Chapter 4: Extensions of Mendelian Inheritance
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:02 AM on 2/11/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
Mendelian inheritance
a pattern of inheritance that follows Mendel’s laws; this pattern involves the transmission of eukaryotic genes that are located on the chromosomes found within the cell nucleus.
2
New cards
law of serration, law of independent assortment
traits in eukaryotic species that follow a Mendelian inheritance pattern obey two laws: _____ & _____
3
New cards
simple Mendelian inheritance
an inheritance pattern involving a simple, dominant/recessive relationship that produces observed ratios in the offspring that readily obey Mendel’s laws
4
New cards
single, two, dominant, recessive, 3:1
simple Mendelian inheritance:
* traits that are affected by a _____ gene that is found in _____ different alleles
* _____/_____ relationship
* F2 generation phenotypic ratio: _____
* traits that are affected by a _____ gene that is found in _____ different alleles
* _____/_____ relationship
* F2 generation phenotypic ratio: _____
5
New cards
wild-type allele
an allele that is fairly prevalent in a natural population, generally found in more than 1% of the population
6
New cards
most, proper, normally
wild-type alleles:
* _____ prevalent alle in a population
* a wild-type allele typically encodes a protein that is made in the _____ amount and functions _____
* _____ prevalent alle in a population
* a wild-type allele typically encodes a protein that is made in the _____ amount and functions _____
7
New cards
genetic polymorphism
when two or more alleles occur in population, each allele is found at a frequency of 1% of higher
8
New cards
mutant allele
an allele that has been created by altering a wild-type allele by mutation
9
New cards
wild-type, mutation, defective, rare, recessive
mutant alleles:
* an allele that has been created by altering a _____ allele by _____
* because random mutations are more likely to disrupt gene function, mutant alleles are often _____ in their ability to express a functional protein
* _____ in natural populations
* typically inherited in a _____ fashion
* an allele that has been created by altering a _____ allele by _____
* because random mutations are more likely to disrupt gene function, mutant alleles are often _____ in their ability to express a functional protein
* _____ in natural populations
* typically inherited in a _____ fashion
10
New cards
recessive, single, dominant, recessive, 50%, wild-type, more, up-regulated
heterozygotes in simple dominant/recessive relationship:
* the _____ allele does not affect the phenotype of the heterozygote
* a _____ copy of the _____ allele is sufficient enough to mask the effects of the _____ allele
* first explanation: _____ of the function protein in adequate to provide the _____ phenotype
* second explanation: heterozygote actually produces _____ than 50% of the function protein
* due to gene regulation, the expression of the normal gene may be increased, or _____, in the heterozygote to compensate for the lack of function of the defective allele
* the _____ allele does not affect the phenotype of the heterozygote
* a _____ copy of the _____ allele is sufficient enough to mask the effects of the _____ allele
* first explanation: _____ of the function protein in adequate to provide the _____ phenotype
* second explanation: heterozygote actually produces _____ than 50% of the function protein
* due to gene regulation, the expression of the normal gene may be increased, or _____, in the heterozygote to compensate for the lack of function of the defective allele
11
New cards
less
dominant mutant alleles are much _____ common than recessive mutant alleles
12
New cards
gain-of-function mutation
a mutation that changes a gene product so that it gains a new or abnormal function
13
New cards
dominant-negative mutation
a mutation that produces an altered gene product that acts antagonistically to the normal gene product
14
New cards
haploinsufficiency
the phenomenon in which an individual has only a single functional copy of a gene and that single functional copy does not produce a normal phenotype
15
New cards
incomplete dominance
a pattern of inheritance in which a heterozygote that carries two different alleles exhibits a phenotype that is intermediate to those of the corresponding homozygous individuals. For example, a heterozygote may have pink flowers, whereas the homozygotes have red or white flowers.
