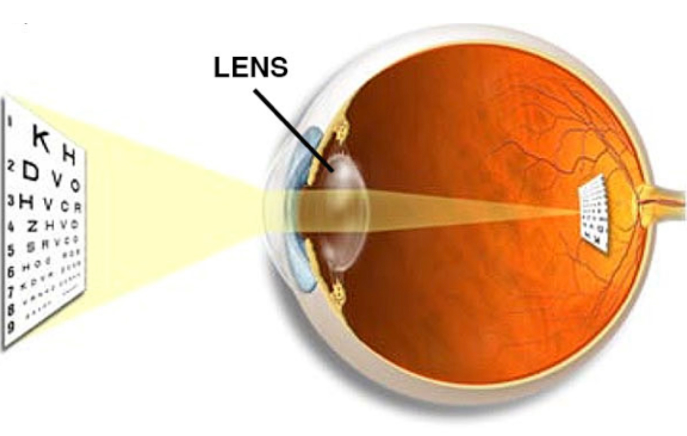
Lens
- Transparent structure behind pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina
- Focus the eye on near or far objects
- Focus the eye on near or far objects
5
New cards
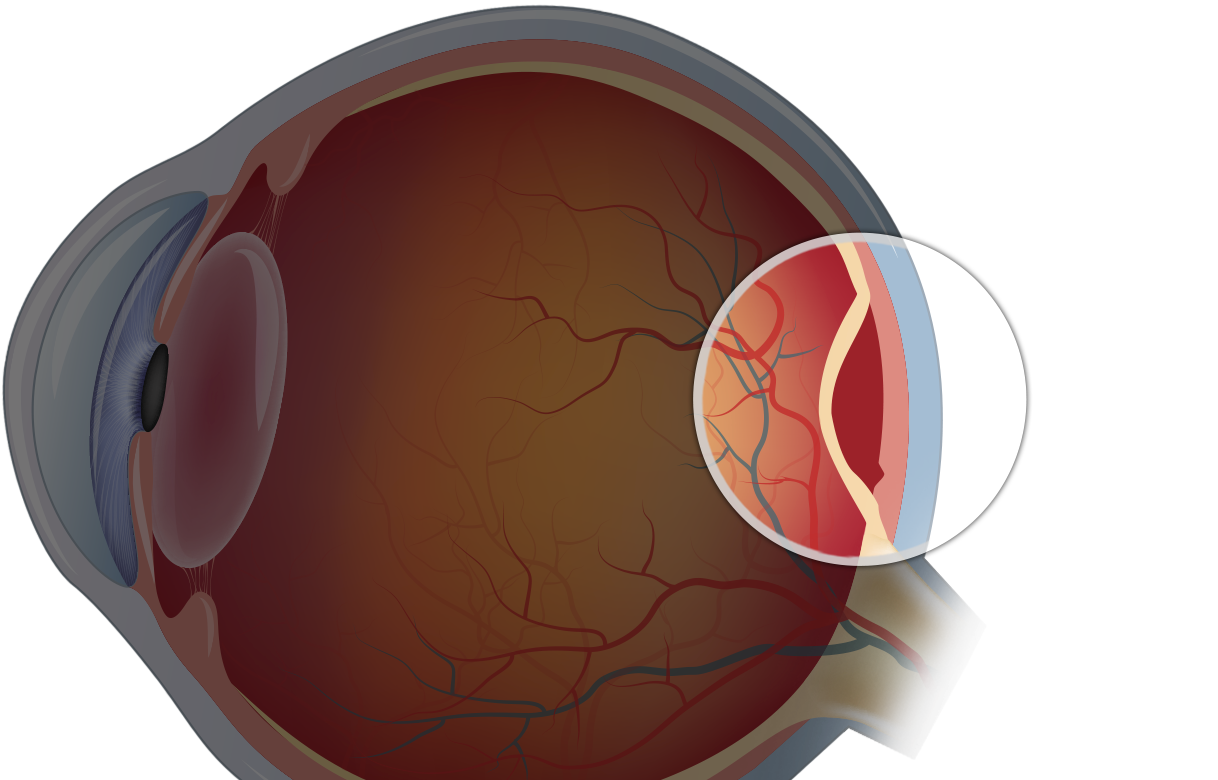
Retina
- Light-sensitive layer that lines the back of the eye
6
New cards
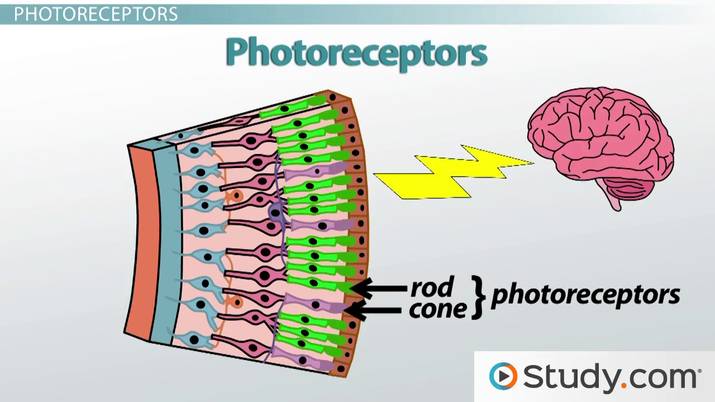
Photoreceptors
- Convert light energy to electrochemical neural impulses that are conducted to our brain
- Rods and cones
- Rods and cones
7
New cards
Rods
- Allow us to see in dim light
- Perception of movement in peripheral vision
- Perception of movement in peripheral vision
8
New cards
Cones
- Function in daylight and well-lit areas
- Ability to see color
- Ability to see color
9
New cards
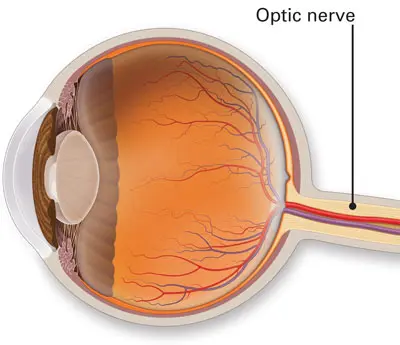
Optic Nerve
- Carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain (occipital lobe)
10
New cards
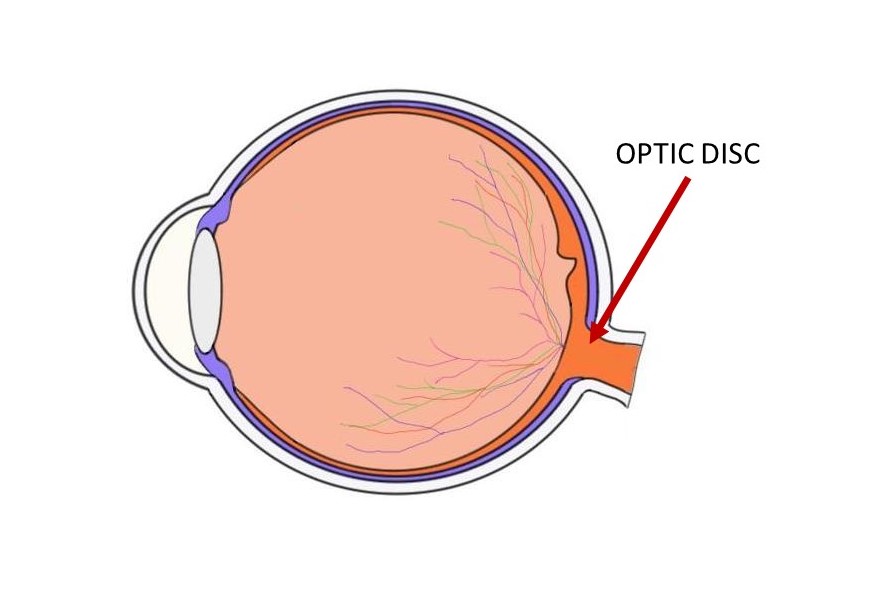
Blind Spot/Optic Disc
- Point where optic nerve leaves the eye
- No receptor cells located there
- No receptor cells located there
11
New cards
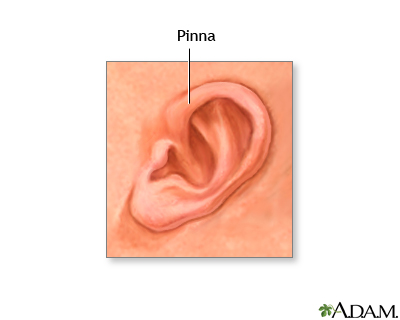
Pinna
- Outer ear, visible part
- Designed to catch sound waves
