psych 223 mideterm 1 flashcards - ualberta
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
down syndrome - description, treatment and incidence
description: a extra chromosome chases mild to severe intellectual disability and physical abnormalities
treatment: surgery, early intervention, infnat stimulation and special learning programs
incidence:
1 in 1900 birth at age 20
1 in 300 births at age 35
1 in 30 births at age 45
kleinefelter sydrome (xxy)
description: extra x chromosome causes physical abnormalities — low testosterone and infertility risk
treatment: hormone therapy can be effective
incidence: 1 in 600 male births
fragile x syndrome
desc: an abnormality in the x chromosome can cause intellectual disabilities or short attention span
treatment: special education, speech and language therapy
incidence: more common in males than in females
turner syndrome (XO)
desc: missing x chromosome in females can cause intellectual disability and sexual underdevelopment
webbed feet, shorter neck
treatment: hormonone therapy in childhood and puberty
incidence: 1 in 2500 fem births
XXY syndrome
desc: an extra y chromosome can cause above average height
treatment: none
incidence: 1 in 1000 male births
cystic fibrosis
desc: glandular dysfunction that interferes with mucus production, breathing and digestion are hampered; resulting in a shortened life span
treatment: physical and oxygen therapy, synthetic enzymes and antibiotics: most individuals live to middle age
incidence: 1 in 2000 births
diabetes
desc: body does not produce enough insulin, which causes abnormal metabolism of sugar
treatment: early onset can be fatal unless treated with insulin
incidence: 1 in 2500 births
hemophilia
desc: delayed blood clotting causes internal and external bleeding ( think tsar of russia)
treatment: blood tranfusion/injections can reduce or prevent damage due to internal bleeding
incidence: 1 in 10 000 males
huntingtons disease
desc: central nervous system deteriorates, producing problems in muscle coordination and mental deterioration
treatment: does not usually appear until age 35 and older, death likely 10 to 20 years after symptoms appear
incidence: 1 in 20 000 births
phenylketonuria (PKU)
desc: metabolic disorder, if left untreated causes intellectual disability ARE U KIDDING
treatment: special diet can result in average intelligence and normal life span
incidence: 1 to 10 000 - 20 000 births
sickle - cell anemia
desc: blood disroder that limits the bodys oxygen supply; it can cause joint swelling as well as heart and kidney failure
treatment: penicillin, medication of pain, antibiotics and blood transfusions
incidence: 1 in 400 african american children (young amongst other groups)
spina bifida
desc: neural tube disorder that causes brain and spine abnormalities
treatment: corrective surgery at biruth, orthopedic devices nd physical/medical therapy
incidence: 2 in 1000 births
tay-sachs disease
deceleration of mental and physical development caused by an accumulation of lipids in the nervous system
treatment: medication and special diet used but deat is likely at 5 years of age
incidence; 1 in 30 american jews are carriers
freud’s oral stage
oral behaviours like sucking your thumb
characteristics: passive, dependant and gullible
birth - 18 months
freud’s anal stage
driven by child’s toilet training — satisfied that infant is not as dependant ie. occurs during toilet training, where children gain pleasure from controlling bowel/bladder movements, leading to a focus on autonomy and self-control
characteristics: (think um.. anal retentive and anal expulsive): control, order v disorganized and messy (respectively) — clench and release you could say
1.5 - 3 years
freud’s phallic stage
focus on genitals — oedipus and electra complex
characteristics: flirtatious, vain, jealous, competitive
3-6 years in age
freud’s latency stage
impulses repressed — for now ig — represses sexual interest and develops social and intellectual skills
6- puberty
freud’s genital stage
basically a continuation of the phallic stage but more repressed
re- awakening of sexual desire etc
puberty onwards
id
primal urges, hedonism, follows pleasure principle
ego
rationalization and reasoning — follows reality principle
superego (superman)
consciousness and morals — whats good and whats bad??