16
New cards
intermediate, blending, 50%, not, dominant, red, pink, white, half
incomplete dominance:
* heterozygote has an _____ phenotype between either corresponding homozygote (_____)
* heterozygotes produce only _____ of the normal protein, but this amount is _____ sufficient to produce the same phenotype as the _____ homozygote, which may make twice as much of the protein
* examples:
* four-o’clock plant flower color
* dominant homozygote: _____
* heterozygote: _____
* recessive homozygote: _____
* Mendel’s pea seed shape
* the heterozygote only has _____ the amount of starch as is found in the dominant homozygote’s seed
* heterozygote has an _____ phenotype between either corresponding homozygote (_____)
* heterozygotes produce only _____ of the normal protein, but this amount is _____ sufficient to produce the same phenotype as the _____ homozygote, which may make twice as much of the protein
* examples:
* four-o’clock plant flower color
* dominant homozygote: _____
* heterozygote: _____
* recessive homozygote: _____
* Mendel’s pea seed shape
* the heterozygote only has _____ the amount of starch as is found in the dominant homozygote’s seed
17
New cards
incomplete penetrance
a situation in which an allele that is expected to cause a particular phenotype does not
18
New cards
dominant, dominant, not, heterozygotes, population, expressivity, polydactyly, dominant, single, dominant, not
incomplete penetrance:
* in the case of _____ traits, this pattern occurs when a _____ phenotype is _____ expressed even though an individual carries a dominant allele (only in _____)
* the measure of penetrance is described at the _____ level
* 60% of the heterozygotes carrying a dominant allele exhibit the trait = 60% penetrant
* _____ = the degree to which a trait is expressed
* influenced by environment and other genes
* example: _____ (additional fingers and/or toes)
* autosomal _____ allele
* a _____ copy of this allele is sufficient to cause the condition
* sometimes, individuals carry the _____ allele but do _____ exhibit the trait
* in the case of _____ traits, this pattern occurs when a _____ phenotype is _____ expressed even though an individual carries a dominant allele (only in _____)
* the measure of penetrance is described at the _____ level
* 60% of the heterozygotes carrying a dominant allele exhibit the trait = 60% penetrant
* _____ = the degree to which a trait is expressed
* influenced by environment and other genes
* example: _____ (additional fingers and/or toes)
* autosomal _____ allele
* a _____ copy of this allele is sufficient to cause the condition
* sometimes, individuals carry the _____ allele but do _____ exhibit the trait
19
New cards