- Designed to catch sound waves
12
New cards
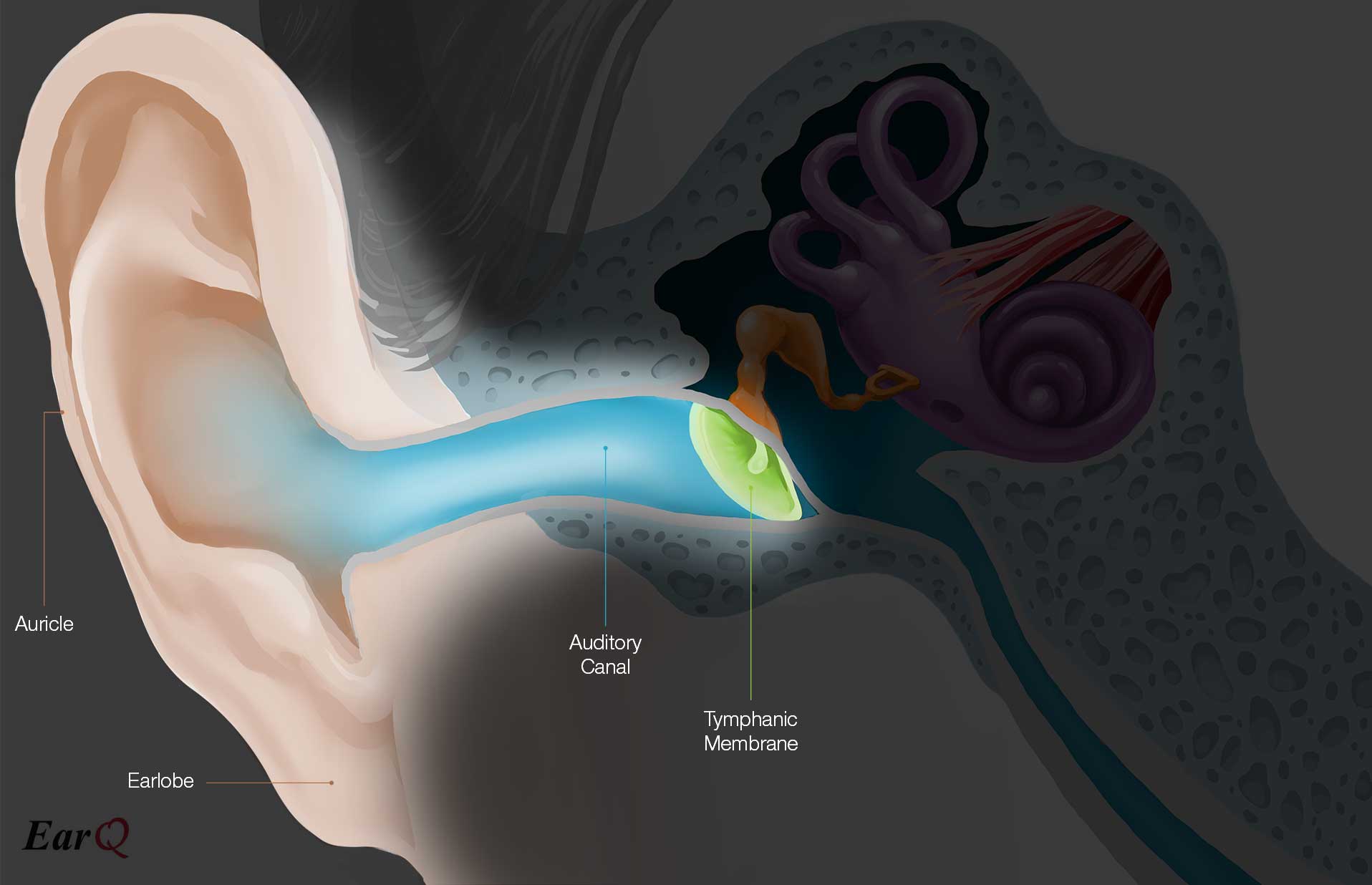
Auditory/Ear Canal
- Small tube in the outer ear between ear flap and eardrum
- Transfers sound waves through ear
- Transfers sound waves through ear
13
New cards
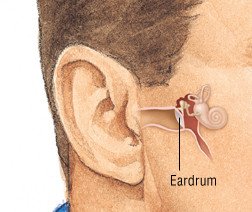
Tympanic Membrane/Eardrum
- Part of the ear that vibrates when sound waves hit it
14
New cards
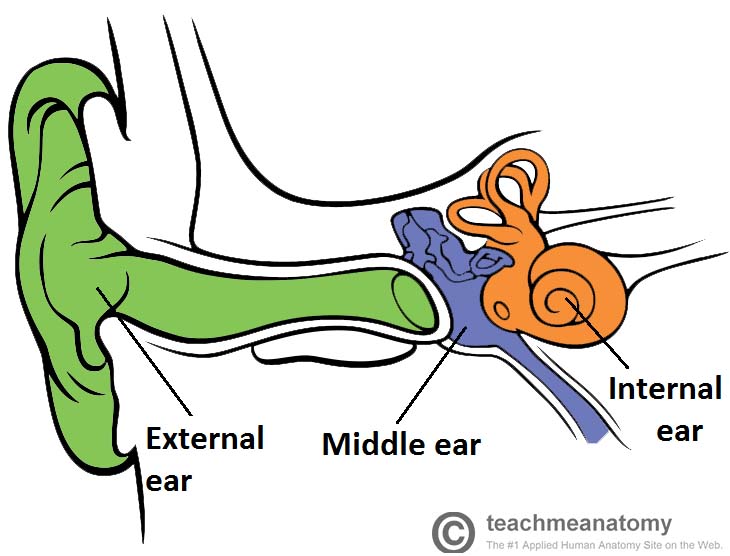
Middle Ear
- Between eardrum and cochlea
- Allow sound waves to vibrate bones (auditory ossicles)
- Malleus, incus, stopes
- Allow sound waves to vibrate bones (auditory ossicles)
- Malleus, incus, stopes
15
New cards
Cochlea
- Snail-looking, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear (sound waves trigger nerve impulses
- Also deals with balance
- Also deals with balance

16
New cards
Auditory Nerve
- Carries sound from cochlea to the brain
17
New cards
Gustation
- A two-phase chemical reaction that involves both our mouth and throat (taste) and nose (smell)
- Processing sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami
- Processing sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami
18
New cards
Olfacation
- Chemical molecules being breathed through the nose