develops around 5-6 yo — possibly follows reality principle as well
sigmund freud
believed in the unconscious forces to determine both personality and behaviour
erik erikson
believed in social motivations and the desire to affiliate with others is a central influence in development
erikson’s psychosocial development theory: age 1
trust v mistrust — infant develops sense of security
erikson’s psychosocial development theory: age 1-3
autonomy v shame/doubt — infant achieves a sense of independence
erikson’s psychosocial development theory: age 3-5
initiative v guilt — child finds balance between spontaneity and restraint
erikson’s psychosocial development theory: age 6- puberty
industry v inferiority — child attains a sense of self confidence, focusing on mastering academic, social and physical skills
erikson’s psychosocial development theory: adolescence
identity v role confusion — adolescent experiences a sense of self by exploring roles, beliefs and career paths (lots of possible change here)
erikson’s psychosocial development theory: early adulthood
intimacy v isolation — adults form personal relationships that are close
erikson’s psychosocial development theory: middle adulthood
generativity v stagnation — adult promotes the well being of other people
erikson’s psychosocial development theory: late adulthood
integrity v despair — adult will look back on their life w satisfaction
watsons' classical conditioning
learning process where a certain stimulus becomes associated with an automatic, involuntary response
eg. throwing a sock at aidan
the degree at which the question is displayed matters the most in order to get the msot truthful response
skinner’s operant conditioning
behaviour is modified by consequences, utilizing the idea of reinforcement — increasing or decreasing the likelihood of voluntary behaviour recurring
skinner box, rats
bandura’s sopcial cognitive theory
the idea that learning occurs in a social context with a dynamic interaction between people, their behaviour and the environment
ie, people learn by observing others and through cognitive processes like self-efficacy, expectations and self regulation
Piaget theory of congitive development
children move through four distinct stages, sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational and formal operational
cognitive development tends to be viewed more in terms of discontinuous and qualitative change (more abstract ideas and approaches)
in an information processing approach: cognitive development is viewed in terms of continuous and quantitative (numerical and logisitical)
sensorimotor stage
infants constructs understanding of the world by coordinating their sensory experiences with -physical actions — its kinda self explanatory
sensory motor — focus on sqesory and motoric systems — eg. picking shit up
Substage 1: 0-1 months: reflexes
Substage 2: 1-4 months: primary circular reactions
Substage 3: 4-8 months: secondary circular reactions
Substage 4: 8-12 months: coordination of secondary schemes
Substage 5: 12-18 months: tertiary circular reactions
Substage 6: 18-24 months: beginnings of mental representation
preoperational stage
child begins to represent world with words and images — increased by symbolic thinking
eg. creating an abstraction — simplification of things in the world
concrete operational stage
child can now reason logically about concrete events - ie. their brain set in and now they can think consciously and logically
formal operational stage
adolescence! reasonings are more idealistic, abstract and logical ways (basically it ties everything up an now the adolescent is able to fo anything)
bioecological approach
different cells of the environment simultaneously impact an individual
*** - development reflects the influences of several environmental systems
important to note: theory states that a child needs at least omne adult they can depend on
bioecological approach: micro
immediate environment —> you as a person
eg. age, sex, health
bioecological approach: meso
relationships and immediate networks
eg. family, friends, support groups
bioecological approach: exo
places/people that do not directly involve themsevles with you —> kinda like acquaintances
eg., neighbours, social media, non-invasive coworker relationships
bioecological approach: macro
the outermost layer including bigger ideas in your life
basically its things you associate with in your everday life that you may not even realize
eg. culture, societal values, laws, beleif systems, political ideologies
bioecological approach: chronosystem
broad socio-historical circumstances that influence an individuals development throughout their lifespan
eg. time, major life events (moving , divorce, marriage etc) —> think: a normal person lifecycle. what does everyuone have in common that they are most likely to do in their lives??
vygotskys sociocultural theory
complex forms of thinking originate in social interactions rather than private explorations
similar to albert bandura?
fuck around and find out mentality —> going in blind lol
scaffolding
a process in wihch an individual learns new skills as result of being guided by someone who is more skilled (like an older sibling or parent)
zone of proximal development
tasks that are too difficult for a child to complete, therefore they need to be accomplished with guidance
its the sweet spot where tasks are challenging but achievable with support (scaffolding)
optimal learning (maximizing the gathering of info and gaining knowledge in ways that are not too extreme)
evolutionary perspective
behaviour can be understood in terms of our genetic inheritance from our ancestors
martin seligman
according to evolutionary theorists, many of the mental health struggles of today is a result of disconnection from community. — we are hard wired for it
contextual perspective
considers the association between individuals and their physical , cognitive, personality and social worlds
bioecological theory
bronfenbremmer, vygotsky
ethological theory
proposes the idea that behaviour in both animaals and humans is rooted in biology and evolution, serving adaptive functions for survival
imprinting
the rapid, irreversible attachment a young animal/ human (baby lol) forms to the first moving object it encounters during a critical early period, often following it as a parent
specific time frames during which the presence or absence of certain experiences has long lasting influences (think your emo era, your bikeriders era)
jacob imprinting on renesmee
chromosomes
threadlike structures located in the nucleus of each human cell
DNA
deoxyribosenucleicacid - complex molecule with double helix shape
red blood cell do not carry DNA since they need all the space they can get to move oxygen
genes
basic units of hereditary info
direct cells to reproduce and assemble proteins that direct body processes
human genome project
mapping of complete set of developmental instructions for creating proteins to create human organism
for some, genetic variability is extrememly important as it can protect from illnesses
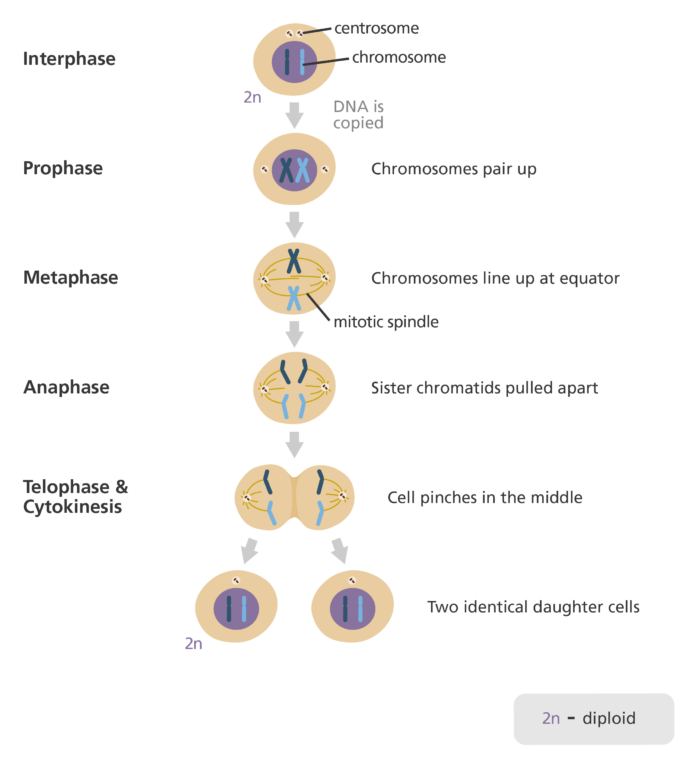
mitosis (standard)
cells nucleus including chromosomes duplicates itself and divides into two cells formed with identical genetic makeup
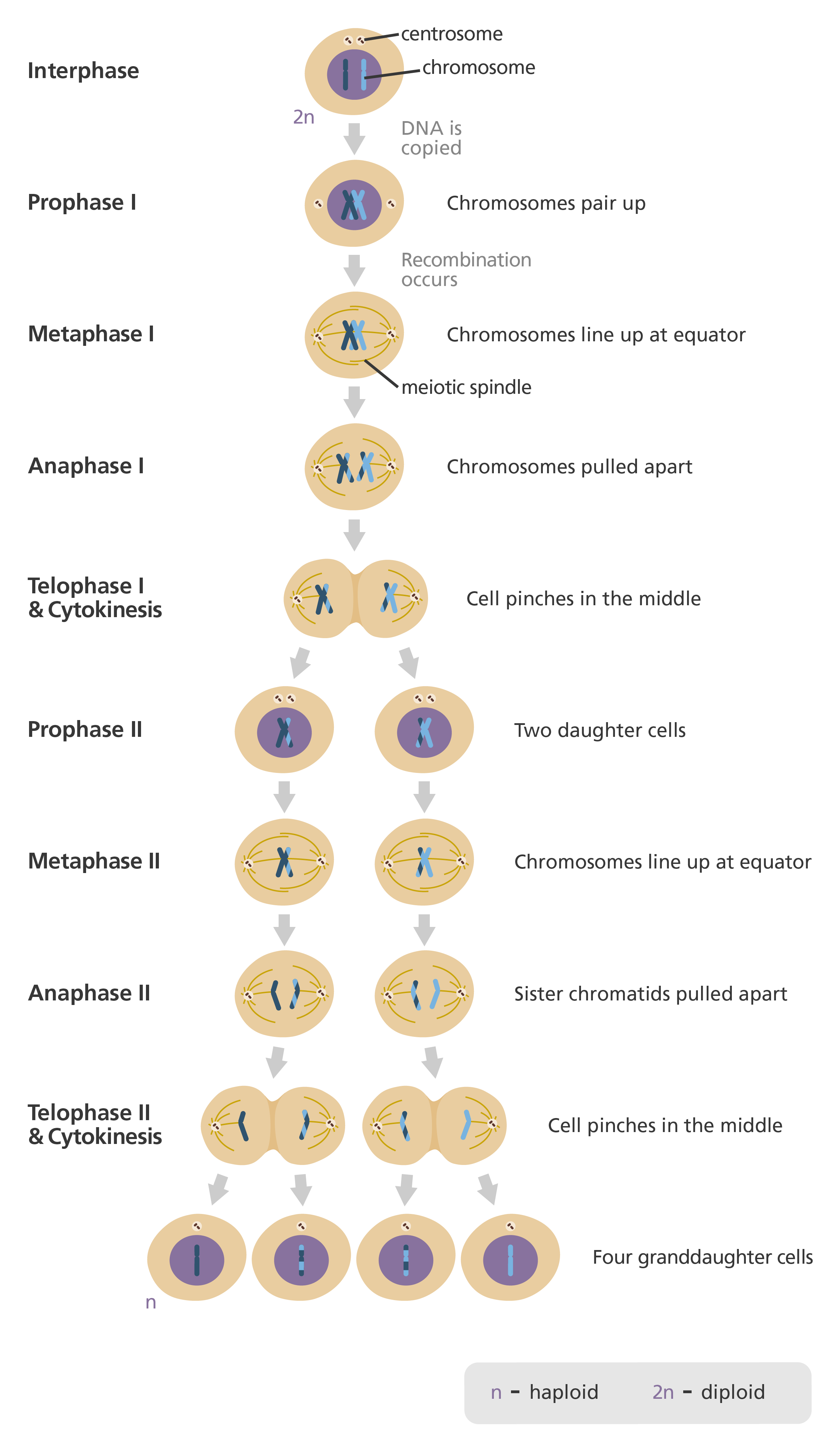
meiosis (sex cells)
specialized process of cell division using the sex cells — egg and sperm — cell nucleus duplicates twice to make 4 new cells
each cell with 23 unpaired chromosomes (haploid) —> one copy of each chromosome
dominant - recessive gees
dominant geens overrides the expression of recessive genes
sex linked genes
x-links inheritance results when a mutated gene is carried on the x chromosome
females are carriers, while males may EXHIBIT x-linked disease
polygenetic inheritance
when multiple gene pairs are responsible for the production of a trait
ultrasound sonography
high frequncy waves scan womb to produce image
choriononic villus sampling
test that takes samples of placenta tissue
used to detect genetic defects
contingent o how far along you are
amniocentesis
identifying genetic disorders by examining a small sample of fetal cells from amniotic fluid
contingent on how far along you are
behavioural genetics
investigates the influence of heredity and environment on ndividual differences in human traits and development
multifactorial transmission
traits are determined by a combination of genetic and environmental factors
twin study
behavioural similarity of identical twins compared with fraternal twins
identical twins share 100% DNA, fraternal twins 50%
adoption study
whether adopted children’s behaviour and psychological characteristics are more like adoptive or biological parents
heredity-environment correlations
indiv. genes may influence environments to which they are exposed
passive genotype-environment correlation
biological parents who are fenetically related to child provide a particular environment
evocative genotype- environment correlation
child’s characteristics will elicit either positive or negative experiences from others depending on their personality
bubbly = bubbly
active (niche picking) genotype-environment correlations
when children seek out environment they found compatible and stimulating
eg, whyte ave
trial child — experiences occurring within the family may be part of nonshared environment
big five
openness - receptivity to new ideas and experiences
conscientiousness — the tendency to be responsible, organized, hardworking etc
extraversion — outgoing, sociable, energetic etc
agreeableness — prosocial behaviour
neuroticism — tendency to experience negative emotions
germinal period
two weeks after conception — shortest stage of fetal development
blastocycst travels through uterus and buries in uterine wall
embryonic period
2-8 weeks after conception — embryo firmly in place, major organs and basic anatomy form
3 layers from out to in: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
ectoderm
hair, skin, sense orans, spinal cord
mesoderm
nuscles, bones, blood, circ. systems
endoderm (indo- inside)
digestive system, liver, pancreas, respiratory system
pregnancy issues include
infertility, miscarriage, abortion and teratogen —- any agent—including drugs, chemicals, infections, or radiation—that can cause structural or functional abnormalities, birth defects, or fetal death when a person is exposed to it during pregnancy.
fetal period
8 weeksuntil birth — somersault, cry, hiccup, clench fists, open and close eyes, suck thumb (start of oral stage)
stages of birth
Beginning of uterine contractions(6-12 hours usually wtf)
8-10 minutes apart
Cervix stretches and opens to 10 cm
Baby begins to move through birth canal (~90 min)
Contraction come almost every minute
Mother bears down to push baby out
afterbirth
placenta , umbilical cord and membranes detached a expelled
However, tremendous variability around birth and around contractions
apgar scale
predictive of survival rate - assess the health of newborns at one and five minutes of birth
Postpartum blues
elings of anxiety upset, ocd, depression, etc especially if there are already risk factors before pregnancy (more likely to have the blues esp if u already seem to have something going on mentally)
Major depression postpartum: major episode that occurs about 34 weeks after delivery
Strong feelings of sadness, anxiety, despair, trouble coping with daily tasks
May worsen without treatment
both mother and father can have this
newborn abilities
Sucking
Swallowing
Rooting
Coughing
Sneezing
Blinking

Cephalocaudal pattern
starts at head, focuses on head etc - top to bottom

proximodal distal pattern
starts ar center of body and works its way out
nervous system
Comprises the brain and nerves that exist throughout the body – born with 100 neurons
infant brain
Infants brain 25% adult weight
Connectivity between neurons blooms (PRUNING AND BLOOMING) – therefore increasing efficiency with these neural connections
sensitive period
limited and specific time in which organism is sensitive to environmental changes etc – it need affection be nice when they cry
In typical infants there is more neural activity, brain tends to be larger,
sleep for infants
usually sleep for 16-17hours
after 6 months — move closer to a regular adult sleeping pattern
half sleep in rem must be nice)
rooting reflex
when infant’s cheek is stroked or side of mouth is touched, infant will turn head and try to suh (k) on sum
gross motor skills
the use of large muscles groups in arms, legs and toso
Nonorganic failure to thrive
infants who receive adequate nutrition but appear as though they have been food deprived - they are actually emotionally deprived and exhibit qualities: – they are touch starved literally
Underdeveloped
Listless
Apathetic
Ecological view
directly perceive information that exists in the world around us
visual perception
at birth, nerves, muscles and lens of eyes are still developing
estimated 20/200 to 20/600 - normal adult vision can see 200-600 ft while infant only 20 ft)
will stare to show interest i human faces - matching fae to voice
color vision corrects slowly
perceptual constancy
sensory stimulation is chaging but perception remains constant
size constancy
recognition of object remains the same even tough retinal images changes as yu move toward or away from the object
shape constancy
recognition that an object remains that same shape even though uts orientation to us changes — mental roation
depth perception
visual perception of depth affected by experience
unknown how early in life infants perceive depth
auditory perception
even in womb, fetus respons to sounds outside
more sensitive to higher and lower frequencies than adults — increases during the first 2 years and assists in linguistic acquisition