white, brown, protein, higher, lower
environmental impacts:
* the arctic fox goes through two color phases (temperature-sensitive allele)
* cold winter = primarily _____
* warmer summer = mostly _____
* phenylketonuria (PKU)
* _____-rich foods = PKU individuals manifest a variety of detrimental traits
* eyes of fruit flies (norm of reaction)
* facet number varies with changes in temperature
* lower temperature = _____ facet number
* higher temperature = _____ facet number
* the arctic fox goes through two color phases (temperature-sensitive allele)
* cold winter = primarily _____
* warmer summer = mostly _____
* phenylketonuria (PKU)
* _____-rich foods = PKU individuals manifest a variety of detrimental traits
* eyes of fruit flies (norm of reaction)
* facet number varies with changes in temperature
* lower temperature = _____ facet number
* higher temperature = _____ facet number
20
New cards
temperature-sensitive allele
an allele for which the resulting phenotype depends on the environmental temperature
21
New cards
norm of reaction
the effects of environmental variation on an individual’s traits
22
New cards
overdominance
an inheritance pattern in which a heterozygote has greater reproductive success than either of the corresponding homozygotes
23
New cards
heterozygote advantage, greater, HbA, HbS, HbSHbS, HbAHbS, malaria, heterozygotes, malaria, increased, malaria, tuberculosis, enhanced, differences
overdominance:
* also known as _____ _____
* a heterozygote has _____ reproductive success compared with either of the corresponding homozygotes
* example:
* sickle-cell anemia
* _____: encodes the normal hemoglobin (hemoglobin A)
* _____: encodes the abnormal hemoglobin (hemoglobin S)
* homozygous _____
* abnormal sickled cells can become clogged in the capillaries throughout the body, leading to localized areas of oxygen depletion
* causes pain and sometimes tissue and organ damage
* shortened life span
* heterozygous _____
* resistant to _____
* red blood cells of ____ rupture when infected with malaria, preventing the propagation of _____
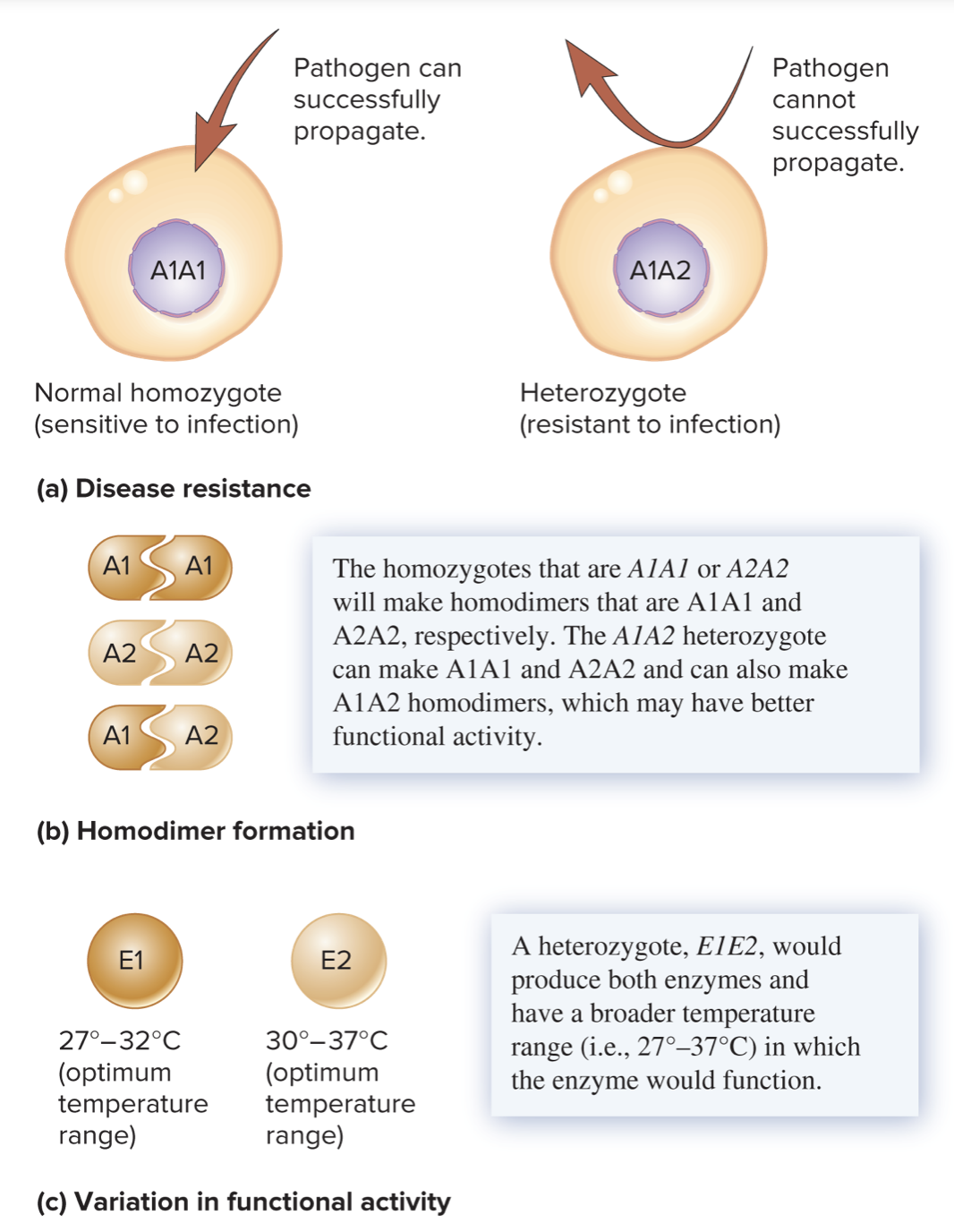
* Disease resistance
* heterozygous cells may have _____ resistance to infections by microorganisms
* heterozygote of sickle cell may be resistant to _____
* heterozygote of tay-sacks may be resistant to _____
* Homodimer formation
* heterozygotes may produce more forms of protein dimers with _____ function
* heterozygous homodimers may have better functional activity because they are more stable or able to function under a wider range of conditions
* variation in functional activity
* proteins encoded by each allele exhibit _____ in their functional activity
* the heterozygote, which makes a mixture of both enzymes, may be at an advantage under a wider temperature range than either of the corresponding homozygotes
* also known as _____ _____
* a heterozygote has _____ reproductive success compared with either of the corresponding homozygotes
* example:
* sickle-cell anemia
* _____: encodes the normal hemoglobin (hemoglobin A)
* _____: encodes the abnormal hemoglobin (hemoglobin S)
* homozygous _____
* abnormal sickled cells can become clogged in the capillaries throughout the body, leading to localized areas of oxygen depletion
* causes pain and sometimes tissue and organ damage
* shortened life span
* heterozygous _____
* resistant to _____
* red blood cells of ____ rupture when infected with malaria, preventing the propagation of _____
* Disease resistance
* heterozygous cells may have _____ resistance to infections by microorganisms
* heterozygote of sickle cell may be resistant to _____
* heterozygote of tay-sacks may be resistant to _____
* Homodimer formation
* heterozygotes may produce more forms of protein dimers with _____ function
* heterozygous homodimers may have better functional activity because they are more stable or able to function under a wider range of conditions
* variation in functional activity
* proteins encoded by each allele exhibit _____ in their functional activity
* the heterozygote, which makes a mixture of both enzymes, may be at an advantage under a wider temperature range than either of the corresponding homozygotes
24
New cards
multiple alleles
two or more alleles of the same gene found within a population
25
New cards
Himalayan, darker
temperature-sensitive conditional allele:
* _____ rabbit coat color
* enzyme is only functional at low temperatures
* _____ fur only in cooler areas of the body
* _____ rabbit coat color
* enzyme is only functional at low temperatures
* _____ fur only in cooler areas of the body
26
New cards
ii, IAIA, IAi, IBIB, IBi, IAIB, glycosyl transferase, A-acetylgalactosamine, glycosyl transferase, galactose
ABO blood types:
* O: _____
* A: _____ or _____
* B: _____ or _____
* AB: _____
* _____ _____ encoded by the IA allele attaches _____ to the oligosaccharide
* _____ _____ encoded by the IB alleles attaches _____ to the oligosaccharide
* O: _____
* A: _____ or _____
* B: _____ or _____
* AB: _____
* _____ _____ encoded by the IA allele attaches _____ to the oligosaccharide
* _____ _____ encoded by the IB alleles attaches _____ to the oligosaccharide
27
New cards
codominance
a pattern of inheritance in which two alleles are both expressed in the heterozygous condition. For example, a person with the genotype *IAIB* has the blood type AB and expresses both surface antigens A and B.
28
New cards
both, without
codominance:
* this pattern occurs when the heterozygote expresses _____ alleles simultaneously _____ forming an intermediate phenotype
* the codominant alleles encode proteins that function slightly differently from each other, and the function of each protein in the heterozygote affects the phenotype uniquely
* this pattern occurs when the heterozygote expresses _____ alleles simultaneously _____ forming an intermediate phenotype
* the codominant alleles encode proteins that function slightly differently from each other, and the function of each protein in the heterozygote affects the phenotype uniquely
29
New cards
sex chromosomes
a pair of chromosomes (e.g., X and Y in mammals) that differ between males and females and determine sex in a species
30
New cards
X-linked inheritance
an inheritance pattern in certain species that involves genes that are located only on the X chromosome
31
New cards
X, Y, males, X
X-linked inheritance:
* when a gene is located on the _____ chromosomes but not on the _____ chromosome
* only _____ are affected
* this pattern involves the inheritance of gene that are located on the _____ chromosome
* when a gene is located on the _____ chromosomes but not on the _____ chromosome
* only _____ are affected
* this pattern involves the inheritance of gene that are located on the _____ chromosome
32
New cards
hemizygous
indicates that a male has a single copy of an X-linked gene. A male mammal is said to be hemizygous for X-linked genes.
33
New cards
X-linked recessive
an inheritance pattern in which a gene is found on the X chromosome and the disease-causing allele is recessive relative to a corresponding dominant allele
34
New cards
reciprocal crosses
a pair of crosses in which the traits of the two parents differ with regard to sex
35
New cards
sex-linked gene
a gene that is located on only one of the sex chromosomes
36
New cards
Y-linked genes
genes that are located only on the Y chromosome
37
New cards
one, both, Thomas Morgan, eye color, hemizygous, males, few, holandric
sex-linked gene:
* a gene that is found on _____ of the two types of sex chromosomes but not on _____
* _____ _____ (“father of molecular genetics)
* _____ _____ of fruit flies
* X-linked
* _____ in males
* _____ are more commonly affected
* Y-linked
* very _____ genes
* _____ genes
* a gene that is found on _____ of the two types of sex chromosomes but not on _____
* _____ _____ (“father of molecular genetics)
* _____ _____ of fruit flies
* X-linked
* _____ in males
* _____ are more commonly affected
* Y-linked
* very _____ genes
* _____ genes
38
New cards
pseudoautosomal inheritance
the inheritance pattern of genes that are found on both the X and Y chromosomes
39
New cards
Mic2
pseudoautosomal inheritance:
* the X and Y chromosomes contain short regions of homology where both chromosomes carry the same gene
* example: _____ gene
* the X and Y chromosomes contain short regions of homology where both chromosomes carry the same gene
* example: _____ gene
40
New cards
sex-influenced inheritance
an inheritance pattern in which an allele is dominant in one sex but recessive in the opposite sex
41
New cards
dominant, recessive, heterozygotes, autosomal, scars, males, females
sex-influenced inheritance:
* an inheritance pattern in which an allele is _____ in one sex but _____ in the opposite sex
* a phenomenon of _____
* the genes that govern sex-influenced traits are _____
* example: _____ (hornlike growth) in cattle
* dominant in _____
* recessive in _____
* an inheritance pattern in which an allele is _____ in one sex but _____ in the opposite sex
* a phenomenon of _____
* the genes that govern sex-influenced traits are _____
* example: _____ (hornlike growth) in cattle
* dominant in _____
* recessive in _____
42
New cards
sex-limited inheritance
an inheritance pattern in which a trait is found in only one of the two sexes. An example of such a trait is beard development in men.
43
New cards
one, autosomal, breast development, beard growth, sexual dimorphism
sex-limited inheritance:
* traits occur in only _____ of the two sexes
* the genes that affect sex-limited traits are _____
* examples:
* _____ _____ limited to females
* _____ _____ limited to males
* sex-limited traits are responsible for _____ _____ in which members of the opposite sexes have different morphological feature
* traits occur in only _____ of the two sexes
* the genes that affect sex-limited traits are _____
* examples:
* _____ _____ limited to females
* _____ _____ limited to males
* sex-limited traits are responsible for _____ _____ in which members of the opposite sexes have different morphological feature
44
New cards
sexual dimorphism
phenomenon in which the males and females of a species are morphologically distinct
45
New cards
lethal allele
an allele that may cause the death of an organism
46
New cards
death, essential, loss-of-function, gain-of-function, recessive, dominant, homozygous, cell division
lethal allele:
* al allele that has the potential of causing the _____ of an organism
* great majority of lethal mutation occur in _____ genes
* a _____ mutation in a nonessential gene will not usually cause death
* on rare occasions, a nonessential gene may acquire a _____ mutation that causes the gene product to be abnormally expressed in a way that may interfere with normal cell function and lead to a lethal phenotype
* usually inherited in a _____ manner
* can be a _____ trait
* Manx cat
* dominant mutant allele is lethal in the _____ condition
* many legal alleles disrupt proper _____ _____ and thereby cause an organism to die at a very early stage
* lethal alleles can exert their effects early or later in life
* al allele that has the potential of causing the _____ of an organism
* great majority of lethal mutation occur in _____ genes
* a _____ mutation in a nonessential gene will not usually cause death
* on rare occasions, a nonessential gene may acquire a _____ mutation that causes the gene product to be abnormally expressed in a way that may interfere with normal cell function and lead to a lethal phenotype
* usually inherited in a _____ manner
* can be a _____ trait
* Manx cat
* dominant mutant allele is lethal in the _____ condition
* many legal alleles disrupt proper _____ _____ and thereby cause an organism to die at a very early stage
* lethal alleles can exert their effects early or later in life
47
New cards
essential gene
a gene that is essential for survival
48
New cards
1/3
approximately _____ of all genes are essential genes
49
New cards
nonessential genes
genes that are not absolutely required for survival, although they are likely to be beneficial to the organism
50
New cards
conditional lethal allele
an allele that is lethal, but only under certain environmental conditions
51
New cards
temperature-sensitive (ts) lethal allele
an allele that is lethal only in a certain environmental temperature range (type of conditional lethal allele)
52
New cards
semilethal alleles
lethal alleles that kill some individuals but not all
53
New cards
some, all, environmental, genes
semilethal alleles:
* lethal allele that kills _____ individuals but not _____
* _____ conditions and the actions of other _____ within the organism may help to prevent the detrimental effects of certain semilethal alleles
* lethal allele that kills _____ individuals but not _____
* _____ conditions and the actions of other _____ within the organism may help to prevent the detrimental effects of certain semilethal alleles
54
New cards
pleiotropy
the multiple effects of a single gene on the phenotype of an organism
55
New cards
more, cell, development
pleiotropy occurs for several reasons, including the following:
1. the expression of a single gene can affect cell function in _____ than one way
2. a gene may be expressed in different _____ types in a multicellular organism
3. a gene may expressed at different stages of _____
1. the expression of a single gene can affect cell function in _____ than one way
2. a gene may be expressed in different _____ types in a multicellular organism
3. a gene may expressed at different stages of _____
56
New cards
cystic fibrosis, CFTR, chloride
_____ _____ (example of a pleiotropic mutation):
* normal allele encodes a protein called the _____
* mutation diminished the function of _____ transport
* thick mucus in the lungs
* excessively salty sweat
* sterility
* normal allele encodes a protein called the _____
* mutation diminished the function of _____ transport
* thick mucus in the lungs
* excessively salty sweat
* sterility
57
New cards
gene interaction
the phenomenon in which two or more different genes influence the outcome of a single trait
58
New cards
height, weight, pigmentation
examples of gene interaction
59
New cards
two, four, rose, pea, codominant, R_pp, rrP_, R_P_, rrpp, 9, 3, 3, 1
two-gene interaction - 4:
* _____ genes influence the outcome of a single trait with _____ phenotypes
* example: comb morphology in chicken
* R: _____ comb
* P: _____ comb
* R and P are _____
* rose comb: _____
* pea comb: _____
* walnut comb: _____
* single comb: _____
* Ratio: _____ walnut : _____ rose : _____ pea : _____ single
* _____ genes influence the outcome of a single trait with _____ phenotypes
* example: comb morphology in chicken
* R: _____ comb
* P: _____ comb
* R and P are _____
* rose comb: _____
* pea comb: _____
* walnut comb: _____
* single comb: _____
* Ratio: _____ walnut : _____ rose : _____ pea : _____ single
60
New cards
epistasis
an inheritance pattern where one gene can mask the phenotypic effects of a different gene
61
New cards
mask, homozygote, common function
epistasis:
* alleles of one gene _____ the phenotypic effects of the alleles of another gene
* recessive epistasis
* _____ of one gene is required to mask the dominant phenotype
* example: flower color in the sweet pea
* homozygous recessive (either cc or pp) mask C or P alleles (purple-color-producing alleles) to produce a white color
* epistasis often occurs because two (or more) different proteins participate in a _____ _____
* alleles of one gene _____ the phenotypic effects of the alleles of another gene
* recessive epistasis
* _____ of one gene is required to mask the dominant phenotype
* example: flower color in the sweet pea
* homozygous recessive (either cc or pp) mask C or P alleles (purple-color-producing alleles) to produce a white color
* epistasis often occurs because two (or more) different proteins participate in a _____ _____
62
New cards
recessive epistasis
a form of epistasis in which an individual must be homozygous for either recessive allele to mask a particular phenotype
63
New cards
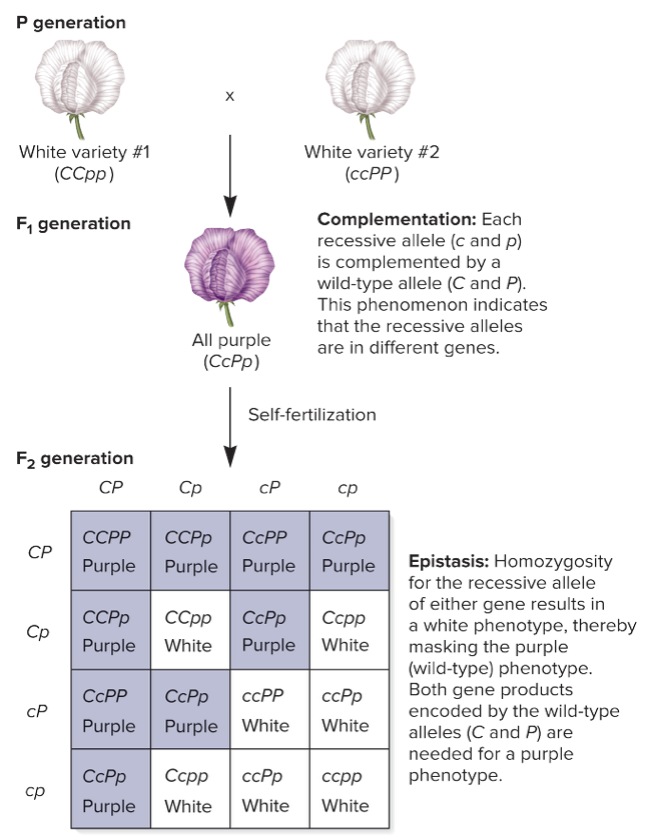
two, two, CCpp, ccPP, CcPp, 9, 7, recessive, homozygous, cc, pp, white, homozygous, white
two-gene interaction - 2:
* _____ genes influence the outcome of a single trait with _____ phenotypes
* flower color in the sweet pea
* P generation: _____ x _____
* F1 generation: _____
* F2 generation: _____ purple : _____ white
* _____ epistasis:
* _____ recessive (either _____ or _____) mask C or P alleles (purple-color-producing alleles) to produce a _____ color
* a plant that is _____ recessive for either gene will be _____
* _____ genes influence the outcome of a single trait with _____ phenotypes
* flower color in the sweet pea
* P generation: _____ x _____
* F1 generation: _____
* F2 generation: _____ purple : _____ white
* _____ epistasis:
* _____ recessive (either _____ or _____) mask C or P alleles (purple-color-producing alleles) to produce a _____ color
* a plant that is _____ recessive for either gene will be _____
64
New cards
two, C, cc, P, pp, homozygous, one, purple, white
formation of a purple pigment in the sweet pea flower:
* a colorless precursor molecule must be acted on by _____ different enzymes to produce the purple pigment
* enzyme _____: converts the colorless precursor into a colorless intermediate
* homozygous recessive (_____) = lack of production of this enzyme in the homozygote
* enzyme _____: converts colorless intermediate into the purple pigment
* homozygous recessive (_____) = lack of production of this enzyme in the homozygote
* if a plant is _____ for either recessive allele, it will not make any function enzyme C or enzyme P, respectively
* when _____ of these enzymes is missing, _____ pigment cannot be made, and the flowers remain _____
* a colorless precursor molecule must be acted on by _____ different enzymes to produce the purple pigment
* enzyme _____: converts the colorless precursor into a colorless intermediate
* homozygous recessive (_____) = lack of production of this enzyme in the homozygote
* enzyme _____: converts colorless intermediate into the purple pigment
* homozygous recessive (_____) = lack of production of this enzyme in the homozygote
* if a plant is _____ for either recessive allele, it will not make any function enzyme C or enzyme P, respectively
* when _____ of these enzymes is missing, _____ pigment cannot be made, and the flowers remain _____
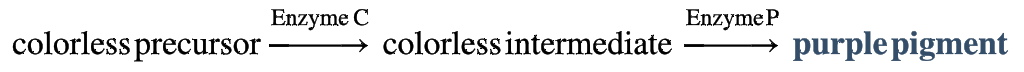
65
New cards
complementation
a phenomenon in which the presence of two different mutant alleles in the same organism produces a wild-type phenotype. It usually happens because the two mutations are in different genes, so the organism carries one copy of each mutant allele and one copy of each wild-type allele.
66
New cards
recessive, wild-type, purple, white
complementation:
* a phenomenon in which two parents that express the same or similar _____ phenotypes produce offspring with a _____ phenotype
* example: flower color in the sweet pea
* _____-flowered F1 offspring were obtained from two _____-flowered parents
* a phenomenon in which two parents that express the same or similar _____ phenotypes produce offspring with a _____ phenotype
* example: flower color in the sweet pea
* _____-flowered F1 offspring were obtained from two _____-flowered parents
67
New cards
two, three, agouti, colored, black, albino, 9, 3, 4
two-gene interaction - 3:
* _____ genes influence the outcome of a single trait with _____ phenotypes
* example: rodent coat color
* A: _____
* C: _____
* aa: _____
* cc: _____
* Ratio: _____ agouti : _____ black : _____ albino
* _____ _____ _____: an outcome in which the allele of one gene modifies the phenotypic effect of the allele of a different gene
* _____ genes influence the outcome of a single trait with _____ phenotypes
* example: rodent coat color
* A: _____
* C: _____
* aa: _____
* cc: _____
* Ratio: _____ agouti : _____ black : _____ albino
* _____ _____ _____: an outcome in which the allele of one gene modifies the phenotypic effect of the allele of a different gene
68
New cards
gene modifier effect
an outcome in which the allele of one gene modifies the phenotypic effect of the allele of a different gene
69
New cards
gene knockout
in the case of diploid species, the condition in which both copies of a gene have been altered to an inactive form
70
New cards
structure, function, phenotypes,
gene knockouts:
* understand how that gene affects the _____ and _____ of cells or the _____ of organisms
* many knockouts have _____ obvious effect on phenotype at the cellular level or the level of discernible traits
* understand how that gene affects the _____ and _____ of cells or the _____ of organisms
* many knockouts have _____ obvious effect on phenotype at the cellular level or the level of discernible traits
71
New cards
gene redundancy
the phenomenon in which one gene compensates for the loss of function of another gene
72
New cards
paralogs
* certain genes that have even duplicated during evolution, so a species may have two or more copies of similar gene, which are not identical due to the accumulation of random changes during evolution
* homologous genes within a single species that constitute a gene family
* homologous genes within a single species that constitute a gene family