19
New cards
Kinesthesis
- Sensing the position and movement of individual body parts
20
New cards
Vestibular
- Located in the inner ear
- Controls balance
- Controls balance
21
New cards
Absolute Threshold
- Smallest level of stimulus that can be detected
- Ex: The instant you start to hear music when gradually turning the volume up
- Ex: The instant you start to hear music when gradually turning the volume up
22
New cards
Just Noticeable Difference/Difference Threshold
- Amount something must be changed to notice the difference
- Ex: Noticing the volume difference between 0 and 10 but not noticing the difference between 10 and 11
- Ex: Noticing the volume difference between 0 and 10 but not noticing the difference between 10 and 11
23
New cards
Weber's Law
- Amount of stimulus needed to notice a change depends on how proportionate the change is from the strength of the original stimulus
24
New cards
Inattentional Blindness
- When our focus is directed at one stimulus, leaving us blind to other stimuli
25
New cards
Change Blindness
- Missing things that change in your environment
26
New cards
Synesthesia
- Condition in which two senses are sensed at the same time, where one type of stimulation evokes the sensation of another
27
New cards
Color Blindness
- Lacking functioning red or green sensitive cones (sometimes both)
- Missing cones that respond to a specific color
- Missing cones that respond to a specific color
28
New cards
Face Blindness
- Inability to recognize people's faces
29
New cards
Monocular Perception
- Clues that can be used in depth perception that only need one eye
30
New cards
Binocular Perception
- Require both eyes to perceive depth or distance
31
New cards
Gestalt Perception
- Brain’s tendency to integrate pieces of information into meaningful wholes
32
New cards
Perceptual Constancy
- Top-down process
- Tendency to perceive an object you are familiar with as having a constant shape, size, and brightness despite the stimuli changes that occur
- Tendency to perceive an object you are familiar with as having a constant shape, size, and brightness despite the stimuli changes that occur
33
New cards
Hubel & Weisel
- Made studies on visual cortex by recording the electrical activity of cat brains
- Sewed some cats eyes shut
- Sewed some cats eyes shut
34
New cards
Gustav Fechner
- Demonstrated that mental processes can be